Every citizen of the Russian Federation is a taxpayer. The state replenishes the budget by deducting interest from wages. Regardless of the field of activity, citizens make mandatory payments. The amount of funds that goes to the state treasury is provided for by the current legislation of the Russian Federation.
The key place in the field of taxation is occupied by the personal income tax. In our publication today, we propose to find out what this tax is, what tax rates exist for personal income tax, what is subject to taxation and what is not, we will figure out how to calculate personal income tax in 2021, we will give examples of calculation.
My contract states that the salary includes personal income tax - this means what amount
You will be paid your salary minus personal income tax. But, in accordance with paragraph 1 of Art. 24 of the Tax Code, tax agents are persons who, in accordance with the law, are entrusted with the responsibility for calculating, withholding and remitting taxes. In particular, these are Russian organizations, individual entrepreneurs, notaries engaged in private practice, lawyers who have established law offices, as well as separate divisions of foreign organizations in the Russian Federation from which (or as a result of relations with which) the individual received income. From this point, by virtue of clause 2 of Art. 226 of the Code, the tax agent is obliged to calculate, withhold and pay the appropriate amount of personal income tax. The exception is income for which the calculation and payment of tax are carried out in accordance with Art. Art. 214.3, 214.4, 214.5, 214.6, 226.1, 227 and 228 of this Code.
Meanwhile, it is not entirely correct to indicate wages taking into account personal income tax, since it is not possible to determine in advance the specific amount of personal income tax that will be withheld and transferred to the budget from the employee’s salary. Therefore, there is no need to fix it in the employment contract. Moreover, in accordance with Part 1 of Art. 136 of the Labor Code, when paying wages, the employer is still obliged to notify each employee in writing about the components of the wages due to him for the relevant period, about the size and grounds of deductions made, as well as about the total amount of money to be paid.
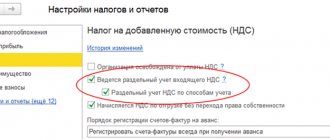
Personal income tax registers and movements on them when paying income categories: Wages and Other income
In ZUP 3, the following accumulation registers are responsible for accounting for personal income tax:
- Income accounting for calculating personal income tax - income is recorded.
- Calculations of taxpayers with the budget for personal income tax - the calculated (by type of movement Income ) and withheld personal income tax (by type of movement Expense ) is registered.
- Calculations of tax agents with the budget for personal income tax - the transferred personal income tax is registered.
An important indicator for personal income tax accounting purposes is the date of receipt of income . In ZUP 3, it depends on the settings specified in the calculation type itself on the Taxes, contributions, accounting - this is Income Tax Code and Income Category .
For example, Premium for the last month , the amount for which is paid in a fixed amount, has the following settings:
In this case, the income date for a given premium is the date it is paid.
In the future, partial payment of income will be considered using examples of accruals for which the Income Category is indicated as Wages or Other income from labor activities / Other income . Therefore, we will first consider the movements that occur in the accumulation register Accounting for income for calculating personal income tax and Calculations of taxpayers with the budget for personal income tax for accruals with such categories in the case of full payment of income.
Employee Berezkin Yu.A. in January 2021, the Premium for the last month , equal to 1,000 rubles, the personal income tax on it amounted to 130 rubles. On the Taxes, contributions, accounting tab for this type of calculation, Personal Income Tax Code the Income Category - Other income from employment :
It is planned to pay this bonus on 02/01/2019:
The date of receipt of income for the Bonus for the previous month is determined as the date of its payment.
The employee is also given a salary payment in the amount of RUB 30,000. and personal income tax - 3,900 rubles, for which on the Taxes, contributions, accounting tab Code is selected and the Income Category as Wages :
Let’s assume that the bonus was actually paid not on February 1, but on February 5. In this case, the premium is paid in full.
Since the date of receipt of income for one-time bonuses, which includes the Premium for the last month , is determined by the date of its payment, then in this case in the accumulation register Income Accounting for calculating personal income tax , the amount of income is transferred from the planned to the actual date of payment (from 1 to 5 February):
At the same time, in the accumulation register Calculations of taxpayers with the budget for personal income tax by type of movement income tax is “transferred” from the planned date to the actual date. Depending on the type of movement, the expense is subject to personal income tax deduction in the amount of 130 rubles. and in the column Amount of income paid, the corresponding amount of income paid is recorded - 1,000 rubles. Entry is made by Income Category - Other income from employment :
Even if the actual date of payment of income with an Income Category equal to Other income from labor activity / Other income coincides with the planned one, then in ZUP 3 according to the above registers, lines of “transfer” of income and calculated personal income tax from the planned date to the actual one will still appear (i.e. in our example from February 1 to February 1):
Salary payment refers to the Income Category - Salary , for which the date of receipt of income is the last day of the month in which such income is accrued. In our case, the date of receipt of income is 01/31/2019. When paying income:
- no movements appear in the Income Accounting accumulation register for calculating personal income tax
- in the accumulation register Calculations of taxpayers with the budget for personal income tax by type of movement Expense, personal income tax on wages in the amount of 3,900 rubles is immediately recorded and the corresponding paid income - 30,000 rubles.
Further information on the withheld personal income tax and the corresponding paid income (on the Bonus for the last month and Payment on salary ) will appear in the 6-NDFL in Section 2 for the 1st quarter of 2019 in the form of two blocks of lines:
Let us consider further examples of partial payment of income.
What is personal income tax and who pays it?
Everything is clear from the name: it is paid by individuals who receive money from various sources and must share it with the state. This tax is also called income tax, or personal income tax. Payers, in turn, are divided into two groups.
Tax residents. These include people who live in Russia for most of the year and earn income here and abroad.
Tax non-residents. They receive income from sources in Russia, but spend less than 183 Tax Code of the Russian Federation Article 207 days in the country in 12 months (we are talking about the next consecutive months, and not about the calendar year). There are exceptions. Those who have traveled abroad still remain residents:
- undergo treatment or study for up to six months;
- for work in offshore hydrocarbon fields;
- for military service;
- on a business trip, if we are talking about government officials.
Citizenship does not matter in the matter of residence.
Conclusions with partial payment of income
With partial payment of income, the following conclusions can be drawn:
- In the Sheet... edit the amounts to be paid in the explanation of the To be paid in order to see on what basis documents the amounts are adjusted.
- After adjusting the amount to be paid, be sure to click the Update tax so that the amount of withheld personal income tax is proportionally reduced to the amount of income paid.
- If one document provides the basis for calculating income for different categories of income , then in case of partial payment, the amount of income and withheld personal income tax will be divided proportionally.
- If according to the Vacation , which begins in the next month and is paid in the current month, it is planned to pay only vacation pay, then you should not calculate the salary of the current month in the Vacation .
Did the article help?
Get another secret bonus and full access to the BukhExpert8 help system for 14 days free of charge
Related publications
- Partial payment of wages and 6-personal income tax Advance payment for August was paid on September 01 and personal income tax was paid with...
- Correct reflection of information in 6-personal income tax: change of the Federal Tax Service on August 26, 2019, vacation pay in August and their recalculation in September upon dismissal. Reflection of these operations in 6-NDFL 1C: Enterprise 8.3 (8.3.16.1148) Salaries and personnel management CORP, edition 3.1...
- Payment of the actual share to the participant, accrual of the share and reflection in 6-NDFL and 2-NDFL Good afternoon! Upon leaving the Company, they paid the actual share to the former...
- Distortion of income in the income accounting register for calculating personal income tax Good afternoon. The employee was hired at his main place of work in the department...
What income is subject to personal income tax?
Tax is paid on income received in cash and in kind. It can be:
- any payment for work - salary, fees, etc.;
- income from the sale of securities and property;
- income from property rental;
- lottery winnings, prizes and gifts from individual entrepreneurs and organizations more than 4 thousand rubles;
- real estate, car or securities received as a gift not from close relatives.
Some income is exempt from personal income tax. First of all, these are various social payments, subsidies and benefits that should improve the financial situation of the recipient, as well as pensions, scholarships, repaid debt, property and shares received as a gift from close relatives or by inheritance. In addition, you do not have to pay tax on income from the sale of an apartment and car that you have owned for more than three years. There is an additional condition for housing: it must be the only one. If you have several apartments, you can sell any of them without taxes after five years of ownership.
What are the income tax rates?
For tax residents
The default rate is 13% of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation Article 224, but there are exceptions. The state wants to receive 35% of some types of income. These include:
- Prizes and winnings, as well as gifts from individual entrepreneurs and organizations worth more than 4 thousand rubles.
- Income from ruble deposits with a rate exceeding the refinancing rate by five points (currently 11%), or foreign currency deposits with a rate of 9%.
- Payment for the use of money from shareholders of consumer credit cooperatives and interest on loans to agricultural credit consumer cooperatives. Only the difference between income under the contract and according to the indicator “refinancing rate + 5%” is taxed.
- Saving on interest when receiving a loan, if it is financial assistance and (or) the loan is issued by an employer or other interdependent organization. And again, not the entire amount is taxed, but the difference between the interest under the agreement and the actual amount of interest is 9% for a loan in foreign currency or ⅔ of the refinancing rate.
For non-residents
The default tax rate is 30%. But again, there are exceptions:
- A tax of 15% is paid on dividends from equity participation in a Russian organization.
- 13% of the income is given by foreigners working under a patent, highly qualified specialists who came to work under a contract, those who moved to Russia under the program of resettlement of compatriots, crew members of Russian ships, refugees and persons granted temporary asylum, as well as residents of countries of the Eurasian Economic union - Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan.
- The tax on dividends on shares and shares of international holding companies that are public is 5%.
What tax breaks are there for personal income tax?
These are different types of deductions. For example, if you sold an apartment or car that you owned for less than three years, you must pay 13% on the money received. But you can reduce your taxable income by an amount specified by law. For housing this is 1 Article 220. Property tax deductions are million, for a car - 250 thousand. So, if you bought an apartment for 2 million, you can take advantage of the deduction and pay tax on only 1 million.
There is another relaxation for housing: if you sold an apartment for 2 million and bought it for 1.5 million, then the income is equal to the difference between these figures. Tax is paid on only 500 thousand. If you sell it cheaper than you bought it, you won’t have to pay tax at all. It is only important that you have documents that confirm the expenses - a check from the developer or a receipt from the seller.
In addition, there are deductions related to your life circumstances that allow you to return your personal income tax in part or in full. Here's what they are like:
- Property - when buying a home, building a house, paying off interest on a mortgage loan, buying property from you for municipal and state needs.
- Standard - for parents and adoptive parents, disabled people, Heroes of Russia, liquidators of the Chernobyl nuclear power plant accident.
- Social - for training, treatment, charity, insurance, including non-state pension.
- Investment - if you transferred money to an individual investment account.
- When carrying forward losses from transactions with securities, derivative financial instruments, and from participation in an investment partnership.
To find out more, read Lifehacker's great article on tax deductions.
Possible risks
When choosing any of the ways to legally save on personal income tax and contributions, you should remember about the correct documentation of payments, so that when audited by the tax authority, you can legally confirm the intended purpose of payments that are not included in wages. You also need to be prepared for the fact that in some situations you may need to defend your case in court. However, if the necessary supporting documentation is provided for all payments, disputes are most often resolved in favor of the taxpayer.
How to pay personal income tax
Tax on official salaries and fees is paid by the employer. In this case, the person himself does not need to do anything. For other income, you must transfer personal income tax yourself.
If the employer pays income tax
For most Russians, there is no need to pay taxes themselves. As mentioned above, personal income tax on official income is paid by the employer. He deducts 13% from the accrued amount of earnings, gives the rest to the employee, and transfers the PFDL to the tax office. You must transfer money once a month on payday or the next day.
It is important that the reporting period for personal income tax is not a month, but a year. Therefore, the tax base is calculated on an accrual basis: the results of the previous month are added to the results of the current month. This is done for the accuracy of calculations. Income tax is paid in full rubles, without kopecks. Due to such rounding at the end of the year, an extra ruble may be lost or lost. This is a small thing for life, but for a report it is a critical value.
In addition, the employer is accountable for the personal income tax paid for the employee. There are two documents for this:
- 2‑NDFL - income certificate;
- 6‑NDFL - calculation of personal income tax amounts calculated and withheld by the tax agent (that is, the employer).
2‑NDFL is submitted to the Federal Tax Service once a year before March 1. 6‑NDFL - for the first quarter until April 30, six months before July 31, three quarters before October 31 and a year before March 1.
If an individual pays income tax independently
This is done once a year. First, you must report your income. To do this, a 3‑NDFL declaration is submitted to the tax office. You must send it before April 30 of the year following the one in which you received the money. If this date falls on a weekend, then day X is shifted to the next working day.
Lifehacker has detailed instructions on how to submit a declaration, including online - without SMS, but with registration.
The accrued tax must be paid by July 15. You will understand exactly how much after filling out the declaration. If you do this online (and this is the easiest way, so there is no point in doing it any other way), the figure will be generated automatically.
If you receive a salary and declare some other income, you only have to pay tax on the latter. The employer has already transferred it from his salary.
Calculation of 3-NDFL
Certificate 3-NDFL is a special document intended to be filled out by certain categories of persons (for carrying out activities that are related to a certain type of income). Such persons include:
- persons who independently calculate taxation (lawyers, individual entrepreneurs);
- residents of the Russian Federation (whose income was received outside of Russia);
- persons with additional income (profit).
The above categories of citizens are required to annually provide the tax service with information about the income received and the taxes that were paid on it.
It should be noted that this document makes it possible to apply for the use of a deduction. To receive it, you need to make the necessary calculations and indicate the amount to be returned.
An example of calculating personal income tax in 2021
Citizen Sidorov bought an apartment worth 1,700,000 rubles. This purchase was subject to tax. At the end of the year, Sidorov plans to submit an application for deduction. Let's calculate what the amount of the deduction will be. The operation was taxed at a rate of 13%.
1,700,000×13% = 221,000 rubles.
Thus, Sidorov will indicate in the 3-NDFL certificate the deduction amount of 221,000 rubles. In addition, to receive a deduction, you must have all supporting documents (purchase agreement, receipts, etc.).
What happens if you don't pay income tax?
Since the tax payer is an individual, responsibility for non-payment falls mainly on him. An employer may be fined under the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, Article 123, for performing the duties of a tax agent in bad faith. In some cases, the additional accrued tax of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation Article 226 will be taken from him - if he previously withheld it not in full.
But in most cases, it is the individual who will be forced to pay the tax. Additional sanctions are also possible.
Fines
For tax evasion, you can be fined 20% of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation Article 122 of the unpaid amount. And if you can prove that you did it intentionally, the sanctions will be 40%.
For failure to file a tax return, you will be charged 5% of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation Article 119 of the unpaid tax amount for each month of delay, but not less than 1 thousand rubles and no more than 30% of the amount owed.
Penalty
For each day of delay in tax payments, you will have to pay a penalty - 1/300 of the Central Bank refinancing rate. Now it is 0.02%.
Criminal liability
A person who owes more than 900 thousand in three years can face a fine of 100–300 thousand rubles (sometimes income for a period of 18 months to three years), or up to a year of forced labor, or up to six months of arrest, under the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation Article 198, or up to a year in prison.
How to calculate personal income tax from salary: calculation formula
Employers calculate the tax base for employee income, taxed at a rate of 13%, based on the results of each month on an accrual basis from the beginning of the year (clause 3 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The amount of income the employee receives must be reduced by the personal income tax deductions provided to him (clause 3 of Article 210 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). That is, the tax base is calculated using the formula:
Once the tax base for personal income tax has been determined, you can proceed to calculating the tax itself using the formula:
To calculate personal income tax, which must be withheld from the employee’s income for the current month, you need to use another formula:
Do not forget that personal income tax is calculated in full rubles. This means that the calculated tax amount must be rounded: amounts less than 50 kopecks are discarded, amounts 50 or more kopecks are rounded to the nearest ruble (Clause 6 of Article 52 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
How to calculate personal income tax on wages in 2021
In order to calculate personal income tax on wages, you need to use a special formula, which looks like this:
N = PS x OS, where:
N - personal income tax, PS - interest rate, OS - taxable amount.
Please note that in order to determine the fixed assets, it may be necessary to make additional calculations due to the fact that tax deductions may be used on the income side.
OS = DC - V, where:
DC - income part of the person, B - deductions.
Procedure for calculating personal income tax: calculation example
/ condition / Salary E.O. Ivanova is 36,000 rubles. per month. She has a daughter aged 12, due to which E.O. Ivanova is provided with a standard deduction for a child in the amount of 1,400 rubles. per month. In addition, in April she was paid an additional bonus of 12,000 rubles. Let's determine the amount of personal income tax withheld from the employee's income for the month of April.
/ decision / The tax base for personal income tax for January-April will be:
36,000 rub. x 4 months + 12,000 rub. – (1400 rub. x 4 months) = 150,400 rub.
Personal income tax amount for January-April: 150,400 rubles. x 13% = 19,552 rub.
Personal income tax withheld from the employee’s income for January-March:
(36,000 rub. x 3 months – (1,400 rub. x 3 months)) x 13% = 13,494 rub.
Personal income tax withheld from income for April: RUB 19,552. – 13,494 rub. = 6,058 rub.
Example No. 4. One category of income in one document (amounts under GPC agreements) and their payment in installments
A GPC agreement was concluded with employee Kiparisov for January-February 2021 for a total amount of 6,000 rubles. according to certificates of completed work:
In February 2021, two Acceptance Certificates for completed work in the amount of 5,000 rubles. and 1,000 rub. with planned payment dates of March 1 and March 5, 2021, respectively:
Accruals of amounts under contracts and personal income tax are made in the document Accrual of salaries and contributions in the context of planned payment dates:
Amounts under GPC agreements belong to the Income Category – Other income from employment . The date of receipt of income corresponds to the date of payment of income.
It is planned to pay 5,000 rubles on March 1, 2021. (including personal income tax) for the first act and on March 5, make a payment for the second act - 1,000 rubles. (including personal income tax).
The general scheme looks like this:
When filling out the Statement... March 1, 2021 with the payment method - Remuneration to employees under GPC agreements, the total amount payable under two acts is loaded - 5,220 rubles. and general personal income tax – 780 rubles:
Since you need to pay the amount under the first act, you need to open the explanation of the To be paid and adjust the amount to be paid by 4,350 rubles:
Next, you should click the Update personal income tax so that when partial income is paid, partial personal income tax is withheld. An amount equal to 650 rubles will be automatically loaded:
In the breakdown of the personal income tax withholding , you can see that personal income tax for the Income Category - Other income from labor activity is reflected in one line:
Since there is a payment of income with the Income Category - Other income from labor activity , then when posting the document Statement... in the accumulation register of Taxpayers' calculations with the budget for personal income tax, the calculated personal income tax is transferred from the planned payment dates to the actual ones in the context of two planned payment dates under GPC agreements. However, since both incomes have one basis document (document Calculation of salaries and contributions ) and belong to the same Category of income - Other income from work , then only one line appears for the withheld personal income tax and the corresponding paid income:
In the 6-NDFL in Section 2 , the amount of income paid will be reflected correctly in one block: in line 130 - 5,000 rubles, withheld personal income tax in line 140 - 650 rubles.
On March 5, 2021, when paying the final debt under GPC agreements, you can see a similar picture in the accumulation register. Calculations of taxpayers with the budget for personal income tax for the amount of withheld personal income tax in the amount of 130 rubles. and the corresponding amount of paid income - 1,000 rubles:
In the 6-NDFL in Section 2 , the amount of income paid will be reflected correctly in one block: in line 130 - 1,000 rubles, withheld personal income tax in line 140 - 130 rubles.
Thus, if one basis document calculates income with the Income Category - Other income from labor activity with different planned payment dates, then with partial payment of such income according to this basis document, the calculated personal income tax is “transferred” from the planned date to the actual date, and withholding of personal income tax and the corresponding paid income is made in one line on the date of payment. And this information is reflected in the 6-NDFL in Section 2 in one block.