Employee meals: organization and tax consequences
Employers often, taking care of their employees, organize meals at the workplace.
And for some businessmen this is a legal obligation. For employees, food from the employer is an important part of motivation. This allows you to save not only money, but also time on preparing lunch or traveling to your home or cafe. But for a businessman, feeding employees at their workplace can lead to additional tax payments.
Let's look at how to make workplace lunches not only convenient for employees, but also beneficial for the business as a whole.
Common mistakes
Error:
The accountant does not withhold personal income tax from the cost of food provided to the employee at the enterprise free of charge, at the expense of the employer.
A comment:
Free food is an employee's income in kind, related to wages. And personal income tax is withheld from wages and other payments related to wages.
Error:
A company that provides buffet meals for employees takes into account the cost of meals as part of the employee's remuneration.
A comment:
In the event that meals are organized according to a buffet system, it is impossible to determine how much lunch a particular employee spent. Accordingly, the cost of food cannot be taken into account as part of remuneration in kind.
Employee meal plan options
For two categories of employees, according to Article 222 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the employer is obliged to organize free meals at the workplace.
- Workers in hazardous conditions are supposed to be given milk or other substitute products.
- For workers in particularly hazardous conditions, the employer is obliged to organize therapeutic and preventive nutrition for them.
In this case, the cost of food for employees within the established norms reduces the base for income tax or the simplified tax system “Income minus expenses” and is not subject to personal income tax and insurance contributions. There is also no need to charge VAT on the cost of such food.
The organization of meals for other categories of employees remains at the discretion of the company management. But many HR specialists believe that this motivation option is very effective. Therefore, the employer, if he has the opportunity, should make additional expenses that will be paid off by the loyalty of employees.
The procedure for providing meals to all “ordinary” employees who do not work in harmful or dangerous conditions is not established by law. Therefore, employers themselves have the right to choose the most convenient option for them:
- Open your own canteen.
- Issue products.
- Order lunch delivery or full catering service.
- Prepare the room for eating.
- Pay employees for food expenses.
However, the employer’s desire to make the work process more comfortable for its employees often runs into legal requirements. From the point of view of regulatory authorities, a businessman, by providing meals to employees, increases their income. In this case, an additional object for taxation arises. Therefore, you need to carefully study each method and choose the most suitable one.
Meals for posting employees - compensation for the cost of meals for employees
Often, an enterprise does not provide free lunches to staff, but simply compensates them for the cost of food. The chart of accounts provides for the use of:
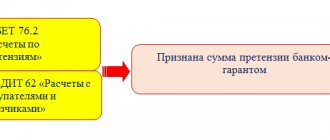
- account 73 “Settlements with personnel for other operations” - it reflects the implementation of payments to personnel not related to wages and compensation of expenses of accountable persons (payment of compensation for the cost of food from funds taken at the cash desk will be reflected in the DEBIT of account 73 in correspondence with the account 50 "Cashier");
- sch. 91 “Other income and expenses” subaccount 91-2 “Other expenses” - to reflect non-operating expenses.
Let's look at an example of how an accountant records the company's expenses associated with paying employees compensation for the cost of lunches. Let’s imagine that employees of Oblaka LLC receive monthly compensation for the cost of food in the amount of 1,500 rubles:
| DEBIT | CREDIT |
| 91-2 | 73 |
| 99-2 | 68 |
| 73 | 68 |
| 73 | 50 |
Meals for employees in their own canteen
There is nothing better and tastier than freshly prepared food. But to organize a full-fledged dining room, you need to take into account many points:
- The premises must be in a non-residential building.
- The dining room must be equipped with a sewerage system, an exhaust hood and a place for collecting food waste.
- There are special requirements for the finishing of the premises.
- It is necessary to hire qualified personnel.
- Organizing your own canteen will significantly complicate your accounting.
- You need to take into account many Sanitary Pins and prepare for regular inspections, since public catering establishments are strictly controlled.
The main disadvantage is that opening your own canteen is very expensive. Therefore, this option is suitable mainly for medium and large organizations.
However, with the right approach, the company will be able to generate additional income by providing the opportunity to use the canteen services not only to employees, but also to third-party clients. As a result, catering may even become a separate type of business.
Having your own dining room also has significant advantages:
- You can control the quality of employee diets.
- The number of sick leaves due to gastrointestinal diseases is decreasing.
- Possibility of additional income for the company.
If an employee pays for lunch himself, then he does not have any additional taxable income. The employer can take into account the costs of maintaining the canteen for tax purposes on a general basis.
If the canteen meets the parameters for the use of UTII in terms of the area of the hall (up to 150 sq. m), then until the end of 2021 it can operate on an “imputed” basis. But for this, the organization itself must have no more than 100 people. But in practice, such companies rarely open their own canteens.
Setting up a program to calculate natural income (cost of food)
Step 1. Open the “Settings” - “Payroll” section.
Step 2. Follow the hyperlink “Setting up the composition of charges and deductions”.
Step 3. On the “Other accruals” tab, check the “In-kind income is recorded” checkbox. Click Apply and Close.
As a result of this setting, the accrual “Income in kind” with the type of accrual purpose - “Income in kind” will become available in the directory of accrual types.
Step 4. Go to “Settings” - “Accruals”.
Step 5. Open the accrual card. This accrual is entered as a fixed amount for a separate document.
This calculation procedure does not coincide with our condition. Therefore, we will create a new accrual.
Delivering lunches or issuing groceries to employees
An organization can enter into an agreement for on-site catering or lunch delivery.
Advantages of this method:
- No need to buy groceries or prepare lunches yourself.
- Possibility of pre-ordering with a choice of menu.
- Corporate volume discounts and free shipping.
- Quality guarantee from a supplier who specializes in catering.
Providing food is a compromise option when the employer does not want to spend large sums on food, but strives to provide employees with everything they need for tea breaks.
The company’s obligation to organize meals for employees in one way or another must be reflected in internal regulations: regulations on remuneration, collective agreement, etc. The documents must detail exactly who is provided with food and in what form.
In this case, the employer has the right to take into account the costs of food for employees for income tax (clause 25 of Article 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, letter of the Ministry of Finance dated July 23, 2018 No. 03-03-07/51494).
For the simplified tax system “Income minus expenses” the approach will be similar, because Labor costs and equivalents are taken into account under this regime in the same way as income tax (clause 6, clause 1 and clause 2, article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
VAT may not be charged on the cost of issued lunches or products (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated 03/06/2015 N 03-07-11/12142). But in this case it will not be possible to deduct input tax. VAT amounts invoiced by the catering company or food supplier can be included as expenses for income tax purposes.
When a company purchases ready-made meals or products for the purpose of providing meals to employees, the question arises about the taxation of payments in kind. Indeed, in the general case, these costs are employee income in kind. Therefore, personal income tax must be withheld from the cost of free food, and insurance premiums must be charged on them.
However, these payments are “personalized”, i.e. when calculating, they must be tied to a specific employee - the recipient of the income. Therefore, if it is impossible to accurately determine which employees received free meals, then these expenses may not be subject to personal income tax and insurance premiums (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated August 3, 2018 No. 03-04-06/55047).
When purchasing ready-made lunches, to make it impossible to identify the income of each employee, it is enough to place a general order, which will not be detailed. If an organization purchases products, then it is also impossible to find out how much and which employee received, for example, sugar and tea. Therefore, in such situations, there is a reason not to accrue mandatory payments - it is simply impossible to specify the income for each employee.
But it is impossible to give a full guarantee that with such a scheme it will be possible to do without paying personal income tax and contributions. Inspectors can calculate these payments by calculation, for example, based on the total costs and the number of employees receiving meals (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated May 17, 2018 No. 03-04-06/33350).
In addition, if the employer does not charge insurance premiums for the cost of food for employees, then, according to tax authorities, he cannot take these costs into account for income tax (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated March 4, 2008 No. 03-03-06/1/133). There is also an opposite position, but you will most likely have to defend it in court (Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow District dated April 6, 2012 No. A40-65744/11-90-285).
Meals for posting employees - buffet lunches
When staff meals are organized in the form of a buffet, it is impossible to determine exactly how much food consumed per subordinate. In this regard, the costs incurred by the company for preparing lunches are subject to a single social tax and personal income tax according to a non-standard scheme for this situation.
As is known, UST and personal income tax are targeted taxes (contributions), since they are calculated separately based on the earnings of each of the company’s employees. A prepared meal at the expense of the organization is the employee’s income in kind, on which taxes must be paid, as on wages.
And when organizing lunches according to the buffet system, when everyone puts dishes in any quantity and assortment on their plate, it is impossible to determine with accuracy exactly how much each of the subordinates received this income (in other words, how much each employee had lunch for). ). For this reason, the amount of payment by the company for food provided to employees free of charge cannot be considered as staff income.
This rule is confirmed by judicial practice; it is enough to read paragraph 8 of the Information Letter of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated June 21, 1999 No. 42. A similar conclusion can be drawn after reading the text of the Federal Law dated December 15, 2001 No. 167-FZ and Chapters 23–24 of the Tax Code - in These regulations do not provide guidance on the procedure for determining an employee’s income in such a case.
Organizing a place to eat
There is an option for those employers who, for some reason, are not suitable for all the previous ones. You can increase employee loyalty by organizing a place to eat. To do this, you will need an empty room, household appliances and furniture. Appliances may include a refrigerator, microwave, kettle, coffee machine. Some employers go even further and provide not just a kitchen where you can heat up food, but also a full-fledged recreation area - with chairs, board games and more.
Firstly, this measure will allow employees not to waste time going to third-party cafes and to comply with safety precautions in the workplace.
Secondly, organizing a place for food requires only one-time investments, since the company only equips the place without further spending money on food for employees. Consequently, the problem with “salary taxes” discussed in the previous section will not arise.
In order for these costs to be taken into account for tax purposes, it is necessary to reflect the employer’s obligation to create conditions for eating in local regulations.
Setting the food cost metric value for your organization
Before entering our indicator, let's do some setup, because... There is no form for entering the indicator in the program yet.
Step 1. Go to the “Settings” “Input Data Input Templates” section.
Step 2. In the “Input Data Entry Templates” reference book, click “Create”.
Step 3. Set the name and presentation. In the "Salary Metrics" section, set the radio button to "Continuous" and select our new "Meal Cost" metric.
Step 4. Save the template using the “Save and Close” button.
What did this give us? Let's look further...
Step 5. Go to the “Salary” - “Data for salary calculation” section.
Step 6: Click Create. An inscription appeared in the menu - “Cost of employee meals” - i.e. This is our template for entering food cost data.
Step 7. Set the date and cost of meals - 4,500 rubles.
So we set the value of the indicator, and this data is recorded in the “Data for Payroll Calculation” journal. When the value of this indicator changes, a document with current data is also entered.
Employee benefits
The simplest method, which does not require the employer to take special measures to organize meals for employees. However, it is also the most “expensive” from a tax point of view. These payments are personalized and therefore are subject to all contributions and personal income tax.
That is, at least 30% of insurance premiums must be added to the amount of costs for lunches and 13% of personal income tax must be withheld from payments.
In order to take into account additional payments for employee meals when calculating income tax and the simplified tax system, they, like other types of similar expenses, must be reflected in internal personnel documents.
But this option may be convenient for many employees, because... they choose how and where to dine.
Posting meals for employees - the company buys lunches for employees from a third-party company
Important!
If the provision of lunches to the company's employees is stipulated by a collective or labor agreement, their cost is part of the salary expressed in kind, that is, accountants should reflect the cost of meals in the same manner as accruals and payment of salaries are reflected.
For the purpose of reflecting payments related to the remuneration of employees, account 70 “Settlements with personnel for remuneration” is used (maintained separately for each employee). Since the cost of staff meals is not charged to employees, it is a type of wages, which means it is also reflected in account 70. According to DEBIT account. 70 must reflect the amounts of wages issued (pensions to working pensioners, wages, bonus payments, additional payments, allowances, benefits), amounts of taxes, various deductions and payments under executive documents. By LOAN account 70, wage payments will be reflected in correspondence with the accounts of production expenses (sales costs).
It is also necessary to pay attention to the following points regarding tax and accounting in an organization that provides meals to its employees:
- The accrual of UST must be reflected on the LOAN account. 69 “Calculations for social insurance and security” in correspondence with DEBIT of accounts for recording production expenses. The amount of UST is recognized as expenses for ordinary activities.
- If the provision of lunches to employees is not stipulated in labor and collective agreements, the company's costs for employee lunches are recognized as non-operating expenses. They are reflected in DEBIT account. 91 “Other income and expenses” subaccount 91-2 “Other expenses” in correspondence with CREDIT account. 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors.”
- Payment for the services of the company from which ready-made meals are purchased, in accordance with the concluded agreement, will be reflected in the DEBIT account. 60 and LOAN account. 51 "Current accounts".
- Costs for the transfer of goods (works, services) for one’s own needs, according to paragraphs. 2 p. 1 art. 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation cannot be taken for deduction for the purpose of calculating income tax. These expenses are subject to VAT, which is necessarily allocated to the account. 19 for subsequent offset from tax amounts transferred to the budget.
- Costs that form the accounting profit of the reporting period and are not taken into account when calculating the taxable base for profit tax of the current and subsequent reporting periods should be recognized as a permanent difference. Permanent differences between reporting periods should be reflected separately in the accounts. They are subject to reflection in the analytical accounting of the corresponding account of assets and liabilities, in the assessment of which a permanent difference has arisen. In the case of providing lunches to staff, this will be analytical accounting for account 91 subaccount 91-2.
- The appearance of a permanent difference means the emergence of a permanent tax liability (a tax amount that increases the amount of tax payments for income tax in the reporting period). The amount of the permanent liability can be calculated by multiplying the permanent difference identified in the reporting period by the income tax rate (according to clause 1 of Article 284 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation - 24%). Permanent tax liabilities should be reflected in DEBIT account. 99 “Profits and losses” in correspondence with CREDIT account. 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees.”
Conclusion
The employer is obliged to provide meals only to certain categories of employees. In all other cases, this is his voluntary decision. Therefore, if a businessman wants to increase the loyalty and motivation of employees, then he can choose a method that is convenient for himself.
With any option for voluntary organization of free meals for employees, this obligation of the employer must be reflected in internal documents. Otherwise, the costs cannot be taken into account to reduce the tax base.
For a large business, the best option is your own canteen. In this case, not only there are no “extra” taxes, but the organization can also receive additional income.
If an employer provides employees with free lunches or groceries, then, according to tax authorities, they should be subject to personal income tax and contributions, even if personalized accounting is not possible. The opposite position will most likely lead to the need to resolve the issue in court.
If you simply add the additional payment for employee meals to the salary, then taxes will have to be paid in any case. But with this option, there is no need to equip the premises, purchase and deliver products, etc.
As a result, the choice depends on the financial capabilities of the employer and his readiness for additional difficulties both in organizing meals for employees and in the event of an inspection.
Taxation of compensation
Compensation payments may or may not be subject to taxation and calculation of contributions to funds. There are several cases when compensation is not subject to personal income tax:
- If such an obligation arises for the employee due to the fact that the employee works at work with harmful working conditions. In such a situation, the costs incurred do not relate to wages, so the organization’s accounting department has the right to include these costs in employee benefits, which will reduce the tax rate on the profit received by the organization.
- When issuing compensation as daily allowance. The legislation stipulates maximum amounts of payments that are not subject to taxes; if the amount is exceeded, the remainder is subject to both personal income tax and contributions.
Attention! If an organization provides buffet meals to its employees, the tax authorities consider this as a payment of income. If the employer can prove that such a desk is available not only to its employees and is not a mandatory part of the employment relationship, then the services may be recognized as tax-free.
Article 210 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation “Tax base”
Read also: The main mistakes of an accountant
Article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation “Income not subject to taxation (exempt from taxation)”