Business entities of all organizational and legal forms, regardless of priority and additional types of activity, in accordance with the requirements of current legislation, must comply with the approved Procedure for conducting cash transactions. The concept of the latter is given in the regulatory document.
ProfBusinessAccounting LLC provides assistance in conducting cash transactions: reflecting cash movements in accounting, drawing up advance reports, creating cash books, etc. The cost of the service depends on the volume of document flow and the availability of cash registers and varies from 50 rubles/operation to 3000 rubles. subscription service for each cash register"
State control over cash transactions
Cash transactions are transactions with cash. If an organization issues or accepts cash, it must adhere to the rules established by law, regardless of its legal form and taxation system.
Basic regulations governing the procedure for conducting cash transactions:
- Directive of the Bank of the Russian Federation dated March 11, 2014 N 3210-U (hereinafter referred to as Directive N 3210-U) is the main document establishing the rules for conducting cash transactions;
- Directive of the Bank of the Russian Federation dated December 9, 2019 N 5348-U (hereinafter referred to as Directive N 5348-U) - establishes the rules for cash payments;
- Federal Law of the Russian Federation dated May 22, 2003 N 54-FZ (hereinafter referred to as Federal Law N 54-FZ) determines the rules for the use of cash register systems.
Cash discipline is compliance with the rules established for:
- cash payments;
- storing cash in the cash register;
- spending proceeds.
Issues of cash discipline also include the use of cash register systems.
Control over compliance with cash discipline in organizations is carried out by tax authorities on the basis of:
- clause 1 art. 7 of the Federal Law of March 21, 1991 N 943-1 “On the tax authorities of the Russian Federation”;
- Art. 7 of the Federal Law of May 22, 2003 N 54-FZ.
Banks, although they are not empowered to control the cash transactions of their clients, are required to provide assistance to the tax authorities within the framework of the program for managing the risk of legalization (laundering) of proceeds from crime and the financing of terrorism developed by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation. They can also request information and documents from a client who raises doubts, or take other measures to prevent dubious transactions, including denial of service (Federal Law of August 7, 2001 N 115-FZ).
Store accounting software
Any entrepreneur is interested in his store developing and making a profit. If you use the commodity accounting system just for show in order to fulfill the conditions of the Federal Law, nothing will change. After all, with the help of an accounting system you can turn your store into a profitable business.
Store accounting software will eliminate most of the routine processes that usually take a lot of time. This saves time on maintaining inventory, assigning and updating prices on the sales floor. The merchandiser will always know how much product is available on the shelves and in the warehouse. He will be able to plan purchases competently.
If you have already chosen the CloudShop cash register system, the accounting program will complement it perfectly. Its capabilities:
- management of purchases, sales and returns
- loading items from tables
- import and export suppliers and buyers
- registration of receipts and expenditures of money
- remote control of balance at the cash register
- built-in loyalty program
- maintaining sales statistics and analytics.
- You can connect an online cash register, a barcode scanner (more than 13 thousand in the database) and an online store to the accounting program.
And most importantly, the store owner does not necessarily have to be on the sales floor. Thanks to the CloudShop accounting program, through a mobile application on Android and iOS or a web version, he will be able to remotely control all work.
Rules for conducting cash transactions
Directive of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation N 3210-U defines the organization's cash desk as a place for conducting cash transactions. There are no requirements for the premises or place where cash is stored. But the provisions are regulated - we will talk about them later.
Cash limit at the cash desk
The organization is obliged to set a cash limit at the cash desk - the maximum permissible balance at the end of the operating day.
A legal entity independently determines the cash balance limit based on the nature of its activities, taking into account (clause 2. Directive of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation N 3210-U):
- revenue volumes;
- volumes of cash disbursements.
The limit is calculated in accordance with the appendix to the Directive of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation N 3210-U. PDF
Cash in excess of the limit may be kept in the cash register:
- on days of payment of wages and scholarships;
- on weekends and non-working holidays, if the organization conducts cash transactions on these days.
In other cases, exceeding the established limit at the cash desk is not allowed (clause 2. Directive of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation N 3210-U).
Separate divisions (SUs) that have a cash desk comply with the limit established and approved by the administrative document of the head division. In this case, the following conditions are met:
- if the OP deposits the proceeds to the bank, the limit for him is calculated separately and is not included in the organization’s limit;
- if the OP transfers revenue to the head division, the limit of the entire organization is calculated taking into account the OP’s limit.
The procedure for cash payments between business entities
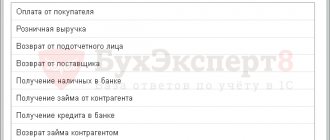
The Bank of Russia has established the purposes for which it is permitted to use cash proceeds received at the cash desk (clause 1 of Directive N 5348-U):
- for payments to employees included in the wage fund and social payments;
- for payment of insurance compensations (insurance amounts) under insurance contracts to individuals who previously paid insurance premiums in cash;
- for issuing cash for the needs of individual entrepreneurs not related to business activities;
- for payment for goods (except for securities), works, services;
- for issuing cash to employees on account;
- for a refund for goods previously paid in cash, work not performed, services not provided, etc.
To issue cash from the cash register for other purposes, you must receive it from your current account.
The maximum permissible amount of settlements between legal entities (IP) for cash under one agreement is 100,000 rubles. All amounts paid under the agreement both during the period of its validity and after its expiration are taken into account (clause 4 of Directive N 5348-U).
Cash payments with the participation of an individual who is not an individual entrepreneur can be carried out without limiting the amount (clause 5 of Directive N 5348-U).
Procedure for using CCP
A separate large section of cash discipline concerns the use of cash register equipment (CCT).
Federal Law of the Russian Federation dated May 22, 2003 N 54-FZ determines that organizations and individual entrepreneurs making payments on the territory of Russia are required to use cash register systems, except in cases established by this law (Clause 1, Article 1.2 of Federal Law N 54-FZ).
More details:
- Hot questions about online cash registers
- Deduction for the purchase of cash registers with UTII
- Required cash receipt details
Online cash register and procedure for processing cash documents
Requirements for the use of online cash registers are specified in Law No. 54-FZ (amended by Law No. 290-FZ). From July 1, 2021, this type of cash registers has become mandatory for use by almost all business entities. The requirements for documents generated online by the cash register have also been updated: cash receipts and BSO. According to the new rules, when registering a BSO, you need to use a device similar to an online cash register. The requirements for a cash receipt and a strict reporting form are specified in Art. 4. 7. Law No. 54-FZ.
Income and expenditure of funds
Receipt and expense transactions are carried out in the operating cash desk. Each cash transaction must be completed on a separate form. The procedure in which cash documents are filled out is prescribed in Decree of the State Statistics Committee No. 88 of August 18, 1998 and the instruction of the Bank of the Russian Federation No. 3210-U.
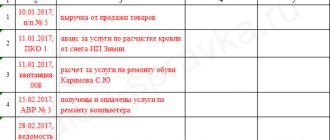
A cash receipt order is issued for the receipt . Documents (if any) confirming the amount of the amount received are attached to it. The receipt (tear-off part of the PKO), with seals and signatures of authorized persons, is given to the depositor.
For expenses, an expense cash order (RKO) of form KO-2 is issued, to which documents are attached with the specified amount of funds issued (check, receipt, copy of the order, memo, etc.). The RKO also indicates the details of the recipient’s identity document.
Receipt and expense orders are first registered in the register of receipt and expenditure cash documents (KO-3). They are assigned serial numbers and the documents are transferred to the cash desk for issuing and accepting payments. In addition to PKO and RKO, the journal also records: payroll statements for the payment of salaries, applications for payment of funds, invoices for payment, etc.
All documents (PKO, RKO) issued during the day are recorded in the cash register book (KO-4). Every day, the totals of turnover by income and expense are summed up and the balance at the end of the day is displayed. Also, footnotes to accounting accounts must be written in the PKO, RKO and in the cash book. This procedure is mandatory for legal entities, but optional for individual entrepreneurs who do not keep accounting (subclause 1, clause 2 of the law dated December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ).
The book of accounting of funds accepted and issued to other cashiers (KO-5) is kept in organizations with a large number of divisions that are serviced by central cash desks. At the beginning of each working day, the senior cashier issues cash to departments for conducting cash transactions. At the end of the day, the cashier is obliged to hand over unused funds for reporting and signature to the central cash desk.
Persons responsible for conducting cash transactions
Cash transactions are carried out by a cashier or other employee appointed by the head of the organization or individual entrepreneur. The manager or individual entrepreneur can perform the duties of a cashier himself.
An employee acting as a cashier must have job rights and responsibilities established, with which he must be familiarized with signature (clause 4 of Directive of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation N 3210-U). In this case, if cash discipline is violated, the employee will be liable as an official.
Responsibility for violation of cash discipline
| Article of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation | Violation | Punishment |
| clause 1 art. 15.1 | Exceeding the established limit at the cash register at the end of the working day | Fine for officials: 4,000–5,000 rubles, for legal entities: 40,000–50,000 rubles. |
| Discrepancy between the cash balance in the cash register at the time of inspection and the documentation (incomplete recording of revenue) | ||
| Exceeding the maximum amount of cash payments between legal entities (IP) | ||
| clause 2 art. 14.5 | Non-use of CCP | Fine for officials: 25%–50% of the amount of a bounced check, minimum 10,000 rubles, for a legal entity: 75%–100% of the amount of a bounced check, minimum of 30,000 rubles. |
| clause 3 art. 14.5 | Repeated violation | Disqualification of officials for up to 2 years; Suspension of the activities of a legal entity for up to 90 days |
| clause 4 art. 14.5 | Use of a cash register that does not comply with legal requirements, or a cash register in violation of the established requirements for registration, re-registration and conditions of use | Fine for officials: RUB 1,500–3,000. for legal entities: 5,000–10,000 rubles. |
| clause 6 art. 14.5 | Failure to issue checks (BSO) to the buyer on paper or failure to send checks (BSO) at the buyer’s request via email or SMS | Fine for officials: RUB 1,500–3,000. for legal entities: 5,000–10,000 rubles. |
Who has concessions in cash management?
Individual entrepreneurs have the right to conduct cash transactions in a simplified manner:
- do not set a limit on the balance of money in the cash register (clause 2 of Directive N 3210-U);
- use the proceeds for personal purposes without restrictions (clause 1 of Directive N 5348-U);
- if they keep a book of income and expenses, they can (clauses 4.1, 4.6 of Directive N 3210-U): not keep a cash register,
- do not draw up cash documents.
Individual entrepreneurs and small enterprises may not set a cash balance limit (clause 2 of Directive of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation N 3210-U). To do this, it is necessary to stipulate in the local regulatory act (LNA) that the organization or individual entrepreneur does not set a limit on the balance of money in the cash register. If this is not done, the limit at the cash register will be zero.
For the purpose of applying Directive of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation N 3210-U, small enterprises include legal entities classified as small enterprises and micro-enterprises in accordance with the criteria established by Federal Law of July 24, 2007 N 209-FZ. The tax authorities maintain a Unified Register of Small and Medium Enterprises, where you can see the category of your enterprise:
- microenterprise;
- small;
- average.
Learn more about small businesses
To access the section, log in to the site.
See also:
- Cash payment procedure has been updated
- Primary documents for the cash register
- Monetary documents: legislation
Did the article help?
Get another secret bonus and full access to the BukhExpert8 help system for 14 days free of charge
Related publications
- Accounting accounts and analytical accounting of cash transactions: legislation and 1C This publication describes the main accounts of cash transactions and...
- Changes in reporting and cash transactions from November 30, 2020 The Central Bank changed the rules for reporting and cash transactions from November 30...
- The procedure for accounting for operations to change the cadastral valuation of land plots has been clarified. The Ministry of Finance in Letter dated 05.29.2020 N 02-06-10/45902 explained that the change...
- The procedure for conducting an inventory: legislation The article discusses: the procedure for preparing for an inventory; cases; its timing...
Choosing a cash register program
There are two types of store programs: a cash register program that simply records sales, and a cash register program as part of an inventory system. Of the two options, experienced entrepreneurs always advise choosing the second. It's simple - when you use a cash register program synchronized with the accounting program, all your sales go into the accounting system, which displays information about purchases, sales, write-offs, and balances. This simplifies the analysis of your work and makes it possible to remotely monitor the operation of the store.
One such program is the CloudShop checkout program. You can download it for free on Android and iOS operating systems. The program works in full compliance with Federal Law-54. Benefits of the cash register program:
- Using CloudShop cash register software is beneficial for an entrepreneur. You just need to download the program and buy a fiscal registrar. There is integration with the Atol brand fiscal printer, as well as the Evotor smart terminal.
- To connect, you can use the detailed instructions for connecting the CCP.
- The CloudShop cash register program records not only sales, but also receipts, expenses, and returns.
- The CloudShop store cash register program automates the work of both one store and the work of a chain of stores. Moreover, the number of stores is not limited.
- The cash register program synchronizes with any barcode scanner.
- Unified technical support. For example, your system is not working correctly. You don’t know what the problem is - in the cash register or in the accounting program. All issues can be resolved in one place.
- And finally, the cash register program opens up wide possibilities for the inventory accounting system.