Incorrectly transferred funds - VAT issue
29.03.2007, 10:49
No, there will be no delivery.
I talked to the director, he promised to send it tomorrow and that the letter would be sent.
29.03.2007, 13:44
29.03.2007, 13:50
"Glavbukh", 2006, N 22
MONEY TO YOUR CURRENT ACCOUNT: HOW TO NOT PAY VAT
Every company has at least once encountered this situation: money was received into the bank account from an unknown counterparty. And here the accountant inevitably has a question: is it necessary to charge VAT on the amount received? Read about how to act in this case in order not to overpay the tax in our material.
If money has been deposited into the company’s account, even by mistake, the tax authorities may consider it an advance. And they will force the organization to charge VAT on the amount received. Moreover, if the money transferred by mistake is returned, the accountant will not be able to deduct VAT. After all, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not provide for a deduction for this case. In paragraph 5 of Art. 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation only states that VAT can be deducted from an advance received only if the advance payment is returned due to a change in conditions or termination of the contract. But in the situation under consideration, there are no relations between the parties at all and no agreement was concluded.
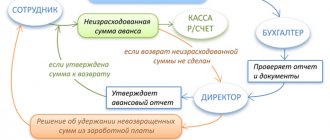
The VAT tax base includes funds received as advance payments from buyers. If the receipt of money is not related to payments for goods, works or services, then there is no reason to pay VAT. Therefore, if there is “other people’s” money in your current account, prepare the documents! Only with the help of papers can you prove your right not to pay VAT. To avoid claims from tax authorities, you need to ask the organization that transferred the money to you to issue a special letter addressed to you. It should say that the money was credited to the bank account by mistake and that your company is obliged to return it using such and such bank details. Based on this letter, you will debit money from your account. In addition, we advise you to write an explanatory note. It must indicate that the company does not have any agreements with the company from which the money was received, and there are no plans to conclude them in the near future. Please note that when receiving money from a company with which you do not have a contractual relationship, the amount must be taken into account in account 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors”. It is more convenient to create a special sub-account, for example “Calculations for unclear amounts”.
Source
simplified tax system
Erroneously received amounts do not form the organization’s taxable income (clause 1 of Article 346.15 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). They do not relate to either sales income or non-sales income (Articles 249, 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). These amounts are not recognized as the economic benefit of the organization (Article 41 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In the ledger for accounting income and expenses, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 22, 2012 No. 135n, erroneously received amounts do not need to be reflected. A similar point of view is contained in letters from the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 7, 2006 No. 03-11-04/2/231 and the Federal Tax Service of Russia for Moscow dated December 16, 2004 No. 21-09/81715.
It is not always known in advance that a deposit into a bank account is erroneous. Therefore, a situation may arise when the amount received will nevertheless be included in taxable income (reflected in column 4 of Section I of the book of accounting for income and expenses). In this case, corrections must be made to the book of income and expenses (clause 1.6 of the Procedure approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 22, 2012 No. 135n).
If the bank writes off erroneously received funds from the organization’s account, then they also do not need to be reflected in expenses. This is due to the fact that when the simplification is applied, the list of expenses is closed (Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). And amounts that were mistakenly credited to the organization’s account and then written off by the bank are not included in this list. In addition, the indicated amounts do not meet the expense criteria specified in paragraph 1 of Article 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (clause 2 of Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Notifying the bank about erroneous receipt of funds
A company that has received an erroneous payment must send a written notification to the bank within 10 days of receiving the bank account statement showing the excess funds. The form of such a written message to the bank is not established by law, therefore banks establish such forms with their own internal documents. If the bank does not have an approved form, the organization draws up a message in free form.
Bank, depending on the terms of the bank account agreement:
- if it is possible to write off erroneously credited amounts from the company’s bank account without acceptance, writes off the erroneously credited funds without a separate order from the organization;
- If there is no such possibility under the agreement between the bank and the organization, the erroneously transferred funds are written off only upon receipt of the corresponding order.
Accounting and tax accounting of cash return transactions
In accounting, when returning funds, a posting is used that mirrors the one with which the funds were accepted for accounting:
- Dt 51 K 62 - cash receipt;
- Dt 62 Kt 51 - refund.
In tax accounting:
- simplified tax system: crediting funds is reflected in taxable income on the date of receipt of funds to the current account; upon return, taxable income is reversed by the date of return;
- BASIC: crediting and returning funds transferred by mistake is not reflected.
VAT upon return of advance payment to the buyer
The main criterion for the transition period is the rule: regardless of the size of the tax rate accrued on the advance payment (in 2018 - 18%, in 2021 - 20%) for shipments made in 2021, VAT is taken into account in the shipping invoice at the rate of 20%. There are no other innovations regarding VAT on prepayments.
The algorithm of operations remains the same: upon receipt of the advance, the supplier charges VAT and pays it, and no later than after 5 days, registers a “preliminary (advance) invoice” in the sales book and issues it to the buyer. The advance is recorded in the reporting quarter when it was received, and is reflected in the VAT return on page 070 of section 3.
When shipping goods and materials as an advance payment, the seller has the right to reimburse the amount of tax from the budget. But if the contract is terminated or its provisions are revised, and only part of the goods is shipped or the delivery is canceled completely, then the seller is obliged to return the previously received advance payment (or the unused balance). Its return is also associated with a VAT adjustment, since the seller has the right to claim a deduction from the amount of the unused advance payment if the basis for non-fulfillment of obligations was the termination of the contract or a change in its terms. In this case, the supplier issues an adjustment invoice, recording the refund.
The supplier can deduct VAT when returning the advance payment to the buyer on the date of return of the advance payment. VAT is calculated as the amount of the advance received multiplied by the rate that was applied when receiving the advance payment. The fact of a payment return must be reflected in accounting and confirmed by a payment document. You can claim the right to a deduction within one year from the date of return of payment for a failed (or partially failed) transaction. VAT on the return of the advance payment to the buyer in the declaration is reflected on page 120 of section 3.
Check and save
There is a way to pay less interest for using budget funds. Before drawing up an act and writing a decision, the inspector must collect evidence of the company’s violation of the law, otherwise the company will challenge all the inspectors’ arguments in court. An accountant, having received a request from an inspector for information and documents, will understand on what issues there may be additional charges and how serious the risk of a fine is. When the danger is great, the organization can submit an updated declaration without questionable VAT amounts. In this case, you will have to return the previously received money and transfer interest for the period when the refunded VAT was in the company’s account, that is, less than one quarter. But this period is less than five months - when the organization receives a requirement to pay fines from controllers.
According to PBU 10/99, as well as the Instructions for using the Chart of Accounts, interest accrued by the Federal Tax Service on the amount of excess VAT refunded is not taken into account in the organization’s expenses
The accountant should note that interest is calculated taking into account the double refinancing rate of the Central Bank. You may need to draw up a new bank guarantee, which means new expenses. But if all additional costs are less than the expected additional charges, then it is more profitable to submit an updated declaration as early as possible.
No matter how strong the desire of entrepreneurs to receive their legal VAT as quickly as possible, the declarative procedure can be used only if they are fully confident in the validity of the deductions. Otherwise, the benefit of quick reimbursement may cause more harm to the company.
Refund of advance payment to buyer in 2021: VAT
So, when returning an advance payment received in 2021, VAT in the supplier’s accounting is accepted for reimbursement on the date of return of the advance in its amount multiplied by 18/118.
When shipping goods and materials as an advance payment, VAT is deducted on the date of shipment, and the rate of tax accepted for deduction is equal to the rate at which the advance payment was paid.
The same rules apply if a partial refund of the advance payment is issued to the buyer. VAT is accepted for deduction on the date of shipment, the unused part of the advance payment is transferred to the buyer, the tax on it is reimbursed at the rate applied on the date of receipt of the advance payment. In the purchase book, code “22” is used to encrypt VAT when returning the advance payment to the buyer.
nds_pri_vozvrate_avansa_pokupatelyu.jpg
Related publications
The changes that have occurred with the increase in the VAT rate since the beginning of 2021 have raised many questions regarding settlements between counterparties working with this tax. Let's figure out how to correctly document transactions related to the return of the transferred advance payment to the buyer.
Refund to the buyer: VAT on advance payment
The acquirer has the right to recover previously refunded tax from the prepayment, but it is important to remember that he is not obliged to deduct “advance VAT. Thus, the restoration of VAT when returning the advance payment to the buyer is relevant for him, unless the tax deduction has already been accepted.
Let us remind you that you can accept a deduction only if the following conditions are met:
the agreement between the parties provides for an advance;
the buyer has the following documents:
— invoice for advance payment;
— payment order confirming the transfer of the advance payment.
The buyer must declare the deduction in the quarter when all the specified conditions are met; it cannot be transferred to future reporting periods.
On the deduction of advance VAT when returning the advance payment to the buyer (Zaitseva S.
A payment order, in the “Purpose of payment” field, the basis for the transfer will be indicated “Return of advance payment under supply agreement N.”, and can serve as such a document-based basis for deducting “advance” VAT from the amount that falls on the withdrawn advance payment. If in the “payment” for a refund to the buyer the details of letters demanding the return of previously transferred money and a reference to the reasons for withdrawing the advance (part of the advance) are indicated, claims from controllers will generally be minimized. The capital's tax authorities, explaining a similar issue, indicated: in the event of a change in the terms of the supply contract or its termination, as well as the return of advance amounts against the upcoming supply of goods, the amounts of VAT calculated by the supplier of such goods and paid by him to the budget from the specified advance amounts are subject to full deduction in the amount after the corresponding adjustment transactions are reflected in the accounting in connection with the return of the advance, but no later than one year from the date of its return (Letter dated March 14, 2007 N 19-11/022386).
Clause 4 art. 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation specifies: deductions of tax amounts specified in paragraph 5 of Art. 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, are carried out in full after the corresponding adjustment operations are reflected in the accounting in connection with the return of goods or refusal of goods (work, services), but no later than one year from the date of return or refusal.
But the wording (you will agree) is such that there is no doubt: clause 4 of Art. 172 is directly related only to paragraph. 1 clause 5 art. 171. Then it is not clear whether the annual limitation on the deduction of “advance” VAT applies to the cases provided for in paragraph.
2 clause 5 art. 171. If yes, then from what moment should the time be counted?
The agreement to terminate the contract, drawn up on 9.2013 (later than the deadline for submitting “clarifications” with the declared deductions - June 2013), did not save the situation: the company’s arguments that the right to deduct amounts of “advance” VAT arose only from the moment of termination of the contract (from the date of drawing up the agreement), were not accepted by the cassation authority. The court issued a verdict: by claiming deductions in June 2013, the company missed the deadline established by law for claiming these deductions.
How to calculate VAT? Example
How to calculate VAT payable? For a more complete understanding of what a tax such as VAT is, it is worth considering two simple examples.
First example
Let's say an entrepreneur opened a small store selling denim clothes.
However, to get started, he should find a wholesale supplier from whom he could purchase goods.
Let's say a supplier was found and fifty pairs of jeans were purchased from him for a total of ten thousand rubles (two hundred rubles for one pair of jeans).
In such a case, eighteen percent of the tax has already been included in the cost of the clothing, which the wholesale supplier will have to pay.
Two hundred rubles is 118 percent (or 1.18). The price of one pair of denim clothes excluding value added tax (from a wholesale supplier) is 169.5 rubles (the cost has been rounded for ease of calculation).
Consequently, thirty and a half rubles from each pair of jeans is the VAT paid by the entrepreneur, or 1,525 rubles for the entire batch of denim clothes. This amount will be taken into account as an “input” contribution.
When purchasing materials for their subsequent retail sale, an entrepreneur must prove that the cost of goods already includes VAT; in this case, this proof is an invoice, check or invoice with the corresponding tax lines. Accounting must be clear and transparent for the tax service.
Before the value of products ready for sale is generated, the entrepreneur should subtract the value added tax from the purchased goods - the amount of money deducted will serve as the basis for the subsequent calculation of the tax. After having already created the finished product, it is necessary to take into account the tax, namely eighteen percent.
Let’s say that an entrepreneur was able to sell jeans purchased from a wholesaler at a price of 1,000 rubles per piece.
In this case, after selling the entire batch, revenue in the amount of 50 thousand rubles will accrue.
This amount is similar to the previous 118 percent; in other words, the “outgoing” VAT base will be equal to:
- 50 thousand rubles / 1.18 = 42,373 rubles (100 percent);
- 50 thousand rubles – 42,373 = 7,627 rubles.
Ultimately, the entrepreneur will have to pay 7,627 – 1,525 = 6,102 rubles.
Second example
Clothing was purchased at a price of 2,000 rubles, and sold for 3,000 rubles. In this example, the amount of money required to pay value added tax can be calculated even more simply: the entire added value (one thousand rubles) is taken as 1.18 or 118 percent. Therefore, the VAT amount at eighteen percent will be:
- 1,000 / 1.18 = 847.5 rubles;
- 1,000 – 847.5 = 152.5 rubles.
If an identical number of goods were sold as purchased, then the VAT that must be paid can be calculated simply on the value added per unit of goods (the difference between the cost of purchase and sale).
Deduction of VAT from the seller when returning advances and goods
CORRECT OPTION OF CALCULATIONS At the time of provision of services: DEBIT 62 CREDIT 90-1 – 107,600 rubles. — revenue from the provision of services is reflected; DEBIT 90-3 CREDIT 68 – 16,414 rub. — VAT is charged on the sale of services; DEBIT 68 CREDIT 62 “Advance received” – 16,414 rubles. — previously accrued VAT was accepted for deduction in the part of the realized CREDIT 62 – 107,600 rubles. - offset of advance payment. At the time of transfer of the unused advance: DEBIT 62 “Advance received” CREDIT 51 – 10,400 rubles. — return of the advance payment to the buyer; DEBIT 68 CREDIT 62 “Advance received” – 1586 rubles. — accepted for deduction of VAT on the returned part of the advance. Please note that in practice a situation may arise when the seller returns the unused advance payment to the buyer for the upcoming delivery of goods, performance of work or provision of services. In this case, the return of the advance payment is not related to the termination of the contract.
As a rule, the amount of tax previously accrued upon receipt of this amount has already been taken for deduction. With a literal interpretation of the provisions of the Tax Code, in the case of a refund of an advance payment not related to a change or termination of a contract, a deduction of previously accrued tax is not provided. Therefore, there is a high probability of tax disputes related to the legality of deducting VAT previously accrued on payment amounts for upcoming deliveries of goods (performance of work, provision of services). In this case, we recommend that you reverse this tax amount in your accounting and submit an updated VAT return to the tax authorities.
In one of their latest letters, tax authorities explained the procedure for applying VAT deductions in the event that the receipt and return of advance payments are carried out in the same tax period upon termination of the contract. The organization must reflect in the VAT return the amount of tax on the prepayment received and in the same tax period, if there are documents confirming the return of the amounts of this prepayment, and subject to a change or termination of the contract, it has the right to deduct the corresponding amount of tax 5. Upon receipt of the prepayment, the seller ( the contractor) is obliged to charge VAT, including if the advance payment was received in non-monetary means (for example, by a third party’s bill of exchange). In paragraph 5 of Article 172 of the Tax Code, the condition for deducting VAT in the event of a change in conditions or termination of a previously concluded agreement with the buyer (customer) is the return of the corresponding amounts of advance payments. However, it is not indicated that such a return must necessarily be made in cash. In this regard, we can conclude that when an advance payment previously received by the seller is returned by a third party bill of exchange, the corresponding amount of VAT is subject to deduction, regardless of whether this third party bill of exchange was received as an advance from the buyer (customer) or otherwise. This conclusion is also confirmed by a number of court decisions (post. FAS MO dated June 20, 2005 in case No. KA-A40/5402-05, FAS PO dated March 28, 2005 in case No. A12-20637/04-C36, dated April 26, 2007 in case N A55-11874/06, dated January 15, 2009 in case N A65-9611/2008).
Reviewer errors
Having received a request for a VAT refund, the accountant must carefully study it for possible errors by inspectors. The company may go to court to invalidate the received paper. All violations are specified in paragraph 18 of Article 176.1 of the Tax Code, these include: lack of necessary information, errors in VAT or interest amounts, failure to comply with the established deadlines for issuing this document.
A situation is possible when the interest for the use of budget money, calculated by the company independently, does not coincide with the amount of interest of the inspectors. How to correctly calculate this figure? The Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation and the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated October 8, 1998 No. 13/14 states that when calculating interest, the number of days in a year is taken to be 360 (1/360). And according to the official position of the Ministry of Finance, 1/365 (1/366) of the refinancing rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation should be applied.
VAT when returning goods from the buyer
The seller issues an adjustment invoice, guided by legislative acts, registers the transaction in the purchase book and makes corrections in accounting documents. An invoice is issued within five days from the date of registration of the return. Watch a video about adjustments from organizations on the simplified tax system. The majority of simplified companies operate without VAT due to the specifics of the special tax regimes applied.
The buyer can return the money or replace it with a similar product without defects. If the conditions regarding the range of goods were violated. Return of goods from the buyer with VAT to the supplier without VAT 506 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). Unless otherwise provided by the rules of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation on the supply contract, the provisions provided for in paragraph 1 of Chapter 30 “Purchase and sale of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation” apply to the contract for the supply of goods (clause
The basis of the “tax-free shopping” system (hereinafter referred to as TFS) is the procedure established in the European Union: if a person permanently resides outside the borders of the European Union, then when leaving it, you can receive a refund of the VAT paid when purchasing goods. The VAT refund mechanism is quite simple. When making a purchase of goods in a TFS store, they issue a special check, on which a customs stamp is placed when leaving the country, then you can receive money using this check. 2 However, keep some details in mind.
The amount is deductible by the seller within a year after shipment. By law, any transaction must be reflected in accounting journals (purchase book, sales book). When shipping, an entry is made in the accounting journals, and returns are also recorded in the journal.
The 1C program, when generating the tax that is payable to the budget, will itself make the necessary deductions. The main thing is to make all entries into the program in a timely manner.