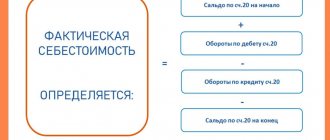
How to register an insurance premium paid to an insurer? How is the standard calculated in the 1C: Accounting 8 program, edition 3.0? How is the bonus paid for dismissed employees taken into account? You will find answers to these questions in the article by 1C experts.
Voluntary medical insurance is a type of personal insurance (Article 934 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation), under the terms of which:
- one party (the insurer) undertakes to pay the insurance amount stipulated by the contract in the event of the occurrence of an event (insured event) specified in the contract in the life of the citizen (insured person) named in the contract;
- the other party (the policyholder) undertakes to pay the insurer the insurance premium stipulated by the contract.
According to paragraph 3 of Article 4 of the Law of the Russian Federation of November 27, 1992 No. 4015-I “On the organization of insurance business in the Russian Federation,” the objects of health insurance can be property interests associated with payment:
- medical and other services due to a disorder of the health of an individual or the condition of an individual requiring the organization and provision of such services;
- carrying out preventive measures that reduce or eliminate the degree of threats dangerous to the life or health of an individual.
Cheat sheet on the article from the editors of BUKH.1S for those who do not have time
- Voluntary health insurance (VHI) is a type of personal insurance.
- The object of VHI is usually property interests associated with payment for medical and other services due to an individual’s health disorder.
- VHI for employees is one of the components of labor costs.
- Insurance premiums for VHI are recognized as expenses under certain conditions specified in subparagraph 16 of Article 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
- An employer may issue employees one or more insurance policies from different companies with insurance coverage for different types of services.
- To be able to reduce the income tax base on the cost of policies, the company must take into account the maximum threshold for labor costs. The standard is calculated based on the amount of labor costs for all employees of the organization, and not just the insured persons.
- VHI expenses are recognized in tax accounting no earlier than the reporting period in which the insurance premium is transferred. Expenses are recognized on a straight-line basis over the term of the contract.
- Amounts transferred under VHI agreements are not subject to personal income tax and are not subject to insurance premiums if the agreement is valid for at least a year.
- In accounting, expenses for voluntary health insurance are included as expenses during the period to which they relate.
- VHI payments are reflected in the debit of cost accounts (for example, account 20 “Main production”, account 26 “General business expenses”, 44 “Sales expenses”).
- Unlike tax accounting, in which expenses for voluntary health insurance are standardized, in accounting such expenses are recognized without restrictions.
Accounting for VHI expenses in 1C: Accounting 8
After posting the document Write-off from the current account, the following entry will be generated:
Debit 76.01.9 Credit 51 - for the amount of the lump sum insurance premium paid to the insurer.
For tax accounting purposes for income tax, the corresponding amount is also recorded in the resource Amount NU Dt 76.01.9.
Thus, the lump sum paid to the insurer is taken into account as part of the receivables of Andromeda LLC, and the insurance premium will be included in expenses for accounting and tax purposes during the term of the insurance contract.
In “1C: Accounting 8”, automatic calculation of VHI expenses is carried out in three stages during the monthly processing process. Closing the month:
- at the first stage - when performing the routine operation Write-off of deferred expenses, part of the insurance premium is written off to cost accounts in accordance with the write-off parameters established in the form of the directory element Deferred expenses;
- at the second stage - when performing a regulatory operation Calculation of shares of write-off of indirect expenses, the maximum amount of expenses for voluntary health insurance to be included in expenses is calculated;
- at the third stage - when performing the routine operation Closing accounts 20, 23, 25, 26 or Closing account 44 “Distribution costs”, the costs of voluntary health insurance reflected in the cost accounts are written off in accordance with the accounting policies of the organization. At the same time, expenses related to the current month for voluntary medical insurance are recognized in full in accounting, and in tax accounting - within the limits of the standard calculated in accordance with paragraph 3 of Article 318 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Let's consider all the stages of automatic calculation of VHI expenses for Example 1, completed in January 2015. The regulatory operation Write-off of deferred expenses determines the part of the insurance premium that can potentially be recognized as expenses:
RUB 480,000.00 / 365 days x 31 days = RUB 40,767.12
It is this amount that is entered into the accounting register entry by posting:
Debit 26 Credit 76.01.9.
Also, for income tax purposes, an entry is entered in the resources Amount of NU Dt and Amount of NU Kt.
Figure 3 shows the Certificate of calculation of write-off of deferred expenses for January 2015.
Rice. 3. Certificate-calculation of write-off of deferred expenses
Using the routine operation Calculation of shares of write-off of indirect expenses, the standard for expenses on voluntary health insurance is calculated:
RUB 300,000.00 x 6% = RUB 18,000.00
The document does not generate accounting entries, but the corresponding entries are entered into the information registers Shares of write-off of indirect expenses and Calculation of standardization of expenses. Figure 4 shows the Help-calculation of cost rationing for January 2015.
Rice. 4. Certificate-calculation of rationing costs for VHI for January 2015
By routine operation Closing accounts 20, 23, 25, 26, VHI expenses are written off by posting:
Debit 90.08.1 Credit 26 - in the amount of 40,767.12 rubles.
Amounts are also entered into special resources of the accounting register intended for income tax accounting:
Amount NU Dt 90.08.1 and Amount NU Kt 26 - for the amount of expenses within the standard (RUB 18,000); Amount PR Dt 90.08.1 and Amount PR Kt 26 - for a constant difference (RUB 22,767.12).
After completing the regulatory operation Calculation of income tax, a permanent tax liability (PNO) in the amount of RUB 4,553.42 will be recognized. Also, VHI expenses will be calculated monthly until the end of the contract. So, in February 2015:
- part of the insurance premium written off from the account on 01/76/9—RUB 36,821.92. (RUB 439,232.88 / 334 days x 28 days);
- the standard cost for voluntary health insurance is RUB 17,820.00. (RUB 597,000.00 x 6% - RUB 18,000.00);
- expenses for voluntary health insurance in tax accounting amount to 17,820.00 rubles, which creates a constant difference in the amount of 19,001.92 rubles.
In December 2015, the lump sum of the insurance premium paid is completely written off from account 76.01.9, and the maximum amount of expenses for voluntary health insurance for the tax period (for 2015) is determined as 436,080.00 rubles. (RUB 7,268,000.00 x 6%). It is this amount that will be included in the indirect expenses reflected in line 040 of Appendix No. 2 to Sheet 02 of the income tax return (approved by order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated November 26, 2014 No. ММВ-7-3 / [ email protected] ).
IS 1C:ITS
For more information about accounting for VHI expenses in the 1C: Accounting 8 program (rev. 3.0), see the Directory of Business Transactions. 1C: Accounting 8" in the "Accounting and Tax Accounting" section - without exceeding the standard and with exceeding the standard of expenses.
What is VHI
VHI or voluntary health insurance in a company can be used if the employer wants to take additional care of the health of employees. It is represented by a wider selection of medical services compared to OCM. If VHI is applied, then the accountant will need to know how it is reflected in accounting and tax accounting.
Unlike compulsory health insurance, the availability of voluntary health insurance in an organization will depend solely on the employer’s desire to insure its employees. Such insurance will allow employees to receive additional medical services in addition to those provided for by the compulsory medical insurance program. Under a VHI policy, the insured person receives such medical services as are provided for by the health insurance program, as well as for which an insurance premium has been paid.
Important! If an employer decides to provide its employees with voluntary insurance policies, then it should organize accounting of insurance costs. This must be done correctly, otherwise tax risks cannot be avoided.
Changing the list of insured persons during the term of the contract
The described technique does not cause difficulties for the user until the list of insured persons specified in the contract begins to change.
During the year, some of the insured employees may quit, and newly hired employees may be included in the list of insured persons by concluding an additional agreement to the insurance contract. If the total number of insured persons does not change, the term of the contract remains the same (more than a year), and other essential terms of the contract do not change, then insurance premiums under such contracts are accepted as a reduction in the tax base for income tax (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated August 27. 2007 No. 03-03-06/4/118). The Tax Code establishes a limitation only for the general period for which the contract is concluded, and not for the period of insurance of a specific employee (Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Ural District dated December 15, 2009 No. F09-9912/09-S3).
If the number of insured persons increases due to newly hired employees, as indicated in the additional agreement to the VHI agreement, then the insurance premium can also be taken into account for taxation (clause 2 of Article 942 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 16, 2010 No. 03 -03-06/1/731).
But if an employee quits and the employer continues to pay for insurance for him without terminating the contract with the insurer, then the part of the insurance premium that falls on dismissed employees must be excluded from the expenses taken into account for tax purposes (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated May 5, 2014 No. 03- 03-06/1/20922).
Let’s change the conditions of Example 1 and see how insurance premiums for VHI can be taken into account, including those paid for dismissed employees.
Example 2
On the last day of February 2015, 5 insured persons specified in the VHI agreement quit their jobs, while Andromeda LLC continues to pay for health insurance for them. The annual cost of the insurance premium paid in respect of each employee is 12,000 rubles. Labor costs for calculating the standard specified in Example 1 do not change.
The number of calendar days in January and February 2015 is 59 (31 days + 28 days). Accordingly, the number of calendar days remaining under the voluntary health insurance contract attributable to dismissed employees is 306 (365 days - 59 days).
Let's calculate the share of the bonus attributable to dismissed employees, which is excluded from expenses:
(RUB 12,000 x 5 people) / 365 days x 306 days = RUB 50,301.37
Let's create an Operation document (section Operations -> Operations entered manually) and date it to the beginning of March. In the document form, to create a new transaction, you must click the Add button and enter correspondence for the debit of account 91.02 and the credit of account 76.01.9 for the amount excluded from further calculations for future expenses (Fig. 5). For tax accounting purposes for income tax, you need to enter the amounts into special resources of the accounting register:
Amount PR Dt 91.02 - for the constant difference in the cost estimate; The amount of NU Kt 76.01.9 is the amount of the insurance premium for dismissed employees.
Rice. 5. Exclusion of VHI expenses for dismissed employees
Starting from March 2015, when performing the regulatory operation Write-off of deferred expenses, the amount of the balance of the insurance premium adjusted downwards according to accounting and tax accounting data, which could potentially be recognized as expenses, will already be used. Further stages of calculating VHI expenses will not differ in any way from the stages described in Example 1. In December 2015, the lump sum of the insurance premium paid is completely debited from account 76.01.9. Taking into account the adjustments made, the amount of the insurance premium that could potentially be included in expenses is RUB 429,698.63. (480,000.00 rubles - 50,301.37 rubles), and the maximum amount of expenses for voluntary health insurance for 2015 is still determined as 436,080.00 rubles.
Obviously, the expenses include the amount of 429,698.63 rubles. as the minimum of two amounts. Figure 6 shows the Certificate of Cost Rationing for December 2015. The indirect expenses reflected in line 040 of Appendix No. 2 to Sheet 02 of the income tax return include the amount of expenses for voluntary health insurance equal to 429,698.63 rubles. In terms of VHI expenses at the end of the year, there are no differences between accounting and tax accounting data.
Rice. 6. Certificate-calculation of rationing costs for VHI for January 2015
In conclusion, we note that a one-time payment of an insurance premium is not always convenient. A more rational option is when the contract provides for payment of the insurance premium in installments, for example, quarterly. At the same time, the amount of the quarterly payment may be adjusted taking into account newly arrived and dismissed employees, an updated list of which is indicated in the additional agreements to the contract. Accounting for VHI expenses in the program will not change with this option: the payment amount will be written off during the quarter through the deferred expenses mechanism, and the standard in any case is calculated on an accrual basis for the year.
IS 1C:ITS
For more information on accounting for the costs of voluntary health insurance for employees, see the reference book “Accounting for corporate income tax” in the “Accounting and tax accounting” section.
Required by law.
Taxpayers using the simplified tax system, when determining the object of taxation, reduce the income received for expenses, including wages, payment of benefits for temporary disability under the legislation of the Russian Federation (clause 6, clause 1, article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In this case, the composition of labor costs is determined in accordance with Art. 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (clause 2 of the said article).
In particular, paragraph 16 of Art. 255, labor costs include, among other things, the amounts of payments (contributions) of employers under voluntary insurance agreements (non-state pension agreements) concluded in favor of employees with insurance organizations (non-state pension funds) that have licenses issued in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation to operate relevant types of activities in the Russian Federation (that is, the cost of voluntary health insurance for employees).
Note:
Voluntary personal insurance is carried out in the form of an agreement concluded between an organization (the policyholder) and an insurance organization that has the appropriate license (the insurer), in writing (Part 1 of Article 927, Part 1 of Article 940 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
The insurance contract may provide for payment of the insurance premium in installments (in parts). This follows from Parts 1, 3 of Art. 954 Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
An insurance contract (including a voluntary health insurance contract under a special insurance policy), unless otherwise provided in it, comes into force at the time of payment of the insurance premium or its first installment (Part 1 of Article 957 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
In other words, “simplified” employers have the right to include contributions under voluntary health insurance contracts for their employees as part of tax expenses for wages. But at the same time they must comply with the same restrictions as income tax payers. This is confirmed by officials of the Ministry of Finance (see Letter dated February 10, 2017 No. 03-11-06/2/7568).
Article 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation defines three restrictions.
Firstly, the indicated amounts relate to labor costs under the simplified tax system, if contracts for voluntary personal insurance of employees, providing for payment by insurers of medical expenses of insured employees, are concluded for a period of at least one year.
Secondly, contributions under such agreements are included in expenses in an amount not exceeding 6% of the amount of labor costs.
Thirdly, the insurance organization must have a valid license.
We emphasize: labor costs to establish the limit are calculated on an accrual basis, starting from the date of actual transfer of the first contribution within a given tax period. The calculation of the maximum value in the last tax period is made before the expiration date of the VHI agreement. Such recommendations for calculating the maximum value (standard) of VHI expenses recognized for tax purposes are given in Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated September 16, 2016 No. 03-03-06/1/54205.
Amounts of payments under contracts of voluntary medical insurance for employees, concluded for a period of at least one year, with an insurance company licensed to conduct the corresponding type of activity, are taken into account as expenses when determining the object of taxation with “simplified” tax, subject to the maximum amount of payments - 6% the amount of labor costs under the simplified tax system.
Voluntary health insurance agreement
The parties to the VHI agreement are the employer and the insurance company. The employer is obliged under the contract to pay insurance premiums, and the insurance company is to provide employees with medical services in the volumes stipulated by the contract. For this purpose, the insurance company, in turn, enters into contracts with medical organizations, which ultimately provide services to employees. When concluding a VHI agreement, it is important to pay attention to its validity period, as well as the moment when the agreement comes into effect.
"Simplified" features.
Organizations using the simplified tax system recognize expenses for tax purposes after they are actually paid (clause 2 of article 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Any features of accounting for the costs of voluntary health insurance for employees Ch. 26.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation has not been established. In this regard, questions arise about the procedure for accounting insurance premiums in the tax base for the “simplified” tax.
Both under the general taxation regime and under the simplified taxation system, only paid contributions for voluntary health insurance are taken into account in expenses.
But is it necessary to distribute the paid amount evenly across reporting (tax) periods (that is, in proportion to the number of calendar days in this period - clause 6 of Article 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation)? After all, as a rule, the insurance premium for the entire term of the contract is transferred in one or two payments.
On the one hand, the amounts of such payments must be distributed over the entire term of the contract. Indeed, by virtue of paragraph 2 of Art. 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, payment for services is recognized as the termination of the organization’s counter-obligation to the contractor directly related to their provision. Therefore, the actual transfer of the amount of the insurance premium under the VHI agreement (or part thereof) cannot be the basis for recognizing an expense on the date of its payment, since at that moment the insurer has not yet fulfilled its obligations to provide services.
On the other hand, the costs of voluntary health insurance relate to labor costs under the simplified tax system, which are taken into account in the manner established for profit tax purposes, Art. 255 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. And wages are recognized as expenses at the time of repayment of debt to employees, that is, on the date when funds are debited from the current account or paid from the cash register. This follows from paragraphs. 1 item 2 art. 346.17 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. This means that the amount of the insurance premium must be recognized as taxable expenses in the period in which it was paid. There is no need to distribute these costs over the term of the VHI agreement.
According to the author, in this case, the second option for rationing expenses for the purposes of calculating the “simplified” tax is preferable, since it takes into account the specifics of the costs incurred. In this case, to determine the standard, the amounts actually paid to personnel are taken into account.
Example:
A company using the simplified tax system entered into a voluntary health insurance agreement for the period from 11/15/2017 to 07/31/2019. The terms of the VHI agreement provide for payment of the insurance premium in three payments:
- first – December 25, 2017 – in the amount of 500,000 rubles;
- second – 07/31/2018 – in the amount of 250,000 rubles;
- third – 01/31/2019 – in the amount of 250,000 rubles.
At the same time, 6% of the payroll amounted to:
- for the period from November 15, 2017 to December 31, 2017 – RUB 53,800;
- for the period from 01/01/2018 to 07/31/2018 – 251,066 rubles;
- for the period from 01.08.2018 to 31.01.2019 – 226,955 rubles.
- for January 2021 – 37,825 rubles;
- for the period from 02/01/2019 to 07/31/2019 – RUB 281,040.
For the entire period of validity of the contract, 6% of the payroll amounted to 850,686 rubles. (53,800 + 251,066 + 264,780 + 281,040), and the total amount of the insurance premium is 1,000,000 rubles. (500,000 + 250,000 + 250,000).
Therefore, a company can include in the tax base under the simplified tax system the costs of voluntary health insurance only in the amount of 850,686 rubles:
- in 2021 – 53,800 rubles;
- in 2021 – 478,021 rubles. (RUB 251,066 included in expenses for nine months, RUB 226,955 for the year);
- in 2021 – RUB 318,865. (37,825 rubles were included in expenses based on the results of the first quarter, 281,040 rubles – based on the results of nine months).
Personal income tax and insurance premiums.
Personal income tax.
Formally, in the situation under consideration, employees receive income from the employer company in the form of insurance premiums paid for them under a VHI agreement.
However, due to the direct indication in paragraph 3 of Art. 213 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, when determining the taxable base for personal income tax, the amounts of insurance contributions are taken into account if they are paid for individuals from the funds of employers or from the funds of organizations or entrepreneurs who are not employers in relation to individuals for whom they make insurance contributions, except for cases when insurance of individuals is carried out under compulsory insurance contracts, voluntary personal insurance or voluntary pension insurance.
It follows from this that income received by employees in the form of paid insurance premiums under a VHI agreement does not need to be taken into account when determining the taxable base for personal income tax.
Note:
[email protected] dated 08/01/2016 explained that the calculation according to Form 6-NDFL does not reflect income that is not subject to personal income tax, listed in Art. 217 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. At the same time, about the income listed in other articles of Chapter. 23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, in particular in paragraph 3 of Art. 213, they didn't mention it. The tax agent must decide independently whether to include data on VHI expenses in the calculation on Form 6-NDFL. At the same time, the reflection or, on the contrary, non-reflection of this information in the specified calculation will not in any way affect the tax base and the amount of tax.
If a VHI agreement is concluded between an insurance company and an employer company in favor of employees, but insurance premiums are deducted from their salaries, the taxpayer (employees) has the right to exercise their right to receive a social tax deduction provided for in paragraphs. 3 p. 1 art. 219 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. In this case, a deduction for the amount of payment for the cost of medical services and (or) payment of insurance premiums is provided to the taxpayer if (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 11, 2018 No. 03-04-05/89998):
- medical services are provided in medical organizations (individual entrepreneurs) that have appropriate licenses to carry out medical activities, issued in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation;
- as well as when the taxpayer submits documents confirming his actual expenses for medical services provided, the purchase of medicines for medical use or the payment of insurance premiums.
Such documents, in particular, include payment documents (payment orders) confirming the employer’s payment of contributions to the insurance company, a copy of the voluntary health insurance agreement, a certificate issued by the employer indicating the amount of contributions transferred to the insurance company, which were withheld from the taxpayer’s salary during tax period.
Insurance premiums.
The insurance premium under voluntary health insurance contracts for employees concluded for a period of at least a year is not subject to insurance contributions to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, to the Social Insurance Fund (including contributions for injuries) and to the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund (clause 5, clause 1, article 422 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 5 Clause 1, Article 20.2 of the Federal Law of July 24, 1998 No. 125-FZ).
Thus, the insurance premium for the period when employees were in an employment relationship with the organization is not included in the base for calculating insurance premiums.
What do we write in the contract?
Let's start with the employment contract. It is clear that this condition must be enshrined in employment contracts with employees, but this can be done in different ways.
So, this may be a direct indication in the contract that the employer is obliged to insure the employee under the VHI program. Or there may be a link to a local regulatory act - Regulations on Social Guarantees, Internal Labor Regulations, etc., which contains a similar condition. Moreover, if the first option is chosen, then all the “particulars” (such as: from what moment insurance is provided, whether it is valid upon dismissal, transfer, transfer to another position, the scope of this insurance) must be recorded either also in the contract, or by reference to the corresponding local act.
You also need to clearly ensure that the list of insured persons coincides with the list of employees of the organization. After all, the expenses taken into account when taxing profits can only include those amounts that are paid under insurance contracts for persons who have a valid employment contract with the organization. Of course, paying for insurance for family members of employees or for persons with whom the organization has civil contracts is possible. But such expenses will not reduce the tax base for profits.
Accounting of costs in the form of the amount of insurance premium.
The insurance premium under a voluntary health insurance contract concluded in favor of employees in accordance with the terms of employment contracts is recognized as part of expenses for ordinary activities (clauses 5, 16, 18 of PBU 10/99 “Organization expenses”).
The procedure for recognizing such expenses is not regulated by law. Therefore, the organization must develop it independently, based on the assumptions and requirements given in clauses 5 and 6 of PBU 1/2008 “Accounting Policy of the Organization”, and consolidate it in the accounting policy for accounting purposes. The procedure is developed, in particular, based on IFRS and recommendations in the field of accounting. In this case, IFRS takes priority (clause 7.1 of PBU 1/2008).
IAS 19 Employee Benefits is used to account for employee benefits.
Based on clauses 5, 9 of IFRS (IAS) 19, expenses under voluntary health insurance contracts for existing employees are related to their short-term remuneration (as non-monetary benefits). In the situation under consideration, the company, according to clause 11 of IAS 19, has an asset in the form of a prepaid expense. This approach is reflected in the Interpretation “Participation of an organization in insurance contracts as an insured”.
With this approach, the paid premium is taken into account as an advance payment as part of accounts receivable (clause 3, 16 of PBU 10/99). It is recognized as an expense as insurance services are consumed, that is, as the insurance period expires.
In other words, the insurance premium under a VHI agreement concluded in favor of employees is recognized as an expense for ordinary activities as insurance services are provided (regardless of the time of their actual payment), that is, monthly on the last day of the corresponding month in an amount calculated based on the number of days the contract is valid in each current month. This follows from clauses 5, 16, 18 of PBU 10/99.
In the example above, the VHI agreement was concluded for a period from November 15, 2017 to July 31, 2019, that is, for 624 days. Therefore, for example, in December 2021 the company recognizes RUB 49,679.49 as other expenses. (RUB 1,000,000 / 624 days x 31 days).
In this case, it is more appropriate to reflect settlements under VHI agreements in accounting using account 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors”, subaccount 1 “Settlements for property and personal insurance”.
Recognizing VHI expenses as deferred expenses reflected in account 97 with the same name is not entirely correct. The fact is that this type of asset, such as deferred expenses, is currently mentioned only:
- in clause 16 of PBU 2/2008 “Accounting for construction contracts” - in relation to costs incurred in connection with upcoming construction work (for example, the cost of materials transferred to the construction site);
- in paragraph 39 of PBU 14/2007 “Accounting for intangible assets” - in relation to the cost of licensed software.
At the same time, the use of account 97 to reflect the amount of the insurance premium will not be considered a gross error, since no current PBU specifies a specific procedure for reflecting costs of a certain type in accounting. Therefore, if a company has expenses that relate to the following reporting periods, it has the right to take them into account using account 76-1 or 97.
“On compulsory social insurance against accidents at work and occupational diseases.”
Put into effect on the territory of the Russian Federation by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 28, 2015 No. 217n.
Adopted by the BMC Committee on Interpretations on May 27, 2011, approved. in the final version on June 30, 2011.
Recognition of VHI in tax accounting
In accordance with paragraphs. 16th century 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, these amounts are included in labor costs, but subject to the following conditions:
- The medical organization must have a license.
- The contract must be valid for at least a year.
- You can reduce the income tax on the insurance premium, but if it is no more than 6% of the payroll volume (without VHI). The amount exceeding this limit is not accepted for reduction.
It should be taken into account that in accordance with paragraph 3 of Art. 318 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, if the insurance period covers two calendar years, then the payroll to determine the maximum amount by which income tax can be reduced is calculated incrementally:
- from the date of commencement of the contract until the end of the first year of its validity;
- from the beginning of next year until the end of the contract.
This procedure is confirmed by the Ministry of Finance in letter dated September 16, 2016 No. 03-03-06/1/54205.
Also clause 6 of Art. 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation establishes the following methods for recognizing contributions as expenses:
- with a one-time payment evenly throughout the entire term of the contract;
- if the payment was made in parts, such payment is recognized for each paid part evenly from the date of payment of each part until the end of the agreement with the medical institution.
In the profit declaration, such expenses are reflected in Appendix No. 1: code 812 is entered in column 3, and in column 4 - the amount of insurance costs, which is taken into account in the tax reduction (Section XVII of the Procedure for filling out the declaration).
There are no reflection features or restrictions in accounting. Insurance premiums are taken into account monthly evenly throughout the insurance period.
VHI, accounting by postings:
| D 76 (97) - K 51 | Contributions transferred |
| D 20 (23, 25, 26, 44) - K 76 (97) | Part of the cost of employee insurance for the month is taken into account. The accounts on which the accrual of wages of insured workers are reflected are debited. |
| D 90, 91.2 - K 20 (23, 25, 26, 44) | Referred to the financial result of the insurance amount |
It is also possible to reflect a permanent difference in accounting by posting Dt 99 Kt 68:
- if the company’s contributions for voluntary insurance exceeded 6% of the payroll;
- if the conditions for recognizing them as expenses are not met.
“Simplers” can include VHI expenses in the tax base
Companies and entrepreneurs using the simplified tax system that calculate tax on income minus expenses have the right to include in the tax base the costs of additional medical insurance (VHI) for their employees, but subject to a number of conditions and restrictions. The Ministry of Finance of Russia spoke about this in more detail in a letter dated February 10, 2017 No. 03-11-06/2/7568.
When calculating the “simplified” tax, special regime officers reduce the income received by expenses incurred, including wages and temporary disability benefits.
The composition of labor costs for taxpayers using the simplified tax system is the same as for taxpayers using the OSNO. It includes payments under voluntary health insurance contracts that the employer has concluded in favor of its employees.
In this case, expenses for voluntary health insurance are included in the tax base subject to two important conditions:
- the voluntary health insurance contract is concluded for a year or more;
- the insurance company has the appropriate license.
Please note that the “simplified” will not be able to take into account the entire amount of expenses for voluntary health insurance, but only 6% of labor costs.
Types of insurance
Let us immediately make a reservation that tax rules, especially in terms of income tax, strongly depend on the type of insurance that the employer decided to include in the “social package”.
So, there may be insurance in case of disability or death. In addition, the legislation provides for the possibility of insurance in case of temporary disability. However, these insurance options are rather exotic, which most accountants do not have to deal with. Most often, the social package includes voluntary health insurance policies, which give employees the opportunity to receive medical care in medical institutions accredited by the insurance company (clinics, hospitals, emergency rooms, sanatoriums, etc.). We will focus on this type of insurance.