VAT accounting registers in 1C 8.3
A general list of VAT registers can be obtained by clicking on the button in the main menu “All functions” - “Accumulation registers” (Fig. 1) (if the “All functions” button is not available to you, follow the following instructions).
Fig.1
A little about the design of registers.
As the name suggests, each register is responsible for a specific section. Thus, according to the “Purchase VAT” register, the “Purchases Book” report is generated, and according to the “Sales VAT” register, the “Sales Book” report is generated.
The structure of all registers is similar and resembles a library directory. The main purpose of registers is to store and systematize information.
Each of the registers is a list of strings (Fig. 2). All lines of the same register have the same format, that is, the same columns. The number and purpose of columns are different in different registers.
Fig.2
Figure 2 shows the contents of the “Purchase VAT” register. If the “Purchases Book” report displays data for one organization, then the “Purchases VAT” register contains data for all organizations at once.
The columns “Period” and “Registrar” are in each accumulation register.
Each line of the register is associated with a document (which one is shown in the “Registrar” column). You can double-click to open the document itself. The concept of “posting a document” in 1C is associated not only with the formation of transactions, but also with the creation of a line in a register (one or several at once). In 1C slang they say: the document “moved” the register, “check the movement of the document.”
Fig.3
By clicking the “More” button (Fig. 3), you can output the contents of the register to a file, print it, filter the information, change the composition of the output columns (the register data does not change).
Refund procedure
The part of the “input” tax that exceeds the amount of calculated VAT is subject to reimbursement.
Sold goods worth 120 rubles (including 20 rubles VAT).
Purchased goods worth 360 rubles (including 60 rubles VAT).
The amount to be reimbursed is 40 rubles (60 – 20 = 40).
In this case, you may need to submit documents for a desk audit.
2 months
VAT refunds are usually made after the completion of a desk audit, which lasts 2 months.
If signs indicating
possible violations
, the period for a desk tax audit may be extended to three months.
The amount to be reimbursed can be offset against debts (arrears, penalties, fines) on federal taxes, offset against upcoming payments, or returned to the current account.
A VAT refund can be received either after the completion of a desk audit (clause 2 of Article 176 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) or, in the case of applying the application procedure for VAT refund (clause 8 of Article 176.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), before the completion of the desk audit.
After conducting a desk audit of the VAT return, the taxpayer submits a refund application to the inspectorate and a VAT refund is issued to him.
12 days
Taxpayers exercise the right to apply the declarative procedure for tax refund by submitting to the tax authority a tax return, a bank guarantee and an application for the application of the declarative procedure for tax refund (clause 7 of Article 176.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The money is refunded to the taxpayer within 12 days, after which a desk audit is carried out.
Exception! taxpayers who paid at least 2 billion rubles over the previous 3 years. taxes may not provide a bank guarantee (
clause 1 clause 2 art. 176.1 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
).
Go Letter dated April 4, 2019 No. ED-4-15/ [email protected] On providing the opportunity to send a bank guarantee to the tax authority in electronic form
Go Software package
“VAT refund: taxpayer”
Preparation of an invoice to reflect VAT
You can change the information in the register from the registrar document.
Let's consider how registers change depending on the posting of documents. We will conduct experiments with the “VAT presented” register. Accounting accounts are set in the settings of accounting accounts in the item.
Fig.4
In Fig. 4, the receipt invoice. Let's check the postings of this document (Fig. 5).
Fig.5
We see two bookmarks, each of which corresponds to one register. The first displays accounting and tax accounting entries (generally speaking, entries are also stored in the register, but this is a register of a different format; the structure and purpose of the accounting register are not discussed in this article).
Fig.6
On the second tab (Fig. 6) there is data from the “VAT presented” register. This register is one of the 12 registers that relate to the VAT accounting system. Note that the type of movement is “Arriving”.
Fig.7
Now let's register the supplier invoice. For this, the receipt invoice below (Fig. 7) contains the necessary fields.
Fig.8
In the generated invoice, check the box “Reflect VAT deduction in the purchase book...” (Fig. 8) and check the movements of the document (Fig. 9).
Fig.9
Acquisition of material assets (services) of general purpose
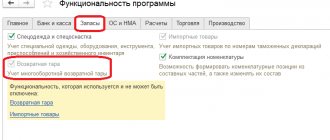
Reflection in 1C of information on received material assets and services intended for use for general production or general economic purposes is carried out in the same manner as described in the previous section. With the exception of one point: when the values (services) in question are simultaneously used in activities subject to and not subject to VAT, the “Distributed” attribute must be set.
How to install it in 1C is clearly shown in the figure below:
Finding errors in 1C for value added tax
The invoice “moved” 4 registers at once (in Fig. 9 we see 4 bookmarks). One of these 4 registers is the already familiar “VAT presented”. But unlike the entry made by the document “Receipt (act, invoice) 0000-000249 dated 08/01/2016 18:00:00”, the type of movement in this case is different (“expense”).
What does this mean? Firstly, the total sum of all similar movements with different signs matters. Let’s filter such movements in the “VAT presented” register using the “Invoice” column (Fig. 10) and sum up the “Amount without VAT” column, taking into account the sign in the “Type of movement” column. Please note that the “Invoice” column indicates the basis document.
Fig.10
As a result, we get zero. This is equivalent to a zero balance on account 19 (for this counterparty and agreement). It would seem, why duplicate in the register what can be seen in the postings?
The fact is that in life there are a wide variety of situations. For example, they forgot to register an invoice; then there will be no line with “expense”, the total amount will not be equal to 0, and the program, when analyzing, will show an error for this counterparty and agreement (Fig. 11)
Fig.11
Conclusion - registers are needed for operational analysis and reporting.
Declaration
Deadline for submitting the declaration
The VAT return is submitted by the taxpayer (tax agent) to the tax authorities at the place of registration as a VAT payer no later than the 25th day of the month following the expired tax period. There is no need to draw up and submit declarations for the location of separate units. The entire tax amount goes to the federal budget.
For example, for the fourth quarter of 2021, the VAT return must be submitted no later than January 25, 2021.
A fine is provided for failure to submit a declaration (Article 119 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The VAT return is submitted electronically.
A VAT return, which must be submitted in electronic form, but is presented on paper, is not considered submitted (clause 5 of Article 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Attention! If the taxpayer fails to submit a tax return to the tax authority within 10 days after the expiration of the established period, transactions on the accounts may be suspended (clause 3
Art. 76 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
).
VAT declaration form
The form of the VAT tax return and the procedure for filling it out were approved by order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 29, 2014 No. ММВ-7-3/ [email protected] taking into account the changes made by order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated August 19, 2020 No. ED-7-3/ [email protected] ]
Procedure for filling out the declaration
The declaration is filled out in rubles without kopecks. Indicators in kopecks are either rounded to the nearest ruble (if more than 50 kopecks) or discarded (if less than 50 kopecks).
The title page and section 1 of the declaration are submitted by all taxpayers. These requirements also apply to those taxpayers whose tax base is zero at the end of the quarter.
Sections 2 – 12 , as well as appendices to the declaration, are included in the declaration only when taxpayers carry out relevant operations.
Sections 4-6 are completed in case of carrying out activities taxable at a VAT rate of 0 percent.
Sections 10-11 are completed in the case of issuing and (or) receiving invoices when carrying out business activities in the interests of another person on the basis of commission agreements, agency agreements or on the basis of transport expedition agreements, as well as when performing the functions of a developer.
Chapter
12
The declaration is completed only if the buyer is issued an invoice with the allocation of the tax amount by the following persons:
- taxpayers exempt from fulfilling taxpayer obligations related to the calculation and payment of value added tax;
- taxpayers upon shipment of goods (work, services), sales operations of which are not subject to value added tax;
- persons who are not taxpayers of value added tax.