Organizations periodically conduct inventories. They are needed in order to obtain the current balances of a particular product. Inventory also allows you to compare actual data with accounting data in the program.
There are cases when such a reconciliation of balances makes it possible to identify thefts among financially responsible persons.
After conducting an inventory in 1C 8.3, the shortage can be written off and the surplus can be capitalized. For this entire sequence of actions and its reflection in accounting, there are special documents, the completion of which we will consider below.
Reflection in accounting of the amount of shortage
To perform operation 1.1 “Reflection in accounting for the amount of shortfall” (see example table), you need to create a document Cash issuance
with the transaction type “Other expense”.
Creating and filling out the “Cash Withdrawal” document (Fig. 1):
1. Menu: Bank and cash desk - Cash desk - Cash document.
2. “Issue” button.
3. Type of transaction “Other expense”.
4. In the “from” field, enter the inventory date.
5. In the “Amount” field, enter the amount of the shortfall.
6. In the “Debit account” field, select account 94 “Shortages and losses from damage to valuables”.
7. Leave the “Issued (full name)” and “By document” fields empty.
8. In the “Base” field, indicate the content of the business transaction.
9. In the “Appendix” field, indicate the details of the cash inventory report (unified form INV-15).
10. “Pass” button.
To draw up a printed form for a cash expenditure order in the KO-2 form, click on the “Cash expenditure order (KO-2)” button.
Rice.
1 Result of conducting the “Cash Withdrawal” document (Fig. 2):
To view document transactions, click the Show transactions and other document movements
Rice. 2
To complete the processing of cash transactions at the end of the day, you need to generate a “Cash Book” report.
Write-off of goods
Let's continue with the previous example. During the inventory, it was found that in the sales area of store No. 23 there was a shortage of 7 chocolate bars (95%). This quantity must be written off from the warehouse, because it simply does not exist.
To do this, we will use the document “Write-off of goods”. We created it based on the previously entered inventory.
Please note that the document is completely filled out automatically. Despite the fact that the program gives us the opportunity to edit it, we will not do this.
After the document was completed, two movements were created: to write off seven chocolate bars 95% and to write off the trade margin. The second posting was created due to the fact that the warehouse with the detected shortage is a sales area and the prices are accordingly different.
The shortage is attributed to the person at fault
To perform an operation, you must create an Operation
.
Creating and filling out the “Operation” document (Fig. 3):
1. Menu: Transactions - Accounting - Transactions entered manually
.
2. “Create” button
3. Select the document type “Operation”.
4. In the “from” field, enter the inventory date.
5. In the “Content” field, enter the content of the operation.
6. To create a new transaction in the tabular section, click the “Add” button.
7. In the “Debit” field, select account 73.02 “Calculations for compensation of material damage.” Next, fill out the “Subconto1 Debit” field by selecting from the “Individuals” directory the person found guilty of the shortage.
8. In the “Credit” field, select account, select account 94 “Shortages and losses from damage to valuables.”
9. In the “Amount” field, you must fill in the amount of the shortfall attributed to the guilty party.
10. In the “Content” field, indicate the content of the operation.
11. The fields “Amount Dt” and “Amount Kt” in the “NU” line are automatically filled in with the value specified in the “Amount” column.
12. “Record” button.
13. To call up a printed form of an accounting certificate, use the “Accounting certificate” button.
Rice. 3
Posting of goods
Now let's look at the second example. During the inventory, it was found that instead of the 110 kilograms of “Assorted (commission)” candies reflected in the program, there are actually 150 of them in the warehouse. In this case, the deviation in the inventory will be 40 kilograms.
Since the deviation occurred in a positive direction, to take it into account it is necessary to capitalize the surplus. Capitalization, just like write-off, can be created from the goods inventory document itself.
The program filled out all the necessary fields automatically, and all we had to do was post the document. After it is carried out, the number of “Assorted (commission)” candies in the program will coincide with the actual quantity in the warehouse.
Video on capitalization and write-off of goods in 1C 8.3 based on inventory:
Inventory of funds in the current account (surpluses identified)
Current accounts are intended for the storage and movement of funds in the currency of the Russian Federation. A foreign currency account stores funds in foreign currencies.
According to Part 1 of Art. 11 of the Federal Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ “On Accounting” (hereinafter referred to as the Accounting Law), the assets and liabilities of an economic entity are subject to inventory.
An inventory of the relevant objects is carried out in order to identify discrepancies between the actual availability of such objects and the data of the accounting registers (Part 2 of Article 11 of the Accounting Law).
In a number of cases, conducting an inventory is mandatory and is established by the legislation of the Russian Federation, federal and industry standards (Part 3 of Article 11 of the Accounting Law). However, there is no list of cases of mandatory inventory in the new Accounting Law.
Inventory of funds held in banks in settlement (current), foreign currency and special accounts is carried out by reconciling the balances of amounts listed in the corresponding accounts according to the organization’s accounting department with data from bank statements (closing balance according to bank statements) (clause 3.43 of the Methodological Instructions on inventory of property and financial obligations, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 13, 1995 No. 49).
Also, when taking inventory of funds in a current account, the identity of the debit and credit turnovers of the accounts is checked to the data contained in the statements of credit institutions. The balance at the end of the period in the previous bank statement of the account must be equal to the balance at the beginning of the period in the next statement.
Example
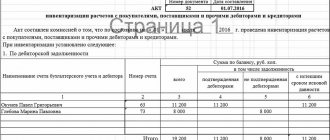
The organization Sewing Factory LLC carries out an inventory of funds in the current account. During the inventory, a discrepancy was revealed: the account balance according to the accounting data was 60.00 rubles. less than the balance according to the bank statement.
Values
The cash desk at an enterprise may contain cash, payment documents, securities and strict reporting forms. Payment documents include not only receipts, but also stamps (postal, bill and state duties), vouchers to sanatoriums, air tickets and other documents. Strict reporting forms include: receipts, certificates, diplomas, subscriptions, tickets, coupons, shipping documents, etc. The cashier bears financial responsibility for the preservation of monetary documents.
Recalculation of forms
The actual availability of Central Bank forms and reporting documents is carried out by name, type and category of forms. For example, shares can be registered, bearer, interest-bearing and ordinary. During the check, the starting and ending numbers of the forms, their series and cost are also recorded.
All these monetary documents are registered based on the results of the inventory in the amount of expenses for their acquisition. The balance of the forms is determined based on the data in the cash book or report. If a shortage of forms is detected, the shortage is registered at the cash desk. Accounting entries are made according to analytical and synthetic accounting accounts. Examples of registration of such operations will be presented below.
Checking bank accounts
An inventory must be carried out before submitting annual reports. Since an organization can open accounts in different banks, before checking it should study in detail all banking agreements, check the legality and feasibility of opening an account.
Inventory is carried out by reconciling the balance of funds with the data of the statements. Additionally, the revolutions for DT and CT are compared. During the inspection, surpluses and shortages in the cash register may be identified. Postings:
— DT76-2 KT51 — identification of amounts erroneously credited to a bank account.
— DT51 KT76-2 – receipt of payments.
This is how cash register inventory is carried out at an enterprise.
An inventory of funds can be carried out either as planned or as needed, for example, when an employee goes on vacation or hires a new cashier.
From the article you will learn:
- How can you carry out an inventory of funds in 1C;
- what documents to reflect its results.
Checking operating cash registers
For settlements with company employees, operating cash desks are used. The procedure for checking them differs from that described above.
The commission, in the presence of the cashier, records meter readings that reflect the amount of revenue. The data is checked against the submitted cash register tape. The difference in the balance at the beginning and end of the day reflects the daily amount of revenue. The numbers in the cash book, on the tape and on the counters must be identical.
Cash recalculation is carried out using the purchase method. The resulting balance is compared with the accounting balance. Based on the results of the inventory, a shortage of funds in the cash register may be identified. The posting, which in this case is entered into the balance sheet, looks like this: DT94 KT50-2.
[Case on UT 11] Carrying out an inventory
What is this article about?
inventory using UT 11 :
- Conversion of goods
- Assistant for registration of warehouse acts
- Distribution of surpluses and write-off of shortages
- Inventory reports
Applicability
The article was written for two editions of 1C: Trade Management - 11.1
and
11.2
. If you use these editions, great - read the article and implement the functionality discussed.
If you plan to start implementing UT 11, then most likely a more recent edition will be used. Interfaces and functionality may vary.
Therefore, we recommend taking the course Practical tasks of level 1C: Specialist in UT 11, KA 2 and 1C: ERP 2
, this will help you avoid mistakes and loss of time/reputation.
Formulation of the problem
consists of two organizations (individual entrepreneurs): “Furniture-Design” and “Furniture-Supply”.
An inter-campaign scheme has been set up between organizations. Accordingly, the remaining stock of the warehouse may contain goods from different organizations.
The company has one warehouse: Wholesale warehouse. The warehouse uses an order-based document flow system for shipping, receiving goods and recording surpluses, shortages and damage to goods. All company processes are reflected using the 1C: Trade Management 11 program.
At the company's warehouse, inventories are periodically carried out, as a result of which shortages or surpluses of goods may be discovered.
Inventory is carried out only on behalf of the Furniture-Supply organization. If at the time of conducting the inventory results (warehouse acts) shortages of goods were discovered in the warehouse and this goods belonged to the Furniture Design organization, then after the execution of warehouse acts the document “Transfer between organizations” should be automatically carried out.
What you need to get
Reflect the inventory taking. Record its results.
Write-off/receipt of goods must be distributed to the “Warehouse Inventory” activity area.
At the end of the month, based on the results of the inventory carried out in the warehouse, print out the regulated printed forms “Inventory list (INV-3)” and “Matching sheet (INV-19)”.
Solving the warehouse inventory problem
Starting with the release of UT 11.1.7, the inventory procedure in the program has been changed.
Now there is no need to create an additional document “Order for Inventory” in the program. Accordingly, in the program settings you will not find a checkbox for setting Inventory Order, as was previously the case. Inventory is done only according to “Recalculations of goods”. You do not need to enable any functional options to use this document. First, let's create the reference books necessary to solve the problem. Two organizations (Regulatory and reference information - Organizations) (in UT 11.2 this is the section “Research data and administration” - “Organizations”):
- "Furniture Design"
- "Furniture-Supply"
Let's set up an inter-campaign scheme between organizations ( Regulated accounting - Settings and directories - Setting up the transfer of goods between organizations
) (in UT 11.2 this is the section “Financial result and controlling”):
Since the company has only one warehouse and it uses an order document flow scheme, in the Administration - Warehouse and Delivery section we will set the Order warehouses flag. Flag We will not install multiple warehouses.
Now let's go to the section Regulatory and reference information - Settings and reference books - Setting up warehouse accounting.
As a result, the warehouse settings window will open.
We will indicate the name of the warehouse, as well as flags for using the order document flow scheme. Let's write down the settings.
Next, we will create several product items and purchase them on behalf of two organizations:
- On behalf of the Furniture Design organization
- On behalf of the Furniture-Supply organization.
- Indicate additional selection of items using the hyperlink Establish selection - if there are a lot of surpluses and shortages, then it is advisable to issue acts not immediately for the entire item, but iteratively, changing the selection by item. In this case, there are few goods, so we will skip this point.
- Inventory inventory period - during the assistant’s work, the “Inventory inventory” document will be drawn up, which is used to print the regulated printed forms INV-3 (Inventory inventory) and INV-19 (Matching sheet). The list of goods that will be printed in these forms in the document is not recorded, nor is their quantity recorded (according to actual availability and according to accounting data) - all this information will be calculated based on the data of recalculations of goods and warehouse acts issued for the specified period.
- Warehouse act date – the date on which the assistant will issue warehouse acts. This date must lie within the Inventory List period.
- Print prices – these settings will be transferred to warehouse reports and inventory lists and will be used when printing regulated printed forms. You can configure the printing of prices, either calculated at the cost of goods, or set according to a specified price type. By default, the price printing settings are filled in according to the warehouse settings. Let's leave these settings unchanged.
Based on receipts from the supplier, it is important not to forget to create two documents “Receipt order for goods”, since in this case an order scheme is used for document flow in the warehouse.
Let's analyze the balances of goods of organizations in the warehouse using the report “Statement of goods of organizations” (section Regulated accounting - Reports on regulated accounting) (in UT 11.2 this is the section “Financial result and controlling”):
Now let's start taking inventory.
Let’s go to the Warehouse – Goods Recounts and create a new document “Goods Recounts”.
Let's go to the Products tab of the document. We will leave the established selection unchanged.
Using the Fill in selection button, fill in the tabular part of the document Products. Let's review the document.
We see that the accounting balance for each item is 11 units.
Let’s imagine a situation where a shortage of the product “Table” and a surplus of the product “Rocking Chair” were discovered in the warehouse. For example, the balance of the product “Table” is 9 pcs., “Rocking Chair” is 12 pcs.
The actual availability of goods in the warehouse is indicated in the “Actual” column of the document.
To enter the results of the inventory, the status of the document must be set to “Entering results”.
Let's set this status and fill in the actual quantity of goods in the corresponding column.
The document has an additional column “Deviation”, demonstrating the difference between the actual quantity and the accounting quantity. This column was not previously in the document. With its help, it is very convenient to quickly monitor the deviation of the actual balances of the item from the accounting quantity.
Great, the goods have been recounted. Now it is necessary to issue warehouse acts for the completed inventory. To do this, based on the document “Recalculation of goods”, we will launch the “Warehouse Receipts Assistant”.
Note that before the release of UT 11.1.7, in the warehouse program, which uses an order document flow scheme to reflect surpluses, shortages and damage, it was necessary to first create the document “Order for reflecting the results of recounts of goods”, and only then launch the “Warehouse Receipts Assistant” . Now, starting with release 11.1.7, the document “Order for reflecting the results of recounts of goods” has been removed and does not need to be completed.
Using the assistant, you can issue warehouse acts and distribute identified surpluses and shortages among organizations. At the first step of the assistant, you are asked to make the following settings:
Click Next.
The program will display an error message: “There are no goods available for warehouse receipts.”
What's the problem? The fact is that in the document “Recalculation of goods” you need to set the status Completed.
Let's close the assistant and set the required status in the document.
On the document navigation panel, by clicking on the Registration item, you can generate a report on unregistered surpluses and shortages of goods.
As you can see, we have unregistered goods.
Also, the special report “Unregistered shortages and surpluses of goods” can be launched from the list of documents in the Warehouse – Warehouse acts section using a special hyperlink:
Let’s launch the “Warehouse Receipts Assistant” again. There will be no errors now.
We will leave the first step of the assistant unchanged. Click Next.
At the second step, the assistant is asked to offset the surpluses of some goods with the shortages of others. This can be done by misgrading or (if the quality of goods is used) by damage.
But in the case under consideration there is no misgrading or damage to goods. Let's skip this processing step. Click the Next button again.
At the third processing step, we can distribute written-off and capitalized goods among organizations.
To support the decision on which organization to distribute items to, the form provides a report on the balance of goods of organizations, which shows not only the balance of goods that is listed on the organization, but also the balance of goods that is available to this organization according to the settings of the intercampaign scheme.
When choosing an organization to which to assign written-off goods, you can rely on this information, since warehouse acts (starting with the release of UT 11.1.7) take into account the intercampaign settings when carried out.
There are two distribution methods:
1. Distribution according to the balance of goods of organizations.
It is necessary to select the positions that need to be distributed in the specified way and click the appropriate button. For example, let's select all positions (in this case, two lines) using the key combination Ctrl + A and press the Distribute button according to the balance of goods of organizations.
A form will open in which you need to indicate which organizations to distribute to.
The task conditions say that the inventory is carried out only on behalf of the Furniture-Supply organization. Let's try to indicate the organization "Furniture Supply" first in the list. Click the OK button.
The distribution algorithm works differently for different operations.
Capitalization - from those listed, the first organization that currently has the balance of the goods being received is selected.
Write-off – the first organization on the list is located, which has a balance of the goods being written off, the write-off is attributed to this organization. If after this there is an undistributed write-off quantity of goods left, then the next organization that has balances is searched, etc.
Re-grading and Damage – distribution is made according to the balances of the goods being written off according to an algorithm.
After clicking the OK button, the products from the upper tabular part will be transferred to the lower tabular part.
As you can see, the program offers to write off one table on behalf of the Furniture Design organization.
This option is not suitable in this case. All goods must be carried out on behalf of the Furniture Supply organization. Therefore, we do not use this method and delete all rows from the lower table.
Let's consider the second option.
2. Attribution to the selected organization
You need to select the items that need to be distributed and click the Attribute to the selected organization button.
In the form that opens, select the organization to which you want to distribute the allocated items, in this case – “Furniture-Supply”.
As you can see, the program offers to carry out warehouse acts on behalf of the Furniture-Supply organization. This option, according to the conditions of the task, is suitable. Click Next.
When you go to the next page, the assistant will generate warehouse receipts and try to post them. Carrying out may not always end successfully, and some acts will remain unconducted. Errors in performing acts will be displayed in the message panel.
In the case under consideration, the program created the documents “Inventory list”, “Capitalization of surplus goods” and “Write-off of shortages of goods”. But the documents “Capitalization of surplus goods” and “Write-off of shortages of goods” were not carried out.
Double-clicking on the error message will open the warehouse receipt form that could not be completed. It is necessary to manually correct the acts and post them.
In the document “Capitalization of surplus goods” you need to indicate the item of income. Let's create a new article called “Positioning of goods”. The distribution option for the article will be indicated as “Area of activity”. Cost analytics type – “Organization”.
For an income item, you need to indicate the method of distribution. Let's create a new distribution method. We will indicate “Proportional to coefficients” as the distribution rule. In the tabular part you need to indicate the direction of activity. Accordingly, we will create a new area of activity called “Warehouse Inventory.” As a result, the distribution method will look like this:
We will indicate the created distribution method in the income item. Let's write it down. As a result, we get the following income item:
We will indicate this article in the document “Capitalization of surplus goods.”
Let's review the document.
The document “Write-off of shortages of goods” must also be carried out. The document must indicate the expense item.
In the same way, we will create an expense item:
We will indicate the expense item in the document and post it.
In the warehouse receipts assistant, press the F5 button and update the list of documents.
We have now completed all the documents.
Click the Finish button.
In the navigation panel of the “Recalculation of Goods” document, by clicking on Registration again, you can generate a report on unregistered surpluses and shortages of goods. Now the report will be generated empty, since all the necessary documents (warehouse acts) have been completed.
In addition to the documents “Capitalization of surplus goods” and “Write-off of shortages of goods”, we created the document “Inventory list”.
The document is intended for obtaining regulated printed forms Inventory list (INV-3) and Matching sheet (INV-19). Generated automatically by the assistant for issuing warehouse acts for each organization for which warehouse acts are issued.
Algorithm for generating printed forms INV-3 and INV-19:
- All documents “Conversion of goods” are selected for the period specified in the document “Inventory List”
- Goods are selected from the selected “Goods Conversions”, which are used to determine the balance of goods of organizations as of the end date of the period - this quantity is displayed in the “Actual Availability” field
- Warehouse acts are selected for the period specified in the document “Inventory list”
- The number of goods specified in warehouse receipts is added or subtracted to the actual quantity; this quantity is displayed in the “According to accounting data” field.
So, let's print:
1. Inventory list (INV-3)
2. Matching statement (INV-19)
Thus, two “Table” items from the Furniture-Supply organization were written off. Moreover, only one table belonged to the Furniture-Supply organization. The other table belonged to the Furniture Design organization. But warehouse acts were carried out, because, as mentioned earlier, starting with the release of UT 11.1.7, when carrying out warehouse acts, intercampaign settings are now taken into account.
Based on this, you need to carry out the document “Transfer of goods between organizations”, namely: sell the product “Table” from the organization “Furniture Design” to the organization “Furniture Supply”.
We will check this information by generating a report in the “Regulated Accounting” section entitled “Registration of transfers of goods.”
As you can see, we have a balance to process.
Now let's move on to the section Regulated accounting - Transfers and returns of goods
to the For registration tab (in UT 11.2 this is the “Financial result and controlling” section).
Here we display the document for registration.
Click the button Complete the transfer (return) of goods.
In the document that opens, we will see in the tabular section only the product “Table”. That's right.
We will fill out all the necessary details of the document and process it.
Let’s re-generate the “Registration of goods transfer” report.
The report shows that the necessary documents for the sale of goods between organizations have been completed.
Now let's analyze the company's financial results by area of activity.
Let’s start by processing “Month Closing” (section Regulated Accounting).
After this, in the Finance – Financial Reports section, we will generate a “Financial Results” report.
The report is intended to analyze financial results by area of activity, taking into account the hierarchy of income and expense items (indicators that reduce profit are displayed in parentheses).
Based on the report on the area of activity “Inventory in the warehouse”, the company received a loss of 4,000.00 rubles.
By changing the report settings via All actions – Change report variant, you can add an additional “Organization” grouping.
After generating the report, we will see the following information:
- The Furniture Design organization has revenue and cost of RUB 5,000.00 each. (according to the document “Transfer of goods between organizations”). Accordingly, the overall financial result is 0.
- The Furniture Supply organization received a loss of RUB 4,000.00. (according to the documents “Capitalization of surplus goods” and “Write-off of shortages of goods”).
That's right.
So, this case examines the functionality of carrying out an inventory of goods in the 1C: Trade Management 11 program starting from release 11.1.7. The creation of all necessary documents and printed forms was demonstrated, the results were analyzed using the necessary reports.
The settings, as we see, are not complicated, and the functionality has become more convenient compared to previous releases.
PDF version of the article for members of the VKontakte group
We run a VKontakte group - https://vk.com/kursypo1c.
If you have not yet joined the group, do so now and a link to download materials will appear in the block below (on this page)
.
Case in PDF format You can download the case in PDF format from the following link: Link is available for registered users)
If you are already a member of the group
– you just need to log in to VKontakte again for the script to recognize you.
In case of problems,
the solution is standard: clear the browser cache or subscribe through another browser.
Peculiarities
During the inventory you need to check:
- whether the cash balance in the cash register exceeded the established limit;
- targeted use of funds;
- correspondence of the date of the transaction in the cash register and the debit order;
- validity of records;
- timely return of unpaid salary balances to the account;
- correctness of paperwork;
- presence of signatures of the director, chief accountant on blank checks;
- the fact of keeping the checkbook outside the cash register;
- legality of transactions carried out within one transaction;
- correctness of correspondence invoices.
Inventory
The timing of the inspection at the enterprise is established by the manager and enshrined in the order. The inventory is carried out by a specially created commission, which includes representatives of the administration, the chief accountant and the cashier.
Before carrying out the procedure, prepares a cash report. It includes all primary documents that should be at the cash desk. If the inventory reveals unclosed statements (for salary payments), then all unpaid amounts are equated to cash. The amounts paid are recorded separately in the document.
The cashier is required to provide a receipt stating that by the time the inventory begins, payment documents have been submitted to the accounting department, and all cash has been recorded. This must be done so that upon completion of the check the cashier does not declare that he has payment documents. The cashier's report is checked against the information in the cash book and the order.
To conceal the fact of embezzlement of funds, receipts are often used as documents. But they cannot confirm the expenditure of funds, since they are not drawn up in a unified form and do not contain the signatures of the recipient, the chief accountant and the manager. If such documents exist, then it is considered that a shortage was identified during the inventory of the cash register. The entry must be made in the balance sheet on the date of the audit. The chairman of the commission endorses all orders and attaches them to the report. This document serves as the basis for recording fund balances.