Every business manager faces the task of reporting on time about their business activities, paying taxes and fees. Late filing of reports and payment of taxes leads to penalties and fines. Moreover, each tax has its own payment deadline, and each report has its own submission period. Thus, the SZV-M report is submitted to the Pension Fund monthly, and the simplified tax system declaration is submitted to the Tax Office once a year.
How can a taxpayer prepare reports and payment orders for tax payments during the year on time? An accountant's calendar will help - a convenient tool for drawing up a reporting schedule and planning tax payments. The accounting and tax calendar of Kontur.Accounting allows you to track important dates for free in a convenient form and receive explanations on established reports and payments.
Changes for 2021
Big changes for employees. A new ESSS calculation has appeared that replaces RSV-1 and partially 4-FSS.
There are no changes to the deadlines for paying taxes and filing returns.
| Where to submit | What kind of reporting? | Submission deadline |
| Inspectorate of the Federal Tax Service | Unified Social Insurance Tax (USSS) (except for FSS contributions for injuries) | Quarterly no later than the 30th day of the following month: Q1. — May 2, 2021; II quarter — July 31, 2021; III quarter — October 30, 2017; IV quarter — January 30, 2021 |
| Pension Fund | SZV-M | Monthly, within 15 days after the end of the month |
| Pension Fund | Insurance experience report | Every year no later than March 1 of the following year |
| FSS | (FSS NS and PZ) Calculation of contributions for injuries | Quarterly: on paper - no later than the 20th day of the next month, electronically - no later than the 25th day of the next month |
Filing a VAT return electronically: deadlines, main advantages
The tax return can also be filed electronically using the Internet, but it is important to know that even then the filing deadline remains the same. This method is very convenient for the taxpayer, as it has the following advantages:
- There is no need to go to the tax office or stand in line, because you can report at any time from the taxpayer’s office;
- If you submit documents in electronic format, you do not need to print them on paper;
- The possibility of technical errors is reduced;
- Quick update of various reporting formats;
- Receive notifications about confirmation of delivery of the declaration;
- Security of declarations from viewing and modification by others;
- Possibility of sending an information request to the tax authorities.
It is now possible to submit reports using the website of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation.
As for tax agents, they will not be able to use the electronic filing method; they will have to “physically” submit a paper return to the tax office.
Calculation for 2021
| 2018 | Amount of days | Working hours (in hours) | ||||
| Calendar days | Work days | Weekends and holidays | with a 40 hour work week | with a 36-hour work week | with a 24-hour work week | |
| January | 31 | 17 | 14 | 136 | 122.4 | 81.6 |
| February | 28 | 19 | 9 | 151 | 135,8 | 90,2 |
| March | 31 | 20 | 11 | 159 | 143 | 95 |
| I quarter | 90 | 56 | 34 | 446 | 401,2 | 266,8 |
| April | 30 | 21 | 9 | 168 | 151,2 | 100,8 |
| May | 31 | 20 | 11 | 159 | 143 | 95 |
| June | 30 | 20 | 10 | 160 | 144 | 96 |
| II quarter | 91 | 61 | 30 | 487 | 438,2 | 291,8 |
| 1st half of the year | 181 | 117 | 64 | 933 | 839,4 | 558,6 |
| July | 31 | 22 | 9 | 176 | 158,4 | 105,6 |
| August | 31 | 23 | 8 | 184 | 165.6 | 110.4 |
| September | 30 | 20 | 10 | 160 | 144 | 96 |
| III quarter | 92 | 65 | 27 | 520 | 469 | 312 |
| 9 months | 273 | 182 | 91 | 1453 | 1308,4 | 870,6 |
| October | 31 | 23 | 8 | 184 | 165,6 | 110,4 |
| November | 30 | 21 | 9 | 168 | 151,2 | 100,8 |
| December | 31 | 21 | 10 | 167 | 150,2 | 99,8 |
| IV quarter | 92 | 65 | 27 | 519 | 467 | 311 |
| 2nd half of the year | 184 | 130 | 54 | 1039 | 935 | 623 |
| 2017 | 365 | 247 | 118 | 1972 | 1774,4 | 1181,6 |
simplified tax system
For 2021, you need to report using a new declaration form. The form itself, the procedure for filling it out and the electronic format were approved a year ago - by Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated February 26, 2016 No. ММВ-7-3/ [email protected]
There are a number of purely technical changes in the declaration, for example, in the sections there is no longer line 001 indicating the code of the taxable object, since the object is clear from the presented sections. Cells have appeared on the title page for those cases when the organization has been reorganized and the declaration is submitted by its successor. They indicate the reorganization code (1 - transformation, 2 - merger, 3 - division, 5 - merger, 6 - division with merger, 0 - liquidation) and the TIN/KPP of the reorganized organization. In addition, now in the declaration, instead of outdated OKATO codes, there are cells for new OKTMO codes.
1. Section 2.1 is now numbered 2.1.1, and section 2.1.2 has been added to reduce the tax on sales tax amounts. Let us remind you that it is impossible to reduce the sales tax if you have not submitted to the Federal Tax Service a notice of registration as a payer of the sales fee in relation to the relevant trade item (clause 8 of Article 346.21 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
2. In section 1.1, instead of line 120 with a fixed tax rate of 6%, lines 120–123 appeared with the possibility of setting the rate for all periods of tax payment (1st quarter, half-year, 9 months, tax period). This is due to the fact that regional laws from 01/01/2016 may reduce the rate to 1% depending on the categories of taxpayers. And for newly registered individual entrepreneurs, regions can generally establish tax holidays with a rate of 0% (clause 1, 4, article 346.20 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Calculation for 2021
| Month / Quarter / Year | Amount of days | Working time (hour) | ||||
| Calendar | workers | Weekends | 40 hours/week | 36 hours/week | 24 hours/week | |
| January | 31 | 17 | 14 | 136 | 122.4 | 81.6 |
| February | 28 | 18 | 10 | 143 | 128.6 | 85.4 |
| March | 31 | 22 | 9 | 175 | 157.4 | 104.6 |
| April | 30 | 20 | 10 | 160 | 144 | 96 |
| May | 31 | 20 | 11 | 160 | 144 | 96 |
| June | 30 | 21 | 9 | 168 | 151.2 | 100.8 |
| July | 31 | 21 | 10 | 168 | 151.2 | 100.8 |
| August | 31 | 23 | 8 | 184 | 165.6 | 110.4 |
| September | 30 | 21 | 9 | 168 | 151.2 | 100.8 |
| October | 31 | 22 | 9 | 176 | 158.4 | 105.6 |
| November | 30 | 21 | 9 | 167 | 150.2 | 99.8 |
| December | 31 | 21 | 10 | 168 | 151.2 | 100.8 |
| 1st quarter | 90 | 57 | 33 | 454 | 408.4 | 271.6 |
| 2nd quarter | 91 | 61 | 30 | 488 | 439.2 | 292.8 |
| 3rd quarter | 92 | 65 | 27 | 520 | 468 | 312 |
| 4th quarter | 92 | 64 | 28 | 511 | 459.8 | 306.2 |
| 2017 | 365 | 248 | 117 | 1973 | 1775.4 | 1182.6 |
Example
Entrepreneur I.S. Samodelkin has employees, and all of them are involved in activities subject to UTII. The individual entrepreneur pays pension and medical contributions for himself in a fixed amount at the end of each quarter.
In the first quarter of 2021, the amount of calculated UTII amounted to 400 thousand rubles (line 010). In the first quarter, Samodelkin paid 300 thousand rubles in compulsory insurance premiums for employees (for December, January and February), and also paid 25 thousand rubles for sick leave at his own expense (on line 020). Finally, on January 17, the entrepreneur paid for himself mandatory pension and health insurance contributions for the fourth quarter of 2021 in the amount of 12 thousand rubles. In section 3 of the declaration, Samodelkin stated:
- in line 010 - 400 thousand ₽;
- in line 020 - 225 thousand ₽ (200,000 + 25,000);
- in line 030 - 12 thousand ₽.
To fill out line 040, the entrepreneur compared two amounts:
1) line 010 – (line 020 + line 030) = 223 thousand rubles;
2) 50% of line 010 = 230 thousand rubles.
Since the first amount turned out to be less than the second, the second amount was reflected in line 040: 230 thousand rubles.
All other changes in the declaration are technical. In particular, the names of lines 020 and 030 of Section 3 have been adjusted, since in connection with the reform of insurance premiums they are now regulated by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The electronic format of the document and barcodes on declaration sheets have also changed.
Before submitting your return, be sure to ensure that you are submitting it using the updated form. Since, according to clause 28 of the Rules approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance dated July 2, 2012 No. 99n, the old format of the declaration will not be accepted by the Federal Tax Service.
In Externa, reporting forms are always up to date, and the built-in check will ensure that the report is submitted the first time.
To learn more
If necessary, you can check your accounting program. Open the declaration file using notepad and find the desired combination among the set of characters. In the case of the UTII declaration of the new format, it will be like this: VersForm = “5.07”.
Calculation for 2021
| Month / Quarter / Year | Amount of days | Working time (hour) | ||||
| Calendar | workers | Weekends | 40 hours/week | 36 hours/week | 24 hours/week | |
| January | 31 | 15 | 16 | 120 | 108 | 72 |
| February | 29 | 20 | 9 | 159 | 143 | 95 |
| March | 31 | 22 | 9 | 175 | 157.4 | 104.6 |
| April | 30 | 21 | 9 | 168 | 151.2 | 100.8 |
| May | 31 | 20 | 11 | 160 | 144 | 96 |
| June | 30 | 21 | 9 | 168 | 151.2 | 100.8 |
| July | 31 | 21 | 10 | 168 | 151.2 | 100.8 |
| August | 31 | 23 | 8 | 184 | 165.6 | 110.4 |
| September | 30 | 22 | 8 | 176 | 158.4 | 105.6 |
| October | 31 | 21 | 10 | 168 | 151.2 | 100.8 |
| November | 30 | 21 | 9 | 167 | 150.2 | 99.8 |
| December | 31 | 22 | 9 | 176 | 158.4 | 105.6 |
| 1st quarter | 91 | 57 | 34 | 454 | 408.4 | 271.6 |
| 2nd quarter | 91 | 62 | 29 | 496 | 446.4 | 297.6 |
| 3rd quarter | 92 | 66 | 26 | 528 | 475.2 | 316.8 |
| 4th quarter | 92 | 64 | 28 | 511 | 459.8 | 306.2 |
| 2016 | 366 | 249 | 117 | 1989 | 1789.8 | 1192.2 |
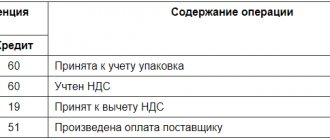
Tax transactions
Carrying out payment for goods and registering them, transferring taxes to the budget and other tax transactions - all this is reflected in accounting. To do this, use postings for specific transactions:
- payment for goods to the supplier: Dt 60 Kt 51;
- receipt of goods from the supplier: Dt 41 Kt 60, Dt 19 Kt 60;
- sales of goods: Dt 62 Kt 90, Dt 90 Kt 68;
- VAT deductible: Dt 68 Kt 19;
- entries for payment of VAT to the budget: Dt 68 Kt 51.
Postings when calculating penalties - Dt 91 Kt 68, fines - Dt 99 Kt 68.
Fines
Penalty for reporting to the Pension Fund
not on time: “1)
if less than 180 days have passed,
5% of the amounts of contributions payable on the basis of this calculation (for example, the fine for an individual entrepreneur with 16159.56 will be 807.98 rubles and it does not matter whether he paid or not) for each month, but no more than 30% and no less than 100 rubles.
2) if more than 180 days have passed
, 10% of the amount, but not less than 1000 rubles” (Article 46 212-FZ).
Penalty for Declarations
to the tax office not on time: “5 percent of the unpaid amount of tax subject to payment (additional payment) on the basis of this declaration, for each full or partial month from the day established for its submission, but not more than 30 percent of the specified amount and not less than 1,000 rubles ." (27.07.2010 No. 229-FZ). Those. If you paid the simplified tax system, but did not submit the declaration, then the fine is 1000 rubles. Fines and penalties are not displayed in the declaration. Fine calculator.
If taxes or payments to the Pension Fund are not paid on time, a penalty
in the amount of 1/300 multiplied by the payment amount and multiplied by the refinancing rate per day. Penalty calculator
Reporting period for financial statements
As soon as 2021 ended, accountants of commercial organizations began preparing reports, which they need to submit not only to Rosstat, but also to the Federal Tax Service. The package of accounting documentation must include (the composition is approved by Federal Law No. 402 of December 6, 2011):
- Balance sheet;
- Income statement;
- Report on intended use, cash flow;
- Statement of changes in capital;
- Various appendices and explanations to the income statement and balance sheet.
Advice : if annual financial statements are prepared by small enterprises, then, in accordance with the regulations of Federal legislation, they are allowed to submit simplified forms of the above reports to Rosstat and the Federal Tax Service.
Federal Law No. 402 and an article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation approved the deadlines for submitting annual reports:
- for 2021 – until March 31, 2021;
- for 2021 – until April 2, 2021.
Results
All business entities are required to submit tax reports to regulatory authorities within the established time frame. Tax reporting reflects data on the formation of the tax base and other information necessary for calculations.
If tax reporting is not sent to the Federal Tax Service or is submitted late, taxpayers will have to pay a fine in accordance with Art. 119 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Timely submission of tax reports, together with the reflection of reliable data in them, will allow taxpayers to avoid additional expenses in the form of fines and other negative consequences.
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
How to include separate income and expenses in the “profitable” base
The Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation has published a number of letters explaining the tax accounting procedure for certain income and expenses.
Work records
When purchasing work books, their cost is taken into account in tax and accounting expenses (letter of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated June 23, 2015 No. GD-4-3 / [email protected] ).
Income not taken into account when determining the tax base is defined in Art. 251 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The list of such income is exhaustive. The fee charged to the employee for the provision of work books or inserts is not mentioned in this article. This means that the indicated income is subject to income tax in the generally established manner (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated May 19, 2017 No. 03-03-06/1/30818). The amount received from the employee to reimburse the cost of the work book must be taken into account for tax purposes in non-operating income (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated May 19, 2017 No. 03-03-06/1/30818).
Salary
The list of labor costs is unlimited
To be recognized for profit tax purposes, expenses must be economically justified, documented, and incurred for activities aimed at generating income. Expenses that do not meet these requirements are not taken into account.
According to Art. 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, labor costs include any accruals to employees provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation, labor and (or) collective agreements.
The list of labor costs is open. These, according to paragraph 25 of this article, also include other types of expenses in favor of the employee, provided that they are provided for by the labor and (or) collective agreement.
Therefore, any types of labor costs incurred on the basis of local regulations of the organization can be recognized, subject to compliance with the criteria specified in paragraph 1 of Art. 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, and provided that such expenses are not specified in Art. 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated May 19, 2017 No. 03-03-06/1/30842).
Awards
Bonuses for production results are included in labor costs (clause 2 of Article 255 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
At the same time, as follows from Art. 129 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, incentive payments are elements of the remuneration system in an organization, which are established by collective agreements, agreements, and local regulations of the company.
The employer has the right to encourage employees who conscientiously perform their job duties: express gratitude, give a bonus, award a valuable gift, a certificate of honor, nominate them for the title of the best in the profession (Article 191 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Other types of employee incentives for work are determined by a collective agreement or internal labor regulations, as well as charters and discipline regulations.
However, for accounting for such expenses, the restrictions established by Art. 270 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Thus, remunerations paid to management or employees and not specified in employment contracts, as well as bonuses paid from the company’s net profit, are not taken into account when determining the profit base.
Therefore, bonuses to employees can be taken into account in expenses if the procedure, amount and conditions of payment are provided for by the local regulations of the organization, and are not specified in Art. 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated April 17, 2017 No. 03-03-06/2/22717).
Bonuses paid on holidays are not recognized as expenses, since they are not related to the production results of employees (letters of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated 07/09/2014 No. 03-03-06/1/33167, dated 04/24/2013 No. 03-03-06/ 1/14283, dated 03/15/2013 No. 03-03-10/7999).
Sport
For income tax purposes, expenses that are economically justified and documented are taken into account. An exception is the expenses listed in Art. 270 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
If events aimed at developing physical culture and sports in work collectives are carried out outside working hours and are not related to the production activities of employees, these expenses are not taken into account in the tax base (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 17, 2017 No. 03-03-06/1 /45234).
Foreign taxes
Any expenses are recognized as expenses if they are justified, documented and incurred for activities aimed at generating income.
Article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation establishes an open list of other expenses. It expressly states only taxes and fees assessed in accordance with Russian legislation. But it is possible to take into account other costs associated with production and sales.
In addition, the list of expenses not taken into account for profit tax purposes is closed and does not include taxes paid on the territory of a foreign state.
Thus, taxes and fees paid in another country can be written off among other expenses in accordance with paragraphs. 49 clause 1 art. 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated February 10, 2017 No. 03-03-06/1/7449).
This does not take into account foreign taxes, for which the Tax Code of the Russian Federation directly provides for the procedure for eliminating double taxation by offsetting them when paying the corresponding tax in Russia. For example, this procedure is defined in relation to income tax and property tax of organizations (Articles 311 and 386.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).