Free receipt of OS in 1C: Accounting department of a state institution 8th edition 2.0
Published 06/24/2017 00:08 Fixed assets can be supplied to an institution not only through acquisition for a fee, but also free of charge. In this article, we will consider the reflection of the gratuitous receipt of OS in the program “1C: Public Institution Accounting 8, edition 2.0”.
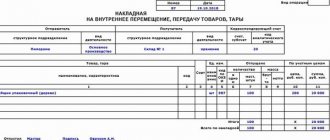
Receipt of fixed assets free of charge can be divided into three types: 1. free receipt from an institution subordinate to the same GRBS (intradepartmental transfer); 2. receipt of fixed assets from the founder; 3. receipts of fixed assets from other budgets (from institutions subordinate to other GRBS). Let's consider all situations sequentially. Reflection of gratuitous receipt of fixed assets in accounting is carried out using the document “Acceptance for accounting of fixed assets, intangible assets, legal acts”. You can find it:
A list of documents opens:
Click the “Create” button to add a new document:
A special window opens with a list of types of receipt of fixed assets:
Type of receipt from account 106 is used in the case when the value of the fixed asset was previously accumulated in this account as a capital investment. The type of receipt to accounts 101,102,103 is used if a finished fixed asset is received. Other types of income are on off-balance sheet accounts for simplified accounting and storage. In our case, you need to select the “Receipt to account 101,102,103” type:
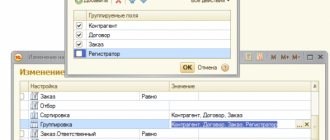
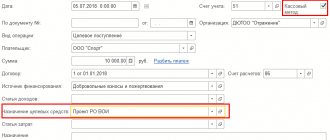
The document details are filled out in the standard way. But I would like to focus attention specifically on the “Financial Security Code” detail: according to which KFO should a fixed asset received free of charge be accepted for accounting? State-owned institutions use KFO 1 - “Activities carried out at the expense of the corresponding budget.” And for autonomous and budgetary institutions, KFO options are possible - 2 “Income-generating activities (institution’s own income)”, 4 “Subsidies for the implementation of state (municipal) tasks” or 7 “Funds for compulsory health insurance”. In general, we can say that two factors play a role in the choice of CFO: - with what means the accepted fixed asset will be maintained (that is, if you accept a fixed asset free of charge, for example, vehicles, then you need to consider from what means the maintenance will be carried out this vehicle); - and the second point concerns gratuitous transfer within the budget (among institutions subordinate to one GRBS): here it is worth considering which KFO the fixed asset is disposed of, usually in this case the OS is accepted for the same KFO. This is due to the fact that the “economy” of one GRBS during a gratuitous transfer among subordinate institutions should not change (that is, the total amount of fixed assets at each of the KFOs does not change, the transfer must be under the same KFO). Next, on the “Fixed assets, intangible assets, legal acts” tab, fill in the initial data of the fixed asset accepted for accounting:
If the fixed asset is transferred with depreciation, the depreciation data is indicated on this tab. After the basic information on the fixed asset is filled in, go to the “Accounting transaction” tab:
The data on the fixed asset do not differ for all three types of gratuitous receipt. The differences only appear in the typical accounting transaction that will be used.
1. Free receipt from an institution subordinate to the same GRBS (intradepartmental transfer) In the case of gratuitous receipt of a fixed asset in the order of intradepartmental transfer from another institution, the following standard operation is used:
In this standard transaction, the corresponding account will be account 304.04. After posting, the document generates the following account movements:
2. Receipt of fixed assets from the founder It can be from the founder (centralized receipt) and from institutions subordinate to the same GRBS. In the case of gratuitous receipt of fixed assets from the founder, the following standard operation is used:
In this typical transaction, the corresponding account will be account 401.10. After posting, the document generates the following account movements:
3. Receipts of fixed assets from other budgets (from institutions subordinate to other GRBS) When receiving property from other budgets, the following operation is used:
In this standard transaction, the corresponding account will also be account 401.10. The difference from the previous operation is KEK: in the previous operation it is KOSGU 180 “Other income”, in this one it is KOSGU group 150 “Receipts from...”:
The document generates the following transactions:
Author of the article: Svetlana Batomunkueva
Did you like the article? Subscribe to the newsletter for new materials
Add a comment
Comments
0 Nailya 08/26/2019 18:46 Good afternoon, please tell me that under the donation agreement they give video recorders and a surveillance camera monitor. How to capitalize in 1C 2.0
Quote
Update list of comments
JComments
How to deliver goods on arrival
Our team provides consulting, configuration and implementation services for 1C. You can contact us by phone +7 499 350 29 00 . Services and prices can be seen at the link. We will be happy to help you!
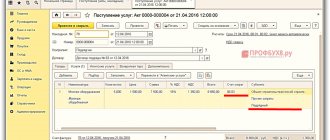
When creating a new document, select the transaction type “Goods (invoice)”.
In the header, indicate the counterparty, contract and department where the goods will be received. You can also additionally configure VAT (included in the cost and calculation method), consignee, consignor and accounting account.
Next, add all the necessary products in the table below. If prices have already been entered in the program for these item items, they will be entered automatically. You can also adjust them manually.
The accounting account in this case is 41.01 – goods in warehouses. It can also be changed. Next, adjust the VAT rate if necessary.
At the bottom of the form, indicate the invoice number and date, then click on the “Register” button. The document will immediately be created automatically and a link to it will be displayed.
As we can see, the document made two entries: for the receipt itself and for VAT (account 10.03).
Watch also the video on posting goods in 1C Accounting:
Receipt of services
This time, when creating a document, select the type of operation “Services (act)”. We will not consider filling out this document in detail due to the fact that everything here is similar to the previous method. Only here item items with the “Service” type are added.
We attributed our lawn mowing service to account 26 and indicated the cost item “Other costs.”
Next, we will post the document and issue an invoice in the manner described in the previous example. This time, one transaction was generated, since VAT was included in the price.
In the case when you need to immediately reflect the receipt of both goods and services, use the “Goods, services, commission” transaction type.
Reflection in legislation
Depending on the branch of legal regulation that controls the process of gratuitous transfer of assets, the meaning of the definition of “financial assistance” changes. The Civil Code considers it in the form of a transfer of property by third parties or founders as a gift.
Free financial assistance in accounting is understood as the result of charity or targeted financing. The Tax Code provides for a number of exceptions and additional comments on the taxation of gifted property.
Creating a new document
In the “Purchases” menu, select “Receipts (acts, invoices)”. A list form for this document will open in front of you.
From the list form that appears, you can create several different types of documents. Let's look at them briefly.
- Goods (invoice). You will only have access to the tabular part for adding products.
- Services (act). Similar to the previous one, but only for services.
- Fixed assets. This document generates transactions for the receipt and acceptance for accounting of fixed assets that do not require installation. There is no additional need to take into account.
- Goods, services, commission. Combination of goods, services and commission trading.
- Materials for recycling. Here the name speaks for itself.
- Equipment. Receipt of OS equipment. Acceptance for accounting is formed separately.
- Construction objects. Receipt of fixed assets - construction objects.
- Leasing services. To calculate the next lease payment when accounting for property on the lessee’s balance sheet.
Let's consider the first two types of operations, because they are the most popular.