- December 3, 2020
- Accounting
- Anna Gorbenko
Fixed assets (FPE) are an essential element of the functioning of any production or enterprise. They include all the equipment, all the tools, all the machine tools - in a word, everything that ensures the uninterrupted operation of an existing manufacturing company. Without these components, the functioning of an enterprise is simply impossible.
For the accounting of each unit of fixed assets at enterprises, the government has prescribed a separate full-fledged resolution No. 1 at the legislative level. “On the classification of fixed assets included in depreciation groups” - this is exactly the name of the above document, dated 01/01/2002.
In July 2021, an updated document was released (Russian Government Decree No. 640, clause 2), in which further amendments were also made (the last of them on December 27, 2019). In accounting, the updated resolution is usually called a classifier.
What is the essence of this resolution and what is its content? Is it possible to determine the depreciation group of fixed assets based on it?
Purpose
Why do you need a classifier of fixed assets by group? It performs the most important function for tax accounting of any operating company: thanks to the useful life of each individual group of fixed assets specified there, the enterprise accountant will be able to correctly determine the method and calculate the amount of depreciation for each accounting unit for tax accounting.
Why is the OS classification introduced?
When an enterprise first acquires a fixed asset, it is taken into account at its original cost in accounting. This also includes all costs associated with transportation, installation and commissioning.
But over time, during the operation of the equipment, these most basic means tend to wear out. Accordingly, to compensate for this wear and tear, depreciation amounts are charged to the fixed assets.
And since the installations and elements of the equipment system used can differ significantly from each other in functionality, cost, and terms of use, a classifier of fixed assets by depreciation groups is introduced specifically to distinguish them and to accurately and accurately account for depreciation charges. How to determine which of them each individual fixed asset belongs to? How many groups does this classifier contain and what exactly is included in each of them?
Summary of the classifier
The classification of fixed assets by depreciation groups includes ten blocks. Each of them involves the inclusion of specific operating systems with specific useful life periods.
1 depreciation group of fixed assets is designed to include short-lived assets such as machinery and equipment. This block has a useful life of one to two years. The first depreciation group of fixed assets includes such elements as communications equipment, special tool kits for telecommunications equipment, measuring machines and instruments, compressors, pumps, forklifts, conveyors, etc. This also includes drilling, metalworking, and tunneling equipment.
2 depreciation group of fixed assets involves the inclusion of equipment that has a slightly longer useful life, namely from two to three years inclusive. This includes a list of conveyor belts, electronic computing equipment, mine lifts, drilling rigs, mining installations, equipment for the manufacture of prosthetics, etc.
Group 3 is the property of an enterprise that has a useful life of more than three but less than five years. What this includes: a number of transfer devices, structures, machinery and equipment, vehicles, as well as household and industrial equipment, elevators, photo and video equipment, heat generators, pipelines, tractors, separators, pumping machines, loading and unloading devices, sorting machines , low power transformers, etc.
Group 4 includes a list of buildings (non-residential), structures, machinery, transport property, perennial plants, draft animals and equipment belonging to the enterprise. The useful life is from five to seven years (inclusive). This includes elements of overhead transmission lines, handling equipment, all types of fences and fences (non-metallic), furnaces and burners, cable equipment, industrial mixers and other things.
Group 5, in fact, represents the list from the previous group, but the useful life here increases to ten years. In more detail, these can be prefabricated buildings, elements of military equipment, CNC installations and machines, livestock buildings, water heaters and heating boilers, metalworking machines, hunting and sporting weapons, combine harvesters, etc.
Group 6 involves accounting for housing, vehicles and equipment, as well as perennial plantings, equipment and various devices, the useful life of which ranges from 10 to 15 years. These include railways, arc steel furnaces, steam boilers, water wells, elements of the pulp and paper industry, fruit plantations, and lake (river) vessels for dry cargo.
Group 7, in addition to the previously listed elements, includes entire buildings. The useful life of such fixed assets exceeds 15 years and reaches 20 years inclusive. Panel, container, panel buildings, sewer networks, packaging machines, musical string instruments, self-propelled and towing sea vessels, vineyards, passenger river vessels, etc. are also taken into account here.
Group 8 also includes buildings, machines, equipment, structures, transport, household equipment, transmission devices, the service life of which is more than 20 years, but not more than 25. This includes blast furnaces, metal fences, power cables and wires, reinforced concrete columns, metro lines, floating sea cranes, piers, gliders, passenger and cargo river vessels, industrial cars, etc.
Group 9 is characterized by taking into account buildings, structures, machinery and transport with a service life exceeding 25 years, up to 30. It lists a number of gas tanks, water treatment facilities, blast furnace shop overpasses, nuclear reactors, fire marine vessels, vegetable storage facilities, take-off - landing strips.
Group 10 includes elements of equipment, as well as movable and immovable property, the service life of which is designed for a period of over 30 years. These include residential buildings, floating docks, subway cars, and other fixed assets.
New okof year for an office chair shock-absorbing group
This method is most appropriate for this property. Obsolescence of furniture occurs slowly; such fixed assets do not affect production indicators, so it is convenient not to accelerate deductions and not make them dependent on the volume of work performed, but to write off the entire service life evenly.
- up to 40,000 rub. – for accounting (set by the enterprise independently within the specified amount, fixed in the accounting policy);
- 100,000 rub. – for tax accounting, all objects cheaper than the specified amount are not considered fixed assets, are not depreciated and are immediately written off.
by order of Rosstandart dated April 21, 2016 No. 458 (hereinafter referred to as the Transitional Key). If it is not possible to determine the OKOF code in the new classifier, the institution should assign a conditional code to the fixed asset object that is remotely suitable in meaning for this fixed asset.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytcopyrightru
Since, in accordance with the new OKOF, production and business equipment does not have a separate grouping, but is included in the group “Other machinery and equipment, including business equipment, and other objects,” then to determine the OKOF code and the correct reflection of fixed assets on line 12, it is necessary to use transitional keys between the editions of the classifiers of fixed assets OK 013-94 and OK 013-2014 (SNS-2008).
Calculation of insurance premiums: how to reflect compensation from the Social Insurance Fund When filling out the calculation of contributions, the amount of compensation from the Social Insurance Fund must be indicated in the months when such compensation was actually received. Moreover, regardless of what period the reimbursable expenses themselves relate to.
Auditors will report suspicious transactions of the client “where appropriate.” The State Duma approved amendments to the anti-money laundering law, according to which audit organizations and individual auditors will have the obligation to notify Rosfinmonitoring about suspicious transactions and operations of the audited entity. {amp}lt;
... It is impossible to give a resigning employee a copy of SZV-M. According to the law on personal accounting, when dismissing an employee, the employer is obliged to give him copies of personalized reports (in particular, SZV-M and SZV-STAZH). However, these reporting forms are list-based, i.e. contain information about all employees. This means transferring a copy of such a report to one employee means disclosing the personal data of other employees. {amp}lt; ...
Using this classifier, you can find how many years you need to depreciate various fixed assets in 2021: a gas cutter, a loudspeaker, trucks, cars and other vehicles, various irradiators, cash registers, traffic lights, electrical equipment.
The all-Russian classification of fixed assets was last changed on May 12, 2021. The innovations came into force retroactively and apply to fixed assets put into operation from January 1, 2021. All changes apply in 2019, we have taken into account the amendments in our article. The changes were made by Government Decree No. 526 dated April 28, 2018.
OKOF OK 013-94 does not contain the elements “play equipment” and “park equipment”. The most acceptable are the following codes: 16 3612254 - “Furniture sets for children's playgrounds” and 14 2944173 - “Equipment for the improvement of populated areas.” Equipment for the improvement of populated areas (code 14 2944173) is included in subclass 14 2944010 “Machinery and equipment for public utilities”, therefore it is more appropriate to classify the sandbox and bench purchased by the kindergarten as code 16 3612254 “Furniture sets for children’s playgrounds”.
Tax legislation regulates the procedure for action in such situations. Clause 6 of Art. 258 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation allows you to set the service life of an asset based on its technical characteristics, recommendations of the manufacturer and operating conditions. Consequently, enterprises have the right to determine the SPI of furniture based on its specific qualities.
Classification of fixed assets included in depreciation groups “Furniture for printing production; cable and wire communications enterprises; medical; children's, school and preschool institutions; trade, catering and consumer services enterprises; libraries, theatrical and entertainment enterprises and cultural institutions; administrative premises, train stations, financial institutions and communications enterprises; other special furniture").
“On approval of the Instructions for filling out federal statistical observation forms N 11 “Information on the availability and movement of fixed assets (funds) and other non-financial assets”, N 11 (brief) “Information on the availability and movement of fixed assets (funds) of non-profit organizations" To production and household equipment include, in particular, children's playground objects, benches that are not structures (firmly connected to the ground, installed on foundations, and so on), furniture, and so on.
Since, in accordance with the new OKOF, production and business equipment does not have a separate grouping, but is included in the group “Other machinery and equipment, including business equipment, and other objects,” then to determine the OKOF code and the correct reflection of fixed assets on line 12, it is necessary to use transitional keys between the editions of the classifiers of fixed assets OK 013-94 and OK 013-2014 (SNS-2008).
Return back to Depreciation groups 2019Office furniture of an organization generally satisfies the conditions for recognizing it as fixed assets (clause 4 of PBU 6/01, clause 1 of Article 257 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). And if it also exceeds the cost limit established by the organization in its Accounting Policy for accounting purposes (no more than 40,000 rubles per unit), then it is subject to accounting as part of fixed assets in account 01 “Fixed assets” (clause.
To find out which depreciation group office furniture belongs to, you need to refer to the Classification of fixed assets included in depreciation groups (Government Decree No. 1 of 01.01.2002). After all, it is on the basis of this Classification that fixed assets are distributed into depreciation groups (clause 1 of Article 258 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
However, office furniture is not mentioned in the Tax Classification itself. The Tax Code of the Russian Federation establishes that if any types of fixed assets are not indicated in depreciation groups, their useful life is established by the organization taking into account the technical conditions or recommendations of manufacturers (clause 6 of Article 258 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Please note that before bringing the Classification in line with the new OKOF, office furniture belonged to the 4th depreciation group, for which the useful life was over 5 years up to 7 years inclusive. If the organization has no other information about the service life of office furniture, it can classify it as the 4th depreciation group.
In grouping 330.00.00.00.000 “Other machinery and equipment, including household equipment, and other objects,” codes have appeared that can be used to classify rafts, furniture for offices and retail establishments, as well as other metal furniture, musical instruments, sports equipment, equipment and other equipment, swimming pools. Separately, please note that now the issue of classifying office furniture and other metal furniture with the OKOF code is closed.
Moreover, the legislator reintroduced the previously canceled OKOF codes 330.31.01.1 “Furniture for offices and trade enterprises” and 330.31.01.11 “Metal furniture for offices.” It is worth noting that before new groupings of types of fixed assets are introduced into the Classification of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 1, the useful life of such objects will be established on the basis of technical documentation for the object (clause.
Copyright: Lori photo bank Since the beginning of 2017, depreciation groups for fixed assets have been determined based on new rules regulated by the adopted Classification of fixed assets by depreciation groups and updated codes. In this regard, ordinary users have many questions regarding the determination of the depreciation group of a particular property.
Important Find The search phrase must be at least 3 characters OKOF code Name Depreciation groups* RESIDENTIAL BUILDINGS AND PREMISES 200.00.00.00.000 BUILDINGS (EXCEPT RESIDENTIAL) AND STRUCTURES, COSTS FOR LAND IMPROVEMENT BUILDINGS (EXCEPT RESIDENTIAL) STRUCTURES COSTS FOR LAND IMPROVEMENT 300.00. 00.00.000 MACHINERY AND EQUIPMENT, INCLUDING BUSINESS INVENTORY, AND OTHER OBJECTS VEHICLES INFORMATION, COMPUTER AND TELECOMMUNICATIONS (ICT) EQUIPMENT OTHER MACHINERY AND EQUIPMENT, INCLUDING BUSINESS INVENTORY ENTAR, AND OTHER WEAPON SYSTEM OBJECTS 500.00.00.00.
In accounting, the useful life of office furniture is established by the organization independently (clause 20 of PBU 6/01). For this purpose, in particular, the expected periods of use and physical wear and tear are taken into account. To bring accounting and tax accounting data closer together, an organization can establish the useful life of office furniture in accounting similar to the “tax” period, justifying this by the fact that such a period is the expected period of use of office furniture.
By virtue of clauses 45, 53, 57 of Instruction No. 157n, accounting entities group fixed assets and intangible assets for accounting (budget) accounting purposes by type of property corresponding to the classification subsections established by OKOF. In other words, OKOF is used to determine the analytical account for accounting for fixed assets when they are registered.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytaboutru
In connection with OKOF, the Classification of fixed assets is used, according to which the useful life of an accounting object is determined for calculating depreciation in accounting and tax accounting. Note that this document was changed and when breaking down property into depreciation groups, OK 013-2014 (SNA 2008) was used.
In order to correctly apply both documents in practice, let us consider the structure of the new OKOF.
What determines the need to use a classifier?
Why is it important for an enterprise to determine the depreciation group of a fixed asset at a specific moment?
Determining and assigning each machine, machine, structure to a specific group in the classifier makes it possible to find out during what period the fixed assets should be depreciated. This is required in order for depreciation to be calculated correctly in tax accounting. And incorrect management of both accounting and tax accounting, as we know, is fraught with consequences.
Requirements for depreciation groups
For new property, special tools are provided for a convenient transition to the new OKOF - transition keys between editions (direct and reverse). OKOF-1994 and 2021 are available in Rosstandart order No. 458 of 2021. They are presented in the form of a comparative table with a comparison of specific property objects. With its help, a new encoding is simply selected.
Control authorities devote maximum attention to checking the correctness of accounting, especially those conducted simultaneously with tax accounting. Therefore, it is important to know all the nuances and innovations in reflecting fixed assets in reporting documents. This will eliminate the risk of filling it out incorrectly and receiving fines.
What are the consequences of incorrectly determining the depreciation group of fixed assets?
Errors that occur when choosing a depreciation group are dangerous due to the additional assessment of two additional taxes, namely, on property and on profit. The tax inspectorate quite often finds violations of this kind - this was discussed on the official website of the Federal Tax Service when reviewing the most common typical distortions in reporting. That is why it is very important to determine the depreciation group of fixed assets correctly when calculating taxes.
Which depreciation group does the MFI belong to in 2021?
There are also cutting plotters (cutters) that perform contour cutting of paper, vinyl or self-adhesive film. And an external storage device allows you to greatly expand the amount of stored data without upgrading computers or servers.
A server is convenient not only because all computers work on a single network, but also because the information available on the server is usually available 24/7. Both plotters and drives for serious tasks cost more than 40,000 rubles.
It is necessary to depreciate, but with what SPI? If you search for these devices in the Classification exactly by their names, you will not find anything. But in the 2nd group there are printing devices for computers and information storage systems.
The plotter is quite suitable for the first, and the external drive is suitable for the second. This means that group 2 is SPI over 2 and up to 3 years inclusive. Classification.
The meaning of the OKOF code for the printer
OKOF 320.26.20.15 - Other electronic digital computers, containing or not containing in one housing one or two of the following devices for automatic data processing: storage devices, input devices, output devices 04/18/2021
- Additionally
- Additionally
- Selecting a depreciation group for property with OKOF 320.26.20.13
- Question:
- Answer:
- Rationale:
Additionally, the third depreciation group is property with a useful life of over 3 years up to 5 years inclusive;
Methods for finding out a specific OS group
There are two available ways to assign any fixed asset to a specific depreciation group. Depreciation of fixed assets assumes a legally prescribed useful life. In addition, you need to take into account the specific functional focus of each OS. Thus, the accountant has the opportunity to determine whether any of them belongs to a particular group by using two methods:
- through a search in the classifier - the resolution on depreciation groups of fixed assets;
- through the recommendations of equipment manufacturers, if it was not possible to identify the group of ownership of the OS according to OKOF (All-Russian Classifier of Fixed Assets).
Meaning of the OKOF code for the printer
When purchasing a new office printing device, the question of how to place it on the balance sheet of the enterprise certainly arises. Confusion often arises regarding MFPs, since these devices simultaneously include a printing device, a fax machine, and a scanner.
The OKOF code for a printer and scanner within one device is selected according to the maximum depreciation group of individual components, in this case we are talking about blueprinting equipment.
Next, we describe in detail how OKOF is selected for new multifunctional office equipment, including the 2021 version of the classifier.
Okof - features and principles of code selection
OKOF is an all-Russian classifier of fixed assets, which is used to account for fixed assets of an enterprise. Taken together, the use of certain codes helps government statisticians assess the nature and quality of enterprise property.
Laser printer
Laser printers and MFPs are classified as office equipment; their service life is 3-5 years.
Timely write-off of depreciation cost allows the company to timely generate funds for the purchase of new equipment.
The nature of the decrease in the value of fixed assets is described using the rules by which depreciation is carried out, where OKOF is the normative source.
Computers and printers - second depreciation group
According to the classifier of fixed assets, any digital printing devices that are computer peripherals can be classified into the following categories:
- OKOF code for a laser printer (from January 1, 2021) is 320.26.2, the category “Computers and peripheral equipment” includes personal computers, various peripheral devices, including printers. Code 320.26.20.13 is used if the printer has a central processor (by default on all modern models).
- OKOF code until January 1, 2021 – 14 3020000, category “Electronic computing equipment”.
On January 1, 2021, a new classifier of fixed assets came into force, it is also known as OKOF-2.
Accordingly, new coding for fixed assets should be used, while the old classifiers continue to be valid. For quick translation, the OKOF-2 converter is used.
At the same time, the new version also lacks the concept of a multifunctional device, and difficulties arise with coding the equipment.
MFU - third depreciation group
To register an MFI on its balance sheet, the tax regulator recommends using one of the options of the third depreciation group. The device is evaluated as a whole and individually, so that the maximum amount of depreciation is selected as a result.
Due to the lack of multifunctional devices in the classifier of fixed assets (2021 inclusive), to select OKOF its components are used: printer, scanner, copier and fax, if available, which subcategory should be selected:
- Printing devices belong to depreciation group II - 320.26.20.13;
- If a specialized device is installed that does not have a processor or other features, it may be classified as 330.28.99 “Special-purpose equipment not included in other groups” or 330.28.23.2 “Office equipment” not related to computer peripherals;
- Copiers and blueprinting equipment are classified in depreciation group III - 330.28.23.21, this subcategory includes contact copiers, including thermal copiers;
- Faxes also belong to the office equipment of the second group - 320.26.30.23 “Other telephone devices.”
Accordingly, the resulting OKOF code for the printer and MFP is 330.28.23.21. The depreciation life of a copier is 2-3 years.
Conclusion
Why is correct group selection required, and what coding should be done if not explicitly stated? We are talking about writing off depreciation value. According to the third category, equipment is written off within 2-3 years.
On the one hand, this is true in large companies. On the other hand, modern peripherals are designed to operate for at least 3 years.
The manager of the enterprise will not encourage the write-off of expensive color laser printing equipment with a scanner from fixed assets. What conclusion can be drawn from this?
The fact is that a multifunctional device can be classified as a computer peripheral and be operated according to the classifier for 3-5 years.
With high work intensity in large offices, you can completely use the third category and write off a multifunctional black-and-white laser printing device with a copier within 2 years, otherwise you need to use subcategory 320.26.20.
13 and write off, for example, an infrequently used color printing device within 5 years. There is no further clarification in the new 2021 version.
Source: //printergid.ru/expluataciya/kod-okof
Search by classifier
This is the initial way to find the desired group for a specific OS. It is considered optimal, since the classifier describes in sufficient detail all available groups with a detailed listing of specifically possible elements of equipment for the enterprise.
The importance lies in studying it carefully. Once you carefully read the contents of the classifier, you will be able to use it constantly and quickly navigate this impressive list. Here you can glean useful information from the names of fixed assets included in each specific group and by paying attention to the notes provided. The information is provided in the form of codes, that is, each depreciation group corresponds to a specific OKOF value.
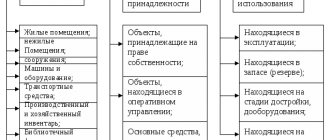
It is important to know that the fastest way to determine the depreciation group for each object taken into account is to focus on the grouping characteristics. There are several of them in the classifier:
- A sign of functional purpose - these can be production or non-production fixed assets.
- A sign of industry affiliation - this may include means for use in industry, agriculture, the agricultural industry, etc.
- The sign of materiality is determined by the naturalness of the composition of each product, that is, it is assumed that the OS is divided into structures, buildings, transmission devices, equipment, working machines, etc.
- A sign of ownership - it means that any fixed asset is either owned by the enterprise or leased for a certain period from lessors.
- Sign of use - fixed assets may be in operation at the time of the accounting period, or they may be in reserve (under conservation conditions).
What has changed in depreciation of fixed assets
A computer is one of the main types of property of an organization, regardless of its industry, scale and other features of its activity.
ATTENTION. There are OKOF codes with less than 12 digits. In particular, for office machines, including a computer and a printer - 330.28.23.23. For steam boilers, including water heaters - 330.25.30, etc. This is due to the fact that OKPD2 codes for these objects consist of less than nine characters.
Leave a comment if 1) you have additional information on the classifier code, 2) you have noticed errors and inaccuracies, 3) you want to ask a question that can be answered by other site users.
The residual value of fixed assets is the price indicator at which the property is indicated in the annual financial statements - the balance sheet.
Manufacturer's recommendations
In cases where it was not possible to find the required position in the list of depreciation groups for OKOF, you should refer to the recommendations of the manufacturer of this or that equipment. This may be a technical passport or any other documentation on the fixed asset.
In addition, enterprises are allowed to submit requests for clarification to the Ministry of Economic Development of the Russian Federation or use the uniform standards established by Resolution No. 1072 of October 22, 1990 “On uniform standards of depreciation charges for the complete restoration of fixed assets.”
Depreciation on fixed assets
Determining the depreciation group, as mentioned earlier, is necessary so that the accountant can correctly calculate depreciation for each fixed asset subject to accounting. So, if the enterprise has property assets that were previously registered, then the direct responsibility of the accountant is to monthly transfer the cost of the fixed asset in parts based on its wear and tear. This is the calculation of depreciation. The deductions themselves are made for the period of operation from the first day of the month following the month the OS was accepted for accounting (this is stated in clause 21 of PBU 6/01).
Tax accounting provides for the calculation of depreciation on fixed assets and groups from the first day of the month following the month the asset was put into operation (this is stated in clause 4 of Article 259 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Depreciation in accounting is calculated using four methods:
- linear;
- reducing balance;
- write-off of cost by the sum of years of SPI;
- write-off of cost in proportion to the volume of services, work, goods.
Depreciation in tax accounting involves the use of only two methods:
- linear;
- nonlinear.
As you can see, in both cases the linear method is recommended for use.
Structure OK 013-2014 (SNA 2008)
– 100 “Residential buildings and premises”;
– 200 “Buildings (except residential) and structures, expenses for land improvement”;
– 300 “Machinery and equipment, including household equipment, and other objects”;
– 400 “Weapon systems”;
– 500 “Cultivated biological resources”;
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytadvertiseru
– 600 “Costs for the transfer of ownership of non-produced assets”;
– 700 “Objects of intellectual property”.
| Code | Name |
| 310 | Vehicles |
| 320 | Information, computer and telecommunications (ICT) equipment |
| 330 | Other machinery and equipment, including household equipment, and other objects |
| Code | Name |
| 330.32.50.21 | Therapeutic instruments and devices; breathing equipment |
| 330.32.50.30 | Medical furniture, including surgical, dental or veterinary furniture |
| 330.32.50.50 | Medical products, including surgical, other |
| Code | Name |
| 330.32.50.21.111 | Therapeutic instruments |
| 330.32.50.21.112 | Therapeutic equipment |
| 330.32.50.21.120 | Breathing equipment |
| 330.32.50.21.121 | Devices for inhalation anesthesia |
| 330.32.50.21.122 | Breathing resuscitation devices |
| 330.32.50.21.129 | Other breathing equipment, not included in other groups |
| 330.32.50.30.110 | Medical furniture, including surgical, dental or veterinary furniture, and parts thereof |
Next, we draw the attention of readers that the new OKOF is used when grouping fixed assets acquired and accepted for accounting from January 1, 2021. It is not used for old objects (accepted for accounting before 01/01/2017); operations to transfer fixed asset balances to new groups are not performed. These clarifications are given in Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 27, 2016 No. 02-07-08/78243.
Additional Information
To make it easier for enterprises to navigate, Rosstat published a comparative list in the form of a table, the use of which greatly simplifies the life of accountants. The meaning of the table is to show, through a certain coding of the existing fixed asset, its correspondence to a certain group.
If the fixed asset was not found in the classifier, you can determine the useful life yourself. Supporting documentation here is technical information from the manufacturer of the fixed asset.
Binding equipment, including stitching machines
You can set an entire OS group in the classification. A transcript of the group is presented in OKOF.
An organization should determine which calculation method it will use for office furniture and consolidate its choice in accounting and tax policies. WE TAKE ALL LEGAL APPROVALS, which will inform you about all stages of production and answer questions.
The period of use of containers for collecting municipal solid waste (MSW) is determined by the All-Russian Classifier and Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of January 1, 2002 No. 1, where material objects are described according to their belonging to depreciation groups.
If all conditions, including the cost limit, are met, then the useful life of this property should be established in accounting and tax accounting.
Articles, comments, answers to questions: OKOF furniture Answer Office furniture belongs to the Fourth depreciation group. Accordingly, the useful life of furniture can be set in the range from 5 years and 1 month to 7 years.
The next step is to establish the useful life of the OS. You can select any number of years within the established limits. For property worth more than 100 thousand rubles, it is advisable to establish the same period in tax and accounting in order to avoid discrepancies.
It is worth noting that before new groupings of types of fixed assets are introduced into the Classification of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 1, the useful life of such objects will be established on the basis of technical documentation for the object (clause.
At the final stage, you need to check the service life of the OS according to the documentation - enter information into the inventory card. When establishing different deadlines for tax and accounting, this must be reflected.
DECREE of the Government of the Russian Federation dated 01-01-2002 1 (as amended on 02/24/2009) ON THE CLASSIFICATION OF FIXED ASSETS INCLUDED IN…
In addition, the legislation does not contain the concept of “land improvement”. At the same time, representatives of tax authorities believe that in the context of use for the purposes of tax legislation, it is possible to be guided by its generally accepted meaning. This means that when determining the useful life of objects not included in the Classification, organizations can be guided by the technical passport of the manufacturer or other similar technical documentation. If it is impossible to determine the useful life of a fixed asset using these documents, you can contact the manufacturer with a corresponding request.
The property class differs from the property type code in that the seventh, eighth and ninth digits in it are always zeros. For example, a rotary pump belongs to class 14 2912000 (pumps and compressor equipment).
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation distributes depreciable property into depreciation groups in accordance with its useful life. The useful life is the period during which an item of fixed assets or an item of intangible assets serves to fulfill the goals of the taxpayer's activities.
OKOF also provides information on assessing the volume and condition of funds, taking into account their functions, comparisons with international standards, calculating economic stock indicators and the time of diagnostic and repair work.
Any used property can be divided into so-called depreciation groups; the main criterion for such division is the useful life in accordance with regulations. Depreciation is calculated based on the useful life of a fixed asset, which is determined using a classifier in which objects are combined into depreciation groups.
In tax accounting, furniture is recognized as an object of fixed assets if its initial cost exceeds 100,000 rubles per unit. Recognizing furniture as an object of fixed assets, it must be depreciated (clause 17 of PBU 6/01, clause 1 of Article 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). What is the depreciation group for office furniture? And what is the useful life of furniture to set in accounting? We'll talk about this in our consultation.
Garbage containers used in government institutions belong to the sixth group - household and industrial equipment. The service life of waste containers is 10-15 years. This means that after the specified period, the containers must be written off from the balance sheet.