Results
If the export is not confirmed, the exporter must take a number of actions aimed at calculating VAT and deducting tax on unconfirmed exports, as well as submit an updated VAT return for the period of export shipment. It must be remembered that filing an updated declaration must be accompanied by additional payment of tax and penalties.
Sources: Tax Code of the Russian Federation
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Nuances of confirming the zero VAT rate
What is the procedure for collecting documents to confirm zero VAT?
Alexander Lavrov : The composition of the package of necessary documents is established by Art.
165 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. It includes an export contract, customs declarations with customs marks, as well as transport, shipping and (or) other documents with customs marks on the export of goods. All documents confirming the zero VAT rate are submitted in the form of copies. And only for customs declarations there is an exception: their copies can be replaced with a register. From October 1, 2015, the exporter will have this right also in relation to documents confirming the export of goods, for example, invoices (see 452-FZ). The exporter has 180 days from the date of placing the goods under the customs export procedure to collect documents. If the company does not meet this deadline, it must charge tax at a non-zero rate: 18 or 10%. However, the VAT accrued in this case is not charged to the buyer, the contract price for it does not increase and it has no direct relationship to revenue.
How to confirm zero VAT from 10/01/2015?
Natalia Laisha : From now on, exporters and importers will have the opportunity to submit to the tax authorities, instead of copies of customs declarations and transportation documents on paper, registers of these documents in electronic form through an EDI operator. This means that it will be much easier to confirm the validity of applying a 0% tax rate and tax deductions for export and import transactions, and the volume of document flow will be significantly reduced.
To further simplify the process of submitting documents to the tax office, registers can be prepared and transferred to the online reporting system Kontur.Extern from the customs declaration service Kontur.Declarant. Several users with different roles can work in the service at once, even from different offices or cities. In this case, the accountant user gets access to the archive of all “issued” customs declarations: he can upload information to the purchase book, verify data on invoices, create registers of customs declarations, and compile a selection of information to confirm the application of the zero VAT rate.
How to reflect in accounting the amount of VAT accrued on unconfirmed exports?
Alexander Lavrov : There are two main options. The first is recommended by the Russian Ministry of Finance in letter dated May 27, 2003 No. 16-00-14/177. In accordance with it, it is necessary to reflect the accrual of VAT on unconfirmed exports at a non-zero rate by posting Dt 68 “VAT for reimbursement” Kt 68 “VAT for accrual”.
But such VAT in the balance sheet should not affect the state of settlements with the budget, since on the date of tax accrual the organization does not yet have the right to deduct it (reimbursement). This means that its reflection on account 68 can confuse the accountant and lead to errors in reporting. Therefore, it is more logical to reflect the VAT accrued when export is not confirmed on account 19 or 76 (see table).
Reflection of VAT accrued when export is not confirmed
| Contents of operation | Debit | Credit |
| VAT is charged if the zero rate is not confirmed | 19/76 | 68-VAT |
| VAT penalties accrued | 91-2/99 | 68-VAT |
| Input VAT accepted for deduction | 68-VAT | 19 |
| ||
| Accrued VAT written off | 91-2 | 19/76 |
| ||
| Accepted for deduction of VAT accrued earlier | 68-VAT | 19/76 |
| “Input” VAT has been restored | 19 | 68-VAT |
| “Input” VAT has been re-accepted for deduction | 68-VAT | 19 |
How to confirm a zero rate after non-zero VAT has been charged?
Alexander Lavrov : If the company collects all the documents, you can deduct the VAT that was accrued after 180 days. This is allotted three years after the end of the period in which the goods were shipped for export (clause 1, clause 1, clause 9, article 167, clause 2, article 173 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 02/03/2015 No. 03- 07-08/4181).
If the documents are never collected, then the accrued VAT must be written off as other expenses (clause 11 of PBU 10/99 “Organizational expenses”). These expenses can be taken into account when calculating income tax (Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated 04/09/2013 No. 15047/12, letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 12/24/2013 No. SA-4-7/23263).
You can recognize expenses in tax accounting already at the time of accrual (clause 1, clause 7, article 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In accounting, everything depends on the organization’s assessment of the situation and the likelihood of confirming a zero rate. If the organization decides not to confirm the export, the requirement of paragraph. 4 clause 19 PBU 10/99: expenses are recognized when the non-receipt of economic benefits (income) or receipt of assets becomes certain. Therefore, as in tax accounting, already on the date of accrual of VAT you can write it off as other expenses.
If you are still confident that the necessary documents will be collected and the zero rate is confirmed, you need to wait in accounting to recognize expenses. And in tax accounting, in this case, it is better not to rush into recording expenses: if the export is subsequently confirmed, then expenses in the form of VAT will have to be canceled, most likely, with additional tax and penalties.
How to reflect VAT on unconfirmed exports
The company sold goods abroad and did not manage to collect documents confirming export in time. In this case, to account for VAT, you need to open a new subaccount to account 68.
The Ministry of Finance of Russia spoke about this in its Letter dated May 27, 2003 N 16-00-14/177. Since previously there were no explanations, most accountants, in cases where the export of goods was not confirmed within 180 days, made the following entries:
Debit 91-2 Credit 68 subaccount “VAT calculations”
- VAT is charged on the proceeds of goods whose export has not been confirmed;
Debit 68 subaccount “VAT calculations” Credit 51
When the export was confirmed, the following entries were made:
| Debit 91-2 Credit 68 subaccount “VAT calculations” |
- the amount of VAT paid to the budget was reversed;
Debit 51 Credit 68 subaccount “VAT calculations”
- the VAT amount is received in the current account after confirmation of export.
Now the Ministry of Finance has explained that before confirmation of export, VAT is taken into account in a special subaccount of account 68. For clarity, let’s look at this situation using an example.
Example. CJSC Exporter purchased and paid for goods for resale abroad. The cost of goods is 540,000 rubles. (including VAT - 90,000 rubles).
Then the Exporter entered into a supply agreement with the Italian company. The selling price of the goods was 630,000 rubles. On July 1, 2003, the goods were placed under the customs export regime. Ownership of them transferred to a foreign buyer on July 20, 2003.
By December 27, 2003, when the 180-day period allotted to confirm the export expired, the company did not have time to collect all the documents. Therefore, she must pay VAT.
Goods sold are subject to VAT at a rate of 20 percent. The Exporter paid the accrued tax to the budget on December 28, 2003. The company’s accountant must make the following entries:
Debit 68 subaccount “VAT for reimbursement”
Credit 68 subaccount “VAT accrued”
- 105,000 rub. (RUB 630,000 x 20%: 120%) - VAT is charged on the proceeds of goods whose export has not been confirmed;
Debit 68 subaccount “VAT accrued” Credit 51
- 105,000 rub.
FOR UNCONFIRMED EXPORT
As noted in clause 3.8.2, if within 180 days from the date of export the exporter has not submitted a package of documents confirming the export, then on the 181st day the export acquires the status of unconfirmed.
The consequences of recognizing exports as unconfirmed are the filing of an amended VAT return for the period in which the export shipment occurred and the calculation of VAT on unconfirmed exports.
According to paragraph 9 of Art. 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, VAT must be charged at rates of 10 and 18% depending on the type of goods.
The use of settlement rates for unconfirmed exports is not provided.
3.8.5. DEDUCTION OF “INPUT” VAT ON EXPORT OPERATIONS
The basic conditions for obtaining a deduction for “input” VAT also apply to export transactions.
However, in order to receive a deduction for “input” VAT on export goods, it is also necessary to fulfill an additional condition, namely: confirmation or non-confirmation of export.
Clause 10 of Art.
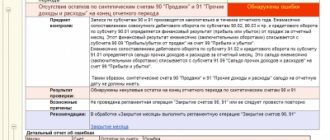
Errors when writing off unconfirmed VAT
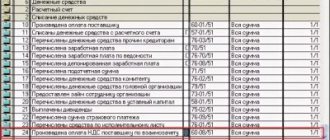
If in the document Confirmation of the zero VAT rate you use an expense item in which the Accepted for tax accounting , a transaction is generated for writing off VAT as expenses not accepted in tax accounting.
When manually adjusting transactions, an error occurs - the data on the accrued tax in SALT and the income tax return differ by 20% of the amount of VAT written off:
- in the declaration, the tax is calculated without taking into account accrued VAT in expenses, since an expense item has been selected that is not taken into account in the NU;
- SALT reflects the amount of tax calculated taking into account the written-off VAT, since the amount in NU in debit 91.02 of account was set manually.
Also, income tax will be calculated incorrectly if you use an Operation entered manually to calculate VAT on unconfirmed exports. In this case, the updated VAT return for the shipment period will not be completed.
Let's check the difference:
- 1,512,000 – 1,152,000 = 360,000 rubles.
- 1,800,000 x 20% = 360,000 rub.
The difference between the tax on SALT and on the declaration is 20% of the amount of VAT written off.
To avoid mistakes, use standard documents and control the selected expense item when writing off VAT.
See also:
- Export of non-commodity goods (products) to the EAEU has not been confirmed within 180 days
- Export of non-commodity goods to non-CIS countries is not confirmed within 180 days
Did the article help?
Get another secret bonus and full access to the BukhExpert8 help system for 14 days free of charge
Related publications
- Profit tax on turnover is calculated incorrectly in 1C Good afternoon. Income tax return (12 months 20)…
- ND for VAT for unconfirmed exports, p.6 and sales book Hello! It is required to submit a corrective ND for VAT for the 2nd quarter of 17....
- VAT declaration for unconfirmed exports Hello. In December 2021, an unconfirmed export document would be issued for...
- Why is depreciation not calculated in 1C 8.3 at the end of the month? ...
Accounting in 1C
On February 15, the products were shipped to the buyer for export.
The organization did not collect a package of documents on time (within 180 days) to confirm the 0% VAT rate for export shipments.
On August 16, VAT was charged in the amount of RUB 1,800,000.
If export sales are not confirmed within 180 days, register this event with the Confirmation of zero VAT rate in the Operations – Period Closing – Regular VAT operations section.
Document header:
- from — the date on which the confirmation period for the zero VAT rate expires;
- Item of other expenses - Write-off of VAT on other expenses .
The expense item on which accrued VAT is taken into account is selected from the Other income and expenses directory:
- Type of article - Taxes and fees (clause 1, clause 1, article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- Accepted for tax accounting checkbox is selected.
Accrued VAT on unconfirmed exports can be taken into account as expenses for income tax purposes on the basis of paragraphs. 1 clause 1 art. 264 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. In the declaration, these expenses may be reflected in Appendix 2 to Sheet 02:
- pp. 041 and 040;
- page 040.
If you want the VAT amount to be reflected on page 041 of Appendix No. 2 to Sheet 02 of the income tax return, you should create a new article with the field Other income and expenses
- Article type - Taxes and fees .
You can also select the predefined item VAT write-off for other expenses with the type Other indirect expenses . Then the VAT amount falls only on page 040 of Appendix No. 2 to Sheet 02 of the income tax return.
The tabular part can be filled automatically with export implementations by clicking the Fill .
- Event - 0% rate not confirmed .
Postings according to the document
The document generates transactions:
- Dt 68.22 Kt 68.02 - VAT is charged on export proceeds;
- Dt 91.02 Kt 68.22 - VAT accrued on export proceeds is included in expenses.
As a result of this reflection:
- when calculating income tax through the regulatory operation Calculation of income tax, the accrued VAT will be taken into account in expenses;
- VAT accrued on unconfirmed export sales is reflected in the income tax return as part of indirect expenses: Sheet 02 Appendix No. 2: page 040 “Indirect expenses - total”: page 041 including “amounts of taxes and fees... "
Export of non-commodity goods not confirmed within 180 days
165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation establishes that the procedure for determining the amount of tax related to goods (work, services), property rights acquired for the production and (or) sale of goods (work, services), transactions for the sale of which are taxed at a tax rate of 0%. is established by the accounting policy adopted by the taxpayer for tax purposes.
Based on this, it is advisable to describe the calculation procedure adopted in the organization in detail and specifically in the accounting policy of the organization for tax purposes. This will help to avoid disputes with tax authorities. In addition, the absence of an established calculation method will allow the inspectorate, when conducting an audit, to apply its own method of calculation, which may be disadvantageous to the taxpayer.
348
Option 1. A package of documents confirming export was submitted on June 18 of the same year.
Export was confirmed on June 30 (the last day of the quarter in which the documents were submitted). The amount of sales taxed at a zero rate is equal to: 200,000 euros x 37 rubles. = 7,400 LLC rub.
“Outgoing” VAT on confirmed exports: 7,400,000 rubles.
x x 0 % = 0 .
“Input” VAT on confirmed exports is 800,000 rubles. Total VAT refundable from the budget is 800,000 rubles.
Option 2. The package of documents confirming export was not submitted. On August 30 (181st day from the date of export), the export becomes unconfirmed.
Corrections are made to the declaration on the date of export shipment (i.e. for the first quarter).
“Outgoing” VAT on unconfirmed exports: 200,000 euros x x 36 rubles. x 18% = 1,296 LLC rub.
“Input” VAT on unconfirmed exports is 800,000 rubles.
Total VAT payable to the budget is 496,000 rubles.
Thus, in the amended VAT return for the first quarter, an additional amount of VAT payable in the amount of 496,000 rubles arises. Additionally, an adjustment will be made to the “outgoing” VAT taking into account the change in the exchange rate on the date of payment.
Reimbursement of “input” VAT on exports is not made automatically (Article 176 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). It is necessary to obtain the consent of the tax authorities, who check the documents submitted by the exporter. The maximum period for such an audit, established by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, is 3 months from the date the exporter submits a tax return.
If a product was purchased for sale in the Russian Federation, and then for some reason was exported, there is a need to restore “input” VAT on the specified product. The reason lies in the special procedure for deducting VAT on exports, discussed in the previous paragraph, namely: VAT cannot be deducted until the export is confirmed or not confirmed.
VAT restoration occurs during the period of export shipment of goods1.
This situation should not be permanent, but rather exceptional, since VAT on goods originally intended for export cannot be deducted. The constant restoration of VAT on export goods at the time of shipment indicates either the absence of separate accounting for ordinary and export goods, or that this accounting is not organized properly.
ACCRUAL OF PENALIES ON THE AMOUNT OF VAT RESULTING FROM NON-CONFIRMATION OF EXPORT
Correction of VAT returns “retroactively” and recalculation of tax liabilities on the date of export leads to penalties for late payment of tax.
A penalty is charged in the amount of 1/300 of the rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation for each day of delay in tax payment, starting from the day following the deadline for tax payment, up to and including the day of tax payment.
Example 3.29. Calculation of penalties on the amount of VAT on unconfirmed exports
Let's return to the data from the previous example. VAT debt - 496,000 rubles. is reflected in the amended declaration for the first quarter and is subject to payment in three equal payments until April 20, May 20, June 20 (inclusive). However, since the declaration for the first quarter was corrected “retroactively” and the VAT could no longer be paid within the deadlines indicated above, there is a delay in tax payment. The penalty will be charged at 1/300 of the rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation for each day of delay (including payment of VAT in three equal payments).
351
Date added: 2014-12-10; ;
Let's go back to the past
The “zero” VAT rate applied to export supplies must be confirmed by the documents listed in Article 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The period for their collection is 180 days from the date of placing the goods under customs export procedures (clause 9 of Article 165 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
But exporters do not always manage to meet this deadline. Or some documents may be missing. In such cases, the seller will have to charge VAT on the cost of goods sold, the export of which has not been confirmed. Moreover, the moment of determining the tax base in this case will be considered the day of shipment of goods (clause 9 of Article 167 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In other words, the exporter has an obligation to pay VAT “retroactively” for the period in which he shipped the goods to a foreign buyer. In this case, the conversion of the “currency” value of the export supply into rubles is done at the rate in effect on the date of shipment (clause 3 of Article 154 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The resulting value must be multiplied by a rate of 18 (or 10) percent, that is, VAT will be “inflated” from above and paid at the expense of the exporter.
In this case, the exporter must issue an invoice again. But it, unlike the “primary” invoice, will indicate the amount of VAT at a rate of 18 (or 10) percent. This invoice is prepared in a single copy. This procedure follows from clause 22.1 of Section II of Appendix No. 5 to the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2011 No. 1137.