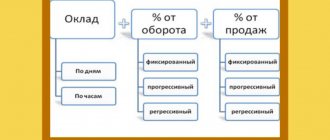
Prize
A bonus is a stimulating additional payment of an incentive nature, which is paid in addition to the salary, i.e. the employee's basic income.
In accordance with Article 135 of the Labor Code, an organization can independently establish a bonus system for its employees, providing for various types of incentive payments and allowances. A representative body of workers, for example, an industry trade union, can take part in the development of such a system. In addition, sometimes the bonus procedure is stipulated in the collective agreement.
The documents must determine at what performance indicators the employee is entitled to a bonus, record the terms of the bonus and the amount of payments in each specific case.
Bonuses can be paid either on an ongoing basis or one-time, for example, for improving product quality, increasing labor productivity or many years of conscientious work.
Healthy
How to calculate sick leave during quarantine
Is it possible to reduce the monthly bonus if its amount is specified in the employment contract?
If the accrual of a bonus is stated in an individual employment contract, and even more so if its exact amount is specified, it will not be possible to cancel or reduce the payment without the consent of the employee who signed the agreement. This is the position of the courts - often an employment contract has greater weight than the internal regulations of the company.
However, if at the very beginning of the employment relationship the employer was concerned about the correct wording of the provision for the payment of bonuses in the employment contract, its size can be reduced. So, if it is said that a subordinate will receive a bonus in a certain amount with the condition that he fulfills the work plan or achieves any clear indicators, the employer has the opportunity to reduce the incentive payment if the listed conditions are not met.
How to register
The bonus is paid on the basis of a management order, which is drawn up in accordance with the forms approved by the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated January 5, 2004 No. 1. If a bonus is given to one employee, form No. T-11 is used, if several - No. T-11a.
The order must indicate the details of the persons receiving the bonus, their positions and the name of the company division in which they work, as well as the reason and basis for paying the bonus. Reasons such as exceeding the production plan, achieving certain planned labor indicators, improving the production process, etc. can be cited. The basis for payment of a bonus may be a memo from the head of the department in which the mentioned employees work.
And, of course, the order specifies the amount of the bonus, which is determined on the basis of the bonus regulations or the established bonus system. The regulations usually indicate the indicators upon achievement of which the bonus is paid, the bonus scale and the amount of payments, as well as additional conditions and the source of payments. The circle of employees to whom the bonus can be paid is also determined.
Interesting
Regional coefficient and bonuses
Thus, on the basis of this document, the employee has the right to demand a bonus upon achieving certain indicators, and the employer must pay it. If we are talking about a one-time bonus paid by the employer, he can refuse payment, and the employee does not have the right to challenge these actions.
The bonus is usually paid along with the salary according to the statement or cash receipts.
Is the bonus part of the salary?
Before understanding the reasons for reducing the bonus or completely eliminating it, you need to understand when this payment is part of the salary and when it is not:
| Bonus - part of salary | Bonus is not part of salary |
| If the employer has indicated in the company’s internal regulations that the employee’s salary is formed from the salary or tariff rate and the bonus part, the bonus will be recognized as a component of the salary. In such a situation, the bonus cannot be reduced or eliminated altogether, because it is prohibited to reduce employee salaries. However, if clear criteria for assigning bonus payments have not been approved, the bonus can be regarded as an incentive for conscientious work, which gives the company’s management the right to refuse to accrue it to employees. | If the payment of a bonus is not stated in the wage regulations and in the individual employment contract, its accrual to the employee depends on the employer’s desire to reward the employee for certain work results or for a responsible approach to business. Such a payment will not be guaranteed to the subordinate, which means it may not be accrued. |
Deprivation of bonus
According to the Ministry of Labor, which it expressed in its letter No. 14-2/OOG-15428 dated September 28, 2020, the Labor Code does not indicate the criteria under which bonuses are paid, as well as the procedure for calculating them. Accordingly, it is not specified when the employer has the right to deprive an employee of a bonus. This information is not in the Tax Code either.
The regulations on bonus payments to employees may define a number of grounds for depriving a bonus or reducing its size. Among them is the presence of disciplinary action. Deprivation of the bonus can be applied along with it, although in itself it is not a penalty.
The Moscow Labor Inspectorate previously explained in its letter No. 77/7-5692-20-OB dated February 26, 2020 that if an employee of a company has a disciplinary sanction, it is possible to deprive him of a bonus only in the period for which it is accrued.
Refusal criteria and violations
The grounds for refusal to award bonuses must also be clearly formulated, defined and communicated to staff. As a rule, the following criteria are distinguished:
- The employee does not fulfill the job duties provided for in the job description and employment contract.
- Violation of deadlines for the delivery of projects or work specified in contracts with contractors.
- Presence of errors and erroneous data in reports and documentation.
- Receipt of claims, claims and complaints from customers.
- Failure by the employee to comply with labor discipline and standards of conduct, namely:
- absenteeism (absence from work without prior notice for more than four consecutive hours during a work shift);
- going to work in a state of alcohol or other intoxication;
- violation of safety requirements;
- causing damage to the organization’s property and losses in connection with its damage;
- failure to comply with orders from superior officials.
6. Receiving a reprimand or reprimand for the reporting period.
Along with serious violations, there may also be minor ones, but also used for deduction or partial accrual of bonuses, for example, being late for work or leaving the workplace before the due time.
Order not to accrue bonuses
The order on depreciation does not have a unified form. That is why many people face problems in compiling it. Since there is no single sample document at the legislative level, you can be guided by a form found on the Internet.
It must be said that the order must necessarily contain the information that is necessary for calculating the payment - for which the employee receives a bonus. In addition, a list of the employee’s actions that caused his deprivation of bonuses is written down. In the process of leaving a document, it is necessary to refer to legislative acts regulating the rules for deprivation of additional remuneration.
There is a special procedure for drawing up an order.
order not to accrue bonuses free of charge in word format
Attention! Any employee drawing up a document must follow it:
- in the upper right corner the name of the enterprise and its OKVED code are written. This part is called the header. The paper number and date of its preparation are also reflected here,
- the name of the document is reflected in the center, in our case: “order on depreciation”,
- First of all, the text of the order reflects basic information about the employee. His last name, first name, patronymic, as well as his position and structural unit where he works,
- the grounds for depriving the employee of a bonus must be indicated, as well as the reasons that led to the commission of the offense,
- Next, the exact amount of the premium is reflected. In fact, the person is not deprived of money, but simply not paid additional remuneration,
- After the basic information has been presented, it is worth making reference to the legislative acts that establish the rules for awarding and depriving bonuses.
The order is signed by the head of the company. The organization's seal is affixed to it.
The document is drawn up in two copies. One remains with the HR employee, the second is given to the employee for familiarization with it.
13 salary.
Appealing the decision
Since the employer’s right to deprive a bonus depends on how bonuses are drawn up in local documentation, an employee may not always complain about deprivation of a bonus. So, if bonuses are of an incentive nature, then complaints about deductions are meaningless . But if the bonus is part of the salary, then the employee is obliged to demand payment in full.
In order to challenge the employer’s decision to deprive a bonus, an employee can seek protection of his rights:
- to the labor inspectorate (State Labor Inspectorate - GIT);
- to the prosecutor's office;
- to court.
Based on an application to the state labor inspectorate, State Labor Inspectorate inspectors must conduct an inspection of the employing organization. If it is discovered that an employee has been deprived of funds due to him in the form of a bonus, inspectors will issue an order for the employer to pay the bonus, and will also oblige him to reimburse all untransferred funds, taking into account penalties and fines. The prosecutor's office has similar powers.
When going to court, an employee can demand not only the return of an illegally withheld bonus, but also compensation for moral damages and legal costs (compensation for damage cannot be recovered as a result of an appeal to the prosecutor’s office or State Tax Inspectorate). In order to prove the unauthorized actions of the administration, the employee must present arguments that clearly indicate a violation of labor laws . To apply to the court, an employee should prepare the following papers:
- A copy of the employment contract.
- Bonus rules, Regulations on bonuses and other documents adopted by the organization. If the employee does not have this document, then he has the right to request it from the employer, and he is obliged to provide information within 3 days after receiving the relevant request.
- An order on deprivation of bonuses or a note signed by management.
- An act of recording the violation that caused the imposition of a penalty (if any).
When preparing a statement of claim, the employee must write down:
- Full details of the employing company, position and full name of the citizen.
- Circumstances of the incident: when the employer deprived the employee of the bonus and for what reason.
- On what basis does the employee believe that the deprivation of bonuses was illegal?
- Requirements to the court: restore violated rights and return the amount of the premium, compensate for moral damage, etc.
A set of information along with the petition is sent to the court , and the applicant is notified of the hearing in written format. The employee has the right to submit an application to the court within a year after becoming familiar with the order to deprive him of bonuses. These cases are under the jurisdiction of magistrates.
Is it possible to change the terms of employee bonuses?
If the employer decides to change the provisions of the internal regulatory act, which mentions the payment of a bonus to an employee, the text of employment contracts with employees will have to be changed, but only when the bonus is part of the remuneration. The current legislation allows you to accomplish the intended goal through reaching an agreement with subordinates or by carrying out the procedure described in Article 74 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. It is safer to choose the first option, since if a change in the terms of the employment contract is challenged in court, you will have to prove that such measures were necessary (technological changes took place, organizational measures were taken, etc.).
It happens that the employment agreement mentions a bonus, but does not talk about its fixed amount - only a reference is made to the provision on remuneration. According to Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the conditions for paying bonuses must certainly be present in the employment contract, and a reference to the company’s internal document is a form of compliance with this requirement. That is, even if there is no mention of the amount of the bonus in employment agreements, it is necessary to obtain the consent of employees to change the terms of the bonus.
Finally, if the bonus is not related to wages, but is only an incentive measure and is paid at the discretion of the manager, the employees’ consent to change the terms of the bonus may not be taken - it is enough to familiarize subordinates with the new version of the internal act.
The procedure for reducing the premium: the main stages of registration
Depreciation (reduction or deprivation of bonus payments) is a whole procedure consisting of several stages. Each of them must be documented. You can conditionally display the entire process as follows:
- Drawing up an act or report on the fact of a violation (committed offense). That is, the circumstances that served as the reason for reducing the premium should be recorded.
- Demanding an explanation from the perpetrator. The offending employee must write an explanatory note and submit it to his supervisor within the next two days. If he does not do this, then the absence of such explanations (explanatory) is formalized in an act.
- The manager's memorandum, together with an explanatory note from the potentially guilty employee (or a report on her absence), is presented to the employer.
- Review of the submitted documents and adoption of a decision on them by the employer (usually carried out within a month).
- Drawing up and issuing an order based on the employer’s decision. It indicates: sanctions (reduction of the premium), the basis for their application.
- Familiarization with the employee's order against signature within 2 working days. days after its publication. If you refuse to familiarize yourself, an act will be drawn up.
The described standard procedure for registration and documentation is used for the most part when applying disciplinary sanctions. Meanwhile, its use cannot be ruled out when reducing the size of premiums. The key point when registering: the presence of documentary evidence of the employee’s guilt indicates that the reduction in the bonus is legal and legally justified.
Is deprivation of bonuses a disciplinary sanction?
Disciplinary punishment under labor legislation is provided for failure to perform and improper performance by an employee of labor functions through his fault.
An employer does not have the right to impose a disciplinary sanction against its employee in the form of deprivation of bonuses . This is due to the fact that this type of recovery is not listed in Part 1 of Art. 192 of the Labor Code. This legal norm contains reference only to the following types of collection:
- comment;
- rebuke;
- dismissal.
The employer himself chooses the appropriate form of punishment depending on the severity of the offense committed: for example, with regular and systematic violation of labor discipline, he faces dismissal.
As you can see, deprivation of bonuses is not included in this list. Federal laws and regulations on the discipline of certain categories of employees may provide for other types of punishment: for example, a representation of incomplete official compliance, a severe reprimand, etc.
At the same time, the absence of deprivation of bonuses in the list of disciplinary sanctions does not make deprivation of bonuses illegal. The basis for depreciation may be bringing the employee to disciplinary liability in the form of a reprimand, reprimand and dismissal in the time period in which the bonus is awarded.
It is necessary to note that imposing a disciplinary sanction is a right, not an obligation of the employer (based on Article 22 of the Labor Code). Based on the results of considering the severity of the offense, the commission may come to the conclusion that there is no need to punish the employee. In such a situation, if the basis for deprivation of bonuses is the presence of an outstanding penalty, then the employer does not have the right to deprive the employee of a bonus.
Also, the employer should formalize disciplinary action and deprivation of bonuses in the form of separate orders.
Cases when an employee cannot be deprived of remuneration
Separate reasons when deprivation of a bonus is illegal were discussed above, but, summarizing all of the above, the following reasons can be identified:
- The bonus is part of the salary.
- The basis for deprivation of the bonus is not provided for by internal documents.
- The procedure for deprivation of bonuses was violated (for example, the employee was deprived of a bonus before disciplinary action, etc.).
- There is no order to deprive an employee of a bonus if the execution of such a document is mandatory (for example, local documents indicate that deprivation of bonuses is issued by the decision of the manager or the employer needs to fix the amount of reduction in bonuses). When registering a depreciation through an order, one more important condition must be met: the employee must be familiarized with the order under his personal signature.
The employer may not issue any orders at all . For example, state in the Regulations that the bonus is awarded only based on the results of a positive financial result at the end of the quarter. In this case, in case of unprofitable operating activities, the bonus will simply not be awarded for the entire team and, in fact, there will be no reduction in bonuses.
An employer can develop a mandatory system of indicators that an employee must comply with in order to receive a bonus. If they are not followed, the employee will not receive a bonus.
If the reason for dismissal is listed in local documents, and the employee was previously familiarized with it, then the employer does not need to issue any additional orders.
Is it permissible for a pregnant woman to be deprived of her bonus? A pregnant woman can be deprived of her bonus for violating labor discipline. No concessions are provided for her: she must comply with labor discipline and job responsibilities.
The employer does not have the right to deprive an employee after the expiration of the penalty. Once the penalty is repaid, all the consequences it had are eliminated.
Legal ways to reduce monthly premium
Current labor legislation allows only 3 ways to reduce bonuses to employees of an enterprise:
- At the time of drawing up the company’s internal regulations, provide for the wording of the bonus provision, which would give management the right to accrue or not accrue a bonus. The law requires that bonuses be mentioned in employment contracts and local regulations, and therefore this cannot be avoided, however, you can write something like “based on the results of the profit received, the management of the LLC may decide to award a bonus to employees for the month/quarter/year. In this case, the payment of the bonus is made within the time frame and in the amount specified in clause 1.1 of these Regulations on bonuses.”
- Change the internal act on the payment of bonuses, coordinate the decision of management with the trade union organization, implement the change and not charge bonuses legally. The disadvantage of this option is the demotivation of subordinates. They realize that they have lost their bonus not for some time, but for good, and will stop trying to achieve higher results.
- Individually change the internal act on bonuses if the organization does not have a trade union. However, if the amount and procedure for paying bonuses are specified in employment contracts, the consent of the employees will have to be obtained.
How to appeal a decision
claim in court for the recovery of unpaid premiums free of charge in word format
If an employee does not agree with the decision of the company management to deprive him of his bonus, the employee must file a complaint with the Labor Inspectorate.
In addition, you can file a claim in court. You can file a complaint with the Labor Inspectorate within three months from the date the employee was deprived of his bonus.
To resolve the issue in court, you will need to provide irrefutable evidence that you are right.
Employer's liability
If the court finds an employer guilty of violating the rules for calculating bonuses, then his actions fall under Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
According to paragraph 6 of Art. 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses, a company management that wrongfully deprived an employee of a bonus is punishable by an administrative fine:
- for officials in the amount of 10,000 to 20,000 rubles,
- for individual entrepreneurs from 1000 to 5000 rubles,
- for legal entities from 30,000 to 50,000 rubles.
Watch the video. Salary fines, deprivation of bonuses and other monetary penalties at work:
Step-by-step instructions for depriving an employee of a bonus under the Labor Code of the Russian Federation
The employer has the right to independently establish the procedure for depriving bonuses in its regulatory documents. If it is fixed, then it should be strictly followed, otherwise the employee will be able to challenge the legality of the bonus deduction in court.
Recommended course of action:
- The heads of structural units or the head of the organization can initiate a reduction or deprivation of bonuses. In the first case, an official or memorandum with the reason for the deprivation of bonuses is submitted to the director. The basis may also be an act of misconduct committed by the employee.
- Before making a decision to deprive a bonus, study all the documentation in accordance with which the organization has adopted a team incentive system:
- local documents regulating the bonus procedure. From their text it should be clear that the payment of bonuses is of an incentive nature and is not a guaranteed payment. It is also important to note that the employer decides to pay it depending on the results of the team’s work and the activities of the organization as a whole, establishing the appropriate amount;
- employment contract. If the employer fixes the payment of the bonus in a fixed amount and stipulates this in the employment agreement with the employee, then it cannot be deprived. It is more expedient to indicate in the contract that the bonus is a payment that is established by the decision of the employer and in a manner consistent with local regulations;
- collective agreement. The employer has the right to provide for a system of incentives for employees through a collective agreement.
- The employee may be asked to provide a written explanation as to why a situation occurred that resulted in non-compliance with the terms of the employment contract.
- If the grounds comply with the conditions for deprivation of bonuses prescribed in the local acts of the organization, an order for deprivation is issued.
Legislative acts on the topic
| Art. 57 Labor Code of the Russian Federation | The fact that an employment contract must specify only the amount of salary or tariff rate, but not bonuses |
| Art. 191 Labor Code of the Russian Federation | The fact that a bonus is an encouragement |
| Art. 74 Labor Code of the Russian Federation | About the procedure for changing bonus conditions |
| Ruling of the Moscow City Court dated June 22, 2011 in case No. 33-16736 | That deprivation of a bonus is not a disciplinary measure |