Legal regulation of wage payments
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation regulates the legal aspects of wage payments. Chapters 20 and 21 reveal the concept, calculation procedure, and forms of payment of wages.
Remuneration depends on the qualifications of the employee, the volume of work performed, its conditions, and complexity. The salary includes additionally:
- compensation payments (harmful working conditions, special climatic difficulties, overtime);
- incentive payments (bonuses, allowances).
The main part of the salary is set in two ways:
- In the form of a tariff rate. The employee is paid a fixed amount for fulfilling the established norm per unit of time.
- Job salary. Payment for work that an employee performs during a calendar month in accordance with job descriptions.
ATTENTION! The difference between salary and rate is that the former is awarded for the performance of job duties, where there is no established norm. The rate is charged for fulfilling the norm as agreed.
There are 2 types of salaries:
- nominal salary - payment in monetary terms, paid for a period of working time without taking into account inflation;
- real salary is the volume of goods and services that a person can purchase with the amount received.
The employer is obliged:
- Set the salary to be no less than the minimum wage. From January 1, 2021 it is 11,280 rubles. The maximum size is not limited.
- Take measures to increase salaries.
- Limit the amount of taxation and the list of deductions from wages
- Limit the percentage of salary payments in kind (maximum 20%).
- Guarantee the employee's wages in the event of termination of the employer's activities and insolvency.
- Report to higher authorities on compliance with labor laws and bear responsibility for violations.
- Comply with the timing and order of payments.
- Ensure payment of wages in cash or non-cash form.
Any discrimination in establishing conditions of payment and calculation of wages is prohibited.
Tariff-free wage system
The non-tariff wage system is characterized by a close connection between the employee’s salary level and the wage fund, determined based on the specific results of the work of the workforce.
Each employee is assigned a constant qualification level coefficient.
At the same time, when calculating earnings, the labor participation coefficient (LFC) of a specific employee in the company’s performance results is taken into account.
When using a tariff-free system, employees are not given a fixed salary or tariff rate.
In this case:
- amounts of salaries, bonuses, other incentive payments,
- their ratio between individual categories of employees,
are determined by the company independently and are recorded in labor and collective agreements and other local regulations of the organization.
An employee’s earnings under such a remuneration system depend on the final results of the work of the organization, structural unit, as well as on the amount of money allocated by the company to replenish the wage fund.
Accordingly, the salary of each employee is calculated as a share of the total wage fund.
A tariff-free remuneration system is used in situations where it is possible to organize accounting of an employee’s work results.
Such a system stimulates the general interest of the team in the results of work and increases the level of responsibility of each employee for their achievement.
Accordingly, the tariff-free system cannot be used by large companies.
Moreover, if the activities of companies are related to the production of products and, accordingly, the use of a tariff-free system may infringe on the interests of employees in terms of the guarantees provided for by the Labor Code.
In such cases, companies use mixed remuneration systems, with elements of tariff and non-tariff systems. We will talk about them below.
Procedure for payment of wages
The payment system is established in accordance with labor legislation and local regulatory legal acts of the organization.
ATTENTION! Every year, the commission for the regulation of social and labor relations develops unified recommendations for establishing a remuneration system. Based on the recommendations, the volume of financial support is determined. Due to rising prices for services and goods, wages are indexed.
The procedure for paying wages depends on the type of labor system:
- Time-based. This form of payment is divided into simple time (the rate is multiplied by hours worked) and premium time (with an additional percentage in the form of a bonus).
- Piecework. Depends on the amount of work performed, most often used in production. The piecework form is divided into direct (payment for the number of units), bonus (a bonus for exceeding the norm), and progressive (payment for one unit increases during processing).
- Chord. Payment for each stage of work.
Additionally, overtime work is paid for the first two hours of work at one and a half times the rate, for subsequent hours - at double rates. At the request of the employee, overtime work is compensated for by additional rest time.
Work on weekends and holidays is paid at an increased rate or compensated by providing another day of rest.
Each hour of work at night is paid at an increased rate, based on a collective agreement.
Payment terms
The terms of salary payment are specified in the employment contract and discussed upon hiring. The interval between the advance payment and the main part does not exceed 15 calendar days. If the approved salary date falls on a weekend, the money is paid the day before.
ATTENTION! It is possible to establish different payment days in the organization for individual departments.
Payment methods
- Payment of wages in cash. The currency of the Russian Federation is rubles. In cases provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation on currency control, payment is allowed in foreign currency.
- Salary in kind. Does not exceed 20% of the accrued amount.
IMPORTANT! It is prohibited to issue earnings in the form of coupons, credit documents, temporary paper notes, promissory notes, toxic substances, weapons.
Tariff system of remuneration
Many companies use tariff systems for remunerating employees.
As follows from the provisions of Article 143 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, tariff wage systems are wage systems based on a tariff system of differentiation of wages for workers of different categories. At the same time, it is necessary to take into account that only tariff systems of remuneration are directly provided for by the Labor Code. Other types of systems are not established by the Labor Code, however, in accordance with the provisions of Article 135 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer has the right to install at his enterprise any remuneration systems that must meet one single condition:
- they must not contradict the requirements of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other documents containing labor law norms.
In accordance with the provisions of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the tariff system for differentiating wages for workers of various categories includes:
- tariff rates,
- salaries (official salaries),
- tariff schedule,
- tariff coefficients.
The tariff schedule is understood as a set of tariff categories of work (professions, positions), determined depending on the complexity of the work and the qualification requirements of workers using tariff coefficients.
Quite often, the tariff schedule is drawn up in the form of a table, which summarizes the categories and coefficients - the higher the category, the higher the tariff coefficient. In order to determine the tariff coefficient of each category, you need to divide the tariff rate of the category by the tariff rate of the first category. Tariff category is a value that reflects the complexity of work and the level of qualifications of the worker. A qualification category is a value that reflects the level of professional training of an employee. Tariffication of work is the assignment of types of labor to tariff categories or qualification categories depending on the complexity of the work. The complexity of the work performed is determined based on their pricing.
Tariffication of work and assignment of tariff categories to employees are carried out taking into account the unified tariff and qualification directory of works and professions of workers, the unified qualification directory of positions of managers, specialists and employees, or taking into account professional standards.
These reference books and the procedure for their use are approved in accordance with the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of October 31, 2002. No. 787 “On the procedure for approving the Unified Tariff and Qualification Directory of Work and Professions of Workers, the Unified Qualification Directory of Positions of Managers, Specialists and Employees.”
Tariff systems of remuneration are established by collective agreements, agreements, local regulations in accordance with labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law standards.
Tariff systems of remuneration are established taking into account:
- unified tariff and qualification directory of works and professions of workers,
- a unified qualification reference book for positions of managers, specialists and employees or professional standards,
- state guarantees for wages.
At the same time, according to the opinion of the official bodies, expressed in the Letter of Rostrud dated April 27, 2011.
No. 1111-6-1, when establishing salaries in the staffing table for positions of the same name, the salary amounts should be set to the same. At the same time, the “above-tariff part” of wages (allowances, additional payments and other payments) may be different for different employees, including depending on:
- qualifications,
- difficulty of work,
- quantity and quality of labor.
Rostrud bases its opinion on the fact that although Article 143 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which provides for a tariff system of remuneration, provides the basis for establishing a range of official salaries*, when establishing a range of salaries for positions of the same name, one should remember the employer’s obligation to provide employees with equal pay for labor of equal value (Article 22 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
At the same time, the salary of each employee depends on his qualifications, the complexity of the work performed, the quantity and quality of labor expended (Article 132 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
At the same time, any discrimination in establishing wage conditions is prohibited.
*That is, establishing the official salary for a vacant position from the minimum to the maximum.
The main forms of the tariff system of remuneration are time-based and piece-rate.
The difference between time-based and piece-rate wages is that with time-based wages, payment depends on the amount of time worked, and with piece-rate wages, on the quantity of:
- units of production produced,
- completed operations.
- Time-based form of remuneration.
The wages of time-based employees are determined based on their qualifications and the amount of time they work.
This form of remuneration is used when the employee’s work is not subject to rationing or it is too difficult to organize records of completed operations.
Typically, a time-based wage system is used to pay administrative and managerial personnel, as well as employees of auxiliary production and service facilities.
In addition, this form of payment is used when paying part-time workers.
With a simple time-based form of remuneration, wages are paid for a certain amount of time worked and do not depend on the number of operations performed.
The calculation is based on the tariff rate or salary and the amount of time worked.
The amount of wages is determined as the product of the tariff rate (official salary) by the amount of time actually worked.
If an employee does not fully work a month, the employee will be paid only for the time actually worked.
If a company uses an hourly or daily wage system, then the employee’s salary will be determined based on the hourly (daily) rate multiplied by the number of hours or days actually worked.
With a time-based bonus form of remuneration, when calculating wages, not only the time worked is taken into account, but also the quantity/quality of work, based on which the employee is awarded a bonus.
The amount of the bonus can be set as a percentage of the salary (tariff rate) of the employee, in accordance with the current rules in the company:
- regulations on bonuses,
- collective agreement,
- by order of the head of the company.
Thus, the amount of an employee’s earnings will be determined as the product of the tariff rate by the amount of time actually worked plus a bonus based on the results of work.
- Piecework form of remuneration.
When applying piecework wages, wages to employees are calculated based on the final results of their work (taking into account the quantity and quality of products produced and work performed).
The piecework form of remuneration encourages employees to increase productivity and quality of work performed.
The amount of wages is determined on the basis of piece rates provided for the implementation of each unit of production or operation.
The piecework form of remuneration is used in organizations that have the ability to clearly record the quantity and quality of products produced and operations performed.
The piecework form of remuneration, in turn, is divided, depending on the chosen method of wage calculation, into the following types:
- Direct piecework wages.
- Piece-bonus wages.
- Piece-progressive wages.
- Indirect piecework wages.
- Accordal payment.
Below we will look at these varieties in more detail.
When using direct piecework wages, employees' wages directly depend on the number of units produced and operations performed.
Salaries are calculated based on piece rates. The number of units manufactured (operations performed) is multiplied by the corresponding piece rates.
With piece-rate wages, employee salaries consist of two parts:
- The first part is calculated based on output and piece rates.
- The second part consists of a bonus calculated as a percentage of the amount of piecework earnings.
At the same time, the procedure for calculating the bonus, as well as the list of conditions on which it depends (for example, fulfilling and exceeding the plan, reducing the percentage of defects, reducing the time for completing work) is established in the company’s bonus regulations.
When using the piece-rate progressive form of remuneration, employee wages are calculated as follows:
- For manufacturing products/performing operations within the norms, wages are calculated at fixed rates.
- For manufacturing products/performing operations in excess of established standards, wages are calculated at increased (progressive) rates.
At the same time, prices for products/work in excess of standards may increase depending on the volume of overfulfillment in accordance with the pricing table approved by the company.
The use of the indirect piecework form of remuneration is usually carried out when calculating wages with employees of auxiliary production and service facilities.
The salary of such employees depends on the output of the main working personnel and is paid at indirect piece rates for the number of products/operations performed by the company.
Also, the earnings of service workers can be set as a percentage of the wages of the main workers.
With lump sum wages, employees' wages do not depend on the volume of units produced/operations performed, but are set for a set of works.
At the same time, depending on how the production process is organized at the enterprise, piecework wages can be individual piecework and collective piecework.
In the case of individual piecework wages, an employee’s salary is calculated based on the quantity of products he produces and its quality.
The amount of earnings is calculated based on piece rates.
With collective piecework wages, employees' salaries are determined in total, taking into account the actual products produced and work performed, and their piecework rates.
The salary of each individual employee is calculated based on the volume of products produced by the entire department (team) and the quantity (quality) of his labor in the total volume of work performed.
Thus, the salary of one employee with collective piecework wages depends on the total output.
Salary calculation procedure
Stages of labor accounting:
- Salary calculations.
- Payroll.
- Deductions from wages in the form of personal income tax (13%). The employer pays insurance contributions to the Social Insurance Fund, Pension Fund, and Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund.
- Direct payment of the remaining amount through a cashier or bank.
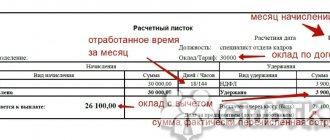
The employer is obliged to notify each employee in writing of the amount of all payments and the justification for the deductions made through a payslip.
Sample salary slip
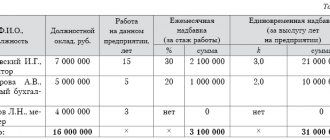
The statement of form T-53, which is registered in OKUD under No. 03010111, is recommended by the fiscal authorities when calculating wages to employees. The statement is filled out by the accountant and signed by the director, handed over to the cashier for the issuance of funds.
A sample statement is available for download via this link. The accountant enters the data of his organization and his employees according to the sample.
Salary calculation example
To calculate payroll, the following data is required:
- about the salary established for the employee;
- about the required deductions for personal income tax;
- on the number of days worked per month;
- about the total salary from the beginning of the year (for an incomplete month, the salary is calculated using the formula: days worked in this month * salary / number of all working days in this month).
Employee Petrov with a salary of 20,000 rubles. I worked 20 days in September.
Salary for September: 20,000 * 20 days. (number of days worked) / 21 days. (number of working days in September) = 19,048
The employee is not entitled to deductions, since he has no grounds for this (minor children, veteran status, disabled person)
Personal income tax withheld: 19,048 * 13% = 2,476
Thus, Petrov will receive 19,048 – 2,476 = 16,571.43 rubles. in September.
What forms of remuneration exist?
You can pay a fixed amount that does not depend on the amount of work performed, or, conversely, the income will depend on its quantity and quality. You can tie payments to the time spent completing assigned tasks or simply agree on a fixed remuneration.
Piece form
The piecework method is most often applied to the type of work associated with the production or sale of goods and services. The presence of piece rates allows the employee to influence his income, since there is a direct dependence of income on meeting the norm.
Time form
When using a time-based system, income depends on the time spent working, not the tasks completed. The unit of measurement can be hour, week or month. In this case, a fixed amount per unit of time is established and how many units were spent on completing tasks is counted.
IMPORTANT! Terms and methods of payment cannot be changed unilaterally. Changes must be communicated to the employee in writing at least one month in advance.
Other types
The payment of wages and other employee benefits is regulated at the legislative level. There is a division of payment depending on the qualifications of the employee, the complexity of the tasks and the professional training of the person. All this can be applied in the form of various allowances to the established form or have an independent character.
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation distinguishes three main payment methods:
- Tariff rate means completing a volume of work in a certain time. This method is used for professions where it is not so much the result that is important, but the amount of time worked.
- The official salary is a fixed amount for performing work during the month. This is the most common and effective method. Earnings do not change depending on performance, which guarantees income stability. For most people, this is more important than chasing wealth with minimal or inconsistent income.
- The basic salary applies to employees of municipal or state institutions and is the minimum value taking into account the qualifications of the employee. Typically, various types of allowances are applied to the base salary for performing a certain type of work and length of service.
Despite the large selection of forms of remuneration under the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, it is important to adhere to the requirements of the law and take into account the performance of employees. You shouldn’t turn your work into a race to the bottom for the sake of your own progress and profit. The manager’s task is to provide workers with decent wages and create conditions for high-quality implementation of assigned tasks.