Current as of February 13, 2021
As of 2021, there are some changes to the BCC. In particular:
- approved by the KBK for a 15% personal income tax calculated on income exceeding 5 million rubles - 182 1 0100 110;
- KBK was introduced for payment of land tax in relation to plots located within the boundaries of municipal districts, it is necessary to transfer to KBK 182 1 0600 110;
- BCC appeared to pay the tax levied in connection with the use of PSN, credited to the budgets of municipal districts - 182 1 0500 110;
- The BCC was introduced for the payment of mineral extraction tax on the extraction of other minerals, in respect of which a rental coefficient other than 1 is established for taxation, - 182 1 07 01080 01 1000 110.
BCCs for basic taxes/contributions remained unchanged.
Below you will find tables with the BCC for 2021 for basic taxes and insurance premiums.
KBK 2021 - Personal Income Tax (NDFL), transcript
| Name of tax, fee, payment | KBK |
| Corporate income tax (except for corporate tax), including: | |
| — to the federal budget (rate — 3%) | 182 1 0100 110 |
| — to the regional budget (rate from 12.5% to 17%) | 182 1 0100 110 |
| VAT | 182 1 0300 110 |
| Property tax: | |
| - for any property, with the exception of those included in the Unified Gas Supply System (USGS) | 182 1 0600 110 |
| - for property included in the Unified State Social System | 182 1 0600 110 |
| Personal income tax (individual entrepreneur “for yourself”) | 182 1 0100 110 |
| Name of tax, fee, payment | KBK |
| Personal income tax on income the source of which is a tax agent | 182 1 0100 110 |
| VAT (as tax agent) | 182 1 0300 110 |
| VAT on imports from Belarus and Kazakhstan | 182 1 0400 110 |
| Income tax on dividend payments: | |
| — Russian organizations | 182 1 0100 110 |
| - foreign organizations | 182 1 0100 110 |
| Income tax on the payment of income to foreign organizations (except for dividends and interest on state and municipal securities) | 182 1 0100 110 |
| Income tax on income from state and municipal securities | 182 1 0100 110 |
| Income tax on dividends received from foreign organizations | 182 1 0100 110 |
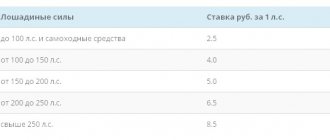
| Transport tax | 182 1 0600 110 |
| Land tax | 182 1 06 0603х хх 1000 110 where xxx depends on the location of the land plot |
| Water tax | 182 1 0700 110 |
| Payment for negative impact on the environment | 048 1 12 010x0 01 6000 120 where x depends on the type of environmental pollution |
| MET | 182 1 07 010хх 01 1000 110 where хх depends on the type of mineral being mined |
| Corporate income tax on income in the form of profits of controlled foreign companies | 182 1 0100 110 |
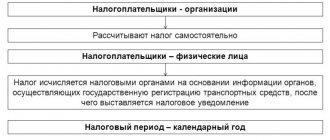
Depending on what kind of legal entity the organization is and for whom personal income tax is paid, three cases are distinguished. So, when paying personal income tax for employees, the tax agent uses the code for taxes (not penalties or fines!) from the first row of the table. The same code is used for the tax agent paying personal income tax on dividends paid. The third case is a payment from an individual entrepreneur for himself, in which the tax BCC from the second line is used.
In a number of cases, individuals are forced to file an income statement in form 3-NDFL and enter the correct BCC into it. Here are some of the most common cases:
- Selling a car less than 5 years old
- Receiving income from renting out an apartment/car
- Receiving dividends (from which personal income tax was not withheld by tax agents)
- Winning the lottery
All these cases use the BCC from the third row of the table and are regulated by Art. 228 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. It is worth noting that the KBK of personal income tax differs for individuals who are tax residents and non-residents of the Russian Federation. Codes for non-residents are indicated in the last row of the table. Let us remind you that in order to obtain the status of a tax resident of the Russian Federation, an individual must stay in the territory of the Russian Federation for at least 183 days in total for 12 consecutive months.
- Pension contributions. Decoding codes for the budget classification of pension contributions for 2021.
- Contributions to compulsory social insurance. Decoding codes for the budget classification of contributions to compulsory social insurance for 2021.
- Contributions for compulsory health insurance. Decoding codes for the budget classification of contributions for compulsory health insurance for 2021.
- Value added tax (VAT). Decoding the budget classification codes for value added tax (VAT) 2021.
- Income tax. Decoding the 2021 income tax budget classification codes.
- Excise taxes. Decoding the codes for the budget classification of excise taxes for 2021.
- Organizational property tax. Decoding the codes of the budget classification of property tax for organizations 2021.
- Land tax. Deciphering the codes for the budget classification of land tax for 2021.
- Transport tax. Deciphering the transport tax budget classification codes for 2021.
- Single tax with simplification. Decoding the codes of the budget classification of the single tax during simplification for 2021.
- Unified tax on imputed income (UTII). Decoding codes for the budget classification of the single tax on imputed income (UTII) 2021.
- Unified Agricultural Tax (USAT). Decoding the codes of the budget classification of the Unified Agricultural Tax (USAT) 2021.
- Mineral extraction tax (MET). Deciphering the budget classification codes for mineral extraction taxes (MET) 2021.
- Fee for the use of aquatic biological resources. Decoding the budget classification codes of the fee for the use of aquatic biological resources for 2021.
- Fee for the use of fauna objects. Deciphering the codes of the budget fee for the use of wildlife objects in 2021.
- Water tax. Decoding the codes of the budget classification of water tax for 2021.
- Payments for the use of subsoil. Decoding codes for the budget classification of payments for the use of subsoil for 2021.
- Payments for the use of natural resources. Decoding codes for the budget classification of payments for the use of natural resources for 2021.
- Gambling tax. Deciphering the budget classification codes for the gambling tax for 2021.
- Government duty. Decoding the codes of the budget classification of state duty for 2021.
- Income from the provision of paid services and compensation for state costs. Decoding codes for the budget classification of income from the provision of paid services and compensation for state expenses in 2021.
- Fines, sanctions, payments for damages. Decoding codes for the budget classification of fines, sanctions, payments for damages in 2021.
- Trade fee. Decoding the codes of the budget classification of trade tax for 2021.
- News. All news on changes in (KBK) budget classification codes for past and current years.
| Payment Description | KBK |
| Income tax, which is charged to the federal budget (except for consolidated groups of taxpayers) | 182 1 0100 110 |
| Income tax, which is charged to the budgets of constituent entities of the Russian Federation (except for consolidated groups of taxpayers) | 182 1 0100 110 |
| Income tax, which is charged to the federal budget (for consolidated groups of taxpayers) | 182 1 0100 110 |
| Income tax, which is charged to the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation (for consolidated groups of taxpayers) | 182 1 0100 110 |
| VAT, excluding import | 182 1 0300 110 |
| Tax on property not included in the Unified Gas Supply System | 182 1 0600 110 |
| Tax on property included in the Unified Gas Supply System | 182 1 0600 110 |
| Simplified tax with the object “income” | 182 1 0500 110 |
| Simplified tax with the object “income minus expenses”, including the minimum tax | 182 1 0500 110 |
| UTII | 182 1 0500 110 |
| Unified agricultural tax | 182 1 0500 110 |
| Personal income tax for a tax agent | 182 1 0100 110 |
| Transport tax | 182 1 0600 110 |
| Land tax from plots of Moscow, St. Petersburg, Sevastopol | 182 1 0600 110 |
| Payment Description | KBK |
| Pension contributions at basic and reduced rates | 182 1 0210 160 |
| Pension contributions at an additional tariff that does not depend on the special assessment (list 1) | 182 1 0210 160 |
| Pension contributions at an additional tariff depending on the special assessment (list 1) | 182 1 0200 160 |
| Pension contributions at an additional tariff that does not depend on the special assessment (list 2) | 182 1 0210 160 |
| Pension contributions at an additional tariff depending on the special assessment (list 2) | 182 1 0200 160 |
| Medical fees | 182 1 0213 160 |
| Social contributions | 182 1 0210 160 |
| Contributions for injuries | 393 1 0200 160 |
| Payment Description | KBK |
| Pension contributions at basic and reduced rates | 182 1 0210 160 |
| Pension contributions at an additional tariff that does not depend on the special assessment (list 1) | 182 1 0210 160 |
| Pension contributions at an additional tariff depending on the special assessment (list 1) | 182 1 0200 160 |
| Pension contributions at an additional tariff that does not depend on the special assessment (list 2) | 182 1 0210 160 |
| Pension contributions at an additional tariff depending on the special assessment (list 2) | 182 1 0200 160 |
| Medical fees | 182 1 0213 160 |
| Social contributions | 182 1 0210 160 |
| Contributions for injuries | 393 1 0200 160 |
Individual entrepreneurs pay the BCC on their own. If an individual entrepreneur simultaneously works as an employee, he still must pay contributions for himself - as an individual entrepreneur.
Entrepreneurs are required to pay mandatory contributions to their own pension and health insurance until they are “listed” as individual entrepreneurs and have a Unified State Register of Entrepreneurs (USRIP) entry about them. The age of the entrepreneur and occupation does not matter. And most importantly, contributions must be paid even if the individual entrepreneur does not receive any income.
| TAX | KBK |
| Personal income tax on income the source of which is a tax agent (personal income tax for employees of individual entrepreneurs, LLCs and JSCs) | 182 1 01 02010 01 1000 110 |
| PENALIES, INTEREST, FINES | KBK | |
| Penalties, interest, personal income tax fines on income the source of which is a tax agent (personal income tax for employees of individual entrepreneurs, LLCs and JSCs) | penalties | 182 1 01 02010 01 2100 110 |
| interest | 182 1 01 02010 01 2200 110 | |
| fines | 182 1 01 02010 01 3000 110 | |
For individual entrepreneurs
| TAX | KBK |
| Personal income tax on income received by citizens registered as: individual entrepreneur; private lawyers; notaries; other persons engaged in private practice (personal income tax for individual entrepreneurs for themselves) | 182 1 01 02020 01 1000 110 |
KBK Personal Income Tax in 2021 (IP “for oneself”, dividends and other income)
| PENALIES, INTEREST, FINES | KBK | |
| Penalties, interest, personal income tax fines on income received by citizens registered as: individual entrepreneur; private lawyers; notaries; other persons engaged in private practice (personal income tax for individual entrepreneurs for themselves) | penalties | 182 1 01 02020 01 2100 110 |
| interest | 182 1 01 02020 01 2200 110 | |
| fines | 182 1 01 02020 01 3000 110 | |
For individuals
| TAX | KBK |
| Personal income tax on income received by citizens in accordance with Article 228 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (personal income tax for individuals who must independently pay tax on their income) | 182 1 01 02030 01 1000 110 |
| PENALIES, INTEREST, FINES | KBK | |
| Penalties, interest, personal income tax fines on income received by citizens in accordance with Article 228 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (personal income tax for individuals who must independently pay tax on their income) | penalties | 182 1 01 02030 01 2100 110 |
| interest | 182 1 01 02030 01 2200 110 | |
| fines | 182 1 01 02030 01 3000 110 | |
From dividends and working under a patent
| TAX | KBK |
| Personal income tax on dividends, the recipient of the dividends is a tax agent | 182 1 01 02010 01 1000 110 |
| Personal income tax on dividends, dividend recipient - individual | 182 1 01 02030 01 1000 110 |
Every accountant knows that in order to make a payment correctly, be it taxes, contributions or penalties, it is important to enter the correct budget classification code. Therefore, it is necessary to update the database of new codes, since the old ones will become invalid, and payments made using them will be returned to the sender or will be regarded as unclear. Such a development of events is fraught with the accrual of penalties and the application of fines .
There are no small things in life, especially when it comes to finances and paperwork. To avoid administrative penalties and other troubles, you should carefully study the changes in the maintenance of documentation on fees for income for employees and the transfer of deductions for 2021. We will talk about the nuances associated with wages, sick pay, vacation pay and travel allowances.
must be paid no later than the day following the day the employee (individual) is paid income. For example, the employer paid the salary for January 2021 on February 5, 2021. The date of receipt of income will be January 31, 2021, the tax withholding date will be February 5, 2021. The date no later than which personal income tax must be paid to the budget, in our example – February 8, 2021 (since the 6th and 7th are weekends).
- Documents will not be accepted if there are errors in personal data. Such a source will be considered unreliable.
- You should be more careful about paying bonuses in the month of filing the declaration. The absence of such payments in the total amount may be interpreted by the tax office as a reduction in the figure.
- Lateness of more than one day with the transfer of tax in cases where the employee received wages, travel allowances, compensation for unused vacation.
- The tax transfer occurred later than the previous month, in which sick leave and vacation pay were paid.
First of all, you should carefully carry out calculations when drawing up documents - this is the best way to avoid fines. If a problematic situation arises, you can provide clarifying documents. In this case, payment must be made before delivery of additional documents. A fine for late payment may not be imposed in cases where the declaration was submitted on time and did not contain errors. It should be understood that in this situation it is necessary to deposit funds with the tax office until the actual discovery of the shortfall.
| Payment Description | KBK |
| Income tax, which is charged to the federal budget (except for consolidated groups of taxpayers) | 182 1 0100 110 |
| Income tax, which is charged to the budgets of constituent entities of the Russian Federation (except for consolidated groups of taxpayers) | 182 1 0100 110 |
| Income tax, which is charged to the federal budget (for consolidated groups of taxpayers) | 182 1 0100 110 |
| Income tax, which is charged to the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation (for consolidated groups of taxpayers) | 182 1 0100 110 |
| VAT, excluding import | 182 1 0300 110 |
| Tax on property not included in the Unified Gas Supply System | 182 1 0600 110 |
| Tax on property included in the Unified Gas Supply System | 182 1 0600 110 |
| Simplified tax with the object “income” | 182 1 0500 110 |
| Simplified tax with the object “income minus expenses”, including the minimum tax | 182 1 0500 110 |
| UTII | 182 1 0500 110 |
| Unified agricultural tax | 182 1 0500 110 |
| Personal income tax for a tax agent | 182 1 0100 110 |
| Transport tax | 182 1 0600 110 |
| Land tax from plots of Moscow, St. Petersburg, Sevastopol | 182 1 0600 110 |
The KBK budget classification codes for 2021 were approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 06/08/2020 No. 99n. These codes must be indicated in payment orders when paying penalties on taxes in 2021.
| Payment Description | KBK |
| Income tax, which is charged to the federal budget (except for consolidated groups of taxpayers) | 182 1 0100 110 |
| Income tax, which is charged to the budgets of constituent entities of the Russian Federation (except for consolidated groups of taxpayers) | 182 1 0100 110 |
| Income tax, which is charged to the federal budget (for consolidated groups of taxpayers) | 182 1 0100 110 |
| Income tax, which is charged to the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation (for consolidated groups of taxpayers) | 182 1 0100 110 |
| VAT | 182 1 0300 110 |
| Tax on property not included in the Unified Gas Supply System | 182 1 0600 110 |
| Tax on property included in the Unified Gas Supply System | 182 1 0600 110 |
| Simplified tax with the object “income” | 182 1 0500 110 |
| Simplified tax with the object “income minus expenses” | 182 1 0500 110 |
| UTII | 182 1 0500 110 |
| Unified agricultural tax | 182 1 0500 110 |
| Personal income tax for a tax agent | 182 1 0100 110 |
| Transport tax | 182 1 0600 110 |
| Land tax from plots of Moscow, St. Petersburg, Sevastopol | 182 1 0600 110 |
BCC for 2021 was approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 06/08/2020 No. 99n. These codes must be indicated in payment orders when paying tax fines in 2021.
| Payment Description | KBK |
| Income tax, which is charged to the federal budget (except for consolidated groups of taxpayers) | 182 1 0100 110 |
| Income tax, which is charged to the budgets of constituent entities of the Russian Federation (except for consolidated groups of taxpayers) | 182 1 0100 110 |
| Income tax, which is charged to the federal budget (for consolidated groups of taxpayers) | 182 1 0100 110 |
| Income tax, which is charged to the budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation (for consolidated groups of taxpayers) | 182 1 0100 110 |
| VAT | 182 1 0300 110 |
| Tax on property not included in the Unified Gas Supply System | 182 1 0600 110 |
| Tax on property included in the Unified Gas Supply System | 182 1 0600 110 |
| Simplified tax with the object “income” | 182 1 0500 110 |
| Simplified tax with the object “income minus expenses” | 182 1 0500 110 |
| UTII | 182 1 0500 110 |
| Unified agricultural tax | 182 1 0500 110 |
| Personal income tax for a tax agent | 182 1 0100 110 |
| Transport tax | 182 1 0600 110 |
| Land tax from plots of Moscow, St. Petersburg, Sevastopol | 182 1 0600 110 |
The Ministry of Finance of Russia approved new budget classification codes for payment orders for insurance contributions by order No. 99n dated 06/08/2020.
| Payment Description | KBK |
| Pension contributions at basic and reduced rates | 182 1 0210 160 |
| Pension contributions at an additional tariff that does not depend on the special assessment (list 1) | 182 1 0210 160 |
| Pension contributions at an additional tariff depending on the special assessment (list 1) | 182 1 0220 160 |
| Pension contributions at an additional tariff that does not depend on the special assessment (list 2) | 182 1 0210 160 |
| Pension contributions at an additional tariff depending on the special assessment (list 2) | 182 1 0220 160 |
| Medical fees | 182 1 0213 160 |
| Social contributions | 182 1 0210 160 |
| Contributions for injuries | 393 1 0200 160 |
Budget Classification Codes (BCC) - Personal Income Tax (NDFL)
| Payment Description | KBK |
| Pension contributions at basic and reduced rates | 182 1 0210 160 |
| Pension contributions at an additional tariff that does not depend on the special assessment (list 1) | 182 1 0210 160 |
| Pension contributions at an additional tariff depending on the special assessment (list 1) | 182 1 0200 160 |
| Pension contributions at an additional tariff that does not depend on the special assessment (list 2) | 182 1 0210 160 |
| Pension contributions at an additional tariff depending on the special assessment (list 2) | 182 1 0200 160 |
| Medical fees | 182 1 0213 160 |
| Social contributions | 182 1 0210 160 |
| Contributions for injuries | 393 1 0200 160 |
| Payment Description | KBK |
| Pension contributions at basic and reduced rates | 182 1 0210 160 |
| Pension contributions at an additional tariff that does not depend on the special assessment (list 1) | 182 1 0210 160 |
| Pension contributions at an additional tariff depending on the special assessment (list 1) | 182 1 0200 160 |
| Pension contributions at an additional tariff that does not depend on the special assessment (list 2) | 182 1 0210 160 |
| Pension contributions at an additional tariff depending on the special assessment (list 2) | 182 1 0200 160 |
| Medical fees | 182 1 0213 160 |
| Social contributions | 182 1 0210 160 |
| Contributions for injuries | 393 1 0200 160 |
Individual entrepreneurs pay the BCC on their own. If an individual entrepreneur simultaneously works as an employee, he still must pay contributions for himself - as an individual entrepreneur.
Entrepreneurs are required to pay mandatory contributions to their own pension and health insurance until they are “listed” as individual entrepreneurs and have a Unified State Register of Entrepreneurs (USRIP) entry about them. The age of the entrepreneur and occupation does not matter. And most importantly, contributions must be paid even if the individual entrepreneur does not receive any income.
- KBK for personal income tax in 2021
- KBK for insurance premiums
- Full table of BCC for insurance premiums 2021
- We pay insurance premiums
- We pay personal income tax for employees
- Innovations for 2021
Now, too, the tax agent maintains separate tax bases for each type of income, for which different tax rates are established. In addition, a separate tax base is maintained for income from equity participation (dividends). This means that for income taxed at a rate of 13%, you need to maintain 2 tax bases.
According to the new procedure, the number of tax bases for income taxed at a rate of 13% increases for tax residents of the Russian Federation to 9, and for non-residents - to 8. Here are the tax bases provided for tax residents of the Russian Federation by the new paragraph 2.1 of Article 210 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation:
- tax base for income from equity participation;
- tax base for income in the form of winnings received by gambling participants and lottery participants;
- tax base for income from transactions with securities and transactions with derivative financial instruments;
- tax base for repo transactions, the object of which are securities;
- tax base for securities lending transactions;
- tax base for income received by participants of the investment partnership;
- tax base for transactions with securities and for transactions with derivative financial instruments accounted for in an individual investment account;
- tax base for income in the form of amounts of profit of a controlled foreign company;
- tax base for other income in respect of which the tax rate provided for in paragraph 1 of Article 224 of this Code is applied (hereinafter in this chapter - the main tax base).
It is clear that many tax agents will not have the majority of such income, so the change will be felt only by those enterprises that pay these incomes.
Please note the new term “basic base”; it will include the majority of employee income: wages, vacation pay, sick leave, financial assistance and others.
Code structure
Each budget systematization code, in order to carry out the procedure for paying both the contribution and any penalties, is based on several parts:
- "administrator";
- “type of income”;
- "subgroups";
- "article";
- "element";
- "program";
- "economic classification".
The combination of numbers located under the name “administrator” includes additional 3 parts. They determine the work of the administrator, who is necessary to redirect funds to the government agency. The Federal Tax Service (FTS) is used to pay transport fees. The category for these tasks looks like 182. The subsequent digital set, called the “type of income,” consists of all digital combinations starting from 4 to 13 digits.
How to correctly fill out a personal income tax payment order in 2021
Tax deductions of all types: standard, social, property, professional - will be applied only to income reflected in the main base.
Calculation of personal income tax
But personal income tax will be calculated not for each individual tax base, but for total income in all tax bases, taxed at the same rate.
This means that in 2021, for tax residents, we will not calculate tax separately from salaries, but separately from dividends, but will calculate accrued wages and other work-related payments and dividends from the total income. Tax calculation will continue to be made at each time the taxpayer receives income, on an accrual basis from the beginning of the year, taking into account the previously withheld tax amount.
Calculation of personal income tax on the income of tax non-residents will be carried out in the same manner: separately dividends at a rate of 15%, separately other income at a rate of 30%.
The progressive personal income tax scale is very simple. As long as the taxable income of the taxpayer, taking into account deductions of all types, on an accrual basis from the beginning of the year does not exceed 5 million rubles, personal income tax is calculated at a rate of 13%. As soon as taxable income exceeds 5 million rubles, personal income tax is calculated as 650 thousand rubles plus 15% of the amount exceeding 5 million rubles.
The difference between the cumulative personal income tax calculated and the tax transferred to the budget for the previous period of the year is paid to the budget. Payment of tax on amounts of income taxed at different rates will be made using different payment orders and, most likely, according to different BCCs.
Changing the rules for calculating personal income tax will require changes to all tax reporting. Perhaps the Federal Tax Service will come up with new reporting forms or abolish existing ones. Let's get ready.
It is worth noting that a bill is being discussed here that has not even passed the first reading. It is possible that changes will be made to it during the discussion. After the final version of the law is adopted, we intend to return to its discussion.
The deadline for paying the fee is specified in Part 6 of Art. 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation - no later than the day following the day of payment of the amount of income to the taxpayer. In accordance with the letter of the Federal Tax Service No. BS-4-11/320 dated January 15, 2016, no tax is paid on the advance, with the exception of the case of transfer of the advance on the last day of the month. Vacation and sick leave benefits are also subject to this mandatory fee, but it is paid no later than the last day of the month in which they were paid to the taxpayer. You can calculate the tax amount using a calculator.
When filling out a payment slip for personal income tax, KBC is required to indicate the correct codes in order to avoid the accrual of penalties for late fulfillment of financial obligations. To avoid mistakes when filling out a payment order, check the table.
| Type of tax, payment | Code in 2021 |
| Personal income tax on employee income | 182 1 0100 110 |
| Penalty | 182 1 0100 110 |
| Fines | 182 1 0100 110 |
| Collection from individual entrepreneurs to OSN | 182 1 0100 110 |
| Penalty | 182 1 0100 110 |
| Fines | 182 1 0100 110 |
BCC “Penalty Tax Penalties”, as well as BCC for fines, differ from the basic values.
Code values often change (in this case, the Ministry of Finance issues an explanatory order), but sometimes they are retained for a longer period. Thus, in 2021, the same BCCs for personal income tax apply as in 2021, in accordance with Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 132n dated 06/08/2018.
What do the codes classify?
The numerical number of budget systematization makes it possible to realize the comparability of characteristics of various types. The BCC is applied in cases where one of the parties to financial transactions belongs to the state. These figures classify the following indicators:
- profit;
- expenses;
- operations;
- ways to finance budget deficits.
The structure of sections and subsections is holistic in nature and is used during the preparation, approval and payment of budgets at various levels. The classification of points is arranged in such an order as to achieve the most complete and detailed specification of each process.
Further specification of costs is carried out at the level of targeted items and standard costs in the process of drawing up the corresponding budgets.