After personal income tax and amounts under enforcement documents have been withheld from wages, the employer, at the employee’s request, can make other deductions in favor of third parties - for example, for charity, for loan repayment. 1C experts tell us how to set up and register such deductions in the 1C: Salaries and Personnel Management 8 program, edition 3.
An exhaustive list of deductions at the initiative of the employer from an employee’s salary is given in Article 137 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and Part 4 of Art. 15 of the Federal Law of December 29, 2006 No. 255-FZ. Other deductions from wages are made by the employer only with a written application from the employee.
| 1C:ITS For more information about what actions an employer needs to take to implement deductions at the initiative of an employee, see the “Human Resources Officer’s Handbook” in the “Personnel and Remuneration” section. |
We will consider the procedure for reflecting deductions in favor of third parties in the 1C: Salaries and Personnel Management 8 program, edition 3, using the following example.
Example
| In accordance with a written statement from an employee of Stil LLC A.A. To Ivantsova, 1,000 rubles are withheld from her salary every month, starting in March 2018, and transferred to a charitable foundation. |
The following actions are performed:
1. Set up the type of hold.
2. Registration and withholding of amounts to third parties.
How to keep child support
Deductions from wages are very diverse, but they can be divided into several types:
- mandatory deductions, which include alimony, deductions based on writs of execution (fines), etc.;
- at the initiative of the employer, fines for violation of traffic rules, etc.;
- at the initiative of the employee, for example, deduction to pay off a loan.
First, let's look at how to withhold alimony in "1C: Salaries and Personnel Management 8", ed.
3.1. If parents do not fulfill their obligations to support their children, then funds are recovered from the parents in court. In turn, the employer is obliged to withhold alimony from the employee’s salary every month and pay the person receiving alimony no later than three days from the date of payment of wages to the debtor.
The organization has received the executive documents, and we are forming the following actions in the system.
First, we configure the system: go to the “Settings” section – “Payroll calculation” – “Setting up the composition of accruals and deductions” – “Deductions” – set the “Deductions by writs of execution” flag.
We register the terms of the writ of execution in the document “Writ of Execution”, which is located in the “Salary” - “Deductions” tab.
In the writ of execution we indicate the employee from whom alimony is required to be withheld, the withholding period, the recipient and his address, and the method of calculation. Calculation methods can be as follows
- Percentage, if the writ of execution specifies to withhold alimony as a percentage.
- Fixed amount.
- A share, if the calculation is similar to the calculation by percentage, however, allows you to avoid errors in the calculation due to rounding (for example, 1/3 instead of 33.33%).
A money transfer through a paying agent is completed if the amount withheld from the employee will be transferred to the recipient using a paying agent: bank or post office.
The deduction itself is made in the document “Calculation of salaries and contributions” when calculating wages. Further, the payment of income occurs without taking into account the amounts under writs of execution.
Deductions from salaries in the 1C program: Enterprise Accounting 8
Published 10/03/2016 12:07 Sometimes situations arise in which it is necessary to withhold certain amounts from an employee’s salary. In one of the previous articles, we already looked at Retention based on a writ of execution in 1C: Enterprise Accounting 8 edition 3.0. In this article we will look at how to work with other types of deductions: debt on accountable amounts, union membership dues and the cost of damaged material assets (defects in the manufacture of products).
How are these deductions fundamentally different from the deductions based on a writ of execution, discussed earlier? The fact is that accounting for such operations is not automated in the 1C: Enterprise Accounting 8 program and therefore raises quite a lot of questions from users.
But before we begin to deal with how these situations are reflected in the program, I would like to remind you that, according to Article 138 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the amount of deductions at the initiative of the employer should not exceed 20% of the employee’s salary. Therefore, if the amount of deductions exceeds the maximum possible, then the balance is withheld in the next month. So, let's look at how to reflect each of the three listed cases in the program.
1. Retention of debt on accountable amounts
Let’s say that an employee did not fully account for the amounts issued on account and did not return the balance of the debt. It was decided to withhold the specified amount from his salary. First of all, we need to add a new Calculation Type . To do this, open the section “Salaries and Personnel”, “Directories and Settings”, “Deductions”
Click on the “Create” button and fill in: - name - code of the calculation type, which must be unique, that is, it must not be repeated. The “Deduction Category” field is not filled in in our case, since there is no suitable category in the list for the “Retention of Accountable Amounts” calculation type.
Write it down and close it. Next, create a “Payroll” document. Open the section “Salaries and Personnel”, “Salaries”, “All Accruals”. After automatically filling out this document, go to the “Deductions” tab, click the “Add” button and fill in: - Full name of the employee - type of calculation - amount of deduction - recipient of the deductions
But if we post the document, we will notice the following peculiarity: the document did not automatically generate postings for this deduction. To register this fact in accounting, you must additionally use the “Operation” document (section “Operations”, “Accounting”, “Operations entered manually”).
We add the posting Dt account 70 Kt account 71.01 “Settlements with accountable persons”
Why then was it necessary to add this deduction to the payroll document if the postings still have to be generated manually? And this must be done so that this amount is reflected in the payroll and payslip, and is also taken into account when determining the amount to be paid. We will generate a pay slip (section “Salaries and Personnel”, “Salary”, “Salary Reports”, “Pay Slip”) and check the amount withheld.
2. Withholding of trade union dues
We start again by setting up the calculation type. As in the first case, fill in the name and code of the calculation type. Only now we select the deduction category “Trade Union Dues”, because she is on the list.
Write it down and close it. We create the “Payroll” document, fill it out and use the “Add” button on the “Deductions” tab to enter the necessary information, selecting the created type of calculation.
Next, we register the amount of deduction in accounting using the document “Operations entered manually.” We create a posting for Dt account 70 Kt account 76.49 “Calculations for other deductions from employees’ salaries”
To check, we will generate a payslip; the amount withheld should be reflected in the Withheld .
3. Retention for marriage.
Let's consider an example when an employee of the organization Maxima LLC manufactured a part with a defect that cannot be corrected, and we must deduct the cost of damaged material assets from his salary. Just as in previous cases, we start by setting up the calculation type. We do not fill out the retention category.
Now we fill out the “Payroll” document and add information about our deduction to the appropriate tab. Click on the link in the lower left corner to view and print the Payslip
We register the amount of deduction in accounting by filling out the document “Operations entered manually.” We create the posting Dt 70 Kt 73.02 “Calculations for compensation for material damage.”
As you may have noticed, the reflection of all three situations in the program is approximately the same, only the postings that need to be generated manually are different. You can use the same algorithm of actions when creating any other deductions that are needed in your organization.
Author of the article: Svetlana Gubina
Did you like the article? Subscribe to the newsletter for new materials
Add a comment
Comments
0 Olga_91 06/19/2018 21:40 Thank you very much for the information! You helped a lot, I wish there were more useful articles like this! =))
Quote
+2 Arthur 10/16/2016 19:34 Dear Olga Shulova! Thank you very much for all this information, you tell us in such detail that everything is immediately clear. I am very glad that I found you on the site and often use your information about 1s 8.3, thank you again!!!
Quote
Update list of comments
JComments
Fines for traffic violations
An organization can pay a fine for violating traffic rules (traffic rules) and withhold the amount from the employee’s salary in accordance with Art.
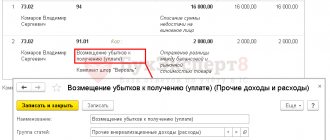
138, 238, 248 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. To do this, in “1C: Salaries and Personnel Management 8”, ed. 3.1, create a new hold. Go to “Settings” – “Holds”. We create a new element in the directory. In it we indicate: “Name” – “Traffic fines”. For the deduction purpose, select “Deduction for settlements on other transactions”; “Calculation and indicators” – the result is entered as a fixed amount; “Type of salary transaction” – “Compensation for damage”.
We enter the amount of the received fine using a special document “Deduction for other transactions”, which is located in “Salary” - “Deductions”. In the new document we indicate the organization, employee, retention period, and amount of retention.
At the end of the month, we calculate wages using the document “Calculation of salaries and contributions”, where deductions according to traffic rules are automatically included in the “Deductions” tab. To reflect the postings, be sure to register “Reflection of wages in accounting.”
Please note: transactions uploaded to the accounting program are generated automatically according to debit 70 and credit 73.02.
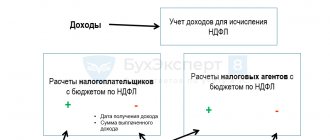
Personal income tax withheld: posting tax withholding from wages
When personal income tax is withheld, the posting is made to the credit of account 68 in correspondence with the debit of one of the accounts for settlements with individuals. The article contains correspondence of accounts and examples, free reference books and useful links.
The following reference books will help you pay salary taxes without any problems; you can download them:
In the most common case of tax calculation, when personal income tax is withheld from wages, accounting entries are made to the personnel payroll account in correspondence with the budget settlement account.
In other cases, when less common income of individuals is subject to taxation, the correspondence of accounts may differ. For example, tax agents withhold personal income tax not only from wages, but also from financial aid, dividends, benefits, bonuses, etc.
Further in the article - details about frequently encountered transactions for accrued personal income tax.
Other tax references
After familiarizing yourself with the personal income tax transactions, do not forget to look at the following reference books, they will help in your work:
Personal income tax reporting – online
Traditionally, the most problematic form of income tax reporting for employers is the calculation on the 6-NDFL form. It was approved in 2015, but starting with the reporting for 2021, changes were made to the title page and the procedure for filling out the calculation.
It is possible that these amendments are not the last, since tax legislation is constantly being improved. In order not to track all changes and save time on filling out the report, it is more convenient to prepare it automatically - in the BukhSoft program.
Calculation according to form 6-NDFL can be generated in the BukhSoft program in 3 clicks. It is always drawn up on an up-to-date form, taking into account all changes in the law. The program will fill out the calculation automatically. Before sending to the tax office, the form will be tested by all Federal Tax Service verification programs. Try it for free:
6-NDFL online
Personal income tax accrued: posting
The accrual of personal income tax is reflected in the accounting records of the tax agent upon the fact of tax withholding from the income of an individual. In what amount should personal income tax be accrued, posting involves the application of a certain formula for calculating tax. If personal income tax is withheld from the income of an individual resident of Russia, then the following formula is applied:
When calculating tax, account 68 for settlements with the budget is credited. By debit for transactions in which personal income tax is accrued, the posting will be made to the accounts that reflect the taxable income of individuals. For example:
- if the tax agent withholds personal income tax from the salary, then account 70 of wage settlements is debited;
- if tax is withheld from an employee’s non-productive income, then the transaction is reflected in the debit of account 73 of settlements with personnel for other transactions.
Read more about personal income tax withholding in Table 1.
Table 1.
Personal income tax accrued: posting
| Dt | CT | Source of tax withholding |
| 70 | 68 | Withholding by the employer from the following payments to the employee:
|
| 73 | 68 | Withholding by the employer from other payments to hired employees, except for amounts reflected in account 70 |
| 75 | 68 | Withholding by a tax agent paying dividends to an individual |
Let us illustrate the correspondence of accounts from Table 1 with a numerical example.
Example 1
Personal income tax accrued: posting
On July 5, Symbol LLC paid the accountant an additional salary for June, the total amount of which is 60,000 rubles, and for the first time in a year, issued financial assistance for the July vacation in the amount of 10,000 rubles. If we assume that the accountant is a tax resident of Russia and does not have the right to deductions, for transactions in which personal income tax is accrued, the posting will be made as follows:
Dt 70 Kt 68 subaccount “Calculations for personal income tax”
– 7800 rub. – tax is withheld from the accountant’s salary;
Dt 73 Kt 68 subaccount “Calculations for personal income tax”
– 780 rub. ((RUR 10,000 – RUR 4,000) x 13%) – tax is withheld from the taxable part of financial assistance to the accountant.
Personal income tax is withheld from wages: posting
As you know, the employer is obliged to pay wages at least twice a month, while withholding income tax is required only upon the final payment at the end of the month. As a result, peculiarities arise in the reflection of transactions in accounting, which can be seen in example 2.
Example 2
Personal income tax is withheld from wages: posting
Trading paid the accountant an advance on his salary on June 20 in the amount of 25,000 rubles. and the remaining amount of the salary was accrued on July 5 in the amount of 35,000 rubles.
Symbol transfers payments to employees to their bank accounts with the execution of separate payment documents.
If we assume that the accountant is a tax resident of Russia and has no right to deductions, the tax amount is 7,800 rubles. ((RUR 25,000 + RUR 35,000) x 13%).
Read about tax withholding operations in Table 2.
Table 2.
Personal income tax is withheld from wages: posting
| Dt | CT | Sum | The meaning of the operation |
| 70 | 51 | 25,000 rub. | Advance payment for June salary transferred |
| 44 | 70 | 35,000 rub. | Payroll accrued for June |
| 70 | 68 | 7800 rub. | Tax withheld from the total wages for June |
| 70 | 51 | RUR 27,200 | The final settlement was made with the accountant for wages for June |
Posting: personal income tax withheld from vacation pay
Calculations for vacation pay are reflected in account 70 payroll calculations. In this case, the source of financing payments for vacation is the estimated liability reflected in account 96. As a result of which transactions the personal income tax withholding from vacation pay is posted, see example 3.
Example 3
Posting: personal income tax withheld from vacation pay
The production department accrued vacation pay to the accountant for the July holiday in the amount of 30,000 rubles. Symbol transfers payments to employees to their bank accounts. If we assume that the accountant is a tax resident of Russia and has no right to deductions, the tax amount is 3,900 rubles. (RUR 30,000 x 13%).
Read about tax withholding operations in Table 3.
Table 3.
Posting: personal income tax withheld from vacation pay
| Dt | CT | Sum | The meaning of the operation |
| 96 | 70 | 30,000 rub. | Vacation pay accrued |
| 70 | 68 | 3900 rub. | Income tax withheld from vacation pay |
| 70 | 51 | RUR 26,100 | Payment for vacation was transferred to the accountant |
Posting: personal income tax withheld from sick leave
Calculations for payment for periods of temporary disability are reflected in the debit of account 70. In this case, the source of financing for “sick leave” payments can be both funds from the social insurance fund and the employer’s own funds. As a result, personal income tax withholding from sick leave is posted as part of the following operations:
Dt 20 (26, 44, …) Kt 70
– part of the benefit is accrued at the expense of the employer;
Dt 69-1 Kt 70
– part of the benefit was accrued from the Social Insurance Fund budget;
Dt 70 Kt 68 subaccount “Calculations for personal income tax”
– income tax withheld.
Posting: personal income tax is transferred to the budget
Firms, entrepreneurs and individuals must pay taxes to the Russian budget in rubles. At the same time, according to the general rule, legal entities - tax agents for personal income tax make tax payments in non-cash form. Therefore, the posting of income tax payments to the budget is made within the framework of the following operations:
Dt 70 (73, 75) Kt 68 subaccount “Calculations for personal income tax”
– income payment is withheld;
Dt 68 subaccount “Personal Tax Payments” Kt 51
– income payment is transferred to the budget.
Source: https://www.BuhSoft.ru/article/2121-uderjan-ndfl-provodka
Deduction for loan repayment
At the request of an employee, an organization can reduce earnings by making transfers to other organizations, for example, paying off an employee’s loan.
First of all, we set up the system: we create a new element in the “Retentions” directory. Fill in a new element: “Name” – “Deduction for loan repayment”; “Purpose of withholding” – “Other withholding in favor of third parties”, “Withholding is carried out” – “Monthly”, “Calculation and indicators” – “The result is entered as a fixed amount”.
In this case, it is enough to create a retention once and then apply it to all employees.
Then we register the terms of deduction in the document “Permanent deduction in favor of third parties” (“Salary” - “Deductions”). Select the employee, in the “Retention” line – the previously created retention. Next, set the switch to “Start a new withholding”, determine the period, and in the “Counterparty” line, select the recipient - the bank. We select an employee in the tabular part of the document and indicate the amount, since when creating the deduction we indicated that the result is a fixed amount.
At the time of calculating the salary for the month, the system will withhold the specified amounts from the employee. When uploading to “1C:Accounting 8”, transactions will be generated for debit 70 and credit 76.49.
Checking the withheld amounts can be done through salary reports: payslip, salary analysis, and so on.
Source: Progressive Accountant newspaper.