The joint stock company is obliged to conduct an annual audit of the annual accounting (financial) statements, present and disclose the audit results (audit report) in accordance with the requirements:
- Federal Law “On Auditing Activities” dated December 30, 2008 N 307-FZ: clause 1, article 5. (until 01/01/2021)
- Federal Law “On Joint Stock Companies” dated December 26, 1995 N 208-FZ: clause 3, article 88.
- Civil Code of the Russian Federation (part one): clause 5 of Art. 67.1.
- “Regulations on the disclosure of information by issuers of equity securities” (approved by the Bank of Russia on December 30, 2014 N 454-P): Chapter 71.
- Federal Law “On State Registration of Legal Entities and Individual Entrepreneurs” dated 08.08.2001 N 129-FZ: clause 7 of Art. 7.1.
IMPORTANT ! Joint-stock companies are required to undergo mandatory audits annually, regardless of financial indicators (amount of income and assets), or affiliation with small businesses. An audit of a joint stock company is required for 2021!
Which organizations are required to conduct a mandatory audit of reporting: 6 cases under Law No. 307-FZ
Which organizations are required to conduct audits? In Art. 5 of the Law “On Auditing Activities” dated December 30, 2008 No. 307-FZ lists cases of conducting a mandatory audit. The law describes the criteria for organizations subject to mandatory audit, as well as other conditions taken into account when deciding when to conduct a mandatory audit:
In fact, the list of cases of mandatory audit is open. This means that companies not listed there may also be subject to mandatory audit if such a requirement is established by other federal laws.
See also:
- “Small businesses have been exempted from mandatory audit: the law has been adopted”;
- “Standard audit for 2021: new criteria and table.”
Next, we will consider the main cases of mandatory audit under Law No. 307-FZ (in the figure these are cases 1-5). Case 6 does not require special decoding, since the law lists specific organizations. They are required to conduct an audit annually, regardless of the fulfillment/non-fulfillment of other mandatory audit criteria.
Find out how to pass a mandatory audit in the Typical Situation from ConsultantPlus. Learn the material by getting trial access to the system for free.
How to avoid liability for failure to conduct an audit?
The cost of a mandatory audit in most cases is significantly less than administrative fines. In addition, by undergoing an audit in our company, you will receive not only an audit report, but also a report on identified risks, which, by preventing them in a timely manner, you can significantly protect your company and avoid serious consequences.
The Central Bank of the Russian Federation (Bank of Russia), Rosstat, the tax inspectorate, the Central Election Commission, as well as the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation can bring an organization to administrative responsibility for failure to conduct a mandatory audit or violation of deadlines.
PJSC or JSC: who needs to audit the statements
Legislators have singled out the obligation to conduct audits by joint-stock companies as a separate case. As soon as the phrase “joint stock company” appears in the legal name of a company, it automatically has an obligation to conduct an audit. It does not matter whether this form was chosen by the owners when the company was founded or whether it acquired this status after a transformation or change of organizational and legal form. The form does not matter: PJSC or JSC.
Which companies are recognized as joint stock companies and what types of them exist are shown in the figure:
Contents of the audit of a charitable foundation
Auditors who evaluate the activities of charitable foundations in the process of work:
- identify the correctness of accounting of allocated funds;
- check compliance with the requirements specified in contracts and agreements;
- determine the quality of reflection of business results in reports;
- identify cases of wasteful spending of funds;
- check the effectiveness of the acquisition and use of resources;
- evaluate analytical and synthetic accounting of expenditure and revenue parts;
- monitor compliance with the tax deduction regime;
- prepare recommendations for eliminating detected violations to improve the efficiency of the fund.
Are you allowed to participate in organized trading? Get ready for the audit!
If an issuing company wishes to include its securities in the quotation list, it must submit an application of a certain form to the auction organizer and provide detailed information about itself. The standards for admission of securities to public placement, circulation and listing are given in Art. 14 of the Law “On the Securities Market” dated April 22, 1996 No. 39-FZ and in the Regulations on the admission of securities to organized trading (approved by the Bank of Russia dated February 24, 2016 No. 534-P).
The fact that the issuing company's securities are admitted to organized trading places it in the category of persons obligated to audit the financial statements.
The intricacies of accounting and taxation of transactions with securities will be revealed in the following materials:
- “Is the sale of securities subject to VAT?”;
- “Accounting for securities in accounting (nuances).”
What is meant by mandatory audit of a JSC
An audit of a closed joint stock company is an inspection carried out by persons who are not part of the joint stock company. The main purpose of the audit is to systematize the documents of the company and objectively assess the legality and reliability of the data specified in the financial statements.
There are several fundamental objectives of statutory audit.
- Assessing the correctness of accounting records.
- Assessing the legality and authenticity of the data specified in the submitted documentation.
- Assistance and assistance to CJSC participants in maintaining accounting records based on identified shortcomings and violations in the organization’s documents.
- Checking for compliance of tax documentation with the current legislation of the Russian Federation.
- Analysis of the prospects for further growth of the company relative to existing financial reserves.
Depending on the type of activity of the JSC, the mandatory audit may be modified and supplemented. The auditor's main opinion about the audited object must be supported by the following criteria: correct classification of the type of activity, validity of maintaining a number of accounting documents, accuracy in reporting and the presence/absence of hidden payments.
How the type of reporting prepared affects the obligation of an audit
If a company presents and/or publishes summary (consolidated) financial statements, it automatically falls under mandatory audit (Clause 5, Article 5 of Law No. 307-FZ).
The requirements for consolidated reporting (its preparation, presentation and disclosure) are established by the Law “On Consolidated Financial Reporting” dated July 27, 2010 No. 208-FZ. The main provisions of this law, which help to understand the nuances of consolidated reporting, are presented in the figure:
Presentation and disclosure of consolidated financial statements is a process monitored by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation (with the exception of certain categories of reporting companies).
Find out more about the specifics of preparing consolidated financial statements here.
Violation of mandatory audit requirements by political parties (Article 5.68 of the Administrative Code)
The head of a political party may be held administratively liable. In this case, the administrative fine may range from 50,000 to 100,000 rubles. A political party can be fined from 500,000 to 1,000,000 rubles.
Administrative liability arises in the event of failure to comply with the requirements for a mandatory audit of the annual accounting (financial) statements and the consolidated financial report of a political party, as well as violation of the deadlines for conducting a mandatory audit of submitting a copy of the audit report to the Central Election Commission of the Russian Federation.
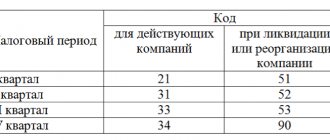
Revenue exceeded the criterion of 800 million by 1 ruble - an audit is inevitable
The number of persons required to conduct an audit may include companies that have never encountered an audit. To do this, it is enough to exceed the threshold level for one or both financial indicators specified in paragraph 4 of Art. 5 of Law No. 307-FZ.
The specific cost criteria in question are shown in the figure:
Who should conduct a statutory audit if the specified financial indicators are exceeded? Does the legal form of the company or its types of activities matter? In this case, exceeding one or both financial indicators is a separate criterion based on which a mandatory audit is assigned.
Example
The production structure of TekhnoStroyProekt LLC has been designing and manufacturing specialized electrical installations for the last 10 years. Thanks to a large contract in 2020, sales revenue amounted to RUB 801,331,120. The amount of assets at the end of this period is RUB 20,678,455.
Of the two criteria, only one was exceeded, however, TekhnoStroyProekt LLC is obliged to conduct an audit for 2021 and submit an audit report.
It does not matter that revenue exceeded the threshold level by only a fraction of a percent. For any excess of the established criterion (even by 1 ruble), the law requires an audit.
The considered cases of conducting a mandatory audit in accordance with the requirements of Law No. 307-FZ are not a complete list. We will tell you further who else is required to audit the annual financial statements.
Find out what is the responsibility for failure to conduct a mandatory audit in ConsultantPlus. If you don't have access to the system, get a free trial online.
Responsibility for failure to conduct a mandatory audit
Gross violation of accounting and reporting requirements (Article 15.11 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation)
A gross violation of accounting and reporting requirements, among other things, also means the absence of an auditor’s report on the accounting (financial) statements (if an audit of the accounting (financial) statements is mandatory).
The fines provided for in Art. 15.11 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation: administrative fine for officials - from 5,000 to 10,000 rubles, and in case of repeated violation - up to 20,000 rubles. or disqualification.
At the same time, the statute of limitations for bringing to administrative responsibility has been increased to 2 years from the date of commission of the administrative offense.
Failure to provide an audit report to Rosstat (Article 19.7 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation)
Failure to submit or untimely submission of information (information), the submission of which is provided for by law, or the presentation of such information (information) incompletely or in a distorted form constitutes an administrative offense under Art. 19.7 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation on administrative offenses. The Federal Tax Service may impose an administrative fine for failure to provide an audit report :
for citizens in the amount of 100 to 300 rubles;
for officials - from 300 to 500 rubles;
for legal entities - from 3,000 to 5,000 rubles.
At the same time , the imposition of an administrative penalty does not relieve a person from fulfilling the obligation for non-fulfillment of which the administrative penalty was imposed (Part 4 of Article 4.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation). Thus, a legal entity must submit an audit report to the tax office.
Results
Cases when a mandatory audit is needed are described in Law No. 307-FZ and many other federal laws. This category includes joint-stock companies, organizations with a certain amount of revenue and amount of assets, as well as many other business entities (whose securities are admitted to organized trading, publish consolidated statements, etc.).
Sources:
- Federal Law of July 27, 2010 No. 208-FZ
- Federal Law of December 30, 2008 No. 307-FZ
- Federal Law of April 22, 1996 No. 39-FZ
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.