» IP management
The activities of individual entrepreneurs are closely related to the acquisition of various goods from legal entities and individuals. Such sales of goods are clearly regulated by tax and civil legislation, since such transactions are subject to taxation, and this business activity must be clearly documented.
If it is easier for an individual entrepreneur to manage his paperwork, especially if he is on a simplified taxation system, then for a legal entity, all movement of his inventory must be reflected in special accounting documentation, which is constantly checked by regulatory authorities. In order to understand how goods are sold to individual entrepreneurs, this publication was written.
- 2 Document flow of legal entities that sell various goods
- 3 Sales of products in cash
- 4 Cashless payment system
- 5 Some features of payment for products
The concept of a product and its sale
Before describing in detail the documentary mechanism for processing transactions for the sale of various goods by legal entities to individual entrepreneurs, it is necessary to have an understanding of what a product is. From a legal point of view, it refers to objects (things) that have specific characteristics and are intended to meet the various needs of the population. In simple terms, goods are things (clothing, household appliances, and other property) that are used by citizens of our country to fulfill their consumer needs. They can be produced in our country or abroad. The sale of a product is the transfer of ownership of it from one person (for example, a legal entity) to another (individual entrepreneur) or citizen for monetary compensation (purchase amount). Each product has its own cost.
We prepare settlements with customers
If the online store will practice non-cash payments, you will need to open a current account. To do this, you need to resort to the services of a reliable banking institution. To open an account, an individual entrepreneur must provide a passport, TIN, and a certificate of registration. If it is an LLC, you will need a certificate of registration, as well as the charter of the company.
To sell goods you need a cash register. It is needed when sales are carried out for cash. It can be registered at the home address if it is an individual entrepreneur, at the legal address if it is an LLC. The corresponding instructions are given in the Federal Law “On the use of cash registers”. When a buyer of an online store purchases products for cash, he needs to be given a receipt. The cash register is registered with the Federal Tax Service. To register it, you need a registration certificate, tax identification number, cashier’s register, as well as paper confirming the right of ownership or lease of the premises. The application for registration is filled out directly to the Federal Tax Service.
Is it possible to conduct business without a cash register? There are two options:
- Concluding an agreement with an intermediary who has a cash register. Intermediary services are provided for a small percentage.
- Selection of UTII at the time of registration of a person. In this case, OKVED 52.61.2 is also not prescribed.
The latter option is only possible if the store operates mostly offline, and uses the Internet only as an auxiliary tool.
Document flow of legal entities that sell various goods
Due to the fact that in most cases the income of various legal entities that are engaged in economic activities is formed precisely through the sale of various goods and services, including to individual entrepreneurs, according to tax legislation it is subject to taxes. So that state tax authorities can track this, special accounting documents have been introduced into the document flow that allow keeping records of such transactions. There are two ways to sell goods:
- individuals;
- subjects of economic relations (legal entities and individual entrepreneurs).
In the first case, a simple cash receipt or an account certificate is sufficient. A cash receipt is a financial document that is issued to the buyer, which indicates the cost of the goods, including VAT (if applicable). An invoice certificate is a special form of a financial document, which can indicate not only the purchase of goods, but also its cost including taxes (VAT), as well as permission to issue the goods at the warehouse by the storekeeper. Typically, this is resorted to by various companies that sell goods at wholesale prices, or sell products from warehouses. In tax documentation, such transactions are recorded in separate accounting records and are confirmation of the purchase and sale. The second method involves the sale of goods to other legal entities or entrepreneurs. Here comes another form of reporting, which includes two forms of calculation:
- spot;
- cashless payments.
Each of them has its own workflow, so each option will be considered in more detail.
It is important to know that individual entrepreneurs have a special status, since when purchasing goods they can act as an individual or as a business entity. If an individual entrepreneur buys products and positions this acquisition for his own needs, then the company can limit itself to a sales receipt. If the acquisition of individual entrepreneurs’ products occurs for commercial purposes (subsequent sale to the public), then such transactions are carried out using other financial documents.
Some companies and individual entrepreneurs are trying to evade taxation and follow the path of selling products to individual entrepreneurs, for their own needs, without subsequent commerce, although the initial goals are subsequent resale of the goods. But the tax authorities are carefully monitoring this, and if such a transaction becomes known, the legal entity and individual entrepreneurs will expect large penalties.
Waybills and invoices
The Russian Ministry of Finance believed that an indirect sign of the presence of an entrepreneurial goal when purchasing goods is the buyer’s requirement, in addition to a cash receipt, to issue him an invoice and a delivery note - see letter of the Russian Ministry of Finance dated January 10, 2006 No. 03-11-04/3/3.
Nothing, by and large, has changed even now. In the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 04/05/16 No. 03-11-06/3/19246 it was said that if, for the purpose of selling goods, for example, contracts are concluded that define the range of goods, the timing of their delivery, the procedure and form of payment for the goods supplied , and also invoices and invoices are prepared and handed over to customers, logs of received and issued invoices, purchase books and sales books are maintained, then such activities relate to business activities in the field of wholesale trade. In this regard, it’s funny to look at the letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 15, 2010 No. 03-11-06/2/156. A company using the simplified tax system acquires property from an entrepreneur who pays UTII for use in business activities. The question was asked about documents confirming the fact of purchase. But this is absurd! This is an obvious supply agreement, and UTII cannot be paid here at all. However, the Russian Ministry of Finance answers the question about the documents, and simply ignores the contradiction itself. It's as if he doesn't exist. The latest letters on this topic - for example, letter from the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated April 29, 2016 No. 03-11-11/25379 - are generally a set of quotes that almost everyone already remembers by heart.
Sales of products in cash
This is a common form of trade turnover in our economic conditions, since most private entrepreneurs carry out their activities by working with cash. Both entities (legal entity and individual entrepreneur) are tax payers, so they must pay taxes on trade turnover. For tax authorities, confirmation of the sale of goods by a legal entity individual entrepreneur will be the following documents:
- waybill, issued when the product is delivered to the place specified by the individual entrepreneur, and payment occurs after delivery, or by agreement between business entities (advance payment, prepayment, full payment before delivery);
- a bill of lading, which is issued to an individual entrepreneur, at the location of the legal entity, before receiving products at a warehouse or other place; payment in this case can be in advance, in full, or with deferred payment.
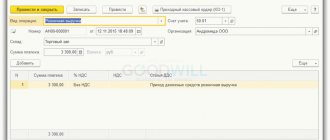
Confirmation of the acceptance of cash will be the issuance of a cash receipt order, which will indicate the amount received. That is, any payment will occur through the company’s cash desk.
In this case, you need to know that if the company does not have a cash register and the corresponding official personnel, then working with cash will be problematic, since regulatory authorities will regard this as a financial violation, which will lead to fines.
In general, working with cash is an additional problem that can lead to a negative attitude of the tax authorities towards the enterprise, so cash discipline and the regulations that regulate it have their own characteristics that you need to be aware of and strictly follow.
Supply contract
According to Art.
506 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, under a supply agreement, a supplier-seller conducting business activities undertakes to transfer, within a specified period or terms, the goods produced or purchased by him to the buyer for use in business activities or for other purposes not related to personal, family, home and other similar use . These two definitions essentially mean that the existence of a retail purchase and sale agreement depends on the will of the buyer of the goods, and the seller has no way to influence it. It turns out that the possibility of a taxpayer switching or not switching to UTII depends on the actions of the buyer of the goods, about which the taxpayer may not be aware, and the buyer, of course, is not obliged to inform him of his intentions (see also the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated 10.22. 97 No. 18).
Cashless payment system
The second method of payment for the goods received is by bank transfer. It is difficult to find a company or entrepreneur who does not have a current account. Nowadays, carrying out non-cash payments is an easy procedure, which boils down to the fact that the parties between whom commercial relations have arisen give the banks where their accounts are opened, payment orders for the transfer and acceptance of funds. Thanks to the Internet, this can be done without leaving your office or office, while complete security is guaranteed. Such relationships occur as follows:
- a legal entity that sells products gives the individual entrepreneur its bank details, where he must transfer money for the goods, and also provides a delivery note or other waybill, which indicates the name of the goods and its cost;
- accordingly, the entrepreneur agrees on the procedure for payment, which can be full or partial, after which he gives an order to his bank (in which he is serviced) to transfer funds, in which he indicates for what services the funds are transferred;
- when the money arrives at its destination, the goods are shipped or delivered to the designated place, and the recipient (in this case, the individual entrepreneur) puts his signature and seal (if any) on one copy of the invoice, and keeps the second for himself.
Thus, each business entity has the necessary financial documents for reporting, from which they will calculate the tax base.
Preparing for an online store
Before starting sales, you need to make sure whether the activity is subject to licensing. The relevant information is contained in the Federal Law “On licensing of certain areas of activity”. This law contains a list of works for which a license is required. Some types of goods require a license. Certification may be voluntary or mandatory. Even if the product being prepared for sale is not included in the list for compulsory licensing, it is recommended to obtain a certificate. This will allow you to earn trust from buyers and win a place in the market.
What happens if an online store operates without documents?
Documentary support is the basis of the legal activities of both individual entrepreneurs and LLCs. If a company operates without registration, it will face liability:
- Administrative. Appointed on the basis of Article 14.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. The fine for work without registration will be 500-2,000 rubles.
- Criminal. Appointed under Article 171 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation. Owners of an online store bear criminal liability only if their illegal activities caused major damage to third parties or the company received large income and did not pay taxes. The grounds for assigning liability are contained in the note to Article 169 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
- Tax office. Appointed on the basis of Article 116-117 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The fine is 10-20% of the online store’s profit. The amount of the fine is determined by the duration of the illegal activity.
The lack of registration documents also entails other disadvantages. This is distrust on the part of partners, the inability to reach a larger level.