Hello, Vasily Zhdanov, in this article we will look at an example of calculating the total capital of an enterprise. As practice shows, concepts such as “your own or your own capital”, “your own or your own funds”, as well as “net assets” are used as synonyms. In fact, they are truly interchangeable since their definitions are largely consistent. The words “own” and “your” are essentially identical. And economists quite rightly use the term “capital” when describing assets. Although its exact definition is capital - a combination of debt and equity capital.
An example of borrowed capital can be virtually any short-term and long-term obligations of an organization to individuals and other legal entities. Most often, credits and loans act in this capacity. Meanwhile, the enterprise’s capital (its own, its own) is considered from different positions.
Take our proprietary course on choosing stocks on the stock market → training course
In general, it is customary to say that your capital is part of the book. balance sheet, which reflects the residual claim of the founders to the legal entity they formed. During each reporting period it may change: decrease or increase. Its value depends on two main factors:
- Additional investments (for example, receiving valuables for free).
- The results of your own activities (for example, the net profit for a specific reporting period).
In fact, the following rule applies. The value of net assets changes (decreases or increases) over a specific period, and accordingly, the enterprise’s capital also changes. One change follows from another.
How to determine the amount of equity capital?
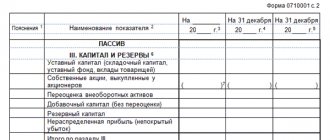
According to the balance sheet, the value of the organization’s equity capital corresponds to the balance of line 1300 “Total for Section III,” i.e., the total amount for Section III “Capital and Reserves” of the balance sheet (Order of the Ministry of Finance dated July 2, 2010 No. 66n, clause 66 of the Order of the Ministry of Finance dated July 29, 1998 No. 34n).
Let us recall that the balance of capital and reserves in the balance sheet is determined as follows:
line 1310 “Authorized capital (share capital, authorized capital, contributions of partners)”
line 1320 “Own shares purchased from shareholders”
line 1340 “Revaluation of non-current assets”
line 1350 “Additional capital (without revaluation)”
line 1360 “Reserve capital”
line 1370 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss)”
It is from the organization's own capital that dividends are paid to participants. And upon termination of the organization’s activities, the size of its equity capital will show the amount of funds that is subject to distribution among participants. However, it is necessary to understand that equity can also be negative. This is possible in the case when the organization operates at a loss and its accumulated value exceeds the sum of other elements of equity capital (authorized, additional, reserve capital).
We talked in more detail about accounting for an organization's equity capital in a separate consultation.
Please note that if the calculation of equity is carried out to determine the maximum amount of interest taken into account in expenses on controlled debt, then the amount of equity will be equal to the sum of the balance of line 1300 and debt for taxes and fees (clause 4 of Article 269 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
We talked in more detail about the use of the equity indicator when determining the interest on controlled debt taken into account in expenses here.
Total assets in the analysis of company activities
Based on information about the gross amount of assets, an analysis of work in the company is built, for which the necessary indicators are calculated. For example, the size of the company's total capital.
Total capital is the sum of all types of capital involved by the company in the production process - its own and borrowed capital, and of these, working capital and invested capital.
Based on information about the gross size of assets, the analyst can calculate the size of:
SC = SA (line 1600) – (DO (long-term loans, line 1400) + KO (short-term liabilities, line 1500));
OK = OA (current assets line 1200) – KO (line 1500);
IR = SA (p. 1600) – KO (p. 1500).
In the balance sheet, total capital is found using the formula:
SK = page 1370 + page 1400 + page 1500
Total assets in the balance sheet (line 1600) is an absolute indicator on the basis of which values are calculated that characterize the degree of efficiency in the use of the company’s property. One of them is the indicator of profitability (profitability) of the SA. This ratio reflects the amount of net profit per unit of capital value (all available resources from various sources) and is calculated by the formula:
Krsa = PE / SA, where PE is net profit.
According to reporting forms, the profitability index is calculated as follows:
Krsa = line 2300 of the financial results report / (line 1600 at the beginning of the year + line 1600 at the end of the year) / 2
The increase in CA profitability may be associated with:
with an increase in the company's net profit;
with an increase in tariffs for the services/goods offered, or a decrease in production costs;
with an increase in SA turnover.
A decrease in the coefficient signals reverse processes occurring in the analyzed period. CA profitability tells the economist whether a company has a strong foundation that provides a good return on equity. Typically, firms that do not achieve fairly high SA profitability indicators cannot ensure a sufficient level of SA profitability and are forced to take appropriate measures, including changing their business strategy.
Own capital: definition, formula, components >
Equity (in English: Shareholder's equity or Stockholder's equity) is the amount of capital provided to a business by its shareholders plus profits received from the company's business activities, less any dividends paid. On the balance sheet, capital is calculated as follows:
Assets – Liabilities = Equity
Alternative calculation of share capital:
Authorized capital + Retained earnings – Treasury shares
Both calculations result in the same amount of equity. This amount appears on the balance sheet as well as the statement of equity.
The concept of equity is important in assessing the amount of money held in a business. A negative equity balance, especially when combined with a large debt load, is a strong indicator of impending bankruptcy.
Components
Own capital includes the following components:
— Ordinary shares. This is the par value of common stock, which is usually $1 per share.
- Extra capital . This is the additional amount that shareholders paid for their shares above the par value. Typically, the amount of additional capital significantly exceeds the size of ordinary shares.
— Treasury shares (in English Treasury stock) – the amount paid to buy back shares from investors. The account balance is negative.
— Retained earnings. This is the total profit and loss minus dividend payments to shareholders. Retained earnings are the profits of a business that have not been distributed as dividends to shareholders, but have instead been used to invest back into the business. Retained earnings may be used to finance working capital, purchase fixed assets, or service debt, among other things.
To calculate retained earnings, the beginning balance of retained earnings is added to net income or loss and then dividend payments are subtracted. The result is published on the balance sheet and a separate statement of retained earnings.
The formula for retained earnings is as follows:
Opening Retained Earnings + Net Income/Loss – Dividends
Equity may be referred to as the book value of a business (or book value), since it theoretically represents the residual value of the business if all liabilities are satisfied from assets. However, the market value and book value of assets and liabilities are not always the same.
Example
As of December 31, 2021, JP Morgan Chase Bank had total assets of $2,533,600 million. and total liabilities of $2,277,907 million.
JP Morgan Chase Net Worth:
$2,533,600 (assets) – $2,277,907 (liabilities) = $255,693
The resulting figure can also be found in the statement of changes in equity, which provides a breakdown by component, including
- preferred shares ($26.068 million)
- ordinary shares ($4.105 million)
- additional capital ($90.579 million)
- retained earnings ($177.676 million)
- accumulated other income (-$140 million)
- Treasury shares (- $42.595 million)
$26,068 + $4,105 + $90,579 + $177,676 – $140 – $42,595 = $255,693
Cost of capital of $255.693 million. represents the amount remaining to shareholders if, theoretically, JP Morgan Chase paid off all of its liabilities.
conclusions
Equity is used in fundamental analysis to determine ratios such as debt to equity ratio and return on equity (ROE).
Debt to Equity Ratio
How to simply calculate an important indicator of fundamental analysis
Capital in the structure of a public company whose shares are traded on the stock market can appear in two ways:
- The company can take out a loan
- The company may issue shares
Sergey Ray
If a private investor wants to invest money in a public company, one of the first and simple steps of fundamental analysis he can do is to compare how much debt the organization has and how much equity it has. These two items can be found on the company's balance sheet. By comparing them with other companies in the same sector, you can assess the business situation.
The purpose of this article is to explain in simple words the concept of Debt-to-Equity Ratio and calculate it using the example of a company’s balance sheet. And also, find out how it can be interpreted during fundamental analysis, that is, what role debt plays in the company’s capital structure.
Debt-to-Equity Ratio
A company's debt-to-equity ratio (D/E) is a relative indicator of a firm's performance that measures its level of debt relative to the total value of its stock. The debt-to-equity ratio is expressed either as a number (ratio) or as a percentage and allows any investor to compare how much of a company's assets and potential profits are generated by debt. The debt-to-equity ratio is easy to calculate since all the information needed for the calculation can be found on the company's balance sheet.
Public companies use debt to finance projects because it is cheaper for the enterprise than obtaining financing by issuing new shares. In addition to being a cheaper option, debt financing is used because it allows a company to use leverage, which can increase the value of the company through the use of borrowed money without increasing the number of members of the company.
How to Calculate Debt to Equity Ratio
The calculation of debt to equity ratio can be done as follows:
Debt/Equity = Total Company Liabilities/Equity
In more detail this can be written as follows:
Debt/Equity = (Long Term + Short Term Debt)/Equity
In English transcription
Debt to Equity Ratio = (Short Term Debt + Long Term Debt) / Shareholders' Equity
If a company's capital structure combines debt and equity, the share capital will correspond to the company's Equity Capital. Since, in the company's balance sheet, their liabilities and share capital must be equal to their assets. For example, at the end of 2014, Apple Corporation published a balance sheet that showed liabilities of $120 billion and total shareholders' equity of $111 billion.
The debt to Equity of this company in this reporting period will be:
120/111 = 1.07 - This means that there is just over $1 of debt for every $1 of equity in the holding company.
For small and medium-sized businesses, equity means the difference between their assets and liabilities. For example, if company ABC has 3,000 thousand rubles in assets and 2,500 thousand rubles in liabilities, they will have 500,000 rubles in Equity (3,000 – 2,500 = 500). Using the above formula it turns out:
Debt/Equity = 2,500,000/500,000 = 5 - this means that the company has a high level of debt, because for every ruble in equity there are 5 rubles of various debts.
Another representative of a small business, the SBA company also has 3,000 thousand rubles in assets, but they only have 1,000 thousand rubles in liabilities. Their Net Worth is 3,000. 000 – 1,000,000 = 2,000,000. Their debt to net worth ratio is:
1,000,000/2,000,000 = 0.5 – This company has a healthy balance sheet since they have 2 rubles of Equity for every ruble of Debt.
Valuation or interpretation of debt to equity in fundamental analysis
The Debt to Equity ratio is one of the most common tools that investors can and should use in fundamental analysis. It is important because large liabilities or the level of leverage that a company uses can create big problems for any company. Especially if her income decreases. In this case, management will have to withdraw money from the business to finance its debts.
The concept of return on total capital
All investments can be formed from two sources: equity capital and borrowed capital. For this reason, there are two coefficients by which return on total capital is determined:
- return on equity (ROE),
- return on borrowed capital (ROCE).
Return on capital owned by an organization reflects the effectiveness of investing funds in the functioning of the company.
The return on employed (borrowed) capital formula reflects the effectiveness of investments in the organization's work, both own and borrowed funds. Using this indicator, management can determine the degree of efficiency of using its own capital and raised funds in its activities in the long term (for example, investments).
Return on invested and permanent capital
Return on invested capital (ROI) characterizes the profitability of funds invested in commercial activities.
- Invested capital consists of the company's own funds and long-term liabilities.
- The profitability of IC is the ratio of profit to the size of IC.
- This indicator is often calculated to assess the feasibility of raising borrowed funds.
It characterizes the level of efficiency of attracting own and borrowed funds into the company’s activities for a long time.
Profitability (PC) is calculated as profit divided by the average cost of equity capital and long-term borrowings.
According to the financial statements, the indicator is calculated as follows:
Line 2400 of the income statement: (line 1300 + line 1530 of the balance sheet).
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Return on Total Capital Formula
The formula for return on total capital (assets, total funds) is determined by the ratio of book profit to the value of all assets of the enterprise. Using this formula, the return that falls on each ruble of assets is recorded.
The return on total capital can be modified if the value of net profit is placed in the numerator instead of book profit. In this case, we get the net return on total capital:
Rsk= PE / SK * 100%
Here Rsk is the return on capital indicator (%),
PE – net profit (rub.),
SC – total cost of capital (rub.).
All profitability values are determined as a percentage.
If you use financial statements in the calculation process, the formula for return on total capital will take the following form:
Rsk = line 2300 / line 1600
Here line 2300 is the amount of profit before tax from the income statement,
Line 1600 – the amount of the enterprise’s assets according to the balance sheet.
What is return on equity?
The most indicative economic coefficient of an enterprise’s activity is return on equity (ROC), which shows the size of the return on invested capital.
For business owners, the IC profitability ratio is very useful, since it characterizes the usefulness of the investment of the participants’ funds, and not the attracted capital.
- The SC profitability formula is the ratio of profit to SC.
- To calculate as a percentage, the result is multiplied by one hundred.
- For a more accurate calculation, use the arithmetic average of equity for the analyzed period.
Based on financial statements, profitability can be determined:
Line 190 (at the beginning of the period): 0.5 (line 490 (at the beginning of the period) + line 490 (at the end of the period).
When determining the profitability of an insurance company, the Dupont formula is also used:
SK profitability = (Net profit : Revenue) x (Revenue : Assets) x (Assets : SK) = Net profit margin x Asset turnover x Financial leverage.
But for the Russian economy with an inflationary component, this figure should be higher.
When analyzing the profitability of an insurance company, the resulting indicator is compared with the value of the alternative return that the owners could receive when investing their funds in another enterprise.
Return on total capital value
The value of return on total capital is influenced by the size of profit, as well as the ratio between liabilities and own resources. This ratio can be determined by the ratio of liabilities to capital (the “financial leverage” of the enterprise).
In the process of increasing obligations and increasing costs of servicing them, the company's management thus reduces profits and profitability.
The return on total capital formula is used in the capital comparison process:
- with similar indicators of other enterprises,
- with interest on bank deposits and the yield of government securities.
If the return on capital is less than the interest on the deposit (bonds) for the same time period, then investing in the project will not make sense. The optimal excess of profitability over these indicators is several times.