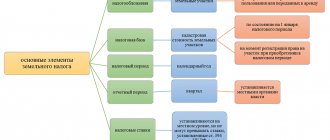
Current tax legislation provides for the obligation of land owners to pay land tax. Payers of this tax are individuals and legal entities that own a land plot on the right of ownership, the right of perpetual use or lifelong inheritable possession. In addition, the obligation to pay this tax arises for tenants of land owned by state and municipal property.
Who should pay
All individuals and organizations owning plots of land must pay this type of deduction to the budget. The frequency of receipt of funds into the budget from individuals is once a year.
As a general rule, payment at the established tax rate of land tax occurs if 3 conditions are met:
- The real estate is recognized by the Land Code of the Russian Federation.
- The owner has title documents.
- The land is listed in the cadastre.
Of course, payers must comply with payment deadlines that:
- prescribed by law (legal entity);
- indicated in the document from the Federal Tax Service (individual).
Only the owner of this property must pay land tax. There is no need to deduct funds to the budget for temporary use.
Financial obligations to the treasury arise from the moment of registration of land real estate.
Position of the tax authority
The inspectorate points out that the reduced tax rate of 0.3 percent applies only to land plots, information about the permitted use of which as agricultural land is contained in the state real estate cadastre. Since in 2013, for which the taxpayer submitted a tax return, the land plot had permitted use for production purposes, and the type of permitted use of this land plot was changed only in 2014, then in the disputed tax period, tax rate 1 should have been used to calculate the tax .5 percent provided for other land plots.
Who installs
Now about who sets the land tax rates. Local authorities have the right to regulate their size. The size can be minimum, average and maximum allowed by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. At the same time, officials always take into account the characteristics of the area.
Basic land tax rates are established by the Tax Code. And on its basis - the legislation of Moscow, St. Petersburg, Sevastopol, as well as representative bodies of municipalities. The rules and terms of payment are also regulated by local administrations and the authorities of federal cities.
REPORTING POINT
Zdorovenko A. O. accounting and taxation consultant at Az-Consultant LLC, member of the Chamber of Tax Consultants
Land tax for 2013
The payer of the land tax may have difficulties with the tax base if during the tax period there was a change in the permitted type of use of the land plot, which led to a change in its cadastral value.
To recognize an organization as a payer of land tax, two criteria must be met in relation to it: firstly, the land plot must be subject to taxation with this tax, and secondly, it must be owned by the organization (clause 1 of Article 388 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation ).
IMPORTANT IN WORK
The use of the simplified tax system is not a basis for exempting an organization from paying land tax. Accordingly, organizations using the simplified tax system pay land tax and report on it on a general basis.
Legal entities that are commercial organizations could, until July 1, 2012, have a land plot with the right of permanent (indefinite) use, being recognized as payers of land tax in relation to such plots. But now this right must be re-registered as the right to lease plots, or the land must be acquired into ownership before the specified date (Clause 2, Article 3 of the Federal Law of October 25, 2001 No. 137-FZ). If this was not done within the approved period, such an organization may be brought to administrative liability under Art. 7.34 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. At the same time, violation of the norms of the Land Code of the Russian Federation will not relieve the organization from the obligation to pay land tax.
The company will not pay land tax if it uses the site under the right of lease or gratuitous fixed-term use (clause 2 of Article 388 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), and also if the site is not subject to land tax. These are plots withdrawn or limited in circulation in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, as well as withdrawn from the forest fund lands (clause 2 of article 389 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clauses 4, 5 of article 27, and article 101, art. 102 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation).
Payment of land tax does not depend on the accounting procedure for the site, that is, regardless of whether it is taken into account as part of fixed assets or inventory, for example, as is provided for the property tax of organizations. Even if a plot is purchased for resale, as long as the organization owns it, it will be required to pay land tax on it.
ORIGINAL SOURCE
Land tax is one of those taxes, the calculation of which must be guided not only by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, but also by regulatory legal acts (laws) of representative bodies of municipalities (legislative (representative) bodies of state power of federal cities of Moscow and St. Petersburg). At the local level, specific tax rates are determined within established limits, the procedure and deadlines for paying land tax, and tax benefits, grounds and procedures for their application can also be established.
The procedure for calculating land tax
The tax base for land tax is the cadastral value of the plot (Clause 1, Article 390 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The cadastral value is approved by the executive authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation. Moreover, it depends not only on the actual location of the land plot, but also on the type of permitted use.
To determine the tax base for the corresponding tax period, the cadastral value of the site is taken as of January 1 of this year (clause 1 of Article 391 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Thus, to calculate land tax for 2013, it is necessary to take into account the cadastral valuation as of January 1, 2013. The only exception is the formation of a land plot during the current tax period. In this case, the cadastral value is taken as of the date the land plot is registered in the cadastral register.
If the cadastral value of the land plot as of January 1 of the current tax period has not been established, on the basis of Art. 65 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation and clause 13 of Art. 3 of Law No. 137-FZ, for tax purposes, the standard price of land is applied (clause 7 of the resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of Russia dated July 23, 2009 No. 54, letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated August 15, 2012 No. 03-05-05-02/85).
The taxpayer may have difficulties with the tax base if during the tax period there was a change in the permitted type of use of the land plot, which led to a change in its cadastral value. As is known, the cadastral value is determined, among other things, taking into account the type of its use.
The regulatory authorities (see letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated March 13, 2013 No. 03-05-04-02/7507) at the request of the arbitrators (see resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of Russia dated November 6, 2012 No. 7701/12) recognized that when the type of permitted use changes land plots, land tax must be calculated taking into account the cadastral value calculated for the corresponding period based on the changed type of permitted use. That is, from the month in which the change in the type of permitted use of the land occurred, the organization calculates the tax for the remainder of the year, taking the cadastral value for the new type of permitted use of the site. It is worth noting that the cadastral value should be taken as of January 1 of the tax period, and not as of the date of the changes that occurred.
ORIGINAL SOURCE
The use of land in the Russian Federation is paid. The forms of payment are land tax and rent.
It is advisable to calculate land tax in relation to a plot whose cadastral value has changed during the tax period as a result of a change in the type of permitted use of the land plot using a coefficient similar to the coefficient established in clause 7 of Art. 396 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Article 394 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation establishes maximum tax rates. However, for the vast majority of land plots it cannot exceed 1.5%. A reduced rate of no more than 0.3% applies to agricultural plots, as well as those occupied by housing stock and engineering infrastructure facilities of the housing and communal complex.
GOOD TO KNOW
If, in accordance with the current legislation on taxes and fees, an organization is recognized as a payer of land tax, the expenses incurred by it in connection with its payment are taken into account when forming the tax base for the tax paid under the simplified tax system, taking into account the provisions of Chapter. 26.2 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Specific tax rates are established by representative bodies of municipalities (legislative (representative) bodies of state power of federal cities of Moscow and St. Petersburg). At the same time, they can set differentiated rates depending on the category of land and the permitted type of use (clause 2 of Article 394 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). However, if tax rates are not determined at the local level, taxation is carried out at the marginal tax rates specified in paragraph 1 of Art. 394 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The taxpayer may also have difficulty determining the tax rate if the actual type of use of the land plot does not correspond to the type indicated in the information of the state land cadastre.
In this case, the Federal Tax Service insists on paying land tax at a rate that corresponds to the established type of use of the site. At the same time, the payer can pay tax based on the actual use of the land, if it is beneficial to him. Thus, in accordance with the legal position reflected in the Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of Russia dated October 28, 2010 No. 5743/10, the type of permitted use of a land plot is displayed in the information of the state land cadastre, and is not established by this document.
If the actual type of use of the land plot corresponds to the types of permitted use provided for by the town planning regulations for this territorial zone (clause 3 of Article 85 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation), the taxpayer has documents that indicate a change in the intended use of the land plot. Moreover, this can be done not only in relation to the entire land plot, but also if there has been a change in the use of certain parts of the land plot (resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of Russia dated November 20, 2012 No. 7943/12, decision of the Arbitration Court of the Krasnoyarsk Territory dated August 22, 2013 No. A33-5297/ 2012).
ORIGINAL SOURCE
The deadlines for paying land tax and advance payments thereon are established by local authorities, and if there are no restrictions on the deadline for paying advance payments, then the deadline for paying the tax cannot be earlier than the deadline for submitting the tax return.
Procedure for paying land tax
For taxpayers - organizations and individual entrepreneurs, in general, reporting periods are established, at the end of which it is necessary to make advance payments (Article 393, paragraph 1 of Article 397 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). It is worth paying attention to the fact that the reporting periods are individual quarters of the calendar year, and not the period from the beginning of the year to the end of the corresponding quarter. However, at the local level, certain categories of taxpayers may have the right not to calculate or pay advance payments during the tax period (clause 9 of Article 396 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If the payer does not own the plot for the entire tax period, then the land tax is calculated taking into account a coefficient defined as the ratio of the number of full months of ownership of the land plot to the number of calendar months in the tax (reporting) period, that is, for example, 12 or 3.
IMPORTANT IN WORK
The tax return for land tax is submitted only at the end of the tax period. The tax return is submitted no later than February 1 of the year following the expired tax period.
Moreover, if the emergence of the right occurred before the 15th day, this month is taken as a full one; if later, this month is not included in the calculations. The opposite situation arises when the rights to own a land plot are terminated: if the right is terminated before the 15th day, then the month is not taken into account; if after, then the month of termination of rights is taken as a full month (clause 7 of Article 396 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Tax return
The tax return is submitted at the location of the land plots, i.e. if the plots are located on the territory of municipalities under the jurisdiction of different tax authorities, a declaration in respect of the corresponding land plots must be submitted to each of them. If a taxpayer has several plots located on the territory of one municipality, a separate sheet of Section 2 of the tax return is filled out for each of them. If land plots are located on the territories of several municipalities and under the jurisdiction of one tax authority, one declaration is submitted with the completion of sections of the declaration according to the relevant OKTMO codes (clause 2.11 of the Procedure, letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 17, 2013 No. ED-4-3/18585).
GOOD TO KNOW
The tax return form and the procedure for filling it out were approved by order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 28, 2011 No. ММВ-7-11/ [email protected]
Full exemption of the taxpayer from paying land tax in connection with the use of benefits does not exempt him from submitting a land tax return (clause 2.13 of the Completion Procedure).
There are a number of other points that you should pay attention to when filling out your tax return. Line 060 is filled in only if the plot is in common shared or joint ownership, that is, a share equal to one should not be indicated (clause 5.8 of the Procedure).
The benefit code consists of two parts, but the second part is filled in only if the first contains a certain value. Thus, the second part of the code on line 070 is filled in if the first part of the indicator contains benefit code 3022100; on line 110 – 3022300; on line 200 – 3022400; on line 240 – 3022200; on line 260 – 3022500 (clauses 5.9, 5.13, 5.22, 5.26, 5.28 of the Order).
ORIGINAL SOURCE
The obligation to calculate and pay land tax is associated with the organization having a document confirming ownership of the land plot. In this case, this obligation arises from the moment of registration of ownership of a land plot, that is, making an entry in the register, and terminates from the day of making an entry in the register about the right of another person to the corresponding land plot.
In the second part of the benefit code indicator, on the specified lines, the number, paragraph, subparagraph of the article of the regulatory legal act of the representative body of the municipality, in accordance with which the corresponding benefit is provided, are sequentially indicated (for each of the indicated positions, 4 acquaintances are allocated. In this case, the second part of the indicator is filled in on the left to the right, and if the attribute has less than four characters, the free spaces to the left of the value are filled with zeros).
Line 160 indicates the coefficient Kv, which is given in decimal fractions accurate to ten thousandths. But if the land plot was owned during the entire tax period, then “0” is indicated only in the third cell, i.e. the line will be filled in like this: “1.0—” (clause 5.18 of the Procedure).
You need to be especially careful when filling out lines 180 and 190. Thus, if line 180 indicates the number of full months of use of a tax benefit by the taxpayer, the coefficient Kl in line 190 is calculated from the number of full months during which there is no tax benefit, i.e. this coefficient will show the proportion of the tax period when the benefit does not apply. Accordingly, if there is no benefit, then Kl will be equal to 1. In this case, “—” is indicated on line 180, and “1.0—” on line 190.
IMPORTANT IN WORK
The calculation of the amount of land tax is carried out taking into account a coefficient defined as the ratio of the number of full months during which the given land plot was owned by the taxpayer to the number of calendar months in the tax (reporting) period.
An example of calculating land tax and filling out a tax return
Trubnik LLC is a small manufacturing enterprise. In 2013, she owned three plots of land:
— No. 1 cadastral number 63:01:0114008:555 with a cadastral value of 15 million rubles. Production workshops are located on this site;
- No. 2 cadastral number 63:01:0115001:505 cadastral value of 2.5 million rubles. There was an office building here, which was in common ownership, and therefore Trubnik LLC owned 12/67 shares of the land plot. This plot was sold, the transfer of ownership was registered on 09/06/2013;
- No. 3 cadastral number 63:01:0114008:004 with a cadastral value of 3.5 million rubles. The plot was purchased on July 12, 2011. New production facilities and the company's office are located here.
ORIGINAL SOURCE
If the emergence (termination) of the specified rights occurred before the 15th day of the corresponding month inclusive, the month of occurrence of the specified rights is taken as a full month. If the emergence (termination) of these rights occurred after the 15th day of the corresponding month, the month of termination of these rights is taken as the full month.
All plots are located on the territory of one municipality (within the boundaries of the urban district), subordinate to one tax authority. In relation to land occupied in this municipality by organizations for production and non-production purposes, the tax rate is set at 1.3%. The OKTMO code of the municipality where the land plots are located is 36701000001. For all industrial enterprises in relation to lands classified as industrial territorial zones, the body of this municipality approved tax benefits in the form of a reduction in the calculated tax amount in the amount of 10%. Plots Nos. 1 and 3 fall under this benefit. The benefit is established by paragraphs. 3.6 clause 4 art. 5 of the regulatory legal act of the representative body of the municipality.
When specifying the BCC, you should not make a mistake in choosing it, since the BCC at which land tax should be paid depends on the rate (subclauses 1 or 2, paragraph 1 of Article 394 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) and on the type of municipality. In the case under consideration, the rate is set by paragraphs. 2 p. 1 art. 394 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, and the settlement is an urban district, therefore BCC 182 1 0600 110.
POSITION OF THE MINISTRY OF FINANCE
If the rights to the land plot were transferred in the second half of the month - after the 15th day, then the payment of land tax for this month falls on the previous owner.
Plot No. 2 was sold on September 6, i.e. to the 15th, therefore September is not included in the calculation of the full months of ownership - the company owned it for eight months. It is also necessary not to forget that this plot is in common ownership, therefore, when calculating the tax base, it is taken into account only in relation to shares owned by the company.
Plot No. 3 was purchased before the 15th, therefore July will be considered a full month, so the company owned it for six months.
Land plots Nos. 1 and 3 belong to the category of lands within settlements classified as industrial territorial zones. The code for this category is 003002000090. Plot No. 2 does not belong to any of the special categories highlighted in Appendix No. 5 to the Order, therefore it belongs to other lands - code 003002000100.
Benefit codes are contained in Appendix No. 6 to the Procedure. When choosing a tax return line, you should strictly adhere to the Procedure, because Different types of benefits are indicated on different lines of the tax return. Indicating a benefit in a line not intended for it will most likely cause a discrepancy with the information available to the tax authorities, which may entail the need to provide explanations in accordance with paragraph 3 of Art. 88 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Using the initial data, we will fill out Section 2 for section No. 1. In this case, the calculated indicators will be obtained as follows.
Line 130 = line 050, because the plot belongs to the taxpayer entirely, and there are no benefits.
Line 170 = line 130 x line 140 x line 160 = 15,000,000 rub. x 1.3% x 1 = 195,000 rub.
Line 250 = line 170 x benefit percentage = 195,000 rubles. x 10% = 19,500 rub.
Line 280 = line 170 – line 250 = 195,000 rubles. – 19,500 rub. = 175500 rub.
The tax base on line 130 for plot No. 2 will be calculated somewhat differently. In this case, line 050 must be multiplied by line 060, because the taxpayer owns only a share of the land plot.
GOOD TO KNOW
From January 1, 2011, organizations and individual entrepreneurs who pay land tax do not need to submit calculations for advance payments during the tax period. The land tax declaration is submitted once a year no later than February 1 of the year following the previous one.
Considering that the land tax declaration is submitted only at the end of the tax period, and advance payments are paid each reporting period, Section 1 indicates not only the amounts of calculated (line 021) and payable tax based on the results of the tax period (line 030), but also the amounts advance payments for each reporting period (lines 023, 025, 027).
What parameters influence tax rates for land tax
The indicator under consideration depends on various factors:
- categories of land;
- purpose of the site;
- location;
- total area (indicated in the technical passport);
- permission to use property;
- presence/absence of benefits, etc.
If local authorities do not approve the exact amount of tax for their territory, then they should focus on specific land tax rates. They are established by Article 394 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The tax for a site for residential construction, but temporarily not developed by the owner (for example, preparatory or repair work is being carried out), may be paid at a reduced rate. This right is provided by Art. 394 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and clause 8 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation of 2009 No. 54.
Maximum land tax rates for 2017 according to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation
Federal legislation sets limits that cannot be exceeded when determining the percentage tax rate. Thus, permissible sizes are regulated by Article 394 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. They depend on the parameters discussed above, and also partly on the category of the payer. Let's look at them in more detail.
| Basic land tax rates in 2017 | |
| Size | Explanation |
| According to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the interest rate on land tax cannot exceed 0.3% of its cadastral value | The site is usually used for: · construction of residential real estate; · farming; · growing plants or animals, etc. Similar land tax rates in 2021 apply to lands intended for customs purposes, protection of the state and its security. |
| The maximum land tax rate for individuals and legal entities in 2021 is 1.5% | The acquired land area can be used for: · production; · construction of trading platforms; · offices. It is important to understand that taxes are paid only on your own property. When an enterprise has entered into a land lease agreement, tax deductions continue to be made by its owner. A similar tax rate is relevant in all other cases. |
When engaged in agricultural activities, the amount of land tax cannot be more than 0.3%.
Local authorities should be guided by the indicators presented in the table above, since they do not have the right to exceed the land tax rates established by the Tax Code.
Disadvantages of the new tax principle
These shortcomings directly relate to the determination of cadastral value. Three years ago there were a huge number of them. Appraisers with an independent official status determined a price that had no specific basis: even such important factors as the location of the sites and their distance from local infrastructure were not taken into account. This approach caused a lot of dissatisfaction on the part of taxpayers, as it expanded the scope for unfair manipulations by appraisers. Compared to previous years, in 2016, land owners will be given all the necessary powers with which they will be able to prove their case (including by going to court).
Amendments made to the legislation on taxation of land plots will enter into force this spring. The benefits established for taxpayers will remain the same, but the parameters of existing buildings on the site will be taken into account.
At this stage, the powers and actions of local officials play a big role: they have the right to reduce the rate, but cannot exceed it in any way, due to the effect of the maximum tax limit.
Despite some shortcomings of the amendments made (the possibility of manipulation by local authorities and a “paid” rate reduction), the new legislation is more consistent with the realities of the modern land market and meets international taxation standards.
Interest rate of land tax in Moscow
The type of mandatory payment in question is regulated by Law No. 74, which also establishes benefits and payment terms.
Thus, organizations must transfer the final tax no later than February 1 of the following year. Otherwise, the procedure and requirements coincide with the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Interest rates on payments for residents of the capital are presented in the table:
The 2021 land tax for individuals also provides for categories of beneficiaries:
- Pensioners
- Heroes of the Soviet Union or Russia, or persons with the Order of Glory of 3 degrees.
- Persons with disabilities of 1 or 2 groups or citizens who have had disabilities since childhood.
- Participants of the Great Patriotic War and other participants in the war who have the appropriate document.
- Military personnel are retired based on length of service.
- Members of military families with survivor benefits.
- Citizens with radiation sickness who received a dose of radiation during the liquidation of man-made accidents.
But a beneficiary can receive a deduction for only one property, thus closing the loophole for those citizens who transferred real estate to their relatives who are entitled to benefits, and similarly exempted their, often expensive, real estate from payments.
What are the land tax rates in St. Petersburg
As mentioned, the amount of tax paid, the procedure and terms are regulated by local legislation. St. Petersburg Law No. 617-105 contains a list of persons for whom various privileges are provided. For example:
- pensioners who own a plot of land with an area of up to 2.5 thousand m2;
- Chernobyl victims;
- some types of economic entities.
The table below shows what tax rate for land tax is in effect in the region in question (excerpt from the law).
How to calculate the amount of tax deductions in 2021
For individuals, the payment amount is determined by local tax authorities. They make calculations based on the results of the past year. Typically this calculation method works:
| LAND TAX = RATE × CADASTRE PRICE × FULL MONTHS OF OWNERSHIP PER YEAR |
As for legal entities, they determine the amount of advance payments as follows:
| ADVANCE = RATE × CADASTRE PRICE × 1/4 |
For more information, see “Advance payments for land tax: payment deadlines in 2017.”
It’s easier for individuals: after all, they shouldn’t care about how to determine the tax rate for land tax. They automatically receive a corresponding notification from the Federal Tax Service. Although it will always be a good idea to double-check all the initial data and calculations of the tax authorities.
The cadastral value can be found in the Unified State Register of Real Estate. The payer just needs to log on to the appropriate website and fill out the search form. After reporting the cadastral number and identifying the property, the required information is provided. Other parameters of the site are indicated in technical documents.
Taxpayer position
The taxpayer refers to the fact that the disputed land plot is located in a zone in which it is permitted to use the territory as a storage area for fruits, vegetables, potatoes, and grain.
And since the entrepreneur used the land plot as agricultural land, and also stored the harvested crops in structures built on the land plot, a reduced rate can be used when calculating land tax. The entrepreneur indicated that he is engaged in vegetable growing, growing grains and other agricultural crops, as well as growing potatoes. Thus, his economic activities confirm that the disputed land plot was used for agricultural needs. This is confirmed by the fact that the results of financial and economic activities were formed through the sale of potatoes, this is reflected in the tax return for the unified agricultural tax and the book of income and expenses. Thus, the disputed land plot was used by the taxpayer to conduct agricultural activities, so he lawfully applied a reduced tax rate of 0.3 percent instead of 1.5 percent, at which the tax authority assessed additional tax to him.
Basic value
Many, of course, are interested in who approves the base rate of land tax, which then appears in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. So: the value under consideration appears at the suggestion of the Government of the Russian Federation, as well as relevant ministries and departments. It depends on:
- cadastral characteristics of the site;
- its area;
- other features of the earth.
Typically the base rate applies:
- for lands located outside populated areas;
- when the local administration does not approve its rate.
How to find out
Each payer can find out what percentage of the rate is relevant for his locality. There are 2 main ways to find out the land tax rate:
- Personally visit the local administration (“land” department).
- Through the official website of the Russian Tax Service www.nalog.ru.
Also see “Electronic services for accountants on the Federal Tax Service website: use wisely.”
To determine the land tax rate in 2021, you need to know the category of the plot. It is indicated:
- cadastral passport;
- title document for the land.
The payer can also make a request to Rosreestr to obtain the corresponding extract. Sometimes this can also be used to achieve a recalculation of the land tax rate in 2021 in a specific case.
If an individual learns about the amount of land tax from a notification from the Federal Tax Service, then the land tax rate for legal entities must be determined by them independently. Moreover, it is advisable not to make mistakes, so as not to waste all the calculations of advances and final taxes.
The logic of changing the principle of calculating the amount of taxation
The amount of payment this year is based on the cadastral property value, which is as close as possible to the market value. The difference is significant: before this, there was a tax calculation based on the book value of the land. The Russians had the opportunity to pay a fairly small amount, which did not cause any particular problems.
The tax amount, starting from 2021, for an ordinary taxpayer is based on the cadastral property value, which is as close as possible to the market value.
In practice, the difference is significantly noticeable - previously, tax calculations were made based on the book value of the land. The book value of a land plot may differ radically from the market value. Moreover, such a difference usually indicates a reduced value of the land plot.
In accordance with the new procedure, taxpayers with land plots will take a direct part in the development and filling of local budgets. These funds are planned for the development of the region's infrastructure (in this case, the region that receives funds from the state budget will be determined by the region of the taxpayer's place of registration, and not the location of the land plot).
The tax rate will increase annually by 20 percent and will reach its final volume only in four years (in 2020). Initially, the project covers about 30 regions of the Russian Federation (the most ready for changes and having a developed local government apparatus).
Increased odds
In some situations, double tax rates are used. These include the purchase of a plot of land in order to build a residential property (not individual housing construction). Then the payer makes contributions at a double rate for 3 years until the registration of rights.
At the same time, a legal entity that has received a site for the construction of any structures on the basis of permanent/indefinite exploitation does not apply to the coefficient of the land tax rate.
Also see “Land Tax Declaration for 2021: Sample Completion”.