Author: Ivan Ivanov
Accounting is one of the most precise theoretical and applied sciences, thanks to which any, even the most insignificant movement of cash and non-cash money, goods and other material assets is reflected in full compliance with legislative norms. The origins of orderly accounting go back to ancient times; over the centuries, the system has been improved. Accounting was most developed in England and Italy.
Russian financiers at various levels these days use a strictly regulated chart of accounts, which is approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n.
Definition
Account 71 is one of the most widely used in accounting transactions. Quotes from account 71, which is called “Settlements with accountable persons” or “Calculation of accountable amounts,” are used to reflect data on funds issued from the cash register and received by an employee of a business entity.
The tasks of issuing money to an employee are as follows:
- implementation of economic and operational activities;
- carrying out small wholesale purchases of goods;
- provision of travel and hospitality expenses.
In most cases, the need to issue financial resources arises when an employee completes tasks assigned by management to carry out the direct activities of the organization.
The peculiarity of the essence of account 71 is that the issued amount does not become the property of the accountable person and has a strictly intended purpose.
That is, an employee of an enterprise has the right to spend money only on the goals set by the manager, and also if they are a production necessity. If there is a balance of the amount received for reporting, it is returned to the cashier.
An important point is compliance with cash discipline regarding operating cash. After the employee has fully completed the assigned task, it is necessary to provide a full report on the expenditure of the funds received within three working days.
Otherwise, if for some reason the deadlines for submission are missed or the report is not provided at all, such amounts are regarded by the modern Tax Code of the Russian Federation as income of an individual and are subject to taxation in conjunction with other income of the employee in accordance with Art. 137 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Retention of unused and unreturned funds is carried out on the basis of Art. 138 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation after submitting a written application and within the limits of up to 20% of wages.
The modern regulatory framework of Russia does not regulate the period for issuing accountable funds; these points are stipulated by the internal documents of the organization. As accountable amounts, money can be issued exclusively to employees of the enterprise.
Using account 71 in accounting
The account is maintained by debit and credit. Debit calculations are carried out taking into account the funds deposited. When depositing into an account, the transaction number will be displayed first, followed by the general account number. In the case of credit transactions, the entry is performed in the reverse order. In general, calculations for account 71 can be divided into several categories:
| Operation | Check |
| Purchase by an accountable person of various materials | |
| Delivery by the accountable person of funds issued in advance. Revenue received from product sales | |
| Repayment of debt by an accountable person to the supplier | 60 |
| Various expenses that arose in the course of running a company or traveling on a business trip | , , 10, , |
| Return and issue of check books | 76 |
| Amounts not returned to the cash desk within the agreed time frame | 94 |
| Re-registration of debt of accountable persons due to a change in their place of work | 79 |
These correspondent accounts are accounted for separately, so it is important to have confirmation of each transaction. If the employee does not return the balance of funds to the enterprise’s cash desk, they may be written off as a shortage
When performing all calculations, the accountant must adhere to accepted standards and indicate each expense item in a certain order.
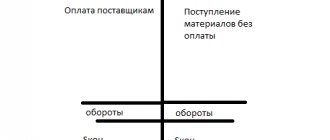
Debit and credit
Account 71 belongs to the category of active-passive. This feature is related to the fact that account balances can be debit and credit:
- Dt 71 reflects the amount of money that was issued from the cash register and received by the employee.
- Kt 71 shows the expenditure of money, confirmed by documents attached to the advance payment.
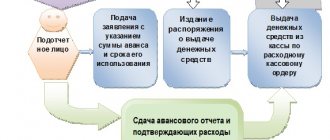
After the manager’s order, money is issued both from the cash register and transferred from a bank account to a plastic card. The basic rule is to receive a report on the use of previous subreports, only after which a new amount is issued. To simplify the systematization of accounting, persons who can receive money for business expenses are assigned by an internal order of the organization and a special document is signed with them - a Liability Agreement.
What it is
Any company interacts with other legal entities and entrepreneurs to achieve mutual benefit. Often interaction occurs through hired workers. Employees representing the interests of their superiors may incur certain expenses in the performance of their professional duties. That is why the heads of organizations or enterprises allocate an accountable amount of money to them. 71 accounts in the accounting department are used specifically to account for this money.
Registration of the operation of issuing funds to an authorized person
Characteristic
The information content of the account defines this account as a register of material accounting of funds. The Order “On the Accounting Policy of an Enterprise” regulates the specifics of maintaining account 71 - on the active or passive side.
- Credit balance. The occasional use of small-scale reporting in enterprises with modest turnover allows you to pay expenses after they have been incurred.
- The balance is debit. Management chooses a policy of advance payment. Advance payment is the most convenient option for enterprises where frequent, long-term business trips or constant large-scale purchases for cash are practiced.
For each accountant, the enterprise maintains detailed analytical records in the context of 71 accounts. If analytical accounting records specific turnover for each individual employee, then thanks to synthetic accounting the total amount of turnover is reflected, balances characterizing the relationship between personnel and the organization in the area of production expenses.
Cash discipline is as follows:
- Seconded employees report on the day of arrival if this happened during working hours. In other situations, the legislation allocates three working days for the report - Directive of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation No. 3210 dated March 11, 2014 in paragraph 6.3.
- Full-time personnel who are constantly at the workplace must report from the moment they receive money on an expense order from the cash register or the receipt of funds on the card.
What is it used for?
Accountable employees are determined by order of the head of the enterprise. They are given goals and given funds. The description of the accounting accounts suggests that such persons are required to use 71 accounting accounts.
Important! Employees are called this because after completing their work for which money was allocated, they are required to provide reports and attached documents on the expenditure of funds to the accounting department of their enterprise.
71 accounting account is a special register that summarizes information about the formation of debts of an employee to a legal entity for money issued to him for the performance of specific tasks. The special account71 also contains information on the repayment of debts for the provision of expenses according to the advance report. However, that's not all. The organization may also owe the employee a certain amount if he wasted his own money on the needs of legal entities. Reimbursement occurs by order of management with an advance report.
Balance sheet for a specific period
Important! It is impossible to place information about loans and credits issued to employees in the 71st special account, since this is the competence of the 73rd position. Many unscrupulous entrepreneurs, under the guise of accountable money, issue microloans to their employees, which is a violation of the law.
The current law in this area suggests that amounts can only be issued for the purposes specified in the orders, and that the employee must return them in case of failure or account for their use. To keep records of accountable employees, journal order No. 7 is used. It records all expenses incurred and money issued for the reporting month.
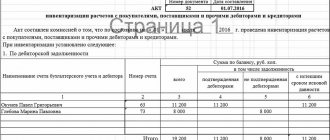
An example of an advance report that may indicate debt repayment
Correspondence
The consistency of general synthetic accounting, the formation of a balance sheet and tax reporting subsequently depends on how correctly and accurately each posting is made.
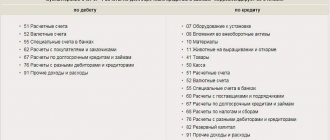
Accounting theory assumes correspondence between account 71 and certain accounts, both debit and credit. Debit - 50 “Cash Accounting”, 51 “Cash Account”, 52 “Currency Account”, 55 “Correspondent Bank Account”, 76 “Settlements with Any Debtors and Creditors”, 79 “Intra-Business Settlements”, 91 “Other Income and Expenses” .
Credit – accounts 10, 11, 15, reflecting settlements for transactions with material assets, fixed assets, and non-current assets. Production section - 20, 23, 25, 26, 28, 29. Commodity accounting category - 41, , 45. Accounting for funds in various forms - 50, , 52, 55, calculations are reflected in the account. 70, 76, 79. Closing turnover and drawing up results for sub-reports is carried out on accounts , , 97. The withdrawal of profits or losses is carried out on the credit side of account 99.
Maintaining double entries must be accompanied by Instructions for using the Chart of Accounts.
Reflection of entertainment expenses in accounting
To account for the issued accountable amounts for the purpose of paying for entertainment events, entries are made for 71 accounts:
- Dt “Calculations for accountable amounts” Ct “Cash” - money was issued for reporting.
- Dt “General business expenses” Ct “Calculations for accountable amounts” - reflects the amount of entertainment expenses.
- Dt “VAT” Ct “Calculations for accountable amounts” – the amount of VAT is taken into account.
- Dt “Cashier” Kt “Settlements for imprest amounts” - unused funds are returned to the enterprise’s cash desk.
- DT “Calculations for accountable amounts” CT “Cash” - funds were issued as compensation to the employee for overexpenditure.
- Dt “Retained profit/loss” Kt “Calculations for taxes” - in case of excess of standardized expenses, the amount of VAT on the overexpenditure is restored.
The amount of entertainment expenses should not exceed 4% of labor costs in the reporting period.
Postings
Active-passive account 71 corresponds with a certain list of accounts reflecting transactions inherent in this part of the company’s activities. First of all, these are accounts for accounting for cash (50 “Cashier”) and non-cash (51 “Bank”), as well as material accounting for goods, services, production - 08, 10, 20, 26, , 44. Correspondence for any accounting activities are reflected in the main register - the Journal of Accounting Transactions, which has the following form:
| № | Operation | Dt | CT | Sum | Document |
| 1 | Money issued from the cash register | 71 | 60 | RKO, cash book | |
| 2 | Credited to the card from the current account | 71 | 51 | Payment order, statement | |
| 3 | Transfer of funds for reporting to a corporate card | 71 | 55 | Extracts from special accounts | |
| 4 | A report on the acquisition of OS was carried out | 08 | 71 | Transfer and Acceptance Certificate | |
| 5 | A report on the acquisition of goods and inventory items was carried out | 10 | 71 | Commodity or consignment note, acceptance certificate | |
| 6 | A report on costs for production purposes was carried out | 20, 23, 44 | 71 | Advance report – JSC | |
| 7 | A report on goods for further sale is carried out | 41 | 71 | Consignment note, JSC | |
| 8 | The balance of the report is entered into the cash register | 71 | 50 | PKO, cash book | |
| 9 | Accrual of debt for non-repayment of money on time from accountable persons | 73 | 71 | JSC |
Settlements with employees are carried out as follows.
- the amount of debt owed by employees to the enterprise;
- the amount of debt the company owes to its staff;
- turnovers on the debit and credit sides are displayed;
- The expanded balance as of the end of the reporting period is displayed.
Basis for writing off costs
When accepting the expense report, the accountant checks the documents confirming the expenses. These can be invoices, invoices and invoices for the purchase of property, cash and sales receipts confirming payment for all kinds of services, i.e. primary documents that are the fundamental basis for assigning costs to 71 accounts.
The main requirement for conducting a business transaction in accounting is written confirmation of the transaction. In other words, all expenses indicated in the advance report must be justified and confirmed by primary accounting documents, correctly executed, with completed details, necessary signatures, seals and stamps. Expenses that are not supported by documents or supported by incomplete documents cannot be accepted and reflected in accounting, and this is fraught with unpleasant consequences. The employee will pay such costs out of his own pocket.
Therefore, the accountable person should take the issue of preparing an advance report seriously and promptly demand correctly completed documents for expenses incurred.
Turnover balance sheet
There are also certain features in filling out the SALT for accounting for advance reporting. It may have a balance on the debit side when the accounting policy of the enterprise is to issue advances for expenses stipulated by law. A credit balance is used in final settlements with “accountants” according to the following scheme: expense – advance report – payment of money.
Due to the nature of operations, expense reports are usually handled by an experienced accountant or financial manager.
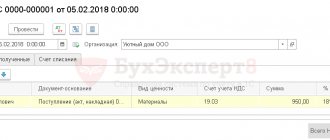
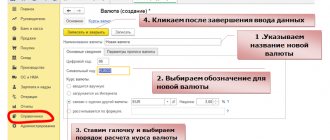
The formation of OSV in 1C is presented below.
How to reflect VAT payment
When a company pays VAT when purchasing goods or services from accountable money at quotation 19, the tax amount is reflected in the transactions:
| № | Debit | Credit | Description |
| 1 | 19 | 71 | Amount of accrued VAT |
| 2 | 68 | 19 | VAT deduction amount |
Basic quotes of the second order
To systematize and combine cash flow data, analytical accounting corresponds with second-order quotes:
| № | In debit | On credit |
| 1 | 50 | 07 |
| 2 | 51 | 08 |
| 3 | 52 | 10 |
| 4 | 55 | 11 |
| 5 | 76 | 15 |
| 6 | 79 | 20 |
| 7 | 91 | 23 |
| 8 | 25 | |
| 9 | 26 | |
| 10 | 28 | |
| 11 | 29 | |
| 12 | 41 | |
| 13 | 44 | |
| 14 | 45 | |
| 15 | 50 | |
| 16 | 51 | |
| 17 | 52 | |
| 18 | 55 | |
| 19 | 70 | |
| 20 | 73 | |
| 21 | 76 | |
| 22 | 79 | |
| 23 | 91 | |
| 24 | 94 | |
| 25 | 97 | |
| 26 | 99 |