What is currency from a tax point of view?
Currency is property. This is what is written in the civil code, and this is what the Ministry of Finance thinks. If you have an iPhone, a car and a sofa, these are assets. If you have dollars, then this is also property. This is a controversial position, because currency is still a means of payment. But the Ministry of Finance has a different opinion on this matter, and so far no one has tried to overcome it.
When the owner sells the property, he receives income. For the state, this is an economic benefit with which it expects deductions in the form of personal income tax. But you don't always have to pay tax.
The tax code does not have special rules for taxing income from the sale of foreign currency. Since it is considered property, then the taxation procedure for it is the same as for an iPhone or a car. Formally, this applies to the sale of currency through a bank and conversion transactions using multicurrency cards.
Documents for transactions with currency
The currency seller will need to present documents if the transaction is carried out for an amount of 15 thousand rubles or more. Otherwise, no documents are required. Documents required to be presented if this limit is exceeded include:
- original passport;
- TIN certificate;
- contact information (email, phone number);
- information about where the money came from.
This list of documents is not exhaustive; banks have the right to supplement it with other documents if necessary. All documents will be required only once. Information from them will be entered into the electronic questionnaire by bank employees.
Results
A transit currency account is opened by an individual entrepreneur, LLC or JSC working with foreign counterparties and serves to pass the currency control procedure. Funds entering the transit account are blocked by bank employees until the documents are verified. The account owner needs to provide the bank with a transaction passport (for transactions worth more than $50 thousand), an agreement with the client, an invoice and a payroll.
To avoid problems with currency control and payment of fines, the client should open a foreign currency account in a bank that prepares documents without the client’s participation. For example, employees of the currency control department independently fill out the transaction passport and send the client a notification about the receipt and release of funds. Most financial institutions provide free consultations on paperwork for currency control, so the client can fill out the paperwork in advance and avoid fines.
Read more
- What is a bank account? What is it for?
- How to deposit money into a bank account?
- Special bank account (40821) of the paying agent: how to use it?
- Anonymous bank account. Revealing secret information
Currency transactions in accounting in 2021 – 2021
In accordance with the above PBU, in 2021–2021, as in previous periods, currency transactions in accounting are reflected exclusively in rubles. This accounting provision does not apply to accounting for currency transactions related to:
- with the recalculation of financial reporting indicators, which are submitted in rubles, into foreign currency according to the requirements of foreign creditors;
- when compiling consolidated accounting, when the parent company processes the accounting of dependent institutions located abroad.
You can get more detailed information about currency transactions in our material “Currency transactions: concept, types, classifications” .
For conversion, the exchange rate of the Central Bank of Russia is used on the date that corresponds to the nature of the transaction. We will tell you more about the procedure for converting into rubles when accounting for foreign exchange transactions.
Terms for transferring funds from a transit account to a foreign currency account
According to current legislation, currency arriving from abroad cannot simply be credited to the recipient’s account. To receive it, the bank must provide documentary evidence within 15 calendar days. Otherwise, the transfer of money from the transit account to the foreign currency account will not be completed, and the financial institution will send the funds back.
Required documents include:
- a certified copy of the contract with a seal and signatures, which specifies the parameters of the transaction indicating the currency, total cost of the goods, units or objects of sale;
- specification (annex to the contract), which confirms the transaction and indicates the specific parameters of this operation;
- certificates of currency transactions, for example, transfer and acceptance certificates.
These documents are well known to exporters sending products abroad. Some banks charge a fee for conducting currency control, so you need to find out this fact before concluding an agreement.
When does the obligation to pay tax arise when trading currency?
Foreign currency is property (Article 141 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). The Ministry of Finance also insists on this (see, for example, letter dated February 20, 2015 No. 03-04-06/8370). And when selling any property, individuals must pay income tax and independently report the profit received (Article 228 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The report is submitted in Form 3-NDFL by April 30 of the year following the reporting year. For example, if you sold currency in 2021, then you need to report by 04/30/2021.
Where and how to report correctly, see the section “How to report to the tax office.”
What if the deal turned out to be unprofitable and there was no income? You will still have to report. In this case, in 3-NDFL you should indicate the amount of income and the amount of expenses. In this case, there will be no tax base for personal income tax, so there is no need to remit the tax. If the declaration is not submitted on time, the tax authorities will impose a fine.
See the size of the sanctions in the section “What are the fines and what are the penalties for the investor?”
If more than three years have passed since the purchase of foreign currency, nothing needs to be declared, and tax on the income received as a result of the transaction is also not paid.
Note! There is no tax charged to individuals when purchasing currency on the exchange.
Receipt of advance payment from a foreign buyer
The organization has the right to carry out transactions not only in rubles, but also in foreign currency in compliance with legislative norms on currency regulation and control (Federal Law of December 10, 2003 N 173-FZ).
Receipt of an advance payment from a foreign buyer is registered with the document Receipt to the current account, transaction type Payment from the buyer in the Bank and cash desk - Bank statements - Receipt button. Let's look at the features of filling out the document Receipt to a current account using our example.
The Bank Accounts directory must first be filled in (Main - Organizations (Organization Details) - Organization Card - Bank Accounts link): information about the Organization's currency account to which payment is received from the buyer must be entered.
Prepayment in foreign currency is credited to a transit foreign currency account.
- The payer is a foreign buyer with whom the contract has been concluded. Selected from the Contractors directory.
- Agreement is a contract under which mutual settlements are carried out with a foreign buyer.
The agreement with the buyer in foreign currency must be completed as follows:
- Type of agreement - With the buyer ;
- Price in - USD : currency in which the contract was concluded;
- Payment in - switch USD : payment currency.
As a result of selecting such an agreement in the Receipt to Current Account , accounts for settlements with the buyer are automatically set in the field:
- Settlement account - 62.21 “Settlements with buyers and customers (in foreign currency)”;
- Advances account - 62.22 “Calculations for advances received (in foreign currency).”
Since payment by the buyer is made in foreign currency, the document states:
- Bank account - a transit currency account in USD, into which funds are received from the buyer;
- Accounting account - 52 “Currency accounts”, is installed automatically when selecting a foreign currency bank account;
- Amount - payment amount in currency according to the bank statement;
- VAT rate — 0%.
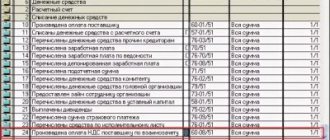
Postings according to the document
The document generates the posting:
- Dt 52 Kt 62.22 - receipt of an advance payment from the buyer to a transit currency account.
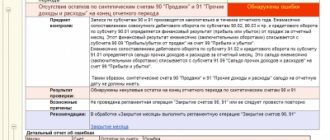
The document is filled out in currency: the contract is concluded in USD and payment is also made in USD. In the postings, the amounts are reflected in both rubles and foreign currency. This is due to the fact that accounting in the Russian Federation is carried out in rubles. The value of assets or liabilities in foreign currency is subject to conversion into rubles (clause 4 of PBU 3/2006).
Advances received and issued in foreign currency are not subsequently revalued in accounting records and in NU. The ruble valuation of the advance is fixed at the rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on the date of the advance (clause 7, clause 10 of PBU 3/2006, clause 11 of Article 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 5 of clause 1 of Article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
What is a transit and currency account
The main payments between clients in our country are carried out in rubles for both individuals and legal entities. If someone conducts foreign economic activity, then such operations will require opening an additional foreign currency account. It is established according to current regulations in parallel with a special transit account.
A number of clients must open transit accounts with banks
Why do you need a transit account?
Transit and current currency accounts are relevant for those who work with the following transactions abroad:
- provision of services to foreign contractors;
- carries out work for non-residents;
- receives funds from abroad, etc.
An existing transit account in euros, dollars, pounds or other foreign money is required to credit foreign currency funds in favor of the Russian recipient. It cannot be used for the same operations that are carried out with a regular settlement account, since it is involved in currency monitoring.
The transit agent ends up in bank transactions when incoming foreign funds are sold on the stock exchange or customs duties are transferred. It is also used to credit revenue in dollars, euros, pounds, etc., or pay for transport services.
It is important to know that foreign funds received for a resident are credited on the basis of documents provided to the bank (copies of contracts, invoices, etc.), therefore, money can remain as transit money (unavailable to the client) for up to 15 days. If confirmation is not received, then the amount is sent back to the payer without being credited to the recipient.
What is the difference between a transit and foreign exchange account
Visually, by the number you can determine how to distinguish a transit account from a foreign currency account. In numbers, in the seventh position, the first has a 1 (one), and the second has a 0 (zero). The remaining signs will be identical. Sometimes some potential recipients of funds from abroad are interested in what numbers are required to be indicated in the concluded agreement in the financial details section.
Experts recommend not specifying a transit account, since in any case the amount will initially be automatically credited to it for currency control. It is enough to indicate in the contracts the numbers p/c or v/c, and the difference between a foreign currency account and a transit account is already clear.
Previously, it was necessary to independently notify the tax authorities about the opening of a military account. Now this is the responsibility of the bank, which automatically sends all data to the fiscal authorities in electronic form.
Transit account may be subject to service charges
BASIC: difference in exchange rates
Both upon receipt and use of foreign currency (foreign exchange earnings), the organization may receive additional income (expenses). These include, in particular:
- differences between official and commercial exchange rates;
- exchange differences;
- Commission of the bank.
When purchasing (selling) foreign currency, an organization may experience a difference between the official and commercial exchange rates. It is formed if the exchange rate at which the bank buys (sells) it differs from the official rate of the Bank of Russia.
When buying a currency, a positive difference arises if the exchange rate at which the bank sold it is lower than the official one. A negative difference occurs if the purchase rate is higher than the official one. When selling currency, the opposite is true.
This follows from the systematic interpretation of the provisions of paragraph 2 of Article 250 and subparagraph 6 of paragraph 1 of Article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
When using currency (foreign exchange earnings), the organization may experience exchange rate differences (positive or negative). They are formed during the revaluation of property in the form of foreign currency values and debt in foreign currency.
For currency received in a foreign currency account and debt to the organization (accounts receivable) in foreign currency, a positive exchange rate difference arises if, on the date of revaluation, the exchange rate to the ruble became higher compared to the date of the previous accounting of funds in the foreign currency account or receivables.
Accordingly, a negative exchange rate difference is formed if, on the date of revaluation, the exchange rate against the ruble has decreased compared to the date of the previous accounting of funds in a foreign currency account or receivables.
For debt to the supplier or buyer (accounts payable) in foreign currency, a positive exchange rate difference arises if, on the date of revaluation, the exchange rate to the ruble became lower compared to the date of the previous accounting of accounts payable. And negative - if the exchange rate to the ruble on the date of revaluation has become higher compared to the date of the previous accounting of accounts payable in foreign currency.
There is an exception to this rule. Exchange differences will not arise if the organization receives (issues) advances. After receiving (issuing) these funds in foreign currency, there is no need to recalculate them due to changes in the exchange rate.
This follows from the provisions of paragraph 11 of Article 250 and subparagraph 5 of paragraph 1 of Article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The exception for foreign exchange advances does not apply if the advance is subject to return, for example upon termination of the contract. In such a situation, the advance should be reclassified as an obligation of one party to return the previously received amount to the other party. Since the indicated amounts do not fall under the advance payment in its generally accepted meaning, they are subject to revaluation on a general basis. Similar clarifications are contained in the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 2, 2010 No. 03-03-06/1/683.
Include the difference between the official and commercial exchange rates for purchasing (selling) currencies in:
- non-operating income - if a positive difference occurs (clause 2 of Article 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- non-operating expenses - if a negative difference occurs (subclause 6, clause 1, article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Using the accrual method, reflect these differences on the date of transfer of ownership of foreign currency (subclause 10, clause 4, article 271, subclause 9, clause 7, article 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). When using the cash method, include the positive (negative) difference in the base on the date of receipt of funds into the organization’s account (clause 1 of Article 273 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
An example of reflection in accounting and taxation of transactions on the sale of foreign currency. The organization applies a general taxation system
Alpha LLC has US dollars in its foreign currency account. Alpha decided to sell them. The amount to sell is $1,000. The exchange rate is conditional.
On February 2, the organization sold currency at the rate of 35.2 rubles. for a dollar. The rubles were credited to the organization's bank account.
When calculating income tax, Alpha uses the accrual method. Income tax is paid monthly.
The US dollar exchange rate on February 2 was 35.4146 rubles. for a dollar.
The bank's commission amounted to 200 rubles.
On February 2, the organization’s accountant made the following entries in the accounting records:
Debit 76 Credit 52 – 35,415 rub. (1000 USD × 35.4146 rubles/USD) – funds intended for sale are debited from a foreign currency account;
Debit 91-2 Credit 76 – 200 rub. – commission fee is withheld by the bank;
Debit 51 Credit 76 – 35,200 rub. (1000 USD × 35.2 rubles/USD) – proceeds from the sale of currency are credited to the current account;
Debit 76 Credit 91-1 – 35,200 rub. – the proceeds from the sale of foreign currency are included in other income;
Debit 91-2 Credit 76 – 35,415 rub. – other expenses from the sale of currency are reflected (including 215 rubles = 1000 USD × (35.4146 rubles/USD – 35.2 rubles/USD) (the difference between the currency sale rate and the Bank of Russia rate)).
When calculating income tax for February, Alpha's accountant took into account 415 rubles. (200 rubles + 215 rubles) as part of non-operating expenses.
Situation: how to reflect foreign currency conversion when calculating income tax? The organization has an account in one currency, and settlements through it are carried out in another currency.
Reflect the differences from conversion as non-operating income (expenses).
Residents can make payments through their bank accounts in any foreign currency, regardless of the foreign currency in which the bank account is opened. If necessary, a conversion operation is performed. For example, if an account is opened in US dollars, but payments need to be made in euros, you can convert from US dollars to euros. For conversion, the rate set by the bank is taken. This procedure follows from Part 7 of Article 14 of the Law of December 10, 2003 No. 173-FZ.
Conversion, in particular, is an operation for the purchase (sale) of one foreign currency for another (Part 7 of Article 14 of the Law of December 10, 2003 No. 173-FZ). That is, in this case, the purchase and sale of foreign currencies occurs.
This means that if, when buying (selling) currency, the commercial cross rate of the bank is more profitable for the organization than the official one, it will generate non-operating income (clause 2 of Article 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). If the commercial cross-rate is less profitable, the organization must include the resulting difference in non-operating expenses (subclause 6, clause 1, article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Using the accrual method, reflect the indicated non-operating income and expenses on the date of transfer of ownership of foreign currency (subclause 10, clause 4, article 271, subclause 9, clause 7, article 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
With the cash method, reflect the positive (negative) difference on the date of receipt of funds into the organization’s account (clause 1 of Article 273 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
How does the bank carry out currency control of client transit accounts?
In the modern financial services market, there are several large banks that provide cash and settlement services for foreign currency accounts. Such banking institutions act as currency control agents, issue transaction passports and allow foreign banknotes to be stored in transit accounts.
As a rule, the bank commission for conducting foreign exchange transactions is about 0.15% of the transaction amount; the control procedure is carried out online. For example, at Tinkoff Bank, notifications of receipts to a transit currency account and a list of required documents are sent through the application. The bank client submits scanned copies of documents, receives approval and the funds are automatically transferred to the current account.
Currency control of transactions of legal entities is carried out in several stages.
Checking the agreement between the account holder and the counterparty. Russian legislation in the field of currency regulation requires the execution of agreements with foreign counterparties, indicating the validity period of the agreement, currency, name and place of registration of the parties. You should also indicate the date of conclusion of the contract. Bank clients working under an offer (a contract for the provision of services or work without a fixed validity period) must provide the bank with a letter indicating the expected completion date of the contract. In practice, banks publish samples of agreements with foreign counterparties on the official website, and the form of the agreement can also be checked with an employee of the currency control department.
Receipt of funds to the transit currency account. Most banking organizations send a notification to clients the next business day after the currency is received in the transit account. The account owner must provide documents for currency control within 15 calendar days to avoid fines and transfer funds to the current account. The best option is to provide the documents in advance so that the bank employee has time to check the papers and not impose fines.
Collection and submission of documents for currency control. The client needs to submit to the bank a completed certificate of currency transactions on the account, an agreement with the client, a payment order or an invoice (invoice). If the payment amount exceeds the equivalent of 50 thousand US dollars, you will additionally need to issue a transaction passport from the bank. The client should check with the bank in advance for which organizations the “green corridor” is open - a simplified scheme for confirming transactions. Typically, banks open a “green corridor” for large foreign companies (for example, Google, Apple). If the counterparty is included in the list of such organizations, the bank client will need to provide a screenshot of the login to their personal account or payroll. The procedure for submitting documents for currency control depends on the specific bank. Usually you need to provide scanned copies of documents by sending files through your personal account; some banks require printed documents to be sent to the office.
Receiving funds. Typically, documents for currency control are checked within two to three business days, then the funds in the transit account are transferred to the current (settlement) account. The bank informs about the successful completion of currency control in an email, or can send an SMS. The procedure for filling out and the period for reviewing documents varies depending on the specific bank. Many financial institutions independently fill out the transaction passport, using an agreement with the counterparty and an invoice provided by the client.
Currency exchange transactions
Please note that in PBU 23/2011 “Cash Flow Report” (approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated February 2, 2011 No. 11n), the expression “purchase and sale of foreign currency” is not used. It uses the term “currency exchange operations” and discusses an organization that, as part of its normal business,
sti “changes the received amount of foreign currency into rubles” or “changes rubles for the required amount of foreign currency” (subparagraph “b”, paragraph 6, paragraph 18 of PBU 23/2011). Moreover, it has been established that foreign exchange transactions (except for losses or benefits from the transaction) do not generate cash flows. By the way, such problems do not arise when moving funds between the bank and the cash desk, when transferring cash to collectors, as well as when transferring money between different bank accounts of the company or transferring cash between different cash desks.
The sale of funds in the form of foreign currency is discussed in PBU 9/99 (clause 7). It is this regulatory requirement that accountants refer to when recognizing income from the sale of currency. Following the recognition of income, the corresponding expense must also be recognized. The grounds for this are stated in PBU 10/99 (clauses 11 and 19).
Meanwhile, the purchase and sale of foreign currency in cash and non-cash forms refers to banking operations. And their implementation is carried out only on the basis of a license issued by the Bank of Russia. In the absence of this license, carrying out currency purchase and sale transactions is unlawful (clause 6, article 5 and article 13 of Law No. 395-1 of December 2, 1990).
At the same time, the rules of PBU 9/99 and PBU 10/99 do not apply to credit organizations. But the orders of the Russian Ministry of Finance cannot allow non-banking organizations to buy and sell currency in the generally accepted sense. And although foreign currency refers to things (Articles 128, 140 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation), a special procedure has been established for its purchase and sale. The domestic foreign exchange market of the Russian Federation operates according to special rules.
And if all companies actually sold currency, they would have to pay VAT on these transactions. Fortunately, no one does this. Foreign exchange transactions in the non-banking sector represent the circulation of Russian or foreign currency, which is not recognized as sales.
Actually, our conclusion is the following: the exchange of foreign currency for Russian currency and back should not be considered the purchase and sale of foreign currency.
If the currency was purchased less than three years ago
When selling currency within three years after purchase, you must submit a declaration in any case. Even if the currency was sold at a loss and lost a million. Such rules.
The deadline for submission is April 30 of the following year. If you sold currency in 2021, then you need to report in 2021. The personal income tax declaration must be paid by July 15 of the following year.
When calculating taxes, you can use property deductions. For currencies they are:
- Purchase costs. From the amount you were paid when you sold the currency, you can subtract the amount you spent to buy it.
- 250 thousand rubles. If there are no documents that confirm expenses, reduce income by deduction, which everyone is entitled to for no reason. 250 thousand rubles is the limit not for one transaction, but for transactions throughout the year with all types of property, except housing.
You choose which deduction to claim, and no one will force you to deduct actual expenses from your income unless it is very profitable.
If you choose the right deduction, then even if you sell currency at a profit, you can file a declaration, but not pay anything to the budget.
How does a transit account work?
A transfer from a non-resident is first credited to a transit account, and then to a bank account in foreign currency. During the day, the bank notifies the recipient of the receipt and requests papers that confirm the legality of the currency transaction.
The money is stored in a transit account until the organization transfers the requested documents to the bank.
Next, the documents are checked by the currency control department, and the bank transfers money to the account in foreign currency or refuses to carry out the operation.
Is an invoice drawn up in foreign currency in 2020-2021?
When issuing an invoice in foreign currency, the taxpayer should consider 2 factors:
- clause 7 art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation allows that an organization has the right to indicate an amount in foreign currency in an invoice if it is the means of payment;
- clause 1 section Government Resolution II “On filling out documents for VAT calculations” dated December 26, 2011 No. 1137 contains a provision according to which, if payments in ruble equivalent are indicated in the contract with the total contract price in foreign currency, the invoice must be issued in rubles.
The resulting inconsistency is a source of trouble for organizations that take the rules of the Tax Code too literally. During audits, tax authorities quite often file complaints on this basis. However, judicial practice shows that in such disputes the taxpayer wins. The judges believe that the Tax Code of the Russian Federation has an advantage over the decision of the Government of the Russian Federation.
Read more about the rules for issuing foreign currency invoices in the material “Invoice in foreign currency - how to issue?” .
What is a transit account
A transit account is an account that is opened for a legal entity (IP/LLC) in a bank along with a foreign currency account. It is necessary for storing money during the period of verification of the legality of a foreign exchange transaction.
Transit and current (c/c) currency accounts have differences:
- Account in foreign currency is opened upon request of a legal entity. persons, while consent is not required to open a transit, it opens automatically.
- In foreign currency funds can be stored as long as necessary, in transit - up to 15 days.
- Cash account in foreign currency is suitable for payments for services, transit - only for temporary storage of money.
- In the transit number the seventh digit is “1”, in the foreign currency number it is “0”.
We recommend reading: Where to open a current account for individual entrepreneurs and LLCs: comparison of tariffs and reviews.