A foreign currency account must be reflected in the balance sheet if there are funds on it at the reporting date. The rules for preparing financial statements are regulated by the norms of Order No. 66n of the Ministry of Finance dated July 2, 2011; the procedure for recording funds in foreign currency in accounting is described in PBU 3/2006. All transactions carried out in foreign currencies must be shown in accounting and tax records in ruble equivalent. Conversion into national currency is carried out at the official rates of the Central Bank on the date of the business transaction and as of the reporting date. Exchange rate fluctuations can lead to negative or positive exchange rate differences when converting currencies into rubles; these amounts are written off as income or expenses.
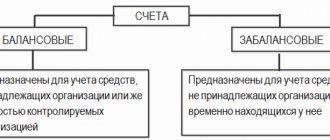
What are active and passive accounting accounts?
Simply put, active financial accounting accounts are those accounts that specialize in accounting for all of a company's assets. While passive type accounts are accounting accounts that are designed to account for the organization’s liabilities, that is, its own funds: capital, reserves and other liabilities.
Based on a more significant difference, it can be noted that active accounting is created to account for the following items:
- Tangible and intangible property of the organization. This includes the company's fixed assets, its inventories and intangible assets.
- Cash in all forms, that is, in paper cash and in current accounts and bank deposits;
- costs associated with the production of the product, work in progress, semi-finished products;
- Various financial investments: short-term and long-term.
Due to the fact that active accounts involve accounting for the property and finances of the enterprise, the balances on such accounts can be exclusively in debit, that is, have a positive value.
The sources of creation of a company's assets reflect the liability side of the financial balance sheet. So, passive accounts are:
- capital of an economic entity;
- obligations assumed by the enterprise to be fulfilled;
- loan, credit and loans received;
- additional expenses, for example, depreciation;
- reserve funds for unfavorable debts.
Accordingly, the passive account has an exclusively credit balance at the end of the reporting period, and the debit balance on the passive account informs about errors in accounting. An increase in the coefficients on a passive account, as a rule, is formalized using credit turnover, and a reduction in the number of liabilities, capital or writing off necessary expenses is considered an operation to debit the passive account.
In the financial balance sheet, passive accounts respectively determine the section - liability. The generated balances at the end of the reporting period are distributed along certain lines of the liability side of the financial balance sheet, in accordance with the current rules for the formation of financial statements.
Active-passive accounts are also used when working with various invoices. In addition, they can highlight settlements with participants in business relationships.
It happens that some financial accounts contain credit or debit balances. Such accounts are also called active-passive. This may include accounting accounts that are capable of reflecting information about settlements with consumers or suppliers. It follows from this that during the shipment of any goods to the consumer, a receivable is created in the accounting account, and when the supplier receives a certain advance payment from the same buyer, an account payable is created in the accounting account.
It is worth considering that some financial accounts cannot be categorically classified as active or passive. For example, account 60, which is aimed at settlements with persons involved in supplies and contractors. The debit of such an account indicates a reduction in credit debt, that is, a liability, as well as an increase in receivables, in other words, an asset. In the same way, using the credit of accounting account 62, aimed at settlements with buyers and customers, it is possible to trace financial transactions that create not only an asset, but also a liability.
For example, if an enterprise bought products, but did not have time to pay for them, this means that on credit 60 of the account, the buyer has a payable debt to pay for goods or services. However, if the company gave an advance to the person supplying the products, then before the goods and materials are delivered on the debit of account 60, a receivable will appear. First we are talking about the passive accounting account, and then about the active one. Based on the fact that account 60 is directly related to certain economic aspects, this account is considered active-passive.
As a rule, it is customary to distinguish two main types of active-passive accounting accounts, namely:
- with one-sided balance;
- with a bilateral balance.
An active-passive accounting account with a one-sided balance implies a debit or credit balance. A striking example is account 99, which implies the company's profits and losses. So, if an organization’s total income significantly exceeds the amount of production and other expenses, then the difference between these amounts gives net profit; accordingly, the balance is considered a credit balance, because the credit turnover exceeds the debit one. Income is the main source of creation of tangible and intangible property of the company, which is visible in the liability side of the balance sheet. However, if losses occur in the organization, then the balance of the accounting account is considered debit, because the debit turnover is greater than the credit turnover.
An active-passive accounting account with a two-way expanded balance indicates simultaneously both a debit and a credit balance. An example is account 76, indicating settlements with various debtors and creditors. In this case, the debit balance refers to the debts of the company's counterparties to it, in other words, accounts receivable, while the credit balance refers to accounts payable. Thus, debit entries in such an account mean an increase in accounts receivable or, conversely, a decrease in the organization’s debt, which it must repay.
Active accounting accounts
First of all, it is necessary to determine the types of active accounting accounts. They are generally divided into the following four categories:
- Inventory accounts that take into account all the property of the organization, namely:
– fixed assets of the enterprise;
– intangible assets of the company, this also includes investments in research and development work;
– materials that are used to account for the quantity of materials, raw materials, semi-finished products, and so on;
- Cash accounts, which reflect the company's funds in both cash and non-cash form;
- Collection and distribution accounts, which serve for various expenses of the enterprise. They are not directly related to the production process, however, they are included in the calculation due to the distribution in proportion to any attribute;
- Cost or costing accounts, which are created to form the cost of finished goods and services.
Here are the main active accounting accounts:
- 01 “Fixed assets”;
- 03 “Profitable investments in material assets”;
- 04 “Intangible assets”;
- 07 “Equipment for installation”;
- 08 “Investments in non-current assets”;
- 09 “Deferred tax assets”;
- 10 "Materials";
- 11 “Animals in cultivation and fattening”;
- 15 “Procurement and acquisition of material assets”;
- 16 “Deviation in the cost of material assets”;
- 19 “Value added tax on acquired assets”;
- 20 “Main production”;
- 21 “Semi-finished products of own production”;
- 23 “Auxiliary production”;
- 25 “General production expenses”;
- 26 “General business expenses”;
- 28 “Defects in production”;
- 29 “Service industries and farms”;
- 40 “Product release”;
- 41 "Products";
- 43 “Finished products”;
- 44 “Sales expenses”;
- 45 “Goods shipped”;
- 46 “Completed stages of work in progress”;
- 50 "Cashier";
- 51 “Current accounts”;
- 52 “Currency accounts”;
- 55 “Special bank accounts”;
- 57 “Translations on the way”;
- 58 “Financial investments”;
- 81 “Own shares”;
- 94 “Shortages and losses from damage to valuables”;
- 97 “Deferred expenses”.
How to show foreign currency accounts on the balance sheet
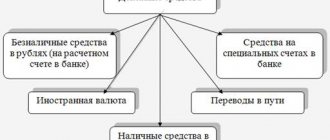
To include in the balance sheet information about the financial resources available to the enterprise, it is necessary to focus on the debit balances of several accounting accounts:
- account 50, recording cash balances in the company's cash register;
- account 51, reflecting non-cash money stored in current accounts in banks;
- account 52, which accumulates data on foreign currency converted into rubles;
- account 55, showing the amounts in special accounts;
- count 57, indicating money in transit.
From the resulting total value of monetary resources, it is necessary to exclude the cost of monetary documents (subaccount 50.3), which are included in other current assets (balance sheet line “1260”) and deposit accounts (subaccount 55.3), reflected as financial investments (lines “1170”, “ 1240"). The foreign exchange account in the balance sheet and other cash accounts are reflected on line “1250”.
In accordance with PBU 3/2006, information in the reporting is entered from accounting registers. Foreign currency funds are reflected in registers only in ruble equivalent by all Russian business entities, regardless of where business activities are conducted - within the Russian Federation or in other countries. An exception is made only for situations where reporting is required for foreign users - in this case, the data is shown in foreign currency without conversion to the ruble equivalent. Exchange differences are recorded in other income or expenses on account 91, so they are not reflected independently in the balance sheet, but are included in the financial result.
Rules for maintaining accounts
It should be understood that the report on financial accounts is submitted based on a certain procedure.
The main characteristic of an active-passive account is that it can be heterogeneous. So, on an active-passive account, the balance can be expressed as a credit or a debit, depending on the situation. Therefore, the balance on synthetic accounts can be determined solely by the final accounting on second-order accounts, as well as on accounts intended for detailed and specific information about the presence, condition and movement of funds and their sources in synthetic accounts, in other words, on analytical accounts.
It is necessary to understand that it is impossible to expand the balance on analytical accounts, however, it can change, that is, for one period it can be debit, and for another – credit. In case of full repayment of obligations, such an account may already be successfully closed. It follows that the sequence of calculations may change based on the instructions for using charts of accounts.
The balance can be expanded on a synthetic active-liability account, provided that there is a balance on both sides of the chart of accounts. Similarly, if a particular form has debts to suppliers or customers, they are reflected in the credit of this account, which is open for accounting, and such debt can be repaid by debiting the corresponding account. But when a receivable is detected, the entire process of repayment occurs on the credit of a specific account.
Definition of active accounts
To group enterprise funds and their sources that are homogeneous in content, appropriate registers are used.
They are called accounts; the movement of each type of material assets, settlements, and capital is represented in them for a certain time period.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=https:tv.youtube.com
Accounting accounts serve to summarize information about a specific type of asset (source) for a certain period of time; on their basis, all existing accounting registers are filled in (revolving balance or memorial, chess sheet, balance sheet with appendices).
Recording of business transactions to the appropriate account is made on the basis of the primary document.
Their processing consists of generating a total (balance) or closing the register.
After this, information from the accounts is transferred to the balance sheet, subject to its basic rule - the correspondence of the values of the active part and liabilities.
Active accounts are accounting accounts designed to record the status, movement and changes of business assets by type.
Active accounts display information about the funds (in monetary equivalent) that the organization has at its disposal; these can be bank accounts, property in the warehouse and in operation.
What is synthetic accounting?
Synthetic accounting is the recording of all information on types of property, business transactions, debts, taking into account their economic characteristics. Such accounting is carried out on synthetic accounts in accordance with the Accounting Law.
Synthetic accounts are of both first order and second, that is, subaccounts. The balance is grouped in Form No. 1 of the accounting report.
Such accounts are used to work with various types of information about large accounting objects, but exclusively in monetary terms. Synthetic accounting can only be carried out in national currency.
What types of accounting accounts are there?
3) Statement of balances of placed and attracted funds.
— client (reflect settlement and monetary relationships with its clients);
— intrabank (used for settlements, income, expenses, results of the bank’s activities)
Synthetic accounting
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytcreatorsru
is general in nature. Synthetic accounting data serves both as a means for analyzing the activities of the bank itself, and can be used to analyze the activities of individual enterprises and organizations and industry analysis.
Synthetic accounting problem
— checking the correctness of analytical accounting. Synthetic accounting is carried out on second-order accounts provided for by the current chart of accounts. The relationship between synthetic and analytical accounting is expressed in the fact that personal (analytical) accounts are opened in the context of second-order accounts (synthetic accounts).
1) Turnover sheet (includes opening balances, turnover, ending balances for each synthetic account).
What is analytical accounting?
Analytical accounting is carried out both in material and in other accounting accounts. It must group certain information about the property, business transactions and debts of all synthetic accounts.
An analytical accounting account is formed in the process of creating a synthetic account for all its components. It includes detailed and complete financial data about the enterprise values and all the activity found inside all synthetic accounts.
Each organization creates such accounts independently, taking into account all the features of its focus. This is how the accounting policy of a particular enterprise appears.
The analytical account provides the receipt of all accounting characteristics, including concluded contracts with the borrower or party to the contract in civil law relations. Such accounting is also carried out in any foreign currency or even together with the national one at the same time.
Features of active and passive accounts
Active and passive accounting accounts form the basis of accounting accounts. However, they differ greatly in appearance.
Thus, active accounts imply objects in which the organization invests its funds. They create entries in ascending order of assets and record the current balance in the debit side. If assets are reduced, it is assigned to credit accounting.
The main difference is that the primary balance and the final balance are always debit. To calculate the value of the final balance, use the following formula: Sk = Sn + Add – Kob Sk.
- Sk – initial balance;
- DOB – debit turnover;
- KOB – loan turnover.
At the same time, passive accounts determine all movements of the organization; they are classified as sources of funds.
Its difference is that the initial and final balances are always credit. Therefore, to calculate the closing balance, use the following formula:
Sk = Sn + ObK – ObD.
- Сн – initial balance;
- DOB – debit turnover;
- KOB – loan turnover.
Chart of accounts: principles and forms
The Ministry of Finance in a separate chart of accounts is a recommendation, since each company independently determines which accounting accounts will be used in accounting.
Accounting is a systematic method of accounting using digital codes that designate (group) the assets of an enterprise, as well as the sources of their formation (appearance, formation). In other words, accounts are codes that designate monetary, property and intangible values owned by an economic entity, as well as the sources of receipt of these values (liabilities, capital, expenses).
All accounts have a special classification type, that is, all accounts can be divided into three standard groups:
- active accounting accounts;
- passive;
- mixed or active-passive accounting accounts.
This type is determined by the balance function. In other words, the account attribute depends on in which part of the balance sheet a specific indicator should be reflected. For example, if an indicator is reflected in the assets of the balance sheet, then such an account is active, in liabilities it is passive, and those accounts whose balances can be in both assets and liabilities are classified as mixed.
Now let's look at each type separately.
Determining the final balance on an active-liability account
In order to identify the final balance on an active-passive account, it is recommended to add up all debit amounts and find out the final credit amount. Thus, the final balance will be on the side where the amount will be greater and, nevertheless, will be equal to the difference between the credit and debit amounts.
The main thing to understand is that receivables arise when an organization is required to return funds after an agreed period of time, but if receivables arise during a loan.
Account grouping, table
To avoid errors when preparing accounting entries, you need to know and take into account the classification attribute. Remembering the types of business accounting accounts is quite difficult. We suggest using a simple table with a list of accounts.
Active, passive and active-passive accounts, table.
| Account type or attribute | Account number according to Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 94n | Characteristic |
| A | 01 | >Fixed assets |
| P | 02 | >Accrued depreciation of fixed assets |
| A | 04 | >Objects of intangible assets |
| P | 05 | Depreciation accrued on intangible assets |
| A | 08 | >Investments in non-current assets |
| A | 10 | >Materials, raw materials, fuel, etc. |
| A | 19 | >VAT |
| A | >26, 28, 29 | Cost accounts - main production, semi-finished products from production, auxiliary production (shops), general production (OPR) and general economic (OKhR) costs, production defects, servicing production (economy) |
| AP | 40 | >Product release |
| A | 41 | >Products |
| A | 43 | >Finished products |
| A | 44 | >Commercial expenses, sales expenses |
| A | 45 | >Shipped products |
| A | >58 | Cash accounts (financial assets) - cash, cash account, currency account, special accounts, transfers in transit, financial investments |
| AP | >68, 69, 71, 73, 75, 76, 79 | Accounts for settlements with suppliers, with customers, with the budget for taxes and insurance premiums, with extra-budgetary funds, with accountable persons, with debtors, creditors, with employees for other operations, with founders and shareholders, internal business settlements |
| P | >66, 67, 70 | Accounts for settlements with the personnel of an economic entity, for loans and borrowings (regardless of the term), for created reserves, in terms of doubtful debts |
| P | 80, 83, 82 | Capital accounts, reserves - statutory, additional, reserve |
| AP | 84 | retained earnings |
| AP | 90 | Sales |
| AP | 91 | >Other income and expenses |
| A | 94 | >Shortages |
| AP | 99 | Profits, losses |