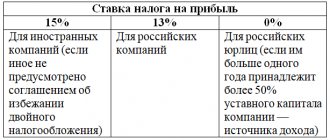
When to issue invoices
The invoice must be issued:
- organizations that have operations subject to VAT (clause 3 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). This rule also applies to those who have received tax exemption under Article 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (clause 5 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- intermediary organizations that sell goods (work, services) on their own behalf under a commission agreement or agency agreement, if the principal or principal applies the general taxation system (clause 1 of article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 20 of section II of appendix 5 to the Government Decree RF dated December 26, 2011 No. 1137);
- organizations that received an advance (partial payment) from the buyer or customer towards the upcoming sale (clauses 1 and 3 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
When to issue a correction invoice
An adjustment invoice is issued in cases where:
- the parties agreed to change the cost of goods already shipped (work performed, services provided, transferred property rights). This is stated in paragraph 3 of paragraph 3 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
- the seller did not transfer the goods in full (non-delivery of goods) (letters from the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated May 12, 2012 No. 03-07-09/48 and dated March 12, 2012 No. 03-07-09/22, Federal Tax Service of Russia dated March 12, 2012 No. ED-4-3/4100).
When not to issue invoices
There is no need to issue invoices in the following cases:
- transactions are not subject to or are exempt from VAT in accordance with Article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. For example, when issuing cash loans (subclause 15, clause 3, article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- the buyer (customer) is not a VAT payer (exempt from paying such tax) and the seller has signed an agreement with him not to issue invoices. In such a situation, invoices may not be issued, even if the transaction is subject to VAT. For example, if a seller – a VAT payer – received an advance from a buyer using a simplified method, if there is a mutual agreement, an invoice for the advance does not need to be drawn up (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 16, 2015 No. 03-07-09/13808). By the way, the seller is not obliged to demand from the buyer documents confirming that he does not pay VAT legally (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 30, 2016 No. 03-07-09/17700);
- in transactions with interdependent persons, for tax purposes, the seller increases the price of goods, works, services to the market level and adjusts the VAT tax base (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 1, 2013 No. 03-07-11/6175).
This procedure is provided for in paragraph 3 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. There is no obligation for the supplier to control the tax status of the buyer when signing the relevant document regarding non-drafting of invoices.
Situation: is it necessary to issue invoices when drawing blood from the population on the basis of contracts with hospitals and clinics?
No no need.
Taking blood from the population under contracts with inpatient medical institutions and clinics is a medical service and is exempt from VAT (subclause 2, clause 2, article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). And in such a situation, the organization is not obliged to issue an invoice. This is directly stated in paragraph 3 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
IN WHAT CASES IS AN INVOICE NOT ISSUED?
For transactions that are not subject to taxation, there is no need to charge VAT and prepare invoices (clause 1, clause 3, article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In addition, invoices are not generated:
1) for transactions that are not subject to VAT in accordance with Art. 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Note
The corresponding norm is addressed to taxpayers. Tax agents in paragraph 3 of Art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are not mentioned.
However, we believe that tax agents are not required to prepare invoices for transactions that, by virtue of Art. 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are exempt from VAT. We come to this conclusion based on the following. Since 2014, in paragraph 5 of Art. 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not contain the previously contained instruction on the preparation of invoices without the allocation of VAT for transactions exempt from this tax (clause 2 of Article 3, Part 1 of Article 6 of Law No. 420-FZ). In addition, in para. 2 p. 3 art. 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation establishes that tax agents prepare invoices when calculating VAT. It does not contain instructions that an invoice must be drawn up for a VAT-exempt transaction for which the tax agent does not assess tax.
The Russian Ministry of Finance also clarifies that the current rules of paragraphs. 1 clause 3 art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, according to which invoices are not issued in relation to transactions that are not subject to VAT in accordance with Art. 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, also apply to tax agents (Letter dated March 19, 2014 N 03-07-09/11822). In this case, the financial department refers, in particular, to paragraph 2 of Art. 24 Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
2) organizations and entrepreneurs who are engaged in retail trade, public catering, performing work (providing services) for the population in cash (clause 7 of article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Note
When selling goods to individuals (performing work, providing services) paid for by bank transfer, the seller is obliged to draw up an invoice (Letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 21, 2011 N 03-07-05/38, dated November 3, 2011 N 03-07- 09/37, dated 05/25/2011 N 03-07-09/14);
3) organizations and entrepreneurs who apply special tax regimes in the form of unified agricultural tax, simplified tax system, UTII or a patent taxation system (with some exceptions), since they are not VAT payers (clause 3 of article 169, clause 3 of article 346.1, p. clauses 2 and 3 of Article 346.11, clause 4 of Article 346.26, clause 11 of Article 346.43 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If such organizations and individual entrepreneurs sell goods (work, services) through an intermediary, then the intermediary does not calculate VAT and does not issue invoices (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated May 31, 2011 N 03-07-11/152);
4) from October 1, 2014 - with the appropriate written consent of the parties to the transaction when selling (goods, works, services, property rights) to persons who are not VAT payers or are exempt from fulfilling the duties of a taxpayer in accordance with Art. Art. 145, 145.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (clause 1, clause 3, article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause “a”, clause 3, article 1, part 1, article 3 of the Federal Law of July 21, 2014 N 238-FZ, clause 5 Article 2, Part 1, Article 4 of the Federal Law of November 29, 2014 N 382-FZ).
The invoice issued by the seller is used for the purposes of VAT calculations and is the basis for a deduction for the buyer - the VAT payer (clause 1 of Article 169, clause 1 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Buyers who are not recognized as VAT payers cannot take advantage of the deduction, and therefore they do not need an invoice. As for “simplified” buyers with the object of taxation “income minus expenses”, if the parties to the transaction agree to not draw up invoices, they can attribute the VAT amount on purchased goods (work, services) to expenses on the basis of payment and settlement documents, cash registers checks or strict reporting forms with the tax amount highlighted in a separate line (Letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 09/08/2014 N 03-11-06/2/44863, dated 09/05/2014 N 03-11-06/2/44783).
We believe that the regulatory authorities will adhere to a similar point of view in relation to buyers - payers of the Unified Agricultural Tax. After all, the object of taxation under the Unified Agricultural Tax is income reduced by the amount of expenses, and VAT on purchased goods (work, services) is one of the types of expenses that reduce the tax base for agricultural tax (Article 346.4, paragraph 8, paragraph 2, Article 346.5 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation ).
The seller must consider the following when obtaining the buyer's consent to not issue invoices. Sales of goods (works, services, property rights), which are recognized as an object of taxation under VAT and are not exempt from tax in accordance with Art. 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, must be reflected in the sales book by registering an invoice, a cash register control tape, a strict reporting form (clause 1, clause 3, article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clauses 1, 3 of the Rules for maintaining the sales book). Therefore, if the seller has no reason to issue a cash register receipt or issue a strict reporting document, we can recommend that he draw up a single copy of the invoice for such an operation and register it in the sales book. The Ministry of Finance of Russia agrees with this approach (Letter dated 09.10.2014 N 03-07-11/50894).
In addition, the official authorities admit that in cases where, on the grounds provided for in paragraphs. 1 clause 3 art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, an invoice is not drawn up, the seller can reflect the following details in the sales book:
- primary accounting documents confirming the fact of the relevant business transactions (Letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 10/09/2014 N 03-07-11/50894, Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 01/29/2015 N ED-4-15/1066);
— other documents containing summary information on the transactions in question performed during a calendar month or quarter. Such a document could be, for example, an accounting statement (Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated January 29, 2015 N ED-4-15/1066).
If the cost of shipped products changes downwards or upwards, the seller will issue an adjustment invoice in a single copy and register it in the prescribed manner.
The parties may provide for consent to not prepare invoices, for example, in a contract or an additional agreement to it.
If an agreement on the sale (of goods, works, services, property rights) has already been concluded, then, in our opinion, it is necessary to draw up an additional agreement to it. It must indicate that the parties agreed on the fact that invoices were not drawn up. In addition, it is advisable to reflect why invoices are not drawn up (use by the buyer of the simplified tax system (UTI, Unified Agricultural Tax, PSN) or exemption from the duties of a taxpayer in accordance with Articles 145, 145.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). We also recommend that you additionally provide a list of documents that will confirm the fact of sale of goods (work, services, property rights).
See a sample of filling out an additional agreement on failure to draw up invoices when executing a contract for the supply of goods to a person who is not a VAT payer.
If the parties are just planning to enter into an agreement, then it is advisable to include a condition on the non-drafting of invoices in the text of the agreement at the stage of preparing its draft.
Let us note that, according to the Russian Ministry of Finance, the written consent of the parties to not prepare invoices can be issued electronically if it is signed with an electronic signature or another analogue of a handwritten signature. In support of their opinion, officials refer to paragraph 4 of Art. 11 of the Federal Law of July 27, 2006 N 149-FZ “On information, information technologies and information protection” (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 21, 2014 N 03-07-09/52963);
5) upon receipt of an advance amount for upcoming deliveries of goods (performance of work, provision of services) (paragraph 3 of clause 17 of the Rules for maintaining the sales book):
- the duration of the production cycle of which is more than six months in the cases provided for in paragraph. 3 p. 1 art. 154 Tax Code of the Russian Federation;
— which are taxed at a VAT rate of 0% in accordance with clause 1 of Art. 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (paragraph 4, clause 1, article 154 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- which are not subject to taxation (exempt from taxation) according to Art. 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (paragraph 5, clause 1, article 154 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- which will be shipped (transferred) by taxpayers using the right to exemption in accordance with Art. Art. 145, 145.1 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Note
You can find out more about cases when an “advance” invoice is not drawn up in section. 22.3.5.1 “When you can not issue an “advance” invoice” and section “Situation: Is it necessary to draw up an “advance” invoice in cases where the shipment (transfer) of prepaid goods (works, services) took place within five days from when the advance payment is received?
Export of goods
Situation: is it necessary to issue invoices when selling goods for export?
Yes need.
Invoices must be issued for all transactions that are subject to VAT. There are some exceptions, but exporting is not one of them. This is stated in paragraph 3 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Therefore, draw up an invoice, as usual, within five calendar days from the date of shipment for export (clause 3 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Similar explanations are in letters from the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 5, 2007 No. 03-07-08/180 and the Department of Tax Administration of Russia for Moscow dated September 19, 2003 No. 24-11/51717. And although the conclusions in them relate to the previous rules for issuing invoices, they are still valid today. Arbitration practice also shows that invoices must be drawn up when shipping for export (see, for example, Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow District dated September 5, 2005 No. KA-A40/8359-05).
An example of issuing an invoice for the sale of goods for export
JSC Alfa is engaged in the production of office furniture. On June 15, Alpha shipped 10 Office furniture sets to Ukraine. The buyer is the Dnepropetrovsk Switch Plant. The selling price of one headset is 150,000 rubles. (taxed at 0% rate). The total transaction amount is RUB 1,500,000. (10 pcs. × 150,000 rub./pc.).
Furniture sets are sold in accordance with the customs export procedure. Therefore, this operation is subject to VAT at a rate of 0 percent. Alpha submitted all the necessary documents confirming the fact of export on time.
Alfa presented the Dnepropetrovsk Switch Plant with an invoice for the cost of the shipped products. At the same time, when filling out line 6b “TIN/KPP of the buyer” of the invoice, the accountant took into account the fact that the accounting of Ukrainian organizations is carried out in accordance with the legislation of Ukraine. All Ukrainian organizations are included in the Unified State Register of Entrepreneurs and Organizations of Ukraine, and each of them is assigned an eight-digit OKPO number (analogous to the Russian TIN). It was this number assigned to the Dnepropetrovsk switch that was indicated in line 6b.
Situation: is it necessary to issue invoices if an organization exports goods, the sale of which in Russia is exempt from VAT?
No no need.
For transactions that are recognized as subject to VAT, but at the same time are not subject to (exempt from taxation) this tax in accordance with Article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, it is not necessary to issue invoices. This is stated in paragraph 3 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Therefore, if an organization exports goods, the sale of which in Russia is exempt from VAT, then it should not issue invoices for the cost of these goods.
Algorithm for responding to a requirement in Kontur.Extern
The form of explanation in the service depends on what type of discrepancies are identified. But initially the procedure is the same. “New” menu item , then go to the “Requirements” and click the “All requirements” :
A list with requirements will open, from which you should select the one you need:
The next window will provide detailed information about the selected requirement. To answer it, in the drop-down menu at the bottom of the screen you need to select “Fill out a response to the requirement” :
If you need to upload a prepared response or explanatory documents, you need to select the menu item “Send requested documents” .
When you select “Create a response to a request,” a form will open in which some of the fields will be filled in automatically. The service takes this information from received requests.
This is what the response form looks like in Kontur.Extern :
an updated declaration is sent , then the information on the invoices that will be included in it will not be filled out in the response to the request.
There may be nuances in the response form that depend on the format in which the request is sent. This can be pdf and/or xml . If you receive a pdf file, the response will contain the following fields:
- "Invoices not included";
- "Unfulfilled control ratios";
- "Explanatory letter".
If the request is sent in xml format, then the last two fields will not be present. The bottom line is that textual explanations cannot be submitted for requirements received in xml format. This is due to the peculiarities of processing responses by the ASK VAT-2 system - it cannot read text messages.
The following image shows what information about possible errors that require clarification looks like. In some sections, data may be missing - this means that such information is not in the request.
Discrepancies with counterparties
To draw up an explanation of discrepancies with counterparties, you need to compare the data from the received request with existing invoices , as well as with information from purchase and sales books and invoice journals. The next steps depend on whether there is an error and on whose side.
There is no error in the data. There is no need to change the line in the response.
The information remained unchanged - there are no discrepancies according to the taxpayer’s data
The invoice was sent incorrectly. The actions are:
- Place a check mark, as shown in the image below, on the line containing the details of this invoice. The Federal Tax Service will receive information that this line should be deleted.
- Submit an updated VAT return.
The mark means that this information should be excluded from the declaration.
The primary document contains correct information, but an error was made when filling out the declaration. The correction can be made directly in the response to the request in the column where the erroneous data is indicated. There is no need to file an adjustment report.
The invoice details in the response to the request should be corrected
Error in tax amount. If such an error is detected, the user should:
- Mark a line, thereby indicating the need to delete it.
- Submit an updated VAT return.
It is not possible to correct an error in the response to a claim, as this must be accompanied by the filing of a new return. Therefore, the data in column 19 is not edited.
You need to delete all requirement lines. In this case, there is no point in answering it; you need to immediately submit an updated declaration. After this, all information in the Federal Tax Service database will be corrected.
Missing invoices
Actions to correct errors depend on the format in which the request was received.
In PDF format
You need to compare the data from the requirement with the source document and find out where the error is.
If there is an error in the declaration, but not in the invoice , then explanatory information is entered into table 1. You need to enter the data specified in the request, as well as the correct information (column “with me” ).
Table 1. Information explaining the discrepancies
If information about the invoice is indicated in the declaration, but in reality there was no transaction, table 2 is filled in. It indicates information on transactions not confirmed by the taxpayer, which must be taken from the request itself.
Information about records for which operations are not confirmed
Repayment of debt to the assignee
Situation: is it necessary to draw up an invoice when returning a debt, the right to claim which was acquired under an assignment agreement? The amount returned is greater than the amount paid to the assignor. The debt is associated with payment for goods (work, services) subject to VAT.
Yes need.
If a monetary claim acquired under an assignment agreement is associated with payment for goods (work, services), the sale of which is subject to VAT, then repayment of the debt is also recognized as an object of taxation. The tax base in this case is the difference between the amount received from the debtor and the purchase price of the debt. This follows from the provisions of paragraph 2 of Article 155 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Determine the amount of VAT at the estimated rate of 18/118 (clause 4 of article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Tax must be calculated on the day the payment is received from the debtor (Clause 8, Article 167 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Since the debtor has no reason to claim VAT for deduction, the invoice can be drawn up in one copy and registered in the sales book.
In line 2 “Seller” of the invoice, indicate the name of the assignee organization, in line 6 “Buyer” - the name of the organization that repaid the debt.
An example of drawing up an invoice for the return of a debt, the right to claim which was acquired under an assignment agreement
In February, LLC "Torgovaya" (assignee) acquired from JSC "Proizvodstvennaya" (assignor) the right to claim the debt for payment of goods subject to VAT and sold under a sales contract. The debtor (buyer under the purchase and sale agreement) is Alfa JSC. The amount of debt is 1,180,000 rubles. (including VAT – 180,000 rubles).
The right to claim the debt was acquired for 1,000,000 rubles. (including VAT - 152,542 rubles) based on the assignment agreement, which was signed on February 19.
On April 10, Alpha repaid the debt, the right to claim which was transferred to Hermes, in the amount of RUB 1,180,000.
Hermes assessed VAT payable to the budget on the amount of the excess of the repaid obligation over the purchase price of the debt: - RUB 27,458. ((RUB 1,180,000 – RUB 1,000,000) × 18/118).
On April 10, Hermes drew up an invoice in one copy and registered it in the sales book.
Receiving a VAT claim
Requirements for clarification may be caused by various violations when preparing a VAT return, for example:
- control relationships between certain form fields did not converge;
- the counterparty does not have an entry for the transaction in its declaration;
- discrepancies were found in the data of the purchase and sales books of the taxpayer and his counterparty.
The primary requirement of the Federal Tax Service is generated and sent automatically by the declaration verification system . Having received it, the taxpayer must notify the tax authority about this within six days - for this purpose a receipt of acceptance of the request is sent. Next, 5 days to prepare an explanation and send it to the Federal Tax Service.