When calculating income tax, some expenses cannot completely reduce the taxable base. For such expenses, a rate is calculated within which they are included in the income tax base and reduced. Such expenses are called standardized. These include:
- expenses for voluntary insurance of employees;
- capital investment costs;
- depreciation rates;
- R&D expenses;
- entertainment expenses;
- advertising expenses;
- expenses for the sale of media and book products;
- expenses for acquiring rights to land plots;
- expenses for the formation of reserves for doubtful debts;
- expenses for creating a reserve for warranty repairs and warranty service;
- expenses for the formation of reserves for future expenses allocated for purposes ensuring social protection of people with disabilities;
- expenses in the form of interest on debt obligations;
- loss from assignment of the right of claim;
- expenses for the formation of a reserve for future expenses for repairs of fixed assets.
What is included in entertainment expenses?
The concept itself is very broad and it may not be completely clear to the average person what exactly is meant. Therefore, before reflecting entertainment expenses in 1C, understand the meaning of the concept. The table below contains a list of possible costs that can be included here.
| No. | Cost type | Characteristic |
| 1 | Entertainment expenses | Transporting people to and from the meeting venue |
| 2 | Catering services for events | |
| 3 | Conducting official receptions for meeting participants | |
| 4 | Payment for translator services during events outside the company's staff |
Tax nuances
In the interests of taxation of company profits, entertainment expenses are taken as standardized. The norms of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation state that during one tax period they are attributed to other expenses no more than 4% of the taxpayer’s expenses on payroll for the same period.
Value added tax deductions have their own nuances. The law stipulates that tax amounts on entertainment expenses related to the deduction when calculating the company’s income tax are deductible.
Advertising expenses
In paragraph 4 of Art. 264 states that advertising expenses can reduce the tax base only within 1% of sales revenue, determined in accordance with Article 249 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. But this does not apply to all types of advertising costs. The following expenses are not standardized for tax purposes:
- for advertising events through the media (including advertisements in print, radio and television) and telecommunication networks;
- illuminated and other outdoor advertising, including the production of advertising stands and billboards;
- participation in exhibitions, fairs, expositions; design of shop windows, sales exhibitions, sample rooms and showrooms; production of advertising brochures and catalogs containing information about goods sold (works, services), trademarks and service marks or about the organization itself; discounting of goods that have completely or partially lost their quality during exhibition.
If advertising expenses have arisen and the amount of revenue is not yet known, then such expenses cannot be written off.
Only after the reporting period for income tax has ended can the accountant take them into account. In this case, actual expenses are compared with those that are subject to rationing. Costs within normal limits are included in the tax base. How to deal with expenses that are incurred in excess of the norm? The tax period for income tax according to paragraph 1 of Article 285 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is a calendar year. The tax base is calculated on an accrual basis from the beginning of the year. Therefore, before the end of the tax period, expenses not taken into account in one reporting period can be recognized in the next reporting period.
Registration procedure in 1C
It is always easiest to use an example to understand the nuances of conducting any accounting procedures. This question will be no exception. Let’s assume that the company in question selling plastic products is a member of the OSN and pays VAT. The company held a meeting of potential buyers with the involvement of a catering company. All services of a third party were provided on the basis of an invoice and act.
Expenses for this event should be included in the costs of core activities, that is, sales expenses. They are fully attributed to the period when the act was signed and provided. In this case, it is worth using accounting account 44.01.
The accountant should include the amount spent on the reception as entertainment expenses as part of other expenses, but by law no more than the four percent threshold of the total payroll for the specified period. The machine, according to the regulations, normalizes all such expenses automatically at each close of the reporting month. However, you should be extremely careful in order for the machine to perform such an action, you need to let it understand what cost item was used. Therefore, it is extremely important to include entertainment expenses as an expense for a cost item.
Entertainment expenses in 1C: Enterprise Accounting 8.3.
Send this article to my email
Representation expenses are understood as the costs of an enterprise associated with organizing the reception of representatives of other companies in order to establish further cooperation with them.
Such expenses reduce taxable profit, but there are restrictions, namely, their amount for the current tax period should not be more than 4 percent of the taxpayer’s labor costs.
I will set up your 1C. Experience since 2004. Read more →
To correctly account for the costs incurred for entertainment expenses in 1C, we will create a special cost item in the program called “Entertainment expenses”, where the type of expense “Entertainment expenses” will be selected. This item will be used to reflect expenses for organizing an event, be it transportation costs for transporting guests, organizing dinner in a restaurant, paying for hotel rooms, etc.
Let's imagine a situation where it is necessary to reflect the cost of lunch in a cafe, where the company's partners are invited and where a presentation of the company's new product will be organized.
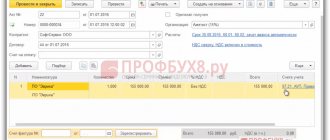
For these purposes, we will formalize the receipt of services, where the counterparty will be the owner of the restaurant; as services provided, we will create one item in the product directory, which will summarize all the services provided by this counterparty. In the cost accounts we will indicate: the accounting account where all costs will be written off (let it be account 26), and the item “Representation expenses” itself. Based on receipt, we will register an invoice.
Because The write-off of expenses of this type for tax accounting is carried out only taking into account restrictions, then it is necessary to carry out the procedure for rationing these expenses. This can be done by closing the month, as a result of which the document “Routine operation” will be drawn up with the form “Calculation of shares of write-off of indirect expenses”. The result of the standardization performed in the database will open when you click the “Show transactions” button.
For a better understanding, I will describe how the calculation occurred.
The costs of the receipt document amounted to 103,890 rubles. because Since these are the only expenses allocated to the expense item “Representation expenses” in this reporting period, they constitute the total amount of expenses for the year.
The amount of the base amounted to 375,000, in order to understand how it developed, you can open a balance sheet for account 70, where the amount of turnover on the loan is the wage fund. It follows that the amount of entertainment expenses written off for tax accounting in 1C cannot exceed 15,000 rubles.
The share of expenses written off is calculated using the formula [amount of entertainment expenses according to the standard] / [amount of expenses for entertainment expenses in total] (15,000 / 103,890= 0.14438348).
88,890 rub. – this is a constant difference, which is formed as the difference between the amount of entertainment expenses and the amount of entertainment expenses according to the standard for the month; when written off, it will be attributed to PR.
Write-off of entertainment expenses will be performed at the close of the month, as a result of which the document “Routine operation” will be generated with the type of operation “Closing accounts 20, 23, 25, 26”.
Watch video instructions on channel 1C PROGRAMMER EXPERT
EVERYONE MUST DO THEIR JOB! TRUST THE 1C SETUP TO A PROFESSIONAL. MORE →
Discuss the article on the 1C forum?
How to reflect the costs of servicing receptions
It is extremely rare for companies to manage on their own in order to organize a decent reception for third parties. Yes, actually, and why. There are special companies that will help with organizing the event and finding a location for it, and will think about what to feed the guests and how to entertain them in between negotiations. The machine contains special functionality for displaying purchased services from the following companies:
- Receipt (acts, invoices);
- Specify the type of service operation;
- In the title, indicate the specific counterparty from whom the services were accepted and under what contract;
- In the table, enter the nomenclature of the service, its price and at what rate VAT is charged;
- Enter accounting account 44.01 with analytical detail as entertainment expenses.
- For taxes, use the 19.04 accounting account and it is recommended to use the same accounts in both types of accounting so as not to bring them into compliance later;
- Register the invoice received for services provided.
Creation of a reserve for doubtful debts
In addition to actual expenses incurred, taxpayers can reduce the tax base for income tax by the amount of accrued reserves, for example, for doubtful debts.
The procedure for accounting for such expenses is specified in Article 266 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Amounts of deductions to reserves for doubtful debts are taken into account as part of non-operating expenses on the last day of the reporting (tax) period, except for the costs of creating reserves for the organization’s debts incurred due to non-payment of interest.
Accruals to the reserve are made after inventory of receivables in the following order. The reserve includes:
- the full amount of doubtful debts with a period of occurrence exceeding 90 days;
- 50% of the amount of doubtful debts with a period of occurrence from 45 to 90 days inclusive.
Doubtful debts with a maturity of up to 45 days are not included in the formation of the reserve.
Expenses can include not the entire amount of the accrued reserve, but only within 10% of the amount of sales revenue, calculated in accordance with Article 249 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Tax accounting
After the document is processed by the machine to record the amounts of such expenses, it separates the total amount spent and the amount of tax. In the interests of forming a purchase book, the machine makes an entry in the special VAT accumulation register in the field of the tax presented. The admission form is shown in the figure.
Only that part of the VAT that is attributed to taxable profit in terms of entertainment expenses can be deducted. But at the moment the number of such losses is unknown.
In order to comply with this provision of the law, it is worth deactivating the flag in the received invoice that reflects the VAT deduction in the purchase book by the date of receipt, of course, in the case when it was marked.
Closing the period
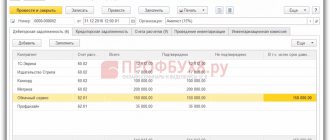
When the accountant begins the period-closing procedure, the machine starts the routine process of calculating the share of write-off of indirect expenses. He greatly facilitates the accountant’s fate and takes on the responsibility of calculating the costs of profit taxation based on standardized expenses. You will not receive accounting records based on the results and simply request a certificate of calculation for it after closing and carrying out the procedure. In it you will see the position that interests us. The help reflects information on:
- The total amount of expenses for representation purposes;
- The amount that can be taken to reduce the tax base;
- The amount of the constant difference for the remaining amount.
Here you will not see the basis for rationing in the form of labor costs. You have the right to check the regulatory processes carried out by the machine through tax accounting registers.
According to the register, the data of the general payroll is visible to the user, and when subordinates make insurance contributions on their own initiative, then this information goes to the expense register. for voluntary insurance
Voluntary insurance for employees
According to paragraph 16 of Article 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, costs for voluntary medical and pension insurance, as well as personal insurance for employees, are taken into account in the tax base as part of labor costs. Voluntary insurance premiums are included in the costs of contracts:
- long-term life insurance concluded for at least five years (within five years no insurance payments are provided, except in the event of the death of the insured person);
- non-state pension provision, subject to the application of a pension scheme that provides for the accounting of pension contributions on the personal accounts of participants in non-state pension funds, with the payment of pensions until the funds in the participant’s personal account are exhausted, but for at least five years;
- voluntary pension insurance, providing for the payment of pensions for life;
- voluntary personal insurance of employees, concluded for a period of at least one year and providing for payment of medical expenses by insurers;
- voluntary personal insurance in the event of death or loss of ability of the insured person to work in connection with the performance of his work duties.
The total amount of payments (contributions, expenses) of employers paid under such agreements is taken into account in an amount not exceeding 12% of the amount of labor costs.
When determining the amount of labor costs, it does not include the costs of voluntary insurance, mentioned in clause 16 of Art. 255 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. For the purpose of calculating corporate income tax, expenses for voluntary medical insurance of employees are recognized in an amount not exceeding 6 percent of labor costs. When determining the amount of labor costs, it does not include the costs of voluntary insurance, referred to in paragraphs. 16th century 255 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Also, expenses for voluntary insurance of employees against accidents for the purpose of calculating income tax in the tax base in the current period can only be included in the amount of 15,000 rubles per year per insured employee, calculated as the ratio of the total amount of contributions paid under these agreements to the number insured workers.