Concept and types
Instruction at the workplace involves setting out the basic requirements for the methods, order and sequence of actions in the production process, where the main requirement is their safety.
Instructions are:
- introductory;
- primary;
- repeated;
- unscheduled;
- targeted.
The procedure is mandatory for both parties: the employer cannot fail to carry it out, and the employee cannot ignore it. If an employee fails to pass, he is suspended from activities at the workplace and may even be fired. And the employer is held accountable, usually administratively. The fine is impressive: from 20,000 to 30,000 rubles for officials, and from 130,000 to 150,000 rubles for companies. Sanctions are established by part 3 of article 5.27.1. Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation.
What is initial training in labor safety?
Initial briefing is a mandatory procedure in the labor protection regulations. And it is needed, first of all, so that the employee, once at the workplace, before starting work and performing duties, becomes familiar with all the safety rules.
Initial instruction is carried out directly at the workplace with new employees of the organization, with employees transferred from another department, with employees who will have to perform new duties for them, with those arriving on a business trip from a third-party organization, with students undergoing practical training, with all persons taking part in the production activities of the enterprise.
Other types of briefings:
→ unscheduled;
→ introductory.
Purpose of the event
The main purpose of the initial briefing is to familiarize them with the rules of work and behavior in the workplace to prevent harm to their life and health. Employees must know and understand how to reduce, and ideally completely eliminate, injuries at work and the creation of emergency situations.
Primary briefing has the following goals:
- familiarize new employees with the activities of the organization, the nature of the work carried out in a particular department;
- organize a safe workplace for employees;
- instruct about the rules of behavior in the workplace, the safe process of preparing equipment for work, and working with equipment;
- introduce unsafe work practices to further minimize risks;
- familiarize yourself with the personal protective equipment used and the procedure for their use, requirements for workwear, safety footwear;
- familiarize yourself with collective protection means - alarms, door locks, braking devices, etc.;
- familiarize the employee with the scheme for the safe movement of the employee around the enterprise, with emergency and fire exits, closed areas;
- familiarize yourself with equipment, incorrect operation of which can lead to danger to life and health;
- train in the application of safety rules at the facility;
- inform about the location of fire extinguishers and the procedure for action in emergency situations;
- discuss the causes of possible emergencies, fires, injuries at work and measures to prevent them, the location of the first aid kit, telephones, and first aid equipment.
When is it carried out?
Initial training is carried out before the employee begins independent work in the organization. Immediately after the induction training. The duration of the briefing is not fixed by law. It is carried out at the discretion of the employer, depending on the quantity, specifics of the equipment and assigned responsibilities.
First of all, workers must become familiar with dangerous and harmful factors that negatively affect health and safety, learn to use personal protective equipment, and work correctly with equipment and tools.
Employees must be provided with all instructions and operating manuals for the equipment used in their work for familiarization, labor safety instructions, and work plans.
Then, once every 6 months, workers must undergo repeated instruction on labor protection, and at high-risk facilities - once every 3 months. The list of works and positions that relate to high-risk facilities must be approved by internal regulations.
Which employees of the organization can be exempt from instruction?
The employer has the right to exempt a number of positions from undergoing initial and subsequent briefings. Most often this applies to office workers who are not directly involved in the use of equipment, power tools, or the use of hazardous raw materials or flammable materials. In other words, those who are not directly in production.
To exempt employees from mandatory training, it is necessary to approve by order of the enterprise a list of positions to which this obligation does not apply. In the absence of a formalized order and violation of the procedure for familiarizing employees with the instructions, a fine will be imposed on the official or organization.
However, you should think several times about whether it is worth exempting an accountant, secretary, engineer and other office positions from undergoing training. They work on computers, which, according to technical regulations, are classified as low-voltage equipment; therefore, if used poorly, they can cause harm.
By removing the obligation for employees to undergo training, the employer assumes risks and responsibility for their safety.
Dates
Induction training is carried out on the day the employee is actually hired by the organization. It is important to understand that the person applying for appointment to the position is not an employee, therefore the procedure is not carried out in relation to this category.
Initial instruction at the workplace is carried out once - before the start of work or internship, if we are talking about student interns. They are no exception. Only those who are not directly involved in the production process are not subject to such inspection. The list of such persons is approved at the local level.
Repeated training on labor protection is regular, since its purpose is to maintain and update previously acquired knowledge. Frequency: once every six months. The six-month interval changes for some personnel when it comes to cases of increased occupational safety requirements.
Unscheduled - upon the occurrence of some circumstances, often negative, such as an accident or death at work.
The target does not have a set deadline. Like unscheduled, it is associated with circumstances, but more often positive, for example, installation of modern equipment or holding a public event.
Persons entitled to conduct training
An important issue is the right to authorize an individual to conduct induction training with employees of the organization. It must be resolved before issuing an order appointing someone responsible for its implementation. The list of persons entitled to be appointed to conduct it is determined by clause 7.8 of GOST 12.0.004-90. These include:
- a trained specialist – labor protection engineer;
- an experienced worker chosen for this purpose by the manager;
- manager or his representative;
- a representative of an accredited organization who is directly involved in labor protection at the enterprise;
- other persons by order of the manager.
ATTENTION. The responsibilities of the responsible person authorized for the correct and timely conduct of induction training must be recorded in a separate order from the head of the organization. This order, confirming the authority of the responsible person, will be presented to the inspectors when conducting an inspection of the organization.
Who is being briefed
Introductory briefings on the first working day should be carried out for those who:
- first hired;
- came to the organization on a business trip;
- is an employee of another organization, but works on the territory during a given period of time;
- is a trainee.
Primary workplace assessments should be carried out for employees who:
- rehired;
- belong to the seasonal category;
- have a temporary contract for a period of up to 2 months;
- are business travelers;
- are trainees;
- perform a new function on behalf of themselves.
In this case, employees are subject to exemption provided that their activities are not classified as dangerous, that is, the functionality is not related to:
- ensuring the operability of the equipment;
- using electrical tools;
- activities related to the storage of various raw materials.
The manager must, by order, approve the list of professions and positions for which employees may not undergo the briefing procedure.
Re-instruction at the workplace, consolidating previously acquired knowledge, must be carried out for workers who have already completed the initial procedure and are included in the following categories:
- newly hired;
- seasonal;
- working on a fixed-term contract;
- on a business trip;
- performing a new function for themselves;
- trainees.
Unscheduled briefing should be carried out for categories of employees if:
- they work in new conditions with changes in standards, processes, and equipment upgrades;
- violated labor safety standards and an accident occurred;
- there is a requirement from control authorities;
- they had a break in their work activity (over 30 days - for harmful and dangerous conditions, over 60 - in other cases);
- there is a manager's decision.
Targeted training should be carried out for those employees who:
- perform one-time work;
- eliminate the consequences of emergency situations;
- work in areas that require admission or permission;
- participate in a mass event held in the organization.
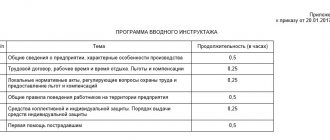
Contents of the induction program
This event, which is carried out on an ongoing basis, must take place according to a pre-prepared plan. Therefore, each organization must have an induction program developed and approved by the head of this enterprise in paper form with all the necessary stamps. It can be developed and created by a labor protection specialist of this enterprise, as well as another organization providing similar services on the basis of a license. The program displays the following information:
- brief content of the briefing;
- careful transcription of all sections;
- information about those authorized to conduct this type of instruction;
- a list of laws, regulations, local documents justifying the legality of the actions performed;
- The timing of the briefing must be specified.
All information must be truthful and up-to-date; if something changes during the validity period of this program, then changes are made to the text by creating a separate document approved in the same form as the program or creating an updated program.
Who conducts on-the-job training?
It all depends on the species. The induction can be carried out by the manager himself, an occupational safety specialist or any other authorized employee. Powers are conferred by order.
To carry out the target, an order is issued, which assigns a person in charge. As already mentioned, it is often carried out when commissioning new equipment. Accordingly, someone who has delved into the essence of technological innovations himself will be able to tell others about innovations.
The rest of the activities at the workplace can be entrusted to the head of the department (head of the workshop, foreman, foreman).
What to talk about
Instructions, including at the workplace, are carried out according to programs. When developing programs, you should focus on GOST 12.0.004-2015. As stated in the document itself, it is a standard or model for organizing training in the workplace.
The program includes questions regarding:
- working conditions;
- dangerous or harmful factors;
- safety and occupational safety requirements;
- technical and operational documentation;
- safe working practices;
- providing first aid to the victim.
The induction program should contain information:
- about the enterprise and those persons who are on its staff;
- features of the activity;
- requirements of current legislation on occupational safety;
- PVTR and labor discipline, responsibility for their violation;
- organizing activities in the field of occupational safety;
- working conditions, including existing harmful and dangerous factors;
- ways to prevent accidents;
- general responsibilities of an employee in terms of occupational safety;
- PPE, its issuance;
- algorithm of employee actions in the event of an accident;
- accident investigation procedure;
- providing first aid.
The on-site initial training program should include the following questions:
- about the employee’s working conditions on site;
- specific production process;
- equipment and tools in the area where functions are performed;
- existing harmful and dangerous factors;
- collective protective equipment;
- PPE at the place of work;
- current requirements for safe operation of equipment;
- procedures for preparing to perform functionality;
- established requirements for special clothing and footwear;
- testing equipment for serviceability;
- routes of movement of employees around the territory of the organization;
- emergency situations;
- their reasons;
- algorithms for action in case of an accident;
- points of location of emergency protection equipment and first aid;
- familiarization of the employee with all documents on occupational safety.
Goals and objectives
The main goal of initial training is to familiarize new employees with the techniques of working on equipment that is safe for life and health. The initial training program covers the following issues:
- information about the nature of the production part, the principle of the enterprise’s activities;
- how to organize a workplace that is safe for life and health;
- where does a shift begin, how to prepare equipment for operation, what needs to be checked before turning it on, how to turn on equipment;
- safe working methods, methods to reduce health hazards;
- what personal protective equipment (PPE) should be prepared before starting work, how to use it;
- how to move around the workshop, what you need to know for your own safety, to prevent unpleasant incidents in the workplace;
- what equipment is potentially dangerous, how to protect yourself when working with equipment;
- what measures to take in emergency situations;
- safety measures during loading and unloading operations; how to prevent injury in the workplace;
- the most common causes of accidents, fires, and industrial injuries;
- where fire extinguishers and emergency assistance tools are located;
- and so on.
First aid program
First aid is a part of training that should be included in all programs.
The employer is obliged to conduct it when hiring a new employee every year in the future. In this case, the employer can attract a third-party employee or organization who has the right to provide this type of service. The first aid program is extensive, consists of a number of sections and is included as an appendix in GOST 12.0.004-2015.
| Chapter | Description |
| Section 1. | Informs about:
|
| Section 2. | Gives an understanding of the basic structure of the human body, briefly informs about vital systems. |
| Section 3. | Contains information about first aid at the scene of an emergency. Including:
|
| Section 4. | Informs about determining the need and mechanisms for performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation. |
| Section 5. | Gives information:
|
| Section 6. | Informs about loss of consciousness, including:
|
| Section 7. | Describes the characteristics of wound surfaces and first aid when receiving them. |
| Section 8. | Contains information about abdominal injuries, their types, and first aid. |
| Section 9. | Contains information about chest injuries, their types, and first aid. |
| Section 10. | Contains information about head injuries, their types, and first aid. |
| Section 11. | Contains information about spinal injuries, their types, and first aid. |
| Section 12. | Contains information about pelvic injuries, their characteristics, and first aid. |
| Section 13. | Contains information about limb injuries, their types, and first aid. |
| Section 14. | This part of the program concerns actions for long-term limb compression syndrome, its causes, and help. |
| Section 15. | Talks about thermal injuries, their types, first aid. |
| Section 16. | Contains information about chemical burns, their types, and first aid. |
| Section 17 and 18. | Dedicated to poisoning and electrical injuries. |
Fire safety briefing
The employer is obliged to teach workers to comply with fire safety measures - this provision is enshrined in the Federal Law of December 21, 1994 No. 69-FZ, that is, to provide instructions on this topic.
Those employees who have not undergone such instruction are prohibited from working.
The program consists of:
- standards and rules for the maintenance of premises and territories of the organization;
- a list of fire safety installations related to the organization’s activities;
- algorithms of actions during fire hazardous work;
- established rules for the use of open fire;
- a list of processes that are carried out by employees during a fire.
The fact that the employer has completed the briefing is recorded in the briefing log and is certified by the signatures of the instructor and the employee.
Difference between industrial safety instruction and PTM training
| Item name | Safety training | PTM training |
| Target | Inform about the following available at the institution:
| Provide special information and knowledge to the heads of enterprises, as well as employees responsible for industrial safety. |
| Employees involved | All employees. | Manager or responsible person. |
conclusions
Initial briefing is a mandatory and important stage during employment or transfer to a new job. This is an opportunity to learn about the specifics of the organization’s work, the tasks and functionality of a specific position, responsibility and safety when operating equipment and mechanisms, as well as the rules of conduct in emergency circumstances at a specific facility.
Conducting initial training on labor protection and work safety is the direct responsibility of the employer. High-quality training of employees will help prevent and prevent the occurrence of situations dangerous to the life and health of people.
How to apply
The briefing log is an A4 size book. Its pages are numbered, stitched and certified by the signature of the head of the organization and its seal (if there is one).
The design of the title page includes the name of the institution, start and end dates of completion.
The briefing log contains a tabular section that includes information regarding:
- dates;
- FULL NAME. employee, his date of birth, profession;
- type of training provided;
- reasons for the instruction being outside the plan;
- hours of instruction;
- Full name, instructor position.
After recording the instruction, it must be certified by the signatures of the employee and the instructor.