Features of taxation of dividends
The rules for taxation of dividends are established by Article 275 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. According to the code, the tax agent is the company that pays the remuneration. That is, it is she who is responsible for calculating and paying fees. Dividend recipients do not need to pay anything. The tax must be paid no later than the next date after the funds are issued.
A special taxation procedure applies to dividends. It is autonomous and is not determined by the tax payment system adopted by the enterprise. For example, even if a legal entity is on the simplified tax system, it is obliged to pay the fee in the accepted amount. The adopted tax rate is the same for everyone, except for persons who are entitled to preferential conditions.
To calculate the amount payable, the following formula is used:
N = K * Sn * (d – D)
The formula uses the following values:
- N – the final amount of tax collection.
- K is the ratio of the remuneration of a particular person to the sum of all dividends.
- Sn – bet.
- d – the sum of all dividends.
- D – the amount of dividends that were paid to the person in the past and current reporting period.
It makes sense to say additionally about the meaning of “D”. The calculations include only those amounts that were not previously taken into account when calculating the taxable base. Remunerations for which the rate is zero are not taken into account. From small “d” you need to extract the amount of remuneration that was transferred to non-residents of the Russian Federation.
IMPORTANT! As a result of calculations, a situation may arise in which the amount of dividends received by the company will be greater than the amount of remuneration distributed to third parties. In this case, the value resulting from the use of the formula will be negative. In such a situation, you do not need to pay any taxes.
When does a participant receive income upon leaving the LLC?
If the actual value of the share of a company participant upon leaving the LLC members exceeds the initial cost of the share, the payment in the part exceeding the contribution of this participant to the authorized capital of the company is recognized for tax purposes as the income of the taxpayer - the company participant.
From January 1, 2021, in accordance with paragraph 1 of Article 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, income from equity participation in other organizations paid in the form of dividends includes income in the form of property (property rights) received by a shareholder (participant) upon exit (disposal) from organization or when distributing the property of a liquidated organization. Amendments were made by Federal Law No. 424-FZ of November 27, 2018.
This means that the difference between the paid price of the share and the amount received from the LLC upon exit from it is equal to income in the form of dividends.
The actual value of the share of a company participant corresponds to a part of the value of the LLC’s net assets, proportional to the size of its share.
The Russian organization paying the dividends will in this case be the tax agent. It is she who must calculate, withhold and transfer income tax to the budget.
Tax rate for residents and non-residents of the country
Let's look at the tax rates adopted for 2021, as well as the laws on the basis of which they operate:
- For residents of the Russian Federation - 13% based on paragraph 1 and paragraph 6 of Article 224 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
- For non-residents – 15% based on paragraph 3 of Article 224 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
It must be said that until 2015, the rates were 15% for non-residents and 9% for residents. However, the rate for the latter was increased.
The tax rate changes annually. You need to consider the value that is current on the date of payment.
What is the zero rate and who is entitled to it?
In some cases, a zero rate applies. It can be used when the following circumstances are present at the time the decision to issue dividends is made:
- The recipient of the remuneration owns more than half of the share in the authorized capital.
- The period of continuous ownership of more than 50% of the capital is at least 365 days.
IMPORTANT! If the legal entity has carried out a reorganization, the period of continuous ownership will be calculated from the date of registration of the new entity. For example, OJSC became CJSC. In this case, the period will be calculated from the moment the closed joint-stock company appears. This procedure is confirmed by letter of the Ministry of Finance dated November 1, 2011 N 03-04-05/3-826.
Non-residents of the country can also use the preferential rate. However, stricter restrictions apply to them. In particular, in addition to fulfilling the above conditions, they should not be located in offshore zones, within which it is possible not to disclose all information about the financial transactions carried out.
You need to confirm your right to a zero rate. To do this, you need to submit the following documents to the tax office:
- Information about the date of receipt of ownership of the management share.
- Deposit receipts on the basis of which rewards are issued.
- Contract of sale.
- Transfer deed.
Any document confirming the ownership of more than half of the share in the management company, as well as the duration of this ownership right, will be suitable.
Calculation example No. 1
To calculate, you can use a simple formula: amount of rewards * bet. Let's look at an example. The recipient of dividends is a resident of the state. His share in the management company is 60%. The rate is 13%. The profit of the organization that pays dividends is half a million. Therefore, the remuneration amount is 300,000 rubles. We multiply 300,000 by 13% and get 39,000 rubles.
Let's look at another example. The person is not a resident of the country. His share in the management company is 40%. The rate for non-residents is 15%. The profit of the company paying the dividends is half a million. The dividend amount will be 200,000 rubles. Personal income tax will be equal to 30,000 rubles (200,000*15%).
Example No. 2
Let's consider using a more complex formula. It is relevant if the company distributing remuneration receives dividends from third-party legal entities. The formula itself: K*Sn*(d – D).
Example: Ivan Ivanov is a resident of the country. He owns a 30% stake in the management company. The profit of the Motor organization this year amounted to 800 thousand rubles. Ivan Ivanov's dividends are equal to 240 thousand rubles. Motor's reward was 100,000 rubles. The following calculations are made:
240 thousand rubles / (800 thousand – 320 thousand – 240 thousand) * 13% (240 thousand – 100 thousand) = 18,200 rubles.
This is exactly the amount that Ivan Ivanovich will have to pay.
Personal income tax
Until 2015, if a citizen received a profit, the income tax on dividends from individuals was calculated at a rate of nine percent. Now the rate is higher and is 13 percent. The amount of mandatory tax is withheld by the organization that pays the dividends.
It turns out that since 2015, the dividend rate has been equal to the “salary” rate, although income tax is not subject to contributions to insurance funds, since it is outside the scope of labor legislation. The general formula for calculating taxes on dividends is provided in clause 5 of Art. 275 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. With its help, both personal income tax and income tax are calculated (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated June 17, 2015 No. 03-04-06/34935).
When is a tax deduction not applied?
According to Article 210 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the profit of an individual, which is taxed at the established personal income tax rate of thirteen percent, can be reduced. The payment is reduced by the amount of various tax deductions. The available types of tax deductions are set out in the Tax Code (Articles 218, 219, 220, 221). I would like to assume that if the dividend rate has become equal to 13%, then deductions can now be applied to dividends as one of the types of income. But don’t rush to rejoice: the new legislative act clearly states that tax deductions cannot be applied to income from participation in a legal entity. Thus, the amount of the tax base for personal income tax will be the same as the dividends paid.
The tax base for personal income tax must be determined separately for each of the existing types of income, in relation to which the law provides for different tax rates.
The rate on “dividend” income increased and became equal to the rate that applies to ordinary average earnings; although the basis for determining taxes still needs to be calculated separately from other income. This means that when calculating personal income tax on dividends and personal income tax on wages, it is necessary to calculate two different bases.
As for the determination and calculation of the tax base of the “dividend” tax, all key points are enshrined in Art. 275 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Personal income tax reporting
According to the Tax Code (clause 4 of Article 230), persons who are recognized as tax agents in accordance with the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (Article 226.1) are required to submit information to the territorial department of the tax inspectorate:
- income for which tax payments are calculated and withheld;
- about persons who are recipients of income (if such information is available);
- about the amounts accrued, withheld and transferred to the state budget.
Information is transmitted in the order and within the time limits specified in Art. 289 Tax Code.
It should be noted that such tax agents are not subject to the general procedure for transferring information on the profits of individuals to the Federal Tax Service by providing a certificate of income of individuals.
The income tax return form is now in effect. It is filled in when tax agents have to pay dividends. The declaration form was approved by a letter from the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 02/05/2015.
Income tax
As mentioned earlier, the tax base for dividends is determined in accordance with Art. 275 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Income tax is withheld at a rate of 13% on the day of payment of dividends, directly by the organization that issues them. It is worth noting that a legal entity must transfer tax to the budget no later than the day following the payment of dividends.
If the income is received from a foreign organization, then the calculation and payment of tax lies on the shoulders of the domestic organization. If the payment is made by a Russian organization, then it is the organization that is obliged to withhold and pay tax for the recipient company.
Tax agent responsibilities exist for Russian companies regardless of the taxation regime.
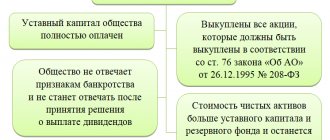
Calculation of net assets
By law, dividends cannot be distributed, for example, if the company’s net assets have become less than the authorized capital. To do this, you need to know how to calculate these “net assets”.
The procedure for determining the value of net assets was approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 84n dated August 28, 2014 and is binding on both JSCs and LLCs.
The value of net assets represents the book value of everything that will exist at the disposal of the founders of the organization if they pay off every single obligation; this value is determined on the basis of accounting data.
When calculating, the receivables of the founders for unpaid contributions to the authorized capital or payment for shares are subtracted from the total assets of the organization.
As for liabilities, they must be reduced by the amount of future income received as government assistance or as property transferred free of charge.
Dividend accounting
The payment of remuneration is preceded by a mandatory decision on the distribution of company profits, taken at a general meeting of auctioneers. The allocation of funds for the issuance of dividends must be reflected in the accounting records as of the date of this decision. In this case, you need to make an entry on DT account 84 with correspondence with KT 75 or KT 70. If the company is the source of dividends, you must pay personal income tax. Tax payment is recorded on DT 75 (subaccount 75-2) or DT 70 CT 68.
Example
must pay dividends to Ivan Sergeevich. Since he is not an employee or co-founder of the legal entity, when transferring money to him, the following transactions are made:
- DT 84 CT 75/2 – debt to the company’s auctioneer.
- DT 75/2 CT 68 – personal income tax withholding.
- DT 75/2 CT 50 or 51 – payment of remuneration minus personal income tax.
Other transactions are used when transferring funds to a company employee:
- DT 84 CT 70 – debt to the founder for dividends.
- DT 70 CT 68 – personal income tax withholding.
- DT 70 CT 50-51 – transfer of remuneration with withholding personal income tax.
Each posting is accompanied by explanations: the amount of the transaction and the primary documents on the basis of which it was made.
Withdrawal of a participant from the LLC
When a participant leaves the company, he is paid the actual value of the share, the size of which is determined according to accounting data as of the last reporting date preceding the withdrawal (clause 6.1 of Article 23 of Law No. 14-FZ “On Limited Liability Companies”).
The participant must be paid the actual value of his share within three months from the date such an obligation arises. It can be paid to the withdrawing participant in one of two ways:
- in cash;
- property (with the consent of the participant leaving the LLC).
General procedure
So, when paying dividends you need to adhere to the following order:
- Convening a general meeting of auctioneers and making a decision on the payment of dividends.
- Determining the amount of dividends.
- Making a corresponding note in accounting (debt has been generated).
- Calculation of tax on remuneration.
- Transfer of funds to the budget.
- Transfer of reward.
All transactions with money must be reflected in accounting using special entries. It is important to adhere to this order. Dividends cannot be transferred before taxes are paid, since personal income tax is transferred by the company.
When do you need to pay tax?
Based on paragraph 4 of Article 287 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation on income in the form of dividends, the tax withheld when paying income is transferred to the budget by the tax agent no later than the day following the day of payment.
If you do not remit the tax on time, the inspectors will charge the tax agent a penalty.
The Ministry of Finance in the commented letter notes paragraph 2 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated July 30, 2013 No. 57 “On some issues arising when arbitration courts apply part one of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.” It states that, given the compensatory nature of penalties as a payment aimed at compensating for losses of the state treasury as a result of failure to pay taxes on time, penalties may be collected from a tax agent who did not withhold tax from the taxpayer’s funds.
Thus, a tax agent may be charged a penalty for the period from the day following the day of payment of income in the form of dividends until the taxpayer, the recipient of the income, independently fulfills the obligation to pay tax.