Home » Payment systems » When do you need to connect a payment agent, and when do you need an online cash register?
0
MasterCode 07/26/2019 3598
Despite the great popularity of online shopping, many people still confuse payment agents and online cash registers. Let's figure it out.
Payment agent is a legal entity or individual entrepreneur engaged in accepting payments from individuals. Not all payment agents meet the modern requirements of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation.
Online cash register is a cash register technology that complies with the new edition of Federal Law 54. Such a cash register sends electronic receipts to the fiscal data operator immediately after payment has been processed. The OFD, in turn, registers checks and redirects them to the tax office.
Thus, the payment agent and the online cash register solve completely different problems: the first was created to increase the number of payments, the second to legalize business activities and issue automatic reports to the tax authorities.
Place of payment - Internet
Cash register equipment is used at the point of settlement with the buyer, therefore all persons making direct settlement with the buyer are required to use cash register equipment (Clause 1, Article 4.3 of Law No. 54-FZ).
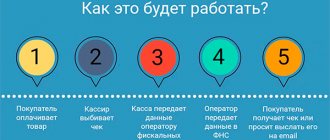
At the same time, Law No. 54-FZ also obliges the use of cash register systems in cases where there is no direct contact between the seller and the buyer. What are these cases? And this is precisely trade using the Internet, i.e. when the buyer and seller do not interact in person.
Thus, when making payments using electronic means of payment, which exclude the possibility of direct interaction between the buyer and the user or his authorized person, and using devices connected to the Internet, which provide the possibility of remote interaction between the buyer and the user when making these payments, the latter are obliged to ensure the transfer to the buyer of a cash receipt or strict reporting form in electronic form to the subscriber number or email address specified by the buyer before making payments.
In this case, the cash receipt or strict reporting form on paper is not printed by the user (Clause 5, Article 1.2 of Law No. 54-FZ).
What do we offer
- High share of remuneration from the volume of transfers
- Transparent payment scheme
- New clients for your business
- Possibility of making payments without opening correspondent accounts
- Preferential conditions for collection of funds within Moscow and Moscow Region
- Active promotion of points of sale through marketing campaigns
- Providing support at all stages of project implementation
- Personnel training and sales seminars
- Individual manager for your company
Ready solution from Nabix
What if we are “ordinary” agents?
Yes, but in our case, the entrepreneur not only intends to trade via the Internet, but it is also planned that he will do this within the framework of agency agreements, i.e.
will not just be a seller, but will act as an agent who will carry out orders for both sellers and buyers. And this is quite logical, because it is planned that the individual entrepreneur will help sellers and buyers find each other. To understand how this will affect the individual entrepreneur’s obligation to use CCP, let us first turn to the norms of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Under an agency agreement, one party (agent) undertakes, for a fee, to perform legal and other actions on behalf of the other party (principal) on its own behalf, but at the expense of the principal or on behalf and at the expense of the principal.
Under a transaction made by an agent with a third party on his own behalf and at the expense of the principal, the agent acquires rights and becomes obligated, even if the principal was named in the transaction or entered into direct relations with the third party for the execution of the transaction.
In a transaction concluded by an agent with a third party on behalf and at the expense of the principal, the rights and obligations arise directly from the principal (Clause 1 of Article 1005 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
From the analysis of this norm it follows that an agent can interact with a third party when making payments, regardless of on whose behalf he carries out these actions - on his own behalf or on behalf of the principal. Moreover, if an agent accepts cash and/or electronic means of payment as part of settlements, then he is obliged to use cash register systems.
The Financial Department in its explanations indicates that in a transaction concluded by an agent with a third party on its own behalf and at the expense of the principal, the agent acquires rights and becomes obligated, even if the principal was named in the transaction or entered into direct relations with the third party for the execution of the transaction .
At the same time, in a transaction concluded by an agent with a third party on behalf and at the expense of the principal, the rights and obligations arise directly from the principal. In this case, CCT is used by the principal (letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated June 26, 2017 No. 03-01-15/39998, dated June 26, 2017 No. 03-01-15/39999).
Thus, if you follow the explanations of the controllers, then the agent should use the CCT only in a situation where he acts on his own behalf, otherwise the CCT is used by the principal.
However, in our opinion, cash register systems should be used when directly accepting cash or electronic means of payment from buyers, regardless of whose name the entrepreneur-agent acts. Let us justify this position as follows.
Firstly, in a situation where the principal is an individual who is not registered as an individual entrepreneur (as is assumed in the situation under consideration), then he is simply not subject to Law No. 54-FZ and the principal—a “physicist” by default cannot apply the CCP .
In addition, in the previously valid version of Law No. 54-FZ (before amendments were made by Federal Law No. 290-FZ dated 03.07.2016), the obligation to use cash registers was established by all organizations and individual entrepreneurs when making cash payments and (or) settlements using payment cards in cases of sale of goods, performance of work or provision of services (clause 1, article 2, article 5 of Law No. 54-FZ as amended).
Attention should also be paid to Resolution No. 9803/06 of 05.12.2006 of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation, where the court indicated that the agent is obliged to use CCT even if, under the terms of the agency agreement, the agent acts on his own behalf, but at the expense of the principal.
The courts, when considering disputes about bringing to administrative liability, are guided by this resolution and make decisions taking into account the position of the Supreme Arbitration Court (Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the West Siberian District dated May 14, 2009 No. F04-2768/2009(6041-A45-29), FAS Central District dated 01/15/2008 in case No. A09-4769/07-31).
Moscow tax authorities also referred to this resolution in their letter dated January 31, 2007 No. 09-10/008098, i.e. The agent was previously obliged to use cash register systems when making payments to clients.
Therefore, in our opinion, given that in the case under consideration, the entrepreneur-agent directly plans to accept payment from buyers, apply cash registers, and issue a cash receipt to buyers, the agent is obliged to issue it, regardless of whether he will act on his own behalf or on behalf of the principal.
Who is a payment agent and how not to become one
In this situation, the entrepreneur plans to carry out online trading.
By organizing its activities, the individual entrepreneur acts as an intermediary within the framework of the agency agreement, and is directly involved in accepting payments from buyers, accepting electronic means of payment. And here the question arises: can’t he himself be recognized as a paying agent, since he accepts money from individuals? Let's take a closer look at who payment agents are. According to Art. 2 of the Federal Law of June 3, 2009 No. 103-FZ “On the activities of accepting payments from individuals, carried out by payment agents”, a legal entity or individual entrepreneur carrying out activities to accept payments from individuals are recognized as payment agents.
At the same time, the activity of accepting payments from individuals is recognized as the acceptance by the payment agent from the payer of funds aimed at fulfilling monetary obligations to the supplier to pay for goods (works, services), as well as the implementation by the payment agent of subsequent settlements with the supplier.
From an analysis of the provisions of Law No. 103-FZ, it follows that the paying agent performs only one action - accepts funds and makes payments to the supplier for goods (work, services). The payment agent does not perform any other legal actions.
In other words, if in the situation under consideration, the agent will only accept cash or electronic means of payment for goods (work, services) of the principal, then he can be recognized as a paying agent with all the ensuing consequences.
What consequences? When accepting payments, the payment agent must have an agreement on the implementation of activities for accepting payments from individuals, as provided. In addition, a mandatory condition is the use of a special bank account with the payment agent when accepting payments for making payments (clause 14 of Law No. 103-FZ).
If an individual entrepreneur is recognized as a paying agent and does not use a special account, then the tax authority may bring him to administrative responsibility under Part 2 of Art.
15.1 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation. The measure of liability for officials and entrepreneurs is a fine in the amount of 4,000 to 5,000 rubles. However, in the case under consideration, the entrepreneur-agent plans not only to accept funds from buyers, but also to provide information services and customer support services.
Accordingly, in this case the intermediary cannot be recognized as a paying agent.
Can a payment agent replace an online cash register?
A number of payment agents actually already have solutions under Federal Law-54, in force and with 100% replacement. We are talking about the “Robocheck” function in Robokassa: instead of buying or renting an online cash register, you use the online cash register of the service itself. Payments are accepted through it and fiscal receipts are sent. The ideal solution for small businesses.
In other cases, you won’t be able to do without an online cash register (unless you plan to work under the table, which is becoming more and more dangerous every month). You will have to buy or rent a modern terminal and “make friends” with the payment system.
List of payment agents that have their own solutions for connecting modern cash registers: Yandex.Kassa, Robokassa, Wallet One Unified Cash Desk, Money Online, PayU, Intellect money, Uniteller, Chronopay. As a client of these companies, you can rent or buy a terminal from their official partners and connect it to your store without any apparent problems. This will save time and nerves, since you won’t have to independently search for where to buy a cash register, how to connect it to the site and make sure everything works.
Let's sum it up
In our opinion, cash register systems should be used when directly accepting cash or electronic means of payment from buyers, regardless of whose name the entrepreneur-agent acts.
In addition, in a situation where the principal is an individual who is not registered as an individual entrepreneur (as is assumed in the situation under consideration), then he is simply not subject to Law No. 54-FZ and the principal—a “physicist” by default cannot apply the CCP. The payment agent performs only one action - accepts funds and makes payments to the supplier for goods (work, services). The paying agent does not perform any other legal actions, i.e. if the individual entrepreneur accepts only cash or electronic means of payment for the principal’s goods, which does not happen in the issue under consideration, then he can be recognized as a paying agent.
In this case, the individual entrepreneur plans not only to accept funds from buyers, but also to provide information services and customer support services. Accordingly, in this case there is no risk of being recognized as a paying agent.
When is a payment agent needed for an online store?
A payment agent is needed when your clients ask to accept payments in various ways that are inaccessible to you: cards of foreign banks, from a phone account, electronic money, cryptocurrencies, and so on.
You can, of course, take care of this issue yourself and register your store’s accounts in all popular banking systems and electronic wallets. But this will take you more than one week, and constant exchanges of electronic currencies and transfers between multiple wallets will not only take a lot of time, but are also fraught with regular blocking of accounts and subsequent proceedings. If you connect a payment agent, all these problems are possible one-time and with only one company.
In addition to their direct duties, payment agents perform additional functions:
- Supports recurring payments. The agent will regularly debit the client's card for subscribing to your services (with his consent)
- Mass payments will allow you to send dozens of payments to investors or freelance employees with one click.
- Collection of data and provision of payment analytics for a specific period
- Safe transaction. Payment agent protects you from fraudulent payments
- Some agents have their own marketplaces where you can list your products and services. You can run a business even without a website