Home Accounting and HR Accounting
How to find out the budget classification code is a pressing question, primarily because budget codes are used very often. They are needed when preparing tax returns, paying state duties, taxes, fines, fees, etc. Let us remind you that each payer must indicate the BCC on payment receipts to repay his payment obligations to the state, since this code indicates the type of payment being made and its recipient. In declarations, it is needed for further correct processing of your documents by the tax service.
In addition, budget codes are needed for the accurate and smooth functioning of the budget system itself. The financial flows of income and expenditure of the state budget are huge. Therefore, all types of cash receipts and their expenditure in state budgets of various levels are coded using a special KBK classifier, which is approved annually by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation. The classification of sections and subsections of the KBK directory is uniform throughout the Russian Federation.
The structure of the encodings provides maximum detail and specification of budget revenue and expenditure items.
Despite the fairly large number of codes used, the general classifier is written in such a way that it is easy to navigate. Thanks to the well-thought-out structure of the classifier sections, you can quite easily find the required code for each specific case.
Although the KBK has a twenty-digit digital designation, we still note that it is quite possible to understand the meaning and purpose of its parts, and therefore learn how to correctly apply budget codes.
Today we will try to understand the structure of such codes, how they are used and where to find them.
How to find out the BCC of an organization by TIN, OKTMO, online
The article provides a brief description of budget classification codes and a definition of the structure of the cipher.
If you want to understand how to find out the BCC of an organization by TIN and OKTMO, then let’s say right away that this is impossible: these concepts are in no way related to each other. However, you can find the KBK online - detailed instructions are given in the corresponding paragraph. Any financial transactions made by the organization are reflected in payment orders when sending funds. When making contributions or paying tax amounts, the payer indicates in the payment slip the type of payment, encrypted under the abbreviation KBK.
How to find out BCC by OKTMO
It is also impossible to find out the BCC of an organization using OKTMO. But, knowing the TIN, you can clarify OKTMO. This can be done on the Rosstat website.
To do this, on the specified site, on the left side, select the region you are interested in and click on it with the cursor. On the page that opens, click the “Legal Entities” tab and then enter the INN, OKPO or OGRN and click the “Search” button.
The search form looks like this.
Code structure
According to Art. 1 Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia No. 65n dated July 1, 2013 (as amended November 26, 2018), budget classification codes (KBK) are a combination of 20 digits that reflect the type of payment. Accordingly, the code is needed to transfer funds for the required operation. If you specify an incorrect code, the payment will remain unclear and will not be counted toward the payment of, for example, a fine or the next fee.
The numbers are divided into three blocks, each covering several combinations. Blocks:
- The first is the code of the main distributor of money from the budget. It always starts with the number 182 (Article 2, Chapter 2 of Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 65n).
- The second is the profit type code (Article 3, Chapter 2 of Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 65n), which contains five subsections:
- profit group, which is numbered with a single digit;
- two-digit profit subgroup;
- the income item is numbered with two single characters;
- the income sub-item contains three figures;
- the profit element consists of a two-digit number.
- The third is coded subtypes of budget profit (Article 4 (1) Chapter 2 of Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 65n), which consists of two subsections:
- profit subtype group containing four numeric symbols: 1000, 2000, 3000 or 4000;
- The analytical group of budget income subtypes contains three numerical values.
Also, the legislation of the Russian Federation in Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 65n separately classifies revenues (Chapter II), expenses (Chapter III), operations of the public administration sector (Chapter V) and sources that finance the budget deficit (Chapter IV). The combination of numbers for other KBKs is different, and accordingly, the codes are also different.
KBK structure
So, KBK consists of 20 characters. It is more convenient to see the structure of the indicator in the table.
| Characters in order | Explanation | Example |
| 1,2,3 | Indicate the body that manages budget funds | 182 – tax service, 392 – Pension Fund of the Russian Federation, 393 – Social Insurance Fund |
| 4,5,6 | Type of contribution paid | 101 – income tax, 102 – insurance fees for pension insurance. |
| 7,8 | Budget level for which funds are intended | 01 – federal level. 02 – local |
| 9,10,11 | Sub-item of income | Determined by the classifier; for personal income tax, for example, 010. |
| 12,13 | Income element | Also determined by the classifier. For personal income tax – 01 |
| 14,15,16,17 | Payment type | 1000 – contribution or arrears of tax, 3000 – fine, 2100 – pennies, etc. |
| 18,19,20 | Type of income | 110 – tax revenue, 160 – social insurance contributions. |
Example. The BCC for paying property tax (which is not part of the Unified Gas Supply System) looks like this: 182 1 0600 110.
The digital digits in this long number indicate the following:
- 182 – this block indicates that the manager of the funds is the Federal Tax Service.
- 106 – numbers indicate a specific tax – property tax.
- 02 – address for receiving funds – local budget.
- 010 – property tax subsection number.
- 02 – code of the income element for this tax.
- 1000 - the symbols indicate the type of payment - this is a tax, and not a fine or penalty, for example.
- 110 – the numbers indicate the type of budget income: this is tax revenue, not a social insurance contribution.
According to OKTMO
OKTMO is an all-Russian classification of territorial municipalities, regulated by the statistics service, which numbers the classifier OK 033-2013. The cipher contains 8 or 11 digits, where the first 8 numeric characters are municipalities, and the remaining ones are settlements. Administrative centers and cities are encrypted in such a way that the Federal Tax Service, where the money is received, knows in which region the payer is located. Simply put, the code according to OKTMO means the region of the country, therefore KBK and OKTMO are not interconnected, and it is impossible to clarify the type of payment using the code of municipalities.
How to find out an organization’s BCC online
The current combination of budget revenues or expenses can be found online only on portals containing official legal documentation:
- Consultant Plus;
- Guarantee;
- State legal information system;
- Official website of the Government of the Russian Federation
or on the Federal Tax Service resource. To clarify information on the tax portal, you need to:
1. Walk along.
2. Select the payer category: individual entrepreneur, legal entity or individual.
3. Select the tax or duty for which payment is made.
4. Select the type of income, and opposite the name there will be a 20-digit budget classification code.
When filling out a payment slip at the bank, you can check the information with an employee of the banking institution.
Examples of using KBK for the most popular cases
Let's look at a few common cases.
Let's look at the example of KBK when paying tax by vehicle owners - 182 1 0500 010.
As noted earlier, the KBK has several informative blocks:
- administrative;
- profitable;
- program;
- classifying.
Administrative block - the first three digits “182” indicate the funds administrator. In other words, the purpose of the payment is tax collection.
Income block - it contains several subsections of information:
- type - tax "1"
- income subgroup - tax on total income “05”
- article - target deduction "04"
- sub-article - “012”
- revenue budget - local budget “03”
Program block – four-digit payment type – taxes and fees “1000”
Classifying block - the last three digits indicate the type of economic activity - tax income “010”.
As you can see, the CBC has a rather complex structure, which is determined by the various areas and types of activities of organizations, the territorial division of our large country, and the various legal forms of business entities. When specifying codes, it is important to use the latest current version of the KBK directory so that when filling out payment documents, you do not accidentally send your payment to a “no longer existing address.” And again, despite the complexity of the KBK structure, the reference book allows users to easily select the KBK they need in a given situation.
Paying personal income tax is also a very common situation.
Personal income tax is one of the most capacious items in the budget revenues; let’s look at it in more detail. KBK for filling out the payment in this case is 182 1 0100 110.
Let's look at the detailed decoding of the KBK:
- tax administrator – budget “182”
- type of payment – tax “1”
- purpose of payment – personal income tax “01”
- article – “02”
- sub-article – “010”
- payment type – taxes and fees “1000”
- tax revenue – “110”.
KBK for entrepreneurs on the simplified tax system:
Taking into account the changes that occurred in 2021, for entrepreneurs using the simplified taxation system, the BCC for transferring tax payments is as follows:
- for the “income only” tax regime, 6% of income is paid, BCC - 182 1 0500 110.
- for the tax regime “income minus expenses” the tax rate is 15%, BCC - 182 1 0500 110.
- for the minimum tax regime on the “simplified” KBK - 182 1 05 01050 01 1000 110.
Well, we've looked at a few of the most common cases. We hope that the use of budget encoding is now clearer.
Understanding the structure of the BCC will help you independently determine the purpose of the payment and avoid inaccuracies when filling out tax returns and various reporting, as well as in drawing up payment documents. Errors or inaccuracies in the instructions of the KBK lead to the transfer of funds “to the wrong address.” Please note that the process of returning funds from the relevant budget is very lengthy and often requires a lot of effort.
How does KBK stand for?
KBK - budget classification codes
The organizations' BCCs, which are necessary for the payment to go where it was intended, change almost every year. And the responsibility for their correct indication lies with the payer!
Let's try to figure out what these mysterious codes are, why they are needed, how they are formed and why they change regularly. We will also tell you what to do if you find an error in the specified code, and what you risk in this case, and most importantly, how to prevent this risk and not end up with accrued fines and penalties for paying taxes and fees on time.
Budget classification - what is it and why?
In July 1998, the Budget Code of the Russian Federation in Federal Law No. 145 first introduced the term “KBK”, used as a means of grouping the budget.
There are 4 types of KBK:
- relating to government revenues;
- related to expenses;
- indicating the sources from which the budget deficit is financed;
- reflecting government operations.
What are KBKs used for?
- organize financial reporting;
- provide a unified form of budget financial information;
- help regulate financial flows at the state level;
- with their help, the municipal and federal budget is drawn up and implemented;
- allow you to compare the dynamics of income and expenses in the desired period;
- inform about the current situation in the state treasury.
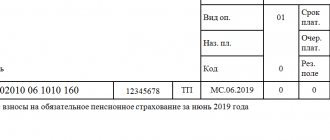
INFORMATION FOR ENTREPRENEURS! KBK is an internal coding necessary, first of all, for the state treasury, where the distribution of incoming funds takes place. Entrepreneurs need these codes insofar as they are interested in complying with the requirements for processing government payments, especially taxes and contributions to extra-budgetary funds. Therefore, do not forget to indicate the correct and current KBK code in field 104 of the payment receipt.
Main functions of KBK codes
As noted above, the KBK classifier is primarily needed to streamline the receipt of funds into the state budget and control their expenditure.
Its other most important function is that with the help of the BCC, the primary grouping of funds occurs when they come from taxes, insurance premiums, etc., and their further redistribution.
KBK also perform a number of other important functions:
- used for drawing up budgets at various levels;
- execution and control of various budgets;
- with their help, the comparability of the necessary indicators is ensured.
By using cash flow coding, it is easy to collect statistical information about financial flows at all levels of the economy. Thus, codes serve as a tool for collecting and analyzing data on financial flows throughout our country. These codes allow you to see how cash transfers for taxes and other obligatory payments from a specific business entity or just an individual end up in the state treasury. Then, using coding, the expenditure of received funds is also controlled.
The BCC must be affixed to the following documents:
- on payment documents, when making transfers of taxes, penalties, fines, state duties, etc.
- on tax returns
- when preparing tax reports
- other documents providing for indication of targeted budget items.
It is important to note that payment documents always indicate only one BCC. If you need to make several payments, fill out several payment documents.
You probably have already had to fill out tax returns containing BCC: returns for personal income tax, VAT, income tax, transport tax, calculations of insurance premiums, etc.
Structure of the KBK
This code consists of 20 characters - numbers, separated by hyphens into groups, it has the following form XX - X XX XX XXX XX - XXXX - XXX.
Each group of characters corresponds to an encrypted meaning determined by the Ministry of Finance. Let's consider the structure of the profitable BCC, since they are the ones that entrepreneurs mainly have to use (expense codes can be found mainly when returning funds under any government program).
- "Administrator". The first three signs show who will receive the funds and is responsible for replenishing this or that part of the budget with them, and manages the received money. The most common codes for businessmen begin with 182 - tax authority, 392 - Pension Fund, 393 - Social Insurance Fund and others.
- “Type of income” includes characters from 4 to 13. This group of characters helps to quite accurately identify income according to the following indicators:
- group – 4th character (that is, the first in this paragraph);
- subgroup – 5th and 6th characters; a two-digit code indicates a specific tax, duty, contribution, fine, etc.;
- article – category 7 and 8 (the value of the purpose of the received income is encoded in the settlement documents for the budget of the Russian Federation);
- subarticle – 9, 10 and 11 characters (specifies the item of income);
- element - 12 and 13 digits, characterizes the budget level - from federal 01, municipal 05 to specific budgets of the Pension Fund - 06, Social Insurance Fund - 07, etc. Code 10 indicates the settlement budget.
- “Program” - positions from 14 to 17. These numbers are designed to differentiate taxes (their code is 1000) from penalties, interest (2000), penalties (3000) and other payments (4000).
- “Economic classification” – last three digits. They identify revenues in terms of their economic type. For example, 110 speaks of tax revenues, 130 - from the provision of services, 140 - funds forcibly seized, etc.
IMPORTANT INFORMATION! The 20-digit code must be entered correctly and without errors in the “Purpose of payment” field (field No. 104) of the payment order. In fact, it duplicates the information indicated in the “Base of payment” field, as well as partially in the “Recipient” and “Recipient’s current account” fields.
Structure of KBK codes
The main meaning of the KBK structure:
- designation of the source of payment
- designation of the form of payment
- designation of the recipient of payment
- designation of the item of expenditure of state budget funds.
The structure of the twenty-digit KBK itself consists of several parts:
- The first initial three digits of the KBK code indicate the recipient of funds, who controls the timeliness and is responsible for the receipt of funds to his current accounts. Such recipients are: the tax office, extra-budgetary funds, municipalities, etc.
- The fourth digit of the code indicates the type of income, i.e. payment of taxes, various fees, state duties, etc.
- • The fifth and sixth digits of the KBK - indicate the tax or fee code. For example, code 01 is income tax, 02 is social insurance fees, 03 is VAT on goods and services on Russian territory, 05 is UTII, etc.
- The seventh and eighth digits of the KBK indicate tax items, and the ninth to eleventh digits indicate tax subitems.
- The KBK categories from twelfth to thirteenth indicate regional or local state budget recipients.
- So, if funds are sent to the federal budget revenue - code 01, to the budget of a territorial subject of the Russian Federation - 02, to the local municipal budget - code 03, and if, for example, to the Pension Fund - then code 06.
- Under the fourteenth number of the KBK - the type of receipt of funds is indicated, so taxes - 1, penalties - 2, fines - 3.
- The fifteenth and sixteenth digits are always set to 0.
- The last three digits of the KBK are the classification of items of state revenue: tax revenue - code 110, forced collections - code 140, etc.
- Before transferring funds for taxes and fees, it is always better to check the current classifier and select the correct code from it. KBK classifiers are periodically updated; in 2017, the classifier that was in 2021 will be in effect. Up-to-date information can be obtained on the website of the tax office, where the BCC is listed in sections for legal entities, individuals and individual entrepreneurs.
Why are budget classification codes changing?
This is the cry from the heart of the vast majority of entrepreneurs: how much easier it would be if these codes were uniform and established once and for all. But the Ministry of Finance makes certain changes to the BCC almost every year. Entrepreneurs and accountants do not always have the opportunity to timely monitor innovations and correct the specified BACs, this is especially evident during reporting periods. Responsibility for incorrectly specified code lies entirely on the shoulders of businessmen, which often results in unexpected expenses and hassle in correcting the error and proving that they are right.
There are various versions put forward by entrepreneurs and the Ministry of Finance and the Ministry of Justice do not comment in any way.
- The more receipts passed through incorrect BCCs, the more funds will be “suspended” for some time as unknown. Until errors are corrected, they can be used for unseemly purposes, and on a national scale this is a huge amount.
- Additional filling of the budget by charging fines and penalties for “overdue” payments that were made through the already inactive BCC. Proving timely payment is quite troublesome.
- Inconsistency between the actions of the Ministry of Finance, which assigns codes, and the Ministry of Justice, which approves them.
- Since the KBK is directly “tied” to the public sector, any changes within the relevant structures, the receipt of new directives, etc. lead to a change in coding.
FOR YOUR INFORMATION! There are opinions that since this coding is an internal matter of the Treasury, it should be done by them, and not by taxpayers. The KBK code can be assigned by bank employees based on the specified data about the recipient and purpose of the payment, or by treasury employees upon receipt of it. However, today the additional work of coding is placed on the shoulders of payers; they cannot avoid it, which means that all that remains is to comply with the current requirements and keep abreast of the latest innovations.
What are the consequences of an error in the KBK?
If the payment purpose code is specified incorrectly, the payment will be transferred to the budget, but it will not be distributed correctly there, which means that the state will not actually receive it. The result may be the same as if the money had not been transferred at all: the tax office will count the arrears under a certain item. At the same time, if the BCC is simply mixed up, there may be an overpayment under another item.
As a result, the tax office will issue a demand for payment of arrears, a fine for late payment of tax or a fee and penalties for late payment. This situation is extremely unpleasant for a conscientious entrepreneur who paid the tax on time, whose entire fault lies in confusion with numerous CBCs.
The usual procedure for an entrepreneur when an error is detected in the KBK
- The most important thing is to make sure that the error did not lead to non-receipt of income to the budget, otherwise it will be considered that the funds were not paid, with the payer being fully responsible for this.
- Submit to your tax accounting office a statement about the detected error and a request to clarify the basis, type and affiliation of the transfer of funds, if necessary, the tax period or tax payer status.
- The application must be accompanied by payment orders for which the tax was paid and received by the budget.
- If necessary, a reconciliation of paid taxes is carried out jointly with the inspector (a report is drawn up about it).
- After a few days (the period is not defined by law), a decision is made to clarify this payment and is handed over to the applicant.
IMPORTANT! When a payment is clarified, it is considered completed on the day the payment order is submitted with an incorrect BCC, and not on the day the decision on clarification and offset is received. Thus, the delay in mandatory payment, which provides for penalties, does not actually occur.
Let's look at various cases that occur due to errors in the CBC and analyze what an entrepreneur should do.
- The inspectorate assessed penalties for non-payment of taxes. If there was a beneficial request from the payer to offset the amount paid, then you should additionally ask the tax office to recalculate the accrued penalties. If the tax office refuses to do this, going to court will most likely allow for a recalculation (there is a rich case law with similar precedents).
- The BCC does not correspond to the payment specified in the assignment. If the error is “within one tax”, for example, the KBK is indicated on the USN-6, and the payment basis is indicated on the USN-15, then the tax office usually easily makes a re-offset. If the KBK does not completely correspond to the basis of the payment, for example, a businessman was going to pay personal income tax, but indicated the KBK belonging to the VAT, the tax office often refuses to clarify, but the court is almost always on the side of the taxpayer.
- Due to an error in the KBK, insurance premiums were unpaid. If the funds do not reach the required treasury account, this is almost inevitably fraught with fines and penalties. The entrepreneur should repeat the payment as quickly as possible with the correct details in order to reduce the amount of possible penalties. Then the money paid by mistake must be returned (you can also count it against future payments). To do this, an application is sent to the authority to whose account the money was transferred erroneously. Failure to comply with a request for a refund or re-credit is a reason to go to court.
- The funds entered the planned fund, but under the wrong heading. For example, the payment slip indicated the KBK for the funded portion of the pension, but they intended to pay for the insurance portion. In such cases, contributions are still considered to have been made on time, and you must proceed in the same way as under the usual procedure. The court can help with any problems with a fund that refuses to make a recalculation, and an illegal demand for payment of arrears and the accrual of penalties.
REMEMBER! According to the law, an error in the KBK is not a reason for which the payment will not be considered transferred. The payment order contains additional information indicating the purpose of the payment and its recipient, therefore, if it is indicated correctly, there is and cannot be a reason for penalties against the entrepreneur; other decisions can be challenged in court.
Is it possible to find out the BCC of a legal entity using the TIN?
When making payments to the budget, taxpayers are faced with the need to indicate in the order the full details of the recipient of the funds, including the KBK. If you do not enter all the required information, it will be impossible to make a payment, so you should know exactly how you can quickly obtain the necessary data.
To understand whether it is possible to find out an organization’s KBK using the TIN, you first need to understand what these abbreviations mean, what they are needed for and where they are used.
Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN)
TIN is used to record taxpayers; both individuals and legal entities have it.
The TIN of a legal entity consists of 10 digits: XXYYZZZZZO, where:
- XX – code of the subject of the Russian Federation;
- YY – Federal Tax Service branch number;
- ZZZZZ – individual taxpayer number;
- O – check digit.
The TIN is contained in all payment documents; using it you can find the name of the organization, and if there is a checkpoint code, then the territorial division.
With the help of the TIN, the state monitors the payment of taxes by taxpayers, will be able to check the employer, track the correctness of payments to extra-budgetary funds, etc.
How to determine the budget classification code
Let's figure out how to determine the number of the required tax payment using the budget classification directory.
In order to find out the required BCC in this particular case, it is most convenient to go to the official website of the Federal Tax Service:
- We open the website of the Federal Tax Service nalog.ru
- Select the “Taxation in the Russian Federation” tab
- The page “Codes for classification of income of budgets of the Russian Federation administered by the Federal Tax Service” will open.
- We select one of the sections we need: “Legal Entity”, “Individual” or “Individual Entrepreneur”
- Next, a list of transfers of taxes, fines, etc. will open; select the item we need, and then the sub-item of our payment.
- In the table that opens, we select the twenty-digit KBK we need, based on its description.
As you can see, finding KBK on the Internet is quite simple. For the convenience of users, the Federal Tax Service Inspectorate website provides meaningful navigation through links with the selection of the desired section. Therefore, it is easy to navigate there.
You can also use the usual paper reference books, if that is more convenient for you. You can use other information resources. The main thing is that you use the latest relevant data.
What is a budget classification code (BCC)?
KBK serves to indicate budget expenses and revenues. With its help, you can find out where the payment was sent from and its intended purpose. It contains information about paid taxes, state duties, and fines in encoded form. With its help, it becomes clear to which budget the payment is made and who the recipient is.
The code consists of 20 digits:
- Code of the chief revenue administrator - 3 digits indicating to whom the payment is made (taxes, extra-budgetary funds, funds from business activities);
- Income codes - 4-13 income options: the first digit is the encoded name of the payment (tax payments, income from the activities of individual entrepreneurs, foreign exchange earnings), 2, 3 digits indicate the purpose of the payment (income tax), the remaining digits indicate the decoding of the payment, for example, 10 – income from export/import operations, etc.;
- Program codes – 14–17 are used to code the type of income (duty, fine);
- Classification codes – 18–20 contain analytical data.
The KBK serves to track tax and non-tax payments; it is a kind of analogue of a current account in a credit institution, so that the funds paid go to exactly the department of the budget or extra-budgetary background that is needed.
With its help, you can prevent payment errors, check the history of transactions, systematize information, and forecast the revenue side of budgets and extra-budgetary funds.
For example, let’s consider the formation of the BCC for the transfer of funds for compulsory social insurance 393 1 02 02050 07 1000 160:
- 393 – FSS;
- 1 – payment is required;
- 02 – payment to the SS fund;
- 02 02050 07 – itemized name of payment;
- 1 – mandatory contribution;
- 000 – check digits;
- 160 – code indicating the contribution item.
The essence of budget classification codes
KBK is a twenty-digit code, the numbers of which indicate the type and purpose of the payment. These codes are used to account for the receipt of income and the correct functioning of each expenditure item of the budget at various levels.
On a government scale, target cash flows are very large, so such encodings were introduced to ensure their identification, transparency and control. The classifier provides maximum specification of budget items.
Commercial organizations and individual entrepreneurs, individuals, usually use that part of the classifier that contains the encoding of sections devoted to budget revenues. Since all payments paid by business entities and individuals are transferred to budget revenues at various levels.
The Tax Service keeps records of cash receipts from taxpayers in full accordance with the current classifier.
Therefore, when paying current payments to taxpayers, legal entities and individuals, you must also strictly observe the correctness of the KBK encodings, in order to avoid that your payments will not reach the desired “addressee”, and the tax debt will remain with you. Let us remind you that in case of failure to pay tax debts on time, penalties will be assessed and fines will be issued.
In addition, BCCs ensure targeting of budget revenues and targeted spending of state budget funds.
The BCC also takes into account the fact that some taxes are distributed to the federal budget, some to the territorial budgets of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, others go to local municipal budgets. There are also taxes that go to the budgets of all three levels at once, since their volumes are the most significant. This applies to corporate income tax and VAT. Moreover, the percentages distributed among budgets differ depending on the region of our country. And it is the KBK codes that ensure the accuracy and transparency of cash flow.
We also note that almost every year some changes are made to the KBK classifier; codes may be excluded, or new codes may be added. This is due to the constant updating of budget items, the emergence of new areas of economic activity and the development of the state as a whole.
Therefore, you periodically need to refer to the current classifier to double-check the BCC.
The current version of the classifier can always be viewed and downloaded on the official website of the Federal Tax Service.
Relationship between TIN and KBK
From the above it follows that INN and KBK are necessary for making payments and are part of the required details. However, they are two completely different codes. The first designates the name of the company, organization, individual, the second serves to provide a unified form of budget financial information.
The TIN is used to make payments between any constituent entities of the Russian Federation; the KBK is primarily necessary for the Federal Treasury for internal coding.
The digital codes of the details do not overlap, so it is impossible to find out the KBK, knowing only the identification number of the organization.