Reflection of estimated liabilities in accounting is mandatory. Most often, accountants record a reserve for vacation pay. But this is not the only case where the obligations in question need to be taken into account. They are recorded only in reporting. The reserves will not appear on the tax return.
Question: How are the organization's estimated liabilities reflected in accounting and financial statements in connection with the emergence of employees' right to paid vacations in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation? According to the accounting policy of the organization, the formation of an estimated liability for payment of vacations to employees is carried out monthly on the last day of each month based on data on average earnings and the number of vacation days for each employee. Administrative expenses as semi-fixed expenses are recognized in the cost of sales in the period of their acceptance for accounting. In tax accounting, the organization does not create a reserve for upcoming vacation payments. View answer
What is an estimated liability?
Provisions are an existing obligation of an enterprise that has an uncertain amount or deadline. If available, a reserve must be created.
If the indicator does not appear in the reporting, this will lead to an overstatement of net profit. For this reason, financial statements will not provide objective information about the position of the enterprise. All this can lead to negative consequences: an increase in dividends and a deterioration in the financial condition of the organization.
Are provisions for doubtful debts classified as provisions?
Estimated liabilities differ significantly from other provisions. Let's look at examples:
- The company plans to repair equipment; this will require funds. A reserve of estimated liabilities will not be created for them, since repair work is not the responsibility of the organization. The company may change its mind about carrying out repairs.
- The reserve also does not need to be organized in the presence of ordinary obligations. The company ordered the goods. The products arrived, but the company did not pay for the contractor’s services. In this case, a reserve for estimated liabilities will not be created, since the existing debt is payable. It does not correspond to an important feature of an estimated liability - uncertainty of the amount and timing. In this example, the company knows how much money it owes and when it needs to be repaid.
- Estimated liabilities and estimated provisions differ. The latter represent an adjustment to the balance sheet indicators of assets associated with the receipt of new information. Valuation reserves are created in the presence of doubtful debts, a decrease in the value of inventories, and a decrease in prices for financial deposits. These indicators are not reflected in the balance sheet. The indicators under consideration will be recorded in the liability side of the balance sheet.
- Provisions that are created on the basis of undistributed earnings will also not be classified as provisions.
Difficulties often arise when fixing OO. To prevent errors, it is important to distinguish an estimated liability from other types of provisions.
Are estimated liabilities reflected in tax accounting ?
Methods for calculating estimated liabilities and reserves for vacations
For accounting, two methods are supported for calculating estimated liabilities:
- Liability method (IFRS) – calculation based on vacation balances (taking into account the recommendations of the Accounting Methodological Center);
- The normative method is a percentage of the payroll (the same methodology as for NU).
For NU it is supported:
- Normative method.
The calculation method is configured in the Organization directory - Accounting policies and other settings tab - Vacation reserves link:
With any method, the calculation of estimated liabilities and reserves is carried out for each employee.
The “boiler” calculation method is not supported in 1C ZUP 3!
The emergence of estimated liabilities
Estimated liabilities may arise due to the following factors:
- Court decisions or agreements with relevant conditions. For example, a company enters into an agreement with its clients, according to which, if services are provided with insufficient quality, the money will be returned. Customers usually have complaints, so it makes sense to create a reserve. These will be estimated liabilities, since there is a high probability of their occurrence, but the exact amount is unknown.
- Actions that are not recorded in legal documents, but oblige the company to certain obligations. For example, a store posted an announcement that it would return money to customers if the purchased products turned out to be of poor quality. Despite the fact that this obligation is not formalized in any way, the store bears its consequences in connection with a public statement.
- A reserve has been formed for restructuring. It can be created only if the following conditions are met: there is a restructuring plan, interested parties are notified about the procedure.
- A deliberately unfavorable agreement was concluded. The company's managers are confident that they will suffer losses in connection with it. The LLC must be reflected in accounting in the same month in which the agreement is executed.
What are the features of inventory of estimated liabilities ?
Estimated liabilities are indicated in accounting only if the following conditions are met:
- Financial obligations cannot be avoided. For example, a company rents premises that, according to the lease agreement, need to be renovated. While repair work has not yet been carried out, it cannot be avoided.
- The probability of incurring expenses exceeds 50%.
- There is information that allows you to estimate the costs of fulfilling the obligation.
To form a reserve, all of the above conditions must be present. If one of them is not met, a contingent liability is recognized. This indicator does not need to be recorded. It is stated in the notes to the report.
Column “Explanations” to the balance sheet for line 1430
Let's consider what information to indicate in the “Explanations” column. The accountant should provide instructions on the disclosure of the indicator. In the “Explanations” on page 1430, you should indicate Table 7 “Estimated Liabilities” (it contains detailed data on estimated liabilities, the planned time of fulfillment of which is at least 1 year after the reporting date) in cases where the company draws up Explanations to the BB and OFR according to the forms from the Example of Explanations*.
* Examples are contained in Appendix 3 to Order No. 66n of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation.
Accounting for estimated liabilities
Estimated liabilities are recorded on account 96 “Reserves for future expenses”. The amount may be reflected both in the list of specific expenses (for example, expenses for repairs under warranty) and in the list of other expenses.
OO accrual transactions will look like this:
- DT 20 (23, 25, 26, 44) CT 96 “Reserves for future expenses”
Repayment of obligations will be reflected as follows:
- DT 96 “Reserves for future expenses” CT 10, 76, 70, 90
The selected accounts are determined by the transaction performed.
Example
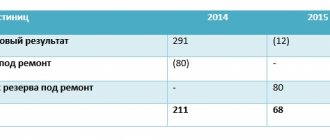
The company is involved in litigation. It is expected that he will have to pay 80,000 rubles. This will be reflected as follows:
- DT 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors” CT 96 “Reserves for future expenses”
A court decision has been received. The company's calculations did not come true. The organization will need to pay 100,000 rubles. The operation can be reflected as follows:
- Repayment of OO: DT 96 “Reserves for future expenses” CT 76 “Settlements with creditors”, subaccount “Settlements for claims”. The transaction amount is indicated: 20,000 rubles.
- Amount that needs to be paid additionally: DT 91 “Other income and expenses”, subaccount “Other expenses” KT 76, subaccount “Calculations for claims”. The amount that needs to be paid is indicated: 20,000 rubles.
All specified transactions must be confirmed by primary documentation. From the accounting it is possible to clearly understand which transactions were carried out.
How accounting data is needed to fill out line 1430
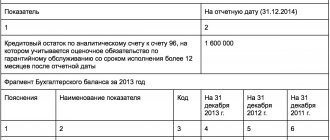
Important! In general, information on page 1430 of the balance sheet as of 31.12 year N and as of the same date of year N-1 must be transferred from the balance sheet for the previous year.
To make an entry in line 1430 “Estimated liabilities”, you will need data on the credit balance of account 96 in terms of estimated liabilities as of the reporting date. In this case, only those estimated liabilities are taken into account, the expected fulfillment period of which is more than 1 year after the reporting date.
Is it necessary to reflect estimated liabilities in tax accounting?
Lack of information about a PA in tax accounting is not an error. You do not have to indicate reserves, as they do not affect the amount of taxes assessed. This information will not be required by the tax authorities. But it will be useful to banking institutions to which the enterprise applies, or to its investors.
Summary
Estimated liabilities require the creation of a reserve. In order for obligations to be recognized as valuation obligations, they must meet a number of conditions. The main signs are the inability to determine the exact amounts of accruals and the timing of their repayment. Commitments must be inevitable. For example, they appear on the basis of agreements with employees. If the obligation does not meet the established requirements, then it is taken into account in a different manner. OO are recorded only in accounting. There is no need to indicate them in the tax return, since the estimated expenses do not affect the amount of taxes. Their appearance in accounting is mandatory.
To what extent are estimated liabilities recognized (line 1430)
Determining the amount of the estimated liability depends on how long the period for its fulfillment will be:
| Estimated time of fulfillment of the obligation established in the accounting policy | Amount of estimated liability | Regulatory regulation |
| Less than 12 months or exactly 1 year | A value reflecting the most reliable monetary estimate of the costs that will be incurred to fulfill this obligation. | clause 15 PBU 8/2010 |
| More than 12 months | The amount of the estimated liability is determined at the present (discounted) value. | clause 20 PBU 8/2010 part 2 clause 20 PBU 8/2010 (requirements for the established discount rate) |
When calculating the amount of estimated liabilities, the following should be taken into account:
- future business events that may affect the amount of the assessed liability;
- probable risks;
- consequences that will become known at the end of the reporting year.
The amount of the identified estimated liability of the enterprise is determined:
- by selecting from a certain range of values;
- as a weighted average of several values of this interval;
- as the arithmetic mean of the smallest and largest value.
Conclusions about what a change in indicator means
If the indicator is higher than normal
Not standardized
If the indicator is below normal
Not standardized
If the indicator increases
Usually a positive factor
If the indicator decreases
Usually a negative factor
Notes
The indicator in the article is considered from the point of view not of accounting, but of financial management. Therefore, sometimes it can be defined differently. It depends on the author's approach.
In most cases, universities accept any definition option, since deviations according to different approaches and formulas are usually within a maximum of a few percent.
The indicator is considered in the main free online financial analysis service and some other services
If you need conclusions after calculating the indicators, please look at this article: conclusions from financial analysis
If you see any inaccuracy or typo, please also indicate this in the comment. I try to write as simply as possible, but if something is still not clear, questions and clarifications can be written in the comments to any article on the site.
Best regards, Alexander Krylov,
The financial analysis:
- V. CURRENT LIABILITIES Section V. Current liabilities is the fifth section of the balance sheet. At the same time, it is also the third section of the liability side of the balance sheet, which shows the sources of financing for the property. AND…
- IV. LONG-TERM LIABILITIES Section IV. Long-term liabilities are the fourth section of the balance sheet. At the same time, it is also the second section of the liability side of the balance sheet, which shows the sources of financing for the property. AND…
- Balance sheet liability The balance sheet liability is the second part of the balance sheet. It contains a list of those financial resources that were used to acquire property, that is, assets that...
- I. NON-CURRENT ASSETS Non-current assets are property used in the activities of an enterprise for more than a year. Its value is transferred in parts to the cost of finished products. A sign of assets is the ability to generate income for the organization.…
- II. CURRENT ASSETS Current assets are property used in the activities of an enterprise for less than a year or used in one production cycle, which also does not exceed one year. Its entire cost...
- III. CAPITAL AND RESERVES Section III Capital and Reserves is the third section of the balance sheet. But what is more important is the first section of financial sources, that is, the liability side of the balance sheet. By this he...
- Absolute economic indicators of an enterprise's activity Absolute economic indicators of an enterprise's activity are indicators that allow us to judge several things: The size of the enterprise and the scale of its activities The level of income and expenses...
- Key performance indicators of an enterprise Key performance indicators of an enterprise are indicators that allow us to judge several things: The size of the enterprise and the scale of its activities The level of income and expenses About ...
- Balance sheet asset A balance sheet asset is a part of the balance sheet containing data on the assets of the enterprise, that is, on its property. The balance sheet asset reflects property, property rights and cash...
- Price of work Hello, my dear reader. On this page you can estimate the value of your work using popular exchanges.