- Property tax rates for individuals in Moscow in 2015 - 2019
- Property tax rates for individuals in Moscow in 2014
- How to calculate tax
- Benefits for property tax for individuals in Moscow
- Why has the property tax on individuals increased in Moscow and the region?
- Procedure for collecting arrears of taxes (penalties, fines)
- Useful links on the topic
Procedure and deadlines for paying property taxes in Moscow
In accordance with the new procedure, effective from 2021, in Moscow and the Moscow region, property tax is calculated on the basis of cadastral value. This tax payment procedure applies to the following property:
- House;
- living space (apartment, room);
- garage, parking place;
- single real estate complex;
- unfinished construction project;
- other building, structure, structure, premises.
Please note that residential buildings located on land plots provided for personal subsidiary farming, dacha farming, vegetable gardening, horticulture, and individual housing construction are classified as residential buildings.
Property included in the common property of an apartment building is not subject to taxation.
The tax is paid at the location of the object of taxation on the basis of a tax notice sent to the taxpayer by the tax authority. In this case, sending a tax notice is allowed no more than 3 tax periods preceding the calendar year of its sending.
Deadline for payment of real estate tax in Moscow
The tax must be paid no later than December 1 of the year following the expired tax period. That is, property taxes for 2021 must be paid by December 1, 2022, for 2022 by December 1, 2023, and for 2023 by December 1, 2024.
The deadline for paying real estate tax in Moscow in 2021 is December 1, 2021.
If the established payment deadline is violated, the tax authority will impose penalties.
Is it possible to reduce the cadastral value
The cadastral value is calculated by independent appraisers based on orders from city/regional authorities. All data on the assessment of objects is entered into a unified real estate cadastre. There is a legal opportunity to challenge the size in court or through a special commission. Therefore, if there are compelling reasons for a revision, then it is advisable to contact a qualified lawyer who will recommend an independent assessment and draw up a competent statement of claim to the court (see also how to challenge the cadastral value of a land plot).
Example: the cadastral value of home ownership was 12,000,000 rubles. The owner considered this amount to be clearly high, since the house was not completed and there were no funds to complete the construction, the toilet was located on the street, the water supply was a well, and the sewage system was a septic tank. From the central networks there is only electricity. Independent accredited appraisers were invited, who indicated in the assessment conclusions the cadastral value of the house in the amount of 3,500,000 rubles. You can go to court with the results obtained.
Property tax rates in Moscow
Property tax rates for individuals in Moscow are set differentially depending on the value of the object of taxation and are in relation to residential buildings, residential premises, single real estate complexes, which include at least one residential premises (residential building), as well as in relation to economic buildings or structures, the area of each of which does not exceed 50 square meters and which are located on land plots provided for personal subsidiary farming, dacha farming, vegetable gardening, horticulture or individual housing construction, in the following amounts: Real estate tax
rates in Moscow (apartments , houses, rooms)
Cadastral value of the taxable object
| Tax rate for 2016-2020, 2021 | |
| Up to 10 million rubles (inclusive) | 0.1 percent |
| Over 10 million rubles up to 20 million rubles (inclusive) | 0.15 percent |
| Over 20 million rubles up to 50 million rubles (inclusive) | 0.2 percent |
| Over 50 million rubles up to 300 million rubles (inclusive) | 0.3 percent |
In relation to other real estate objects, tax rates as a percentage of the cadastral value of taxable objects are established in Moscow in the following amounts (based on the cadastral value of the taxable object): Real
estate tax rates in Moscow (other property)
| Order number | Object of taxation | Tax rate ((in % of cadastral value) | |||
| for 2015-2016 | for 2021 | for 2018-2019 | for 2020-2021 | ||
| 1. | Objects of unfinished construction if the designed purpose of such objects is a residential building | 0,3 | 0,3 | 0,3 | 0,3 |
| 2. | Garages and parking spaces | 0,1 | 0,1 | 0,1 | 0,1 |
| 2 | Objects of taxation included in the list determined in accordance with paragraph 7 of Article 378.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, in relation to objects of taxation provided for in paragraph 2 of paragraph 10 of Article 378.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation | 1.2 (2015) 1.3 (2016) | 1,4 | 1,5 | 1,5 |
| 3 | Objects of taxation, the cadastral value of each of which exceeds 300 million rubles. | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| 4 | Other objects of taxation | 0,5 | 0,5 | 0,5 | 0,5 |
Tax rates are the same as in most cities in the Moscow region.
Question answer
Question: How can I find out the tax debt for an apartment at an address?
Tax arrears can be obtained from the tax office. Either submit a written request to the territorial inspectorate at your place of residence to reconcile settlements with the inspectorate, or obtain information about the status of settlements with the budget through the “Taxpayer’s Personal Account” on the Federal Tax Service website.
Question: What to do if there is no money to pay?
This does not exempt you from responsibility. But the taxpayer, upon application, can receive a deferment (installment plan) for paying tax for no more than 1 year. The reason is a difficult financial situation that does not allow you to fulfill your tax obligation. The application is submitted to the tax service, accompanied by a certificate about the status of his calculations for taxes, fees, penalties and fines and an obligation to comply with the conditions under which the decision to grant a deferment or installment plan is made. The installment plan involves accruing interest at ½ the key bank rate.
Question: If I think the tax is too high, can it be reduced and how?
You can independently recalculate the tax amount and if there was an error in the calculation (the rate, the amount of the cadastral value was indicated incorrectly, a tax benefit was not taken into account, an existing overpayment, etc.), then submit an application for recalculation of the tax, including in electronic form through the taxpayer’s Personal Account or Here.
Question: What to do if there is no cadastral value for the apartment in Rosreestr?
For 2021, accrual based on inventory value is possible. From 2021, accrual is only based on cadastral records. If there is none, then the tax authority must make a calculation based on the market value. The result of determining the applied market value can be challenged.
Question: Do I need to pay tax for a municipal apartment?
No, the employee and his family members make payments under a social tenancy agreement, which provides for all possible costs, including taxes. The employer is not involved in tax issues.
Question: Can a neighbor's tax be lower for an equal area?
Yes, and this is legal, since there are many factors that influence the amount of tax, including tax breaks, overpayments for previous periods, reduction of cadastral value, etc.
Links to legislative acts
- Article 401 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Object of taxation
- Article 403 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The procedure for determining the tax base based on the cadastral value of taxable objects
- Article 405 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Taxable period
- Article 406 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Tax rates
- Article 407 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Tax benefits
- Article 409 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Procedure and deadlines for tax payment
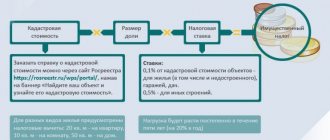
Tax calculation procedure
The tax amount is calculated from the cadastral value established as of January 1 of the current tax period in proportion to the period of ownership.
When calculating tax based on cadastral value, tax deductions are provided (reduction of cadastral value) by the amount of cadastral value:
- 10 sq.m. regarding the room,
- 20 sq.m. regarding the apartment,
- 50 sq. m. in relation to a residential building.
- 1 million rubles - in relation to a single real estate complex with a residential building.
If, when applying tax deductions, the tax base takes a negative value, for the purpose of calculating tax, such a tax base is taken equal to zero.
Correction factors
Due to the fact that the amount of tax calculated from the cadastral value is, as a rule, significantly higher than that calculated from the inventory value, correction factors have been established that are used when calculating the amount of tax:
- 0.2 – when calculating tax for 2015;
- 0.4 - when calculating tax for 2021;
- 0.6 - when calculating tax for 2021;
- 0.8 - when calculating tax for 2021.
Starting from 2021, the correction factor does not apply.
In this case, the tax amount is calculated using the formula:
H = (H1 - H2) x K + H2, where
- N - the amount of tax to be paid;
- N1 - the amount of tax calculated from the cadastral value without taking into account the correction factor;
- N2 - the amount of tax calculated on the basis of the corresponding inventory value of the taxable object;
- K – correction factor.
Calculation example
Let's calculate the tax amount for an apartment with a total area of 70 square meters. m., located in Moscow near the Prospekt Mira metro station with a cadastral value of 6 million rubles. The tax amount for 2014, calculated based on the inventory value, is 950 rubles.
For reference. You can find out the cadastral value of an apartment (residential building) on the Rosreestr website (https://rosreestr.ru/wps/portal/online_request), and then independently calculate the amount of property tax using a calculator.
1. So, the tax deduction is 20 sq.m., that is, the tax base is equal to:
6,000,000 / 70 sq.m. * 20 sq.m. = 1,714,285.71 rubles.
2. The tax rate for this apartment is 0.1%.
(6,000,000 - 1,714,285.71) * 0.1% = 4,285.71 rubles.
3. We apply the tax calculation formula taking into account the correction factor:
H = (H1 - H2) x K + H2
Amount of tax payable for 2015 = (4,285.71-950)*0.2+950 = 1,617.14 rubles.
Amount of tax payable for 2021 = (4,285.71 -950)*0.4+950 = 2,284.28 rubles.
Amount of tax payable for 2021 = (4,285.71 -950)*0.6+950 = 2,951.42 rubles.
Amount of tax payable for 2021 = (4,285.71 -950)*0.8+950 = 3,618.56 rubles.
Amount of tax payable for 2021, 2021 and subsequent years = 4,285.71 rubles.
How is the deduction applied for shared ownership of an apartment?
Each owner pays tax in proportion to his share of ownership. However, the deduction is not provided to each owner-shareholder, but for the entire property as a whole. Therefore, such shareholders may have a question about how much apartment tax to pay each.
Question: An apartment with a total area of 50 sq.m. is in shared ownership of two owners of 1/2 each, how will the deduction be distributed?
Answer: One owner will need to deduct only 10 sq.m. (20 m2/2) as a tax deduction. Thus, he will pay for 25 – 10 = 15 sq. m. A similar calculation will be for the second owner. The cadastral value of housing is 2 million rubles, the area is 44 m2, everyone will have to pay (44 m2/2 - 10 m2) per 12 m2. And 1 m2 costs 45,455 rubles (2 million/44), then the tax will be (12 m2 * 45,455 rubles) * 0.1% = 545 rubles. This is the maximum amount, i.e. in those years when the reduction factor is in effect, the tax will be even less.
If there are three or more owners, then the deduction will be divided among the appropriate number of persons, in proportion to the size of their shares.
Property tax benefits in Moscow
Benefits for paying property tax are available to categories of citizens listed in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (federal benefits). These include:
- Heroes of the Soviet Union and Heroes of the Russian Federation;
- disabled people of disability groups I and II;
- participants of the Great Patriotic War;
- combat veterans;
- Chernobyl victims;
- old age pensioners and others.
For a complete list of property tax beneficiaries, see the article at the link.
New. If the previous legislation provided for a complete exemption from paying tax on all types of objects for a preferential category of persons, then from 2021 the benefit is provided at the choice of the taxpayer for one object of one type: 1) apartment, room; 2) residential building; 3) specially equipped creative workshops, ateliers, studios; 4) garage or parking space, etc.
For example, if a pensioner owns an apartment, a room, a residential building and a garage, then he has the right to a benefit: one object of his choice - an apartment or a room (since the specified housing is included in one type of object), a residential building and a garage.
Tax payments for legal entities
Changes in taxation began in 2014 and primarily affected individuals. Later it is planned that legal entities will also join the new system that takes into account the cadastral value of property. At the moment, this innovation is already being actively introduced to the masses. The transition to a new system of real estate taxation for legal entities will be completed only when the entire real estate fund switches to calculations based on cadastral valuation. The new tax base cannot be fully formed until the cadastral value of each real estate property has been assessed. This means that the transition will be carried out gradually. Those legal entities that are aware of the cadastral valuation of their property can begin paying taxes under the new scheme.
The new property tax for organizations will come into force only after a full cadastral assessment of each property. Today, organizations pay real estate tax based on its book value. The new taxation system will automatically replace it with the cadastral system. This is the main difference between the improved system. The book value of an object most often differs from the cadastral value (as well as the market value), therefore the amount of taxes will vary. This will be most noticeable for new buildings, and the tax value in old buildings is not subject to major changes.
The new bill has one more nuance . Persons who work under UTII and under the simplified tax system will also have to calculate property tax based on its cadastral value. This amendment applies to public catering facilities, buildings of business and shopping centers, as well as exhibition and concert halls.
After the introduction of the new system, the organization is not required to inform the tax service about a change in its bank details. Now this will become the direct responsibility of those banking institutions that serve this company.
Which is more profitable?
It is quite easy to get confused with a large number of bets, especially if you have just started studying this issue. In reality, everything needs to be assessed not only from the standpoint of generating income from commercial real estate, but as a whole. In particular:
- In most cases, it is obviously more profitable for a legal entity to be on the simplified tax system rather than on the OSNO. However, sometimes a general taxation system is a more preferable option - for large companies, for example, that need to demonstrate a large volume of financial statements. True, in this case, receiving income from commercial real estate becomes just one of the sources of profit, and more often than not, not the main one.
- It is most beneficial for an individual to register as self-employed. This can be done in literally a couple of tens of minutes through a special mobile application. It won’t be difficult to set up automatic tax deductions. But this regime is not widespread throughout the Russian Federation. Therefore, it is worth finding out if you have such an opportunity.
- When choosing between 6% of profit on the simplified tax system and 15% of turnover, think about whether you can confirm regular expenses in sufficient volume, which would be associated with such real estate. Choosing 15% makes sense if you often make repairs, constantly spend money on the services of a cleaning company, etc. But in most cases it is better to stop at 6%.
Who is obliged to pay and who is not?
Property tax for individuals is levied on holders of ownership rights to property recognized as an object of taxation. Even minors are not exempt from the mandatory payment if they own this or that real estate. Payments for those under 18 years of age are made by guardians or parents until they reach adulthood.
The following are exempt from tax:
- pensioners or persons receiving a pension;
- payers discharged from military service or serving under conscription for military training in other countries where military operations took place;
- payers who are parents or spouses of military personnel who died while performing military duties;
- arts payers who use their premises as a museum, library or other public space;
- payers who own a building, outbuilding, commercial building, the area of which does not exceed 50 sq.m.
What taxes must be paid on income from commercial real estate?
Please note that you will have to pay commercial property taxes regardless of whether you use it or not. That is why, when purchasing such property, you need to carefully calculate future income generation patterns. Otherwise, you will receive additional losses.
But when you start making profit from such an object, you will have to pay tax on it as well. And here everything depends on the capacity in which the owner acts.
Individuals may pay taxes on commercial real estate at the following rates:
- 13% is if we are talking about personal income tax. That is, in this case, the owner simply acts as an individual who receives income from the disposal of his property. It will be enough for him to indicate the source of such income in the annual declaration and that’s it;
- 6% on income or 15% on turnover if an individual registers as an individual entrepreneur. In this case, the rate is reduced. But you need to take into account that the individual entrepreneur will still have to pay mandatory annual contributions for himself;
- 4% when receiving income from individuals and 6% when receiving income from legal entities, if the individual registers with the tax office as a self-employed person. This is the most profitable betting option for today. No additional fees are required.
For legal entities the picture will be different. It directly depends on which taxation system the organization chooses:
- 6% from income received or 15% from turnover if the company is on the simplified tax system;
- 20% - on income if the company has chosen the general taxation regime (OSNO).
Individual entrepreneurs also have the opportunity to purchase a patent. In this case, it will be enough for them to pay a fixed amount (depending on the region).
Property tax calculator
On the page of the official Internet resource of the Federal Tax Service there is a special calculator intended for calculating property tax. In order for the user to receive ready-made final amounts of tax payments, he will need to fill out the fields of the calculator one by one:
- enter the cadastral number of your real estate (you can find out this number from the cadastral passport or on the Rosreestr website);
- fill in the property characteristics requested by the system (the area of the property, its cadastral price, the category of the property - apartment, room, and so on);
- calculate the period of ownership of the relevant real estate (in order to pay the tax payment in 2021, the owner of the property will have to calculate how many months in 2015 he owned the property);
- enter a tax deduction (it can be viewed there, on the Federal Tax Service website);
- enter the amount of tax benefits provided, the list of which can also be found on the Internet resource of the Russian Federal Tax Service.
Ultimately, the tax calculator will produce all the required calculations for your 2015 property tax due.
Main legislative innovations
In Chapter 32 of the Russian Tax Code, which regulates the application of tax on real estate for citizen-owners, fundamentally new legislative rules have appeared:
- The base for property tax is established by the cadastral value of houses, apartments, dachas and other real estate. Previously, tax calculations were made on the basis of an inventory assessment carried out by BTI employees.
- For the complete transition of the Russian taxation system to the new calculation scheme, the legislator has established an intermediate transition period - from 2015 to 2021. During this five-year period, all Russian regions must switch to calculating the amount of property tax based on cadastral valuation.
- In some situations, the authorities of Russian municipalities have the right to independently determine the tax base, interest rates, and payment terms.
- New terms have appeared regarding the classification of real estate - parking space and a single real estate complex. The named immovable properties are subject to property tax at standard rates.