In total, there are three main types of intermediary agreements: commission agreement, agency agreement and agency agreement. Each of these agreements has its own chapter in the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. Chapter 51 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation regulates issues of commission agreements. Chapter 49 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation covers issues of the agency agreement. Chapter 52 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation considers issues of agency agreements. The agency agreement partially includes the terms of both the commission agreement and the agency agreement, so in this case we will consider the agency agreement.
Working under an agency agreement, as a rule, our accounting clients have questions. On what amount do you need to pay and calculate tax according to the simplified tax system when the object of taxation is “income”? At what point should the Principal recognize revenue received from the Agent?
We propose to examine these issues.
Accounting for income in the simplified tax system
In income when calculating the simplified tax system, take into account only agency fees.
For example, you sell laptops and receive 5% of sales. By selling 10 laptops for 50,000 rubles each, you will receive half a million from buyers, of which your revenue will be only 25,000 rubles. This amount must be taken into account in the income of the simplified tax system. When to take income into account in the simplified tax system depends on the method of payment of remuneration. There may be the following options:
- You deduct remuneration from the money received from the client. Its size is determined by the agency agreement. Take the remuneration into account in the simplified tax system on the day you receive payment from the client.
- The principal transfers the remuneration separately: in advance or based on sales results. Take it into account in the simplified tax system on the day you receive money from the principal.
- You withhold remuneration from the money received from the client, but its amount is not fixed in the contract and is determined in the agent’s report. This is the most unprofitable and difficult accounting method. When receiving payment from a client, the entire amount must be taken into account in the simplified tax system’s income. When the principal approves your compensation in the agent's report, adjust the income. For example, you received 50,000 rubles from a buyer, but you do not know the amount of your remuneration. On this day, you need to take into account the entire amount in the income of the simplified tax system. Then you agree with the principal that your remuneration is 5,000 rubles, and sign the agent’s report. On this day, make an adjusting entry in KUDiR: income of 45,000 rubles with a minus sign.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytpolicyandsafetyru
Most of the costs under an agency agreement are covered by the principal. Do not take into account such costs and their reimbursement in the simplified tax system. If the principal does not reimburse some expenses, and you are using the simplified tax system “Income minus expenses,” you can write them off according to the general rules.
The money that you transfer to the principal based on sales results cannot be taken into account as expenses when calculating the simplified tax system.
Agent on OSNO – principal on simplified tax system
Art. 346.11 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation exempts simplifiers from the obligation to pay VAT, therefore the principal’s agent on the simplified tax system does not calculate tax on transactions relating to the principal. But at the end of the transaction, the agent issues an invoice for the amount of the remuneration, without registering it in the accounting journal (clause 3.1 of Article 169 of the Tax Code). The VAT presented by the agent is subsequently taken into account by the simplified principal in the costs of the simplified tax system in the usual manner.
A peculiarity of the recognition of income by the principal using the simplified tax system is that, according to tax legislation, the simplified person’s revenue is the entire amount of receipts into the account. Therefore, when the agent deducts remuneration from funds received from transactions, the amount of income will be considered all proceeds from sales received to the agent’s account.
At the principal's
The rules provided for in Chapter 1 apply to relations arising from an agency agreement. 51 “Commission” of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, if these rules do not contradict the provisions of Chapter. 52 “Agency” or the essence of the agency agreement (Article 1011 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
According to paragraph 1 of Art. 996 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, things received by the commission agent from the principal or acquired by the commission agent at the expense of the principal are the property of the latter.
Consequently, the receipt of funds to the settlement account or to the agent’s cash desk from buyers in payment for goods sold on behalf of the principal, which are his property, should be taken into account as revenue from the sale of these goods from the principal (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated August 20, 2007 N 03-11- 04/2/204).
The Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 05/07/2007 N 03-11-05/95 explains that the date of receipt of income for the principal will be the day of receipt of funds transferred by the intermediary to bank accounts and (or) to the cash desk of the principal.
The principal's income is the entire amount of proceeds from the sale of goods received to the agent's account. Article 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not provide for a reduction in the income of principals by the amount of remuneration paid by them to agents. Therefore, the income of principals applying the simplified taxation system should not be reduced by the amount of agency fees withheld by the agent from the proceeds from sales received in his current account when it is transferred to the principal.
Based on this, the income of the individual entrepreneur - the principal is not reduced by the amount of remuneration withheld independently by the agent from the amounts received by him on the basis of the agency agreement. The same position is reflected in Letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 25, 2009 N 03-11-06/2/107, dated June 5, 2007 N 03-11-04/2/160, Federal Tax Service of Russia for Moscow dated March 5, 2007 N 18 -11/3/ [email protected]
We suggest you read: MTS office where you can terminate the contract
In this case, the agency fee, paid by the principal to the agent or withheld by the agent independently from the amounts received by him on the basis of the agency agreement, relates to the expenses of the principal on the basis of paragraphs. 24 clause 1 art. 346.16 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Consequently, an individual entrepreneur who is a principal and uses the “income minus expenses” taxation system has the right to reduce the income received by the amount of remuneration paid to agents (Letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 22, 2009 N 03-11-09/145, dated November 29, 2007 N 03- 11-04/2/290, Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia for Moscow dated 03/05/2007 N 18-11/3/ [email protected] ).
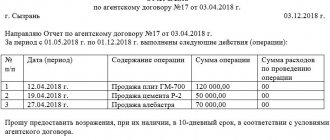
For the principal, draw up an agent report on the work done. Attach documents confirming the expenses that the principal will reimburse. The report also indicates the amount of your remuneration. If the agent's report does not indicate the agency fee, approve it in a separate act.
Agent report template
If you are selling goods on your own behalf to a principal who works with VAT, you will have to issue invoices for buyers and report to the tax office. At the same time, you do not need to pay VAT itself.
You issue an invoice for the client on your own behalf. In the seller's data you indicate your details, and in the buyer's data - the client's details. You give one copy of the invoice to the client, the second one you keep for yourself and send a copy of it to the principal. The principal will issue the same invoice on the same date, but in his own name, and give it to you.
If you work on behalf of the principal, you won’t have to bother with VAT. You can, by proxy of the principal, issue an invoice on his behalf. Or the principal will do it himself. In this situation, you do not need to report to the tax office and pay VAT.
Agent on the simplified tax system – principal on the OSNO
If the principal company uses OSNO, then its agent (even a simplifier), regardless of whose name he acts, is obliged to issue invoices with VAT included in them.
In accordance with the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the principal, transferring the goods to the agent for sale, remains its owner until the moment of sale. The sale is carried out by the principal with the involvement of an intermediary, so the proceeds are taken into account by him when calculating income tax and VAT. An agent on the simplified tax system is remunerated from the principal’s income, and his remuneration will be an expense without VAT, i.e. in this case the agent does not issue an invoice for the remuneration.
Invoices issued by the agent to the purchasers are recorded in the invoice journal, and are not recorded by him in his sales book, but are subsequently transferred to the principal as attachments to the report. The agent using OSNO fills out an invoice for the amount of his remuneration.
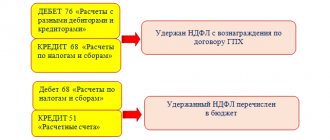
Accounting for transactions according to the scheme “Agent on the simplified tax system – principal on the OSNO ” in accounting will be reflected as follows:
| Operation | D/t | K/t |
| At the agent's | ||
| Sales of services under an agency agreement | 62 | 76/settlements with the principal (RP) |
| Receipt of funds from acquirers | 51 | 62 |
| Transfer of funds to the principal minus remuneration | 76/RP | 51 |
| Revenue from agency fees | 62 | 90/1 |
| Agent's remuneration credited | 76/RP | 62 |
| At the principal's | ||
| Based on the agent's report, the sale of services is reflected | 62 | 90/1 |
| Agency fee accrued | 20 (44) | 76 |
| Costs for intermediary services written off | 90/2 | 20 (44) |
| Purchasers of services are charged VAT | 90/3 | 68 |
| Revenue taken into account minus intermediary fees | 51 | 62 |
| Agent's remuneration taken into account | 76/PDK | 62 |
A type of mediation agreement is a commission agreement. The peculiarity of the status of this agreement in comparison with its agency counterpart is that the commission agent (intermediary) can act in it, carrying out the instructions of the principal (customer of services), only on his own behalf, but at the expense of the principal. Accounting according to the scheme “commission agent on the simplified tax system – principal on the OSNO ” will be identical to that presented above.
At the agent's
Clause 1 of Art. 1005 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation provides that under an agency agreement, one party (agent) undertakes, for a fee, to perform legal and other actions on behalf of the other party (principal) on its own behalf, but at the expense of the principal or on behalf and at the expense of the principal.
The principal is obliged to pay the agent remuneration in the amount and in the manner established in the agency agreement (Article 1006 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
According to clause 1.1 of Art. 346.15 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, when determining the object of taxation, income provided for in Art. 251 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
In particular, income in the form of property (including cash) received by a commission agent, agent and (or) other attorney in connection with the fulfillment of obligations under a commission agreement, agency agreement or other similar agreement, as well as for reimbursement of expenses incurred by the commission agent, is not taken into account. , agent and (or) other attorney for the principal, principal and (or) other principal, if such costs are not subject to inclusion in the expenses of the commission agent, agent and (or) other attorney in accordance with the terms of the concluded agreements. The exception is commission, agency or other similar remuneration (clause 9, clause 1, article 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Thus, the agent’s income is recognized only in the amount of agency remuneration, additional remuneration if its receipt is provided for in the agency agreement, as well as the amount of additional benefit remaining at the disposal of the agent. These conclusions are confirmed in Letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated February 10, 2009 N 03-11-06/2/24, 26.01.
Moreover, if the agent does not participate in the calculations, then the date of recognition of revenue will be the day of receipt of the agent’s remuneration (additional benefit, additional remuneration) from the principal to his current account or to the cash desk (clause 1 of Article 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
It should be noted that when conducting tax audits of individual entrepreneurs who use agency agreements in their activities, the tax authorities carefully check the reality of the transactions concluded by the entrepreneur, including their actual execution. For this purpose, data on cash flows across accounts, information about counterparties, and analysis of primary documents are used. Therefore, individual entrepreneurs should especially carefully keep records of documents in this area of activity.
We invite you to read: Registration of constituent documents with the tax office
At the same time, collecting evidence about the fictitiousness of transactions concluded by an entrepreneur is a rather complex process. Therefore, in the event of legal disputes, entrepreneurs have sufficient chances to defend their position in court.
As an example, we can cite the Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the North Caucasus District dated May 12, 2009 in case No. A53-11082/2008-C5-44, which reflects the position that the courts lawfully satisfied the entrepreneur’s demands to recognize the tax authority’s decision regarding additional assessment as illegal the single tax paid when applying the simplified tax system, the corresponding penalties and fines, since when determining the tax base, income in the form of funds or other property that is received, in particular, under agency agreements is not taken into account.
At the same time, the corresponding opinion is confirmed by the Ruling of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated September 18, 2009 N VAS-11344/09 in the same case, which refused to transfer the case for review in the manner of supervision of judicial acts, since the tax authority unlawfully included in the income of the entrepreneur funds received to his current account in connection with the fulfillment of obligations under agency agreements and commission agreements.
If the agent participates in the calculations and withholds remuneration from the money received from buyers, then it becomes income precisely on the day the money is received in the agent’s current account or cash register. Note that the commission agent takes into account the remuneration as part of the income, regardless of whether at that moment the order is considered completed or not, since with the cash method of determining income and expenses, advances also include advances (clause 1 of Article 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation; Decision Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated January 20, 2006 N 4294/05).
In column 4 section. I “Income and Expenses” The Book of Income and Expenses does not reflect income received in the form of property (including cash) received by the agent in connection with the fulfillment of obligations under an agency agreement (clause 2.4 of the Procedure for filling out the Book of Accounting of Income and Expenses of Organizations and individual entrepreneurs using the simplified taxation system approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 31, 2008 N 154n).
These incomes are not taken into account when determining the maximum amount of income that limits the right to use the simplified tax system (clause 2 of article 346.12, article 248 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Example 1. IP Ivankov I.A. is an agent under an agency agreement with Beta LLC (principal) and applies a simplified system with the object of taxation “income”.
March 1, 2010 IP Ivankov I.A. received from the principal goods for sale in the amount of 590,000 rubles. (including VAT - 90,000 rubles). The agency fee under the contract is 10% - 59,000 rubles.
Payments are made through an agent. April 15, 2010 IP Ivankov I.A. received 590,000 rubles into my bank account for goods sold. (including VAT - 90,000 rubles). On the same day, having withheld the amount of remuneration, he transferred 531,000 rubles to the principal. (590,000 - 59,000).
We invite you to familiarize yourself with: Agreement on gratuitous assignment of the right to claim an apartment to a son
Based on the provisions of paragraphs. 9 clause 1 art. 251 Tax Code of the Russian Federation IP Ivankov I.A. must reflect in taxable income only the amount of his remuneration, i.e. 59,000 rub.
Example 2. IP Novikov A.A. (agent) applies a simplified system with the object of taxation “income”. On February 1, 2010, he received goods for sale from the principal in the amount of RUB 177,000. (including VAT 18% - 27,000 rubles). The cost of delivery of goods amounted to 23,600 rubles. (including VAT - 3600 rubles). The agency fee, in accordance with the terms of the contract, is withheld from the proceeds and amounts to 25,000 rubles. IP Novikov A.A. participates in calculations.
He received the proceeds from the sale of goods to his bank account on February 15, 2010. On the same day, the money was transferred to the principal’s bank account in the amount of 128,400 rubles 0 - 23,600).
Thus, on February 15, 2010, individual entrepreneur Novikov A.A. will include in income only the amount of its agency fee, i.e. 25,000 rub.
With regard to the additional benefit from the sale of goods belonging to the principal, it should be taken into account that the amount received by the agent in the part that is not subject to transfer to the principal under the terms of the agreement is also income for the agent and, accordingly, is subject to a single tax (Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia for the city of No. Moscow dated April 17, 2007 N 20-12/035144).
Example 3. IP Tsvetkova I.A. (agent) applies a simplified system with the object of taxation “income”. On March 1, 2010, she received the goods for sale. According to the terms of the agency agreement, the minimum selling price of the goods is 177,000 rubles. (including VAT - 27,000 rubles). The agency fee is provided in the amount of 25,000 rubles. and is retained by the agent from the proceeds received from buyers for goods sold.
As part of the execution of this contract, the agent sold the goods for 200,600 rubles. (including VAT - 30,600 rubles). The procedure for distributing additional benefits is not specified in the agreement. The costs associated with the provision of intermediary services (not reimbursed by the principal) amounted to 15,000 rubles. In the case under consideration, the agent sold the goods on more favorable terms for the principal, and the agency agreement does not define the procedure for distributing additional benefits. Consequently, in addition to the remuneration (clause 1 of Article 991 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation), the agent is entitled to half of the additional benefit (parts 1, 2 of Article 992 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Thus, the total amount of remuneration due to the entrepreneur, on which a single tax is paid, is 38,600 rubles. (15,000 rubles (200,600 - 177,000) rubles x 50%).
Yu.Suslova
Auditor
LLC "Audit Consult Law"
Documents for the principal
The buyer must complete the same documents as in a regular transaction. For wholesale sales - an invoice, for retail sales - a cash register or sales receipt. When selling services, draw up a deed. If you are selling on your own behalf, please include your details in the documents. If you are acting in a transaction on behalf of the principal, indicate him in the documents.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytadvertiseru
In the documents, indicate the entire amount of the transaction, without separately highlighting the agency fee. After all, it makes no difference to the buyer whether he communicates with the seller directly or with his agent.