The invoice for shipment was issued late
According to the rules of the Tax Code, invoices must be issued within 5 calendar days after shipment of goods (performance of work, provision of services, transfer of property rights) (clause 3 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The date of the shipping invoice also depends on this.
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not allow issuing an invoice later than 5 days.
At the same time, VAT on such an “overdue” document can be deducted. The inspectorate has the right to refuse a VAT refund only if the invoice does not allow identifying the seller, the buyer, the name of the goods (work, services), their cost, the tax rate and the amount of tax (clause 2 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Compliance with the deadline set for issuing an invoice is not on this list.
An invoice issued in violation of the 5-day deadline is not a basis for refusing the buyer a VAT deduction (see letter of the Ministry of Finance dated April 25, 2021 No. 03-07-09/28071).
As for the seller, there are no sanctions for late issuance of an invoice for shipment. Negative consequences can only occur in cases of possible litigation between counterparties.
Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Invoice
Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation with comments and amendments for 2020-2021
1. An invoice is a document that serves as the basis for the buyer to accept the goods (work, services), property rights presented by the seller (including the commission agent, agent who sells goods (work, services), property rights on their own behalf) tax amounts for deduction in the manner prescribed by this chapter.
An invoice can be compiled and issued on paper and (or) electronically. Invoices are drawn up in electronic form by mutual agreement of the parties to the transaction and if said parties have compatible technical means and capabilities to receive and process these invoices in accordance with established formats and procedures.
An adjustment invoice issued by the seller to the buyer of goods (work, services), property rights when the cost of shipped goods (work performed, services rendered), transferred property rights changes downward, including in the event of a decrease in price (tariff) and (or ) reduction in the quantity (volume) of shipped goods (work performed, services rendered), transferred property rights, is a document serving as the basis for the seller of goods (work, services), property rights to accept tax amounts for deduction in the manner prescribed by this chapter.
An invoice is a document that serves as the basis for the acceptance by the buyer, acting as a tax agent in accordance with paragraph 8 of Article 161 of this Code, of the calculated amounts of tax for deduction in the manner prescribed by this chapter.
An adjustment invoice drawn up when the cost of shipped goods specified in paragraph one of paragraph 8 of Article 161 of this Code changes, including in the event of a change in price and (or) a change in the quantity (volume) of goods shipped, is a document serving as the basis for acceptance by the buyer , acting as a tax agent in accordance with paragraph 8 of Article 161 of this Code, tax amounts to be deducted in the manner prescribed by this chapter.
2. Invoices are the basis for accepting tax amounts presented to the buyer by the seller for deduction when the requirements established by paragraphs 5, 5.1 and 6 of this article are met. An adjustment invoice issued by the seller to the buyer of goods (work, services), property rights when the cost of shipped goods (work performed, services rendered), transferred property rights changes downward, including in the event of a decrease in price (tariff) and (or ) a decrease in the quantity (volume) of goods shipped (work performed, services rendered), transferred property rights, is the basis for the seller of goods (work, services), property rights to accept tax amounts for deduction when fulfilling the requirements established by paragraphs 5.2 and 6 of this article.
Errors in invoices and adjustment invoices that do not prevent tax authorities from identifying the seller, buyer of goods (work, services), property rights, the name of goods (work, services), property rights, their value, as well as tax The rate and amount of tax presented to the buyer are not grounds for refusing to accept tax amounts for deduction.
Failure to comply with the requirements for the invoice, not provided for in paragraphs 5 and 6 of this article, cannot be grounds for refusal to accept for deduction the tax amounts presented by the seller. Failure to comply with the requirements not provided for in paragraphs 5.2 and 6 of this article for an adjustment invoice issued by the seller to the buyer of goods (work, services), property rights when the cost of shipped goods (work performed, services rendered) changes in the direction of decrease, including including in the case of a decrease in price (tariff) and (or) a decrease in the quantity (volume) of goods shipped (work performed, services rendered), transferred property rights, cannot be a basis for refusal to allow the seller to deduct the amount of tax.
The provisions of this paragraph also apply to invoices, adjustment invoices issued by the taxpayer to the buyer acting as a tax agent in accordance with paragraph 8 of Article 161 of this Code.
3. A taxpayer (including one who is a tax agent) is obliged to draw up an invoice, keep purchase books and sales books:
- 1) when performing transactions recognized as an object of taxation in accordance with this chapter (with the exception of transactions that are not subject to taxation (exempt from taxation) in accordance with Article 149 of this Code, unless otherwise provided by subclause 1.1 of this clause). When performing transactions for the sale of goods (works, services), property rights to persons who are not taxpayers of value added tax, and to taxpayers exempt from fulfilling taxpayer obligations related to the calculation and payment of tax, invoices are not drawn up by written consent of the parties to the transaction ;
- 1.1) when performing operations for the sale of goods that are not subject to taxation (exempt from taxation) in accordance with Article 149 of this Code, exported outside the territory of the Russian Federation to the territory of a member state of the Eurasian Economic Union;
- 2) in other cases determined in accordance with the established procedure.
3.1. Taxpayers, including those exempt from taxpayer duties related to the calculation and payment of tax, persons who are not taxpayers, in the event that they issue and (or) receive invoices when carrying out business activities in the interests of another person on the basis of commission agreements, agency agreements contracts providing for the sale and (or) acquisition of goods (work, services), property rights on behalf of the commission agent (agent), or on the basis of transport expedition contracts, as well as when performing the functions of a developer, they are required to keep a log of received and issued invoices in relation to the specified activity.
For taxpayers carrying out business activities on the basis of transport expedition contracts, the provisions of the first paragraph of this paragraph apply if they determine the tax base as the amount of income received in the form of remuneration during the execution of these contracts.
For persons carrying out business activities on the basis of transport expedition contracts, who are not taxpayers of value added tax or who are taxpayers exempt from fulfilling taxpayer obligations related to the calculation and payment of tax, the provisions of paragraph one of this paragraph apply if, when determining the tax base in the manner established by Chapters 23, 25, 26.1 and 26.2 of this Code, income in the form of remuneration for the execution of these contracts is taken into account as part of income.
Invoices issued for the amount of income in the form of remuneration for the execution of the contracts specified in this paragraph are not subject to registration in the log of received and issued invoices.
The provisions of this paragraph do not apply to tax agents specified in paragraphs 4, 5 and 5.1 of Article 161 of this Code.
3.2. Foreign organizations subject to registration in accordance with paragraph 4.6 of Article 83 of this Code do not draw up invoices, purchase books, sales books, a log of received and issued invoices regarding the provision of services specified in paragraph 1 of Article 174.2 of this Code , do not lead.
4. Lost force on January 1, 2014. — Federal Law of December 28, 2013 N 420-FZ.
5. The invoice issued for the sale of goods (work, services), transfer of property rights must indicate:
- 1) serial number and date of the invoice;
- 2) name, address and identification numbers of the taxpayer (tax agent) and the buyer;
- 3) name and address of the shipper and consignee;
- 4) the number of the payment and settlement document in case of receiving advance or other payments for upcoming deliveries of goods (performance of work, provision of services);
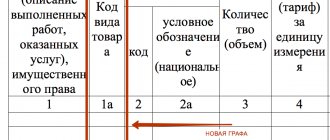
- 5) name of the goods supplied (shipped) (description of work performed, services provided) and unit of measurement (if it is possible to indicate it);
- 6) quantity (volume) of goods (work, services) supplied (shipped) according to the invoice, based on the units of measurement adopted for it (if it is possible to indicate them);
- 6.1) name of the currency;
- 6.2) identifier of the government contract, agreement (agreement) (if any);
- 7) price (tariff) per unit of measurement (if it is possible to indicate it) under the agreement (contract) excluding tax, and in the case of using state regulated prices (tariffs) that include tax, taking into account the amount of tax;
 the cost of goods (work, services), property rights for the entire quantity of goods supplied (shipped) according to the invoice (work performed, services rendered), transferred property rights without tax;
the cost of goods (work, services), property rights for the entire quantity of goods supplied (shipped) according to the invoice (work performed, services rendered), transferred property rights without tax;- 9) the amount of excise tax on excisable goods;
- 10) tax rate;
- 11) the amount of tax imposed on the buyer of goods (works, services), property rights, determined based on the applicable tax rates;
- 12) the cost of the total quantity of goods supplied (shipped) according to the invoice (work performed, services rendered), transferred property rights, taking into account the amount of tax;
- 13) excluded. — Federal Law of December 29, 2000 N 166-FZ;
- 13) country of origin of the goods;
- 14) number of the customs declaration;
- 15) code of the type of product in accordance with the unified Commodity Nomenclature for Foreign Economic Activity of the Eurasian Economic Union. The information provided for in this subparagraph is indicated in relation to goods exported outside the territory of the Russian Federation to the territory of a member state of the Eurasian Economic Union.
The information provided for in subparagraphs 13 and 14 of this paragraph is indicated in relation to goods whose country of origin is not the Russian Federation. The taxpayer selling the specified goods is responsible only for the compliance of the specified information in the invoices presented to him with the information contained in the invoices and shipping documents received by him.
5.1. The invoice issued upon receipt of payment, partial payment for upcoming deliveries of goods (performance of work, provision of services), transfer of property rights, must indicate:
- 1) serial number and date of the invoice;
- 2) name, address and identification numbers of the taxpayer (tax agent) and the buyer;
- 3) number of the payment and settlement document;
- 4) name of the goods supplied (description of work, services), property rights;
- 4.1) name of the currency;
- 4.2) identifier of the government contract, agreement (agreement) (if any);
- 5) the amount of payment, partial payment for upcoming deliveries of goods (performance of work, provision of services), transfer of property rights;
- 6) tax rate;
- 7) the amount of tax imposed on the buyer of goods (works, services), property rights, determined based on the applicable tax rates.
5.2. In the adjustment invoice issued when the cost of goods shipped (work performed, services rendered) changes, property rights transferred, including in the event of a change in price (tariff) and (or) clarification of the quantity (volume) of goods supplied (shipped) (performed) works, services provided), property rights, the following must be indicated:
- 1) name of the “adjustment invoice”, serial number and date of preparation of the adjustment invoice;
- 2) serial number and date of preparation of the invoice (invoices), according to which the cost of goods shipped (work performed, services rendered), transferred property rights is changed, including in the event of a change in price (tariff) and ( or) clarification of the quantity (volume) of goods supplied (shipped) (work performed, services rendered), property rights transferred;
- 3) names, addresses and identification numbers of the taxpayer (tax agent) and the buyer;
- 4) name of goods (description of work performed, services provided), property rights and unit of measurement (if it is possible to indicate it) for which the price (tariff) and (or) quantity (volume) are adjusted;
- 5) the quantity (volume) of goods (work, services) according to the invoice (invoices) based on the units of measurement adopted for it (if it is possible to indicate them) before and after clarifying the quantity (volume) of goods delivered (shipped) (work performed) , services provided), transferred property rights;
- 6) name of the currency;
- 6.1) identifier of the government contract, agreement (agreement) (if any);
- 7) price (tariff) per unit of measurement (if it is possible to indicate it) excluding tax, and in the case of applying state regulated prices (tariffs) that include tax, taking into account the amount of tax before and after changing the price (tariff);
 the cost of the entire quantity of goods (work, services), property rights according to the invoice (invoices) without tax before and after the changes made;
the cost of the entire quantity of goods (work, services), property rights according to the invoice (invoices) without tax before and after the changes made;- 9) the amount of excise tax on excisable goods;
- 10) tax rate;
- 11) the amount of tax determined on the basis of the applicable tax rates before and after changes in the cost of goods shipped (work performed, services rendered), transferred property rights, including in the event of a change in price (tariff) and (or) clarification of the quantity (volume) of goods supplied (shipped) goods (work performed, services rendered), transferred property rights;
- 12) the cost of the entire quantity of goods (work, services), property rights according to the invoice (invoices), taking into account the amount of tax before and after the change in the cost of goods shipped (work performed, services rendered), transferred property rights, including in the event of a change in price (tariff) and (or) clarification of the quantity (volume) of goods supplied (shipped) (work performed, services rendered), transferred property rights;
- 13) the difference between the indicators of the invoice (invoices), according to which the change in the cost of goods shipped (work performed, services rendered), transferred property rights is carried out, including in the event of a change in price (tariff) and (or) clarification of the quantity (volume) of goods supplied (shipped) (work performed, services rendered), transferred property rights, and indicators calculated after changes in the cost of goods shipped (work performed, services rendered), transferred property rights, including in the event of a price change (tariff) and (or) clarification of the quantity (volume) of goods supplied (shipped) (work performed, services rendered), transferred property rights.
The taxpayer has the right to draw up a single adjustment invoice for changes in the cost of goods shipped (work performed, services rendered), transferred property rights indicated in two or more invoices drawn up earlier by this taxpayer.
6. The invoice is signed by the head and chief accountant of the organization or other persons authorized to do so by an order (other administrative document) for the organization or a power of attorney on behalf of the organization. When issuing an invoice by an individual entrepreneur, the invoice is signed by the individual entrepreneur or another person authorized by a power of attorney on behalf of the individual entrepreneur, indicating the details of the state registration certificate of this individual entrepreneur.
An invoice drawn up in electronic form is signed with an enhanced qualified electronic signature of the head of the organization or other persons authorized to do so by an order (other administrative document) for the organization or a power of attorney on behalf of the organization, individual entrepreneur in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
7. If, under the terms of the transaction, the obligation is expressed in foreign currency, then the amounts indicated in the invoice may be expressed in foreign currency.
8. The form of the invoice and the procedure for filling it out, the forms and procedure for maintaining a log of received and issued invoices, purchase books and sales books are established by the Government of the Russian Federation.
9. The procedure for issuing and receiving invoices in electronic form via telecommunication channels using an enhanced qualified electronic signature is established by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation.
The formats of the invoice, journal of received and issued invoices, purchase books and sales books in electronic form are approved by the federal executive body authorized for control and supervision in the field of taxes and fees.
Invoice issued before shipment date
Is it possible to issue an invoice before shipment?
According to such an invoice, the inspectorate will refuse the buyer to deduct VAT (see letters from the Ministry of Finance dated July 12, 2021 No. 03-07-09/51713, dated November 9, 2011 No. 03-07-09/39).
Indeed, according to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, invoices for the sale of goods (works, services) are issued no later than 5 calendar days from the date of their shipment. The Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not provide for issuing an invoice “in advance”.
An invoice cannot be issued to the buyer until shipment.
Signatures on the invoice
An invoice issued by a company must be signed by its director and chief accountant or other persons authorized to do so by an order (other administrative document) for the company or a power of attorney on its behalf.
An invoice issued by an individual entrepreneur is signed by the same individual entrepreneur. Moreover, he should indicate the details of his state registration certificate. These are the requirements of paragraph 6 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Based on these requirements, it is not a violation of the procedure for issuing invoices if the document issued includes “Details of the certificate of state registration of an individual entrepreneur,” and the document issued by an individual entrepreneur contains the details “Head of the organization” and “Chief accountant.”
If an invoice is signed by a person authorized by the company, instead of the surnames and initials of the manager and chief accountant after the signature, it is necessary to indicate the surname and initials of the person who signed this document. Please note that if such an invoice also contains the surnames and initials of the head and chief accountant of the organization, then this is not a violation of the requirements of the Tax Code. Such clarifications are given in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 26, 2006 No. 03-04-11/127.
Since September 2, 2010, paragraph 6 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation has introduced a requirement for signing an invoice, which is drawn up in electronic form. So, this document should be affixed with an electronic digital signature of the head of the organization or other persons authorized to do so by an order (other administrative document) for the organization or a power of attorney on its behalf, or the digital signature of an individual entrepreneur in accordance with the Law of January 10, 2002 No. 1-FZ . This requirement will come into effect when the Federal Tax Service of Russia, in fulfilling its duties under paragraph 9 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, approves invoice formats in electronic form.
Invoice for advance payment
According to the rules of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, when the seller receives an advance from the buyer for an upcoming delivery, he is obliged to issue an invoice within 5 calendar days from the date of receipt of the advance (clause 3 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
You don’t have to draw up an invoice for the advance payment, but limit yourself to just an invoice for the shipment, if the advance payment and shipment occurred in the same quarter, and 5 calendar days have not passed between these events. This is written in the letter of the Ministry of Finance dated April 12, 2021 No. 03-07-08/28182.
But if the difference between them is more than 5 days, even within the same quarter, two invoices will be required.
Also, the seller must issue an invoice for both the advance and the shipment, if the receipt of the advance and the shipment occurred in different quarters. In this case, the number of days between events does not matter at all.
If the seller does not issue an invoice for the advance payment, then there will be negative consequences for him. After all, in this case he underestimates the tax base.
QUESTION:In what cases is it possible not to issue invoices and not to keep books of purchases and sales?
ANSWER:
Invoices are not generated:
1) banks, insurance organizations and non-state pension funds for transactions that are not subject to VAT in accordance with Art. 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (clause 4 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
2) organizations and entrepreneurs who are engaged in retail trade, public catering, performing work (providing services) for the population in cash (clause 7 of article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
3) organizations and entrepreneurs who apply special tax regimes in the form of unified agricultural tax, simplified tax system, UTII, since they are not VAT payers (clause 3 of article 346.1, clauses 2 and 3 of article 346.11, clause 4 of article 346.26 Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated July 24, 2008 N 3-1-11/239). Exceptions are those cases when “secretary regime agents” sell goods (work, services) on their own behalf as commission agents (agents) (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 3, 2009 N 03-07-09/54);
4) organizations and entrepreneurs that sell securities (with the exception of brokers and intermediaries) (clause 4 of article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
It should be noted that in clause 18 of the Rules for maintaining logs of received and issued invoices, purchase books and sales books when calculating value added tax, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 2, 2000 N 914 (hereinafter referred to as the Rules), more There are some situations where the taxpayer may not issue an “advance” invoice. We are talking about the following cases:
1) you have received an advance payment for the future supply of goods (work, services), the duration of the production cycle of which is more than 6 months;
2) you received an advance on a transaction subject to VAT at a rate of 0%.
3) you received an advance on a transaction that is not subject to VAT. Let us remind you that non-taxable transactions include those that are exempt from VAT in accordance with Art. 149 Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
4) you are using the right to be exempt from taxpayer obligations on the basis of Art. 145 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
In addition, the Ministry of Finance of Russia in Letter dated 03/06/2009 N 03-07-15/39 (clause 1) indicated that an invoice can also not be issued if you have received an advance on account of the upcoming delivery and within five calendar days from the moment of its receipt, the goods were shipped (work was performed, service was provided).
Please note that the data may be out of date, so be sure to check it by looking at the relevant articles of the Tax Code as of the current date!
The answer to the user’s question was prepared using materials from the website of the Legal Center of Moscow Lawyers