Checking the status of settlements with personnel is an integral part of the inventory carried out before drawing up annual reports. During the inventory, the actual state of settlements is revealed, which is compared with the data of the accounting registers. Taking into account the specifics of our magazine, we will tell you what you should pay attention to when conducting an inventory of calculations for the accrual and payment of wages and benefits, settlements with accountable persons, settlements for loans issued to employees, as well as settlements with the budget for personal income tax and extra-budgetary funds for insurance premiums.
In accordance with paragraph 3 of Art. 11 of Federal Law No. 402-FZ, the cases, timing and procedure for conducting an inventory, as well as the list of objects subject to inventory, are determined by the economic entity, with the exception of the mandatory inventory. Mandatory inventory is established by the legislation of the Russian Federation, federal and industry standards. In connection with the entry into force of this law on January 1, 2013, many organizations raised the question of the need to conduct an inventory of obligations before drawing up annual financial statements, because there is no direct indication of its implementation in the text of the document.
It should be noted that before the state accounting regulatory authorities approve the federal and industry standards provided for in Art. 21 of this law, the rules of accounting and preparation of accounting (financial) statements approved by the authorized federal executive authorities and the Central Bank of the Russian Federation before 01/01/2013 are applied (Article 30 of Federal Law No. 402-FZ). Let us remind you that today the Regulations on maintaining accounting and financial statements in the Russian Federation are in force, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 29, 1998 No. 34n. Paragraph 27 of this provision establishes that conducting an inventory, including before drawing up an annual report, is mandatory. Taking into account paragraph 1 of Art. 15 of Federal Law No. 402-FZ, in which the reporting year is defined as a calendar year from January 1 to December 31 inclusive, an inventory of liabilities must be carried out as of December 31 inclusive. Explanations from regulatory authorities that the inventory of payments should be carried out as of December 31 are presented in Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated January 09, 2013 No. 07-02-18/01.
What is checked during the inventory of settlements with employees of the organization? Based on clause 3.46 of the Guidelines for inventory of property and financial obligations, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated June 13, 1995 No. 49 (hereinafter referred to as the Guidelines), unpaid amounts for wages are identified for debt to employees of the organization, subject to transfer to the account of depositors, as well as amounts and reasons for overpayment to employees.
For your information
Clause 2.2 of the Methodological Instructions stipulates that the organization must have a permanent inventory commission, and if there is a large amount of work, it also creates working inventory commissions to simultaneously carry out an inventory of property and financial obligations. The commission should include only those specialists who will definitely be present during its conduct, since the absence of at least one member of the commission serves as grounds for invalidating the inventory results.
When making an inventory of accountable amounts, reports of accountable persons on advances issued are checked, taking into account their intended use, as well as the amount of advances issued for each accountable person (dates of issue, intended purpose) (clause 3.48 of the Methodological Instructions).
According to paragraph 3.48 of the Methodological Instructions, the inventory commission, through a documentary check, must also establish:
- correctness of settlements with tax authorities and extra-budgetary funds;
- the correctness and validity of the amount of debt recorded in the accounting records for shortages and thefts;
- the correctness and validity of the amounts of receivables, payables and depositors, including amounts of debt for which the statute of limitations has expired.
Inventory of calculations for accrual and payment of wages
When conducting an inventory, it is necessary to check the compliance of accrued amounts of wages and other payments with the provisions of the wage system, local regulations of the employer, data on actual output, actual time worked, and also determine the nature of the debt in settlements with employees for wages (normal or overdue).
For this purpose, synthetic and analytical accounting data are subject to verification. It is better to start checking with documents that are the basis for calculating wages. Such documents include:
- collective agreement, provisions on wages, bonuses, other local regulations;
- employment contracts;
- orders on involvement in overtime work, work on weekends, combination of professions, other orders establishing the amount of bonuses and additional payments for work in conditions deviating from normal, as well as orders containing specific standards for remuneration and providing for non-systemic payments.
Information about the actual time worked can be obtained from the time sheet.
Information on the amounts of actually accrued wages is contained:
- in personal accounts;
- in work orders and other documents for performing work within a month in accordance with approved standards and prices (with a piece-rate form of remuneration);
- in settlement (settlement and payment) statements.
Information on the payment of wages to employees is presented in payment (settlement and payment) statements and cash receipts.
It should be noted that after the entry into force of Federal Law No. 402-FZ, the issue of using unified forms for documenting events that occur in the field of labor relations (hiring, dismissing an employee, granting him leave, etc.) was repeatedly raised. According to Rostrud, from January 1, 2013, non-governmental organizations have the right to use forms of primary accounting documents developed by them independently (letters dated 01/09/2013 No. 2-TZ, dated 01/23/2013 No. PG/10659-6-1, dated 02/14/2013 No. PG/1487-6-1).
As an example, Rostrud mentions the employee’s personal card (Form E-2) and notes that the primary accounting document must contain all the mandatory details established by Part 2 of Art. 9 of Federal Law No. 402-FZ. Similar clarifications were given regarding Form T-3 “Staffing Schedule” (Letter of Rostrud dated January 23, 2013 No. PG/409-6-1).
The form of the employee’s personal card, as well as other unified forms of primary accounting documents for recording labor and its payment, was approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated January 5, 2004 No. 1 (hereinafter referred to as Resolution No. 1). At the same time, it is necessary to take into account that the requirements for the use of this unified form for maintaining military registration are provided for in clause 27 of the Regulations on Military Registration.
note
In Information No. PZ-10/2012, the Ministry of Finance indicated that from January 1, 2013, the forms of primary accounting documents established by authorized bodies in accordance with other federal laws remain mandatory for use.
Taking into account the above, we can come to the conclusion that the execution of documents using independently developed forms for recording labor and its payment may cause claims from inspection authorities, since the new form may not take into account (not fully take into account) the requirements of labor legislation for a specific document.
For example, an employee’s personal card must contain columns in which it is necessary to enter information about the work performed, transfer to another permanent job and dismissal (clause 12 of the Rules for maintaining and storing work books). At the same time, this information is not included in the list given in Part 2 of Art. 9 of Federal Law No. 402-FZ.
From the above it follows that when drawing up documents for accounting for labor and its payment, it is more expedient for organizations to use the unified forms approved by Resolution No. 1. Moreover, the use of these unified forms must be approved either by a separate order of the head of the organization or by an appendix to the accounting policy.
Once the availability of all necessary documents has been established, it is necessary to verify the data of primary accounting documents and registers with the amounts reflected in the accounting accounts.
Let us recall that in accordance with the Instructions for the use of the Chart of Accounts in accounting, payroll is reflected in the credit of account 70 “Settlements with personnel for wages” and the debit of the accounts accounting for production costs (sales expenses) and other sources (08 “Investments in non-current assets”, 20 “Main production”, 25 “General production expenses”, 26 “General business expenses”, 44 “Sales expenses”, etc.).
When taking inventory of settlements with personnel, turnover on the credit of account 70 is compared with the amounts reflected in the settlement (settlement and payment) statements.
Payment of wages is reflected in the debit of account 70 and the credit of cash accounting accounts (50 “Cash”, 51 “Settlement accounts”). When making various deductions from wages, correspondence is possible with accounts 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees” (when withholding personal income tax), 71 “Settlements with accountable persons” (when withholding the unused amount of the advance received under the report), 73 “Settlements with personnel for other obligations" (for example, to compensate for damage caused to the employer, or to repay a loan provided by the organization), 76 "Settlements with various debtors and creditors" (when withholding alimony).
The instructions for using the Chart of Accounts stipulate that analytical accounting for account 70 is maintained for each employee of the organization.
For your information
The credit balance of account 70 shows the organization's debt to employees for wages accrued but not paid to them (both current and overdue). Amounts accrued but not paid on time (due to the non-appearance of recipients) are listed on the credit of account 76 “Calculations with different debtors and creditors”, sub-account “Settlements for deposited amounts”. When taking inventory of the subaccount “Calculations for deposited amounts” of account 76, the amounts of deposited debt for which the statute of limitations has expired are identified.
EXAMPLE FROM JUDICIAL PRACTICE
The court considered a rather trivial situation when funds were taken by the director from the cash register as settlements with accountable persons and were used for personal needs. At the same time, the director did not report on the use of funds and did not return the money to the cash desk. The court found that the director must return damages to the company in the amount of 336,414 rubles. 37 kopecks (resolution of the Arbitration Court of the North Caucasus District dated September 16, 2015 No. F08-6779/2015). At the inventory stage, it is possible to identify this fact of using funds for one’s own purposes more quickly.
Results of the inventory of settlements with employees
The results of the inventory are documented in an act. Moreover, the company can use both the approved INV-17 form and develop its own act, since according to Law No. 402-FZ “On Accounting”, the company can use its own developed forms, taking into account the availability of mandatory details.
The main thing is that the form reflects:
- accounts receivable;
- accounts payable.
We will reflect the receivables in the act.
Example 2.
Employee P.G. Okunev was accrued excessive vacation pay - 11,200 rubles. The statute of limitations has expired, so the debt can no longer be collected.
Accordingly, when conducting an inventory, this amount is reflected in the act, and in the future it can be written off in accounting.
Another amount included in the act is the accountable amount not confirmed by documents - 8,000 rubles.
In this case, it is necessary to request an explanation from the employee and try to restore the documents. If the amount of debt is recorded due to the fault of the employee, then it will be necessary to recover it from the employee. To do this, it is necessary to invite the employee to voluntarily return the funds. If the employee refuses to return the funds, it would be advisable to go to court. It is clear from the act that the statute of limitations in this case has not expired.
Now let's reflect the accounts payable in the act.
Example 3.
The commission identified the issuance of overexpenditure for a business trip from the cash register on a receipt order.
Also reflected is the deposited salary to an individual providing services under a civil contract. On the days when wages were issued, the individual did not apply for these funds; therefore, the funds were transferred to the depositor.
Inventory lists can be filled out using computers and other organizational technology, or manually. The inventories are signed by all members of the inventory commission and financially responsible persons. At the end of the inventory, financially responsible persons give a receipt confirming the commission’s verification of wage calculations.
GOOD TO KNOW
During the inventory, the commission can identify debit balances on accounts 70, 71, 73. This means that the employees owe the company. For example, they were overpaid wages, vacation pay, employees did not report on accountable amounts on time, did not repay the loan, etc. In each specific case, different rules for debt repayment apply. They are installed in Art. 137, 138, 248 and 392 of the Labor Code, Art. 811 of the Civil Code.
What date should the inventory results be issued?
Inventory can continue for more than one day, especially if we are talking about the presence of structural divisions, each of which calculates and pays wages.
As a general rule, the terms and dates of inventory are formalized in the appropriate order.
The order specifies:
- name or surname, first name and patronymic of the taxpayer in respect of whose property the inventory is being carried out;
- legal address or place of residence of the taxpayer;
- composition of the inventory commission headed by the chairman;
- property subject to inventory and its location;
- timing of inventory (start and end dates).
In this case, the inventory dates in the act must coincide with the dates established in the order for the inventory. The cases, timing and procedure for conducting an inventory, as well as the list of objects subject to inventory, are determined by the economic entity, with the exception of the mandatory inventory (Article 11 of Federal Law No. 402-FZ “On Accounting”).
Inventory at the end of the year is considered mandatory. Before preparing annual financial statements, all organizations, regardless of their organizational and legal forms and applicable tax regimes, are required to conduct an inventory. Typically, inventory results in this case are drawn up at the end of the year, December 31, 2021.
POSITION OF THE MINISTRY OF FINANCE
The inventory of receivables and payables is carried out as of December 31 of the reporting year inclusive. In addition, inventory is mandatory: when changing financially responsible persons; when facts of theft, abuse or damage to property are revealed; in the event of a natural disaster, fire or other emergency situations caused by extreme conditions; during reorganization or liquidation of the organization. In this case, the fact of mandatory inventory is documented on the date the inventory is completed and the corresponding act is drawn up. If the head of an economic entity conducts an inventory more often, for example, once a quarter, then, accordingly, the inventory will be carried out at the end of the quarter.
— Recommendations in the attachment to the letter dated 01/09/2013 No. 07-02-18/01.
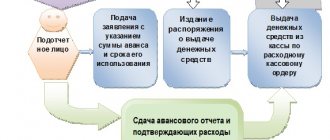
Inventory of settlements with accountable persons
During the inventory, it is necessary to check the reports of accountable persons on advances issued, taking into account their intended use.
Based on the results of the inventory, the commission must establish accountable amounts for which employees did not submit an advance report. Of these, amounts are allocated for which employees did not report on time.
First, you should establish the availability of the following documents in the organization, approved by the head:
- a list of persons who have the right to receive funds on account;
- a list of management personnel authorized to instruct accountable persons to make expenses in the interests of the employer and give instructions to accounting employees to issue accountable amounts.
For your information
, the Order of the organization approves the list of persons who have the right to receive funds on account. The order must establish, in particular, the terms for which accountable amounts are issued, their maximum amount and the procedure for submitting advance reports. If the organization does not have such an order, we can assume that the deadline for issuing accountable amounts has not been established, which means that settlements on accountable amounts must be made within one business day. The Federal Tax Service came to this conclusion in Letter No. 04-1-02/704 dated January 24, 2005.
The issuance of money on account is carried out using a cash order (clause 4.1 of the Regulations on the procedure for conducting cash transactions) or by transferring non-cash funds to the employee’s card. According to clause 4.4 of the Regulations on the procedure for conducting cash transactions for issuing cash to an employee for business expenses, an expense cash order is issued in accordance with a written application of the accountable person, drawn up in any form and containing the manager’s handwritten inscription about the amount of cash and the period for which they are issued, signature leader and date.
note
In order to minimize cash circulation, as well as taking into account the inexpediency of issuing organization cards to every employee sent on a business trip, and the specifics of expenses associated with compensating employees for documented expenses, the Ministry of Finance and the Treasury of the Russian Federation consider it possible to transfer funds to the bank accounts of individuals - employees organizations in order to carry out, using cards of individuals issued as part of “salary” projects, payment of travel expenses and compensation to employees of documented expenses (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 02-03-10/37209, Letter of the Treasury of the Russian Federation No. 42-7.4-05/ 5.2-554 dated September 10, 2013).
What documents confirm the intended use of funds? If money was issued for the purchase of material assets or for entertainment expenses, then these are advance reports, to which are attached sales and cash receipts, receipts for PKO, invoices and other documents confirming the expenditure of funds and the acquisition of valuables.
In the case where money was issued on account for travel expenses, it is necessary to check the availability of the following documents:
- official assignment;
- order to go on a business trip;
- travel certificate;
- an advance report with attached documents confirming expenses (travel tickets, hotel receipts, sales and cash receipts, etc.).
For your information,
the Ministry of Labor, having considered in Letter No. 14-2-291 dated February 14, 2013, the issue of preparing primary documents when sending an employee on a business trip, explained: the relevant documents (in particular, a travel certificate) must be drawn up according to the forms approved by Resolution No. 1 Rostrud, in Letter No. 164-6-1 dated March 4, 2013, also noted that when issuing a travel certificate, you should use the unified T-10 form and follow the instructions for filling it out, approved by this resolution. In addition, para. 3 clause 26 of the Regulations on the peculiarities of sending employees on business trips, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 13, 2008 No. 749, it is directly established that the employee’s report on the work performed on a business trip is submitted to the employer in writing. Unified forms of the official assignment, report on its completion and travel certificate are also contained in Resolution No. 1.
In accordance with the Instructions for using the Chart of Accounts, information on settlements with accountable persons is summarized in synthetic account 71 “Settlements with accountable persons”. The debit of this account reflects the issuance of funds to the employee, and the credit reflects the repayment of his debt: posting of valuables or acceptance of expenses, as well as the return of unused advance amounts.
Analytical accounting for account 71 is carried out for each amount issued for reporting.
Sequence of debt inventory
Legislation and accounting practice of organizations of various forms of ownership have developed a procedure for conducting an inventory of calculations, which is recommended to be followed. In this case, the likelihood of errors, inaccuracies and loss of working time will be minimized. Let's consider the procedure:
- Carrying out reconciliations of mutual settlements with counterparties before the start of the procedure and signing the corresponding reconciliation acts, which reflect the data corrected and accepted for accounting by both parties. They are also recommended in the case of “zero” revolutions for a period. During the reconciliation, previously lost data and documents may be discovered.
- Preparation and publication of an inventory order. Note that in the case of a planned inventory, information about which is already contained in the accounting policy and is unchanged, such an order is not necessary. However, in practice there is a need for it. The document defines the timing, composition of inventory commissions, responsible persons, the nature of the inventory and the accounting areas subject to it. The commission must include at least 3 people who have the appropriate competence to inventory the debts reflected in the accounts. Both internal auditors and persons invited from outside can take inventory of accounting data.
- Inventory process. It is a reconciliation of the amounts in the relevant accounting accounts with the data of primary documents, acts of reconciliation of mutual settlements with counterparties, contracts and payment schedules attached to them. It is also important to determine the amount of overdue debt, the causes and consequences of their occurrence.
- Presentation of results. For this purpose, it is recommended to use an inventory report in the INV-17 form for settlements with suppliers, buyers, and other debtors (creditors). The document must be signed by all members of the commission, as well as the head of the organization. The absence of at least one signature of the auditors makes the document void and the audit invalid, since it is considered that one of the commission members did not take part in it.
Attention! The inventory carried out before filling out the annual accounting forms must be reflected in these forms for the reporting year. Information obtained as a result of the inventory for other reasons must be reflected in the accounting data of the period of its completion (see clause 5.5 of the Guidelines, order No. 49 of 06/13/95).
Inventory of calculations for the accrual and payment of benefits
Verification of calculations for the accrual and payment of benefits is necessary to confirm their validity.
It should be noted that if errors are identified in such calculations and corrected in a timely manner, the organization will be able to avoid problems of offset of benefits at the expense of the Social Insurance Fund. When assigning and paying benefits, the organization is guided by:
Federal Law No. 255-FZ of December 29, 2006 “On compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity” (hereinafter referred to as Federal Law No. 255-FZ );
Federal Law of July 16, 1999 No. 165-FZ “On the Basics of Compulsory Social Insurance” ;
Federal Law No. 81-FZ of May 19, 1995 “On state benefits for citizens with children” ;
Federal Law of December 3, 2012 No. 216-FZ “On the federal budget for 2013 and the planning period of 2014 and 2015” ;
The procedure and conditions for the appointment and payment of state benefits to citizens with children;
The procedure for issuing certificates of incapacity for work;
Explanation “On the procedure for providing and paying additional days off per month to one of the working parents (guardian, trustee) to care for disabled children”;
Federal Law of January 12, 1996 No. 8-FZ “On burial and funeral business” .
First of all, it is necessary to check the availability of all documents that are the basis for the assignment of benefits. Depending on the type of benefit, such documents include:
- certificates of incapacity for work;
- certificates of the amount of earnings from which the benefit should be calculated from places of work with other employers;
- documents confirming insurance experience;
- documents for the assignment of “children’s” benefits listed in the Procedure and conditions for the assignment and payment of state benefits to citizens with children ;
- applications for benefits;
- calculations of benefits made by the organization's accounting department.
When checking the correctness of the calculation and payment of benefits in accordance with Federal Law No. 255-FZ, you should remember:
- temporary disability benefits for the first three days are paid at the expense of the employer ( clause 1, clause 2, article 3 );
- the maximum amount of earnings when calculating benefits cannot exceed the established maximum amount of the base for calculating insurance contributions ( Article 14 );
- Temporary disability benefits when it is necessary to care for a sick family member are paid to the insured person, subject to restrictions (in particular, in the case of caring for a sick child under 7 years of age, the benefit is paid for no more than 60 calendar days in a calendar year, for children from 7 up to 15 years - no more than 45 calendar days) ( clause 5, article 6 );
- the right to a monthly child care allowance is retained if the person on parental leave works part-time or at home and continues to care for the child ( Article 11.1 ).
Next, you need to check the entries in the accounting accounts. The accrual of benefits is reflected in the credit of account 70 in correspondence with the expense accounts when calculating benefits for temporary disability at the expense of the employer (Debit 20, 25, 26, 44) or in the debit of account 69 “Calculations for social insurance and security” (when calculating benefits for temporary disability starting from the fourth day of illness and other benefits paid from the Social Insurance Fund). Payment of benefits is reflected in the debit of account 70 and the credit of cash accounts.
Options for returning missing funds issued on account
If, based on the results of the work of the inventory commission, a person was identified as guilty of the unjustified failure to return funds issued on account, then the missing amount can be withheld from the salary of the guilty employee. The employer has the right to do this. But there are certain conditions for keeping it. Firstly, deductions from wages can be made no later than one month from the end of the advance payment period. Secondly, the employee, for his part, agrees with the accusation and the amount of deductions.
If the employer misses the monthly deadline, then you can give the employee the opportunity to return the missing funds on a voluntary basis, or transfer the documents to the judicial authorities. There is another option that applies to debt amounts; it is that after the expiration of the statute of limitations, this amount is recognized as a bad debt. When an employee is dismissed, his debt to the organization may also be considered uncollectible.
Inventory of settlements for loans to employees
The ability of an organization to issue loans to its employees is provided for in paragraph 1 of Art.
807 Civil Code of the Russian Federation. Loans can be provided either in cash or in kind. In accordance with paragraph 1 of Art. 808 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, a loan agreement between an organization and an employee is drawn up in writing. Funds are issued from the cash register using an expense cash order or transferred in non-cash form according to the details specified by the employee. Accounting for loans issued to employees is carried out using account 73, subaccount “Settlements on loans provided.” If the loan is interest-bearing, it can be reflected in account 58 “Capital investments”, subaccount “Provided loans”.
The accrual of interest on such loans in accounting is reflected in the debit of account 73 and the credit of account 91/1.
If an employee is given an interest-free loan or the rate for using the loan is lower than established by Art. 212 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, a material benefit may arise that is subject to personal income tax in accordance with the provisions of Art. 210 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
What documents relate to local acts that require verification?
- a list of responsible employees who are authorized to receive funds on account;
- a list of employees of the management team of the enterprise who have the power of attorney to give instructions to employees regarding the intended use of advance funds, and to an employee of the accounting service or the cashier of the enterprise - instructions regarding the issuance of amounts of money for reporting.
Expense reports should be checked for:
- compliance of the use of funds with the intended purpose;
- compliance of the deadlines for drawing up the advance report with the deadline for returning the remaining funds;
Important ! The head of the organization closes and approves expense reports.
Inventory of personal income tax payments
Organizations and entrepreneurs from whom or as a result of relationships with which employee-taxpayers receive income are recognized as tax agents.
Tax agents are required to calculate, withhold from the taxpayer and pay the amount of personal income tax calculated in accordance with Art. 224 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). According to paragraph 1 of Art. 230 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, tax agents keep records of income received from them by individuals in the tax period, tax deductions provided by the latter, calculated and withheld taxes in tax accounting registers. The forms of tax accounting registers and the procedure for reflecting analytical data of tax accounting and data from primary accounting documents are developed by the tax agent independently and must contain information that allows identification of:
- taxpayer;
- the type of income paid to him and tax deductions provided in accordance with the codes approved by the federal executive body authorized for control and supervision in the field of taxes and fees. Currently, the Order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated November 17, 2010 No. ММВ-7-3/ [email protected] “On approval of the form of information on the income of individuals and recommendations for filling it out, the format of information on the income of individuals in electronic form, reference books” is in force;
- amounts of income and dates of their payment;
- taxpayer status;
- dates of tax withholding and transfer to the budget system of the Russian Federation, details of the corresponding payment document.
A document confirming the fulfillment by a tax agent of the obligation to transfer taxes to the budget is a payment order.
During the inventory of personal income tax settlements, it is necessary to check the entries in account 68, subaccount “Personal income tax settlements”.
According to paragraphs. 10 p. 1 art. 32 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, tax authorities are obliged to provide the taxpayer, fee payer or tax agent, upon his request, with a certificate about the status of the said person’s payments for taxes, fees, penalties, fines, interest and a certificate of fulfillment of the obligation to pay them based on the data of the tax authority. A certificate on the status of such settlements is transferred (sent) to this person (his representative) within five days, a certificate on the fulfillment of the obligation to pay taxes, fees, penalties, fines, interest - within 10 days from the date of receipt of the relevant request by the tax authority. In addition, by virtue of paragraphs. 11 of the above paragraph, tax authorities are obliged to carry out, at the request of a taxpayer, a responsible participant in a consolidated group of taxpayers, a fee payer or a tax agent, a joint reconciliation of calculations for taxes, fees, penalties, fines, and interest. The results of such reconciliation are documented in an act. The act of joint reconciliation of calculations is handed over (sent by registered mail) or transferred to the taxpayer (responsible participant of the consolidated group of taxpayers, payer of the fee, tax agent) in electronic form via telecommunication channels within the next day after the day of drawing up such an act. The procedure for transmitting the act of joint reconciliation of calculations for taxes, fees, penalties and fines in electronic form via telecommunication channels was approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated December 29, 2010 No. ММВ-7-8/ [email protected]
Based on para. 2 p. 3 art. 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, in the event of detection of amounts of overpaid tax, both the taxpayer and the tax authority can initiate a reconciliation of calculations. The form of the act of joint reconciliation of calculations for taxes, fees, penalties and fines was approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated August 20, 2007 No. MM-3-25 / [email protected] Regulations for organizing work with taxpayers, payers of fees, insurance contributions for compulsory pension insurance and tax agents approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated 09.09.2005 No. SAE-3-01/ [email protected] (as amended on 01.21.2013).
Provision for doubtful debts
If the inventory reveals debit balances, this means that the employees owe the employer. Depending on the specific situation as a result of which the debt was formed, one or another rule for its repayment is applied. They are indicated in Article 811 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation and the following articles of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation: 137, 138, 248, 392.
In some cases, debt is classified as doubtful. For example, if it is not secured by any guarantees, or if the debt is not repaid on time or will not be repaid on time with a high probability. Debt can be classified as doubtful debt for up to three years from the date of its occurrence. If the claim period has expired and the debt has not been repaid, it can be written off. A reserve for doubtful debts is created using the following entries:
D91 subaccount “Other expenses” K63
The amount of doubtful debt is determined for each such debt. If the employee nevertheless repays the debt, it is documented with the following entry:
D63 K91 subaccount “Other income”.
When the claim period has already passed, the receivable can be written off. In this case, the postings will depend on whether a reserve for doubtful debts has been created for this receivable. If yes, then the wiring will be as follows:
D63 K70 (71, 73)
If not, then the debt is written off against the company’s financial results, and the posting will be as follows:
D91.2 K70(71, 73)
In addition, the debt is reflected in account 007 “Debt of insolvent creditors written off at a loss”, where it is taken into account for 5 years. To write off the debt, an inventory act is drawn up, as well as an order from the director.
Inventory of calculations for insurance premiums
Part 1 of Art.
5 of Federal Law No. 212-FZ establishes that employers who make payments to employees are payers of insurance premiums. According to Part 6 of Art. 15 of this law, employers who pay insurance premiums are required to keep records of the amounts of accrued payments and other remunerations, the amounts of insurance premiums in relation to each individual in whose favor the payments were made. To organize such accounting, there are individual cards that are opened for each employee. In order to unify the maintenance of individual accounting in the Letter of the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation dated January 26, 2010 No. AD-30-24/691, the Federal Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation dated January 14, 2010 No. 02-03-08/08-56P “On the procedure for recording the amounts of accrued payments and other remunerations, and also the amounts of accrued insurance premiums by insurance premium payers who make payments and other remuneration to individuals,” the form of an individual accounting card is presented.
During the inventory of payments for insurance premiums, in addition to individual cards, it is necessary to check payment orders. Let us remind you that the payment of insurance premiums is carried out in separate settlement documents sent to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, the Social Insurance Fund and the Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund (Part 8 of Article 15 of Federal Law No. 212-FZ).
The accrual of insurance premiums is reflected in the credit of account 69 “Calculations for social insurance and security” for the corresponding subaccounts. Repayment of debt to extra-budgetary funds is reflected in the debit of account 69.
For your information
If a fact is discovered indicating a possible excessive payment of insurance premiums, at the proposal of the body monitoring the payment of insurance premiums or the payer of insurance premiums, a joint reconciliation of calculations for insurance premiums can be carried out. The results of such a reconciliation are documented in an act signed by the body monitoring the payment of insurance premiums and the payer of insurance premiums (Part 4, Article 26 of Federal Law No. 212-FZ). To confirm settlements with the Pension Fund and the Social Insurance Fund, forms 21-PFR and 21-FSS of the Russian Federation, approved by Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated December 11, 2009 No. 979n, are used.
Salary arrears
If accounts payable are shown on account 70, this means that employees have been accrued wages (vacation pay, benefits), but have not yet been paid. If there is a debit balance on account 70, this indicates that there is a debt due to personnel. In this case, the created commission identifies the reasons that contributed to its occurrence, and also evaluates the possibility of its repayment. After this, a decision is made whether it is possible to create a reserve for doubtful debt, or whether to write off the debt as other expenses (Read also the article ⇒ Cash compensation for salary delays in 2021).