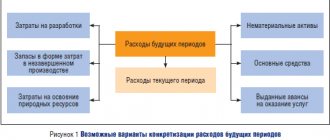
In recommendation:
– what is an electronic invoice (ESF); – when it is not necessary to issue an ESF; – when it is possible to issue an invoice on paper; – in what form to issue the ESF; – within what time frame the ESF is issued; – who signs the ESF.
An invoice is a document certifying the fact of shipment of goods or provision of services and their cost. It is prepared by the seller (supplier) in electronic form according to a strictly established sample (format) and presented to the buyer (customer).
In addition to confirming the shipment of goods (provision of services), the invoice also serves for tax purposes, namely for the purpose of calculating VAT. For the seller it is the basis for reflecting sales turnover, and for the buyer it is the basis for offset.
Attention The buyer of goods (services) has the right to offset the amount of VAT reflected in invoices accepted only in electronic form. If you, as a buyer, do not have an electronic invoice (EFI), your business will not be able to offset the VAT paid on the purchase of goods (services).
Situation
Possibility to offset VAT on an online cash register receipt
A driver refueling a company car at a gas station using a corporate card submitted a report and an online cash register receipt to the accounting department. The gas station did not issue an electronic invoice. Despite the fact that a cash receipt is a document that replaces an invoice, you can offset the “input” VAT on it if you register it through the personal account of a business entity in the system. Or you need to ask the gas station to display ESF.
When selling goods using corporate cards, the ESF is issued at the buyer’s request before the last date of the calendar month in which the goods (services) were sold, but is issued on the date of the actual sale of goods (services).
Indicate the cost of goods (services) in soums on the invoice. In this case, round the amount to hundredths.
If the contract is concluded in foreign currency on the territory of Uzbekistan, issue an invoice in soums at the foreign exchange rate established by the Central Bank on the date of sale of goods (services). Attach to it an invoice (invoice) issued in foreign currency or other documents confirming the sale of goods (services).
VAT when foreign organizations provide services in electronic form
From 2021, “foreigners” must register with the tax authorities of the Russian Federation and independently calculate and pay VAT to the Russian budget. In addition, a foreign seller is required to submit a VAT return quarterly.
Instead of a foreign company, any intermediary of a “foreigner” (also a foreign company) who provides electronic services on its behalf can register. Such an intermediary is recognized as a tax agent. It is registered, pays tax and submits a declaration in the same manner as a foreign company providing electronic services to citizens (Clause 4.6 of Article 83 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Which Internet services are subject to VAT?
VAT is subject to the following services of foreign Internet companies (clause 1 of Article 174.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- sale of computer programs, applications, games and databases, including updates to them;
- advertising services on the Internet and provision of advertising platforms;
- online auctions;
- platforms for posting offers for the sale of goods and services;
- data storage;
- hosting provider services;
- domain registration;
- digital goods (providing rights to digital books, music, audiovisual products, graphic images);
- administration of information systems and Internet sites;
- storage and processing of information, provided that the person providing the information has access to it via the Internet;
- searching and presenting information about potential buyers;
- access to Internet search engines;
- website visit statistics, etc.
VAT deduction for electronic services
The tax base for VAT for the provision of electronic services is defined as the cost of these services, taking into account the amount of tax, calculated on the basis of actual sales prices (clause 2 of Article 174.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The foreign seller will have to calculate the tax at an increased rate – 16.67%.
To obtain a VAT deduction, a Russian buyer will need the documents specified in paragraph 2.1 of Article 171 of the Tax Code:
- agreement and (or) payment document highlighting the VAT amount and indicating the TIN/KPP of the foreign organization;
- documents for the transfer of payment to a foreign organization, including the amount of VAT.
In such a situation, an invoice is not needed for deduction. Foreign companies themselves do not have the right to deduct VAT and do not have to draw up this document for their services. How to keep books of purchases, sales, as well as journals of invoices (clause 3.2 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Please keep in mind: deductions of VAT amounts claimed by foreign organizations for other services, the place of sale of which is recognized as the territory of the Russian Federation, are made in accordance with the general procedure. That is, for the deduction you will need invoices issued by such foreign organizations.
Federal Tax Service on filling out the purchase book
If an organization purchases electronic services from a foreign company or from its intermediary - a foreign organization, the Federal Tax Service of Russia in its commented letter recommends that it fill out the purchase book as follows:
- in column 2 – transaction type code 45;
- in column 3 - the number and date of the agreement or payment document (invoice for payment of services, act of provision of services or other document of a foreign organization). They must contain the foreigner’s tax identification number and checkpoint, as well as the amount of VAT;
- in column 7 - the number and date of the payment, and for non-cash forms of payment - the number and date of the document that indicates the repayment of the debt.
Let us remind you that information from the purchase book will be reflected in section 8 of the VAT return.
About the shopping book
The purchase ledger records invoices received by the company from suppliers. Its form was approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 2011 No. 1137 (hereinafter referred to as Resolution No. 1137), and the format for preparation in electronic form was approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated April 6, 2018 No. ММВ-7-6/ [email protected]
The basic principle of filling out the purchase book is this: documents need to be registered in the book when the company uses VAT deductions.
Organizations and entrepreneurs exempt from paying VAT in accordance with Article 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation may not maintain a purchase book. This is due to the fact that these persons do not have the right to deduct tax amounts.
Supplier invoices are recorded in the purchase ledger if the following conditions are met:
purchased assets (work, services) were acquired for operations subject to VAT and capitalized;
the invoice is drawn up in the prescribed form and filled out in accordance with the rules set out in Resolution No. 1137.
Invoices, adjustment and corrected invoices received on paper or electronically are registered in a uniform manner as the right to tax deductions arises (Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In the purchase book you need to register tickets, hotel bills and other strict reporting forms that confirm expenses for employee business trips. It is only necessary that the VAT amount be highlighted in these documents and that they are included by the employee in the business trip report.
The principal registers invoices received from the commission agent in the purchase ledger. This applies to invoices issued by the commission agent for the amount of his remuneration. When transferring an advance to a commission agent for the upcoming provision of services, the principal must also register an invoice from the commission agent in the purchase book.
Buyers register in the purchase book invoices received from sellers when transferring an advance against the upcoming delivery of goods. When receiving an advance, sellers issue invoices and register them in the sales book (including non-cash payments).
The purchase book is signed by the head of the organization or another authorized person. By the 20th day of the month following the expired quarter, its sheets must be numbered, laced and sealed with the company's seal. It is stored in the organization’s archives for at least four years from the date of the last entry. If you keep a purchase book in electronic form, then it must be signed with an enhanced qualified electronic signature, but only when transferred to the Federal Tax Service via TKS (including as part of a desk audit).
Expert “NA” E.V. Natyrova
PRACTICAL ENCYCLOPEDIA OF AN ACCOUNTANT
Complete information about accounting rules and taxes for an accountant. Only a specific algorithm of actions, practical examples and expert advice. Nothing extra. Always up-to-date information.
Connect berator
Invoice in euros, payments in rubles. Buyer's problem with deduction
Our company entered into a contract for the supply of products in 2014 in euros. Payment is made 100% in rubles at the exchange rate. The supplier issued an invoice in euros and a delivery note in rubles.
Can the buyer accept such an invoice for VAT refund? Or should the supplier still issue an invoice in rubles?
Clause 7 art. 169 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
It has been established that if, under the terms of the transaction,
the obligation is expressed in foreign currency, then the amounts indicated in the invoice can be expressed in foreign currency
.
According to Art. 307 Civil Code of the Russian Federation
by virtue of an obligation, one person (debtor) is obliged
to perform
a certain action
in favor of another person (creditor) , such as: transfer property, perform work, etc., or refrain from a certain action, and the creditor has the right to demand that the debtor perform it responsibilities.
Obligations arise, in particular, from a contract
.
In your case, under the contract, the obligation is for your party to pay money for the goods.
Since the agreement stipulates that payments are made in rubles, the obligation is considered expressed in the currency of the Russian Federation - rubles.
Consequently, to your situation the provisions of paragraph 7 of Art.
169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are not applicable
.
In accordance with paragraph 4 of Art. 153 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation if during implementation
goods (work, services), property rights under contracts,
the obligation to pay for which is provided in rubles in an amount equivalent to a certain amount in foreign currency
, or conventional monetary units,
the moment of determining the tax base is the day of shipment
(transfer) of goods (work, services) , property rights.
When determining the tax base, foreign currency
or conventional monetary units
are converted into rubles
at the rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation
on the date of shipment
(transfer) of goods (performance of work, provision of services), transfer of property rights.
When subsequently paying for goods (works, services), property rights, the tax base is not adjusted.
Differences in tax amount
, arising from the taxpayer-seller upon subsequent payment for goods (work, services), property rights,
are taken into account as part of non-operating income
in accordance with
Art.
250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation or as part of non-operating expenses in accordance with
Art.
265 Tax Code of the Russian Federation .
That is, the seller determines the tax base in rubles
.
P.p. “m” clause 1 of the Rules for filling out an invoice used in VAT calculations
, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 2011 No. 1137, it is established that
line 7
“Currency, name, code” of the invoice indicates the name of the currency, which is the same for all goods (works, services) listed in the invoice , property rights and its digital code in accordance with the All-Russian Classifier of Currencies, including for non-cash forms of payment.
In this case it is directly established
, that
when selling
goods (works, services), property rights under contracts,
the obligation to pay for which is provided in Russian rubles
in an amount equivalent to a certain amount in foreign currency or in conventional monetary units,
the name and code of the currency of the Russian Federation are indicated
.
Thus, your supplier was obliged to issue an invoice in rubles
.
According to paragraph 3 of Art. 168 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
When selling goods, invoices are issued no later than five calendar days, counting from the day of shipment of the goods.
In a letter dated April 11, 2012 No. ED-4-3/ [email protected] the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation explained that for the purposes of applying VAT, the date of shipment of goods
drawing up of the primary document
issued in the name of the buyer or carrier for the delivery of goods to the buyer is recognized
In accordance with Art. 9 of the Federal Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ “On Accounting”
Every fact of economic life
is subject to registration with a primary accounting document
.
This article stipulates that primary accounting documents must contain as mandatory details
the date of preparation of these documents and the content of the fact of economic life.
Thus, tax officials emphasize, the invoice is issued after the shipping documents are completed.
, provided for by the regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation, including consignment notes or invoices.
In this regard, in terms of the name of goods, their quantity, price and value, the invoice must correspond to the shipping document on the basis of which it was issued
.
Simply put, if the invoice is issued in rubles, then the invoice must be issued in rubles.
In the event that when drawing up an invoice for the shipment of goods by the seller, it is incorrect
(
erroneously
)
data is indicated
, for example, on the price (tariff), tax rate and (or) quantity of goods (work, services) shipped, then, according to the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation,
technical errors that have arisen are corrected
.
In this case, no adjustment invoice will be issued.
In these cases, the seller should make appropriate corrections to the invoice issued.
.
These corrections are made by the seller in the manner established by clause 7 of Appendix No. 1 to Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 2011 No. 1137, taking into account the features provided for in paragraph. 4 of this paragraph.
If the supplier does not make the appropriate corrections to the invoice, it is highly likely that you will be denied a deduction.
When it is not necessary to issue an ESF
You have the right not to issue ESF when selling goods (services) if:
- issue a check from a cash register or virtual cash register;
- issue a receipt of the established form, which is a strict reporting form, when making payments to the population;
We remind you
Receipts are used after their registration with the tax authorities only in the following cases:
- transfer of cash register equipment for repair;
- temporary lack of electricity at a retail outlet (place of service provision).
- fill out a cargo customs declaration for the export of goods;
- you are a bank and provide clients with statements from their personal accounts;
- massively publicly distribute free goods;
- transport passengers and issue travel tickets, including electronic ones;
- Payments for utilities and communication services provided to individuals by you are made through the bank using primary documents (receipts).
It is also not necessary to display ESF when selling goods (services) with payment through corporate cards of legal entities or bank cards of individual entrepreneurs. ESF is issued only at the request of the buyer (acquirer) before the end of the month in which the goods (services) were sold, but the date of their actual sale. At the same time, buyers can offset VAT on goods (services) purchased in this way if they register receipts from an online cash register or virtual cash register in the taxpayer’s personal account.
Despite the fact that in the listed cases ESF may not be set, these transactions still need to be reflected in the ESF system. To do this, on the last date of each calendar month, form one generalized unilateral ESF. It must be completed by the 5th of the next month.
Attention
If invoices were issued at the request of buyers, do not include their amount in the overall unilaterally generated ESF.
When exporting goods, customs declaration data are reflected in the ESF system through the exchange of information with customs authorities. Therefore, sales of goods for export should also not be reflected in the general one-sided ESF.
In cases of export of goods (services) without registration of a customs declaration, also generate a one-sided invoice. At the same time, next to the name of the buyer, write o.