To repay debt on contributions to the authorized capital, the organization can contribute fixed assets. For joint stock companies, this is provided for by paragraph 2 of Article 34 of the Law of December 26, 1995 No. 208-FZ, and for LLCs - by paragraph 1 of Article 15 of the Law of February 8, 1998 No. 14-FZ.
The founders must evaluate and agree on the value of non-monetary contributions to the authorized capital. To assess the market value of a fixed asset, a joint stock company must engage an independent appraiser. For an LLC, an independent assessment of the property contribution is mandatory only if its size exceeds RUB 20,000. The founders have the right to value the property contributed to the authorized capital no more expensive than the assessment of an independent expert (i.e. cheaper or in the same amount). This is stated in paragraph 3 of Article 34 of the Law of December 26, 1995 No. 208-FZ and paragraph 2 of Article 15 of the Law of February 8, 1998 No. 14-FZ.
Documenting
When transferring an object of fixed assets to the authorized capital of another organization (i.e. at the time of transfer of ownership of the object to the recipient), draw up a primary document, for example, fill out an act in form No. OS-1 (instructions approved by the Decree of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated January 21, 2003 No. 7, Part 3, Article 9 of the Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ). The basis for drawing up the act is the technical documentation for the fixed asset, as well as accounting data. For example, turnover on account 02 “Depreciation of fixed assets” will allow you to fill in information about the amount of accrued depreciation. Draw up the act in two copies, one of which is given to the recipient. When drawing up the act, do not fill out the section “Information on fixed assets as of the date of acceptance for accounting.” The recipient must fill it out in his copy of the act. Both copies of the act must be signed and approved by both the shareholder organization (participant) and the recipient.
In the act in form No. OS-1, indicate:
- number and date of compilation;
- full name of the fixed asset according to the technical documentation;
- name of the manufacturer;
- place of transfer of the fixed asset;
- factory and assigned inventory numbers of the fixed asset;
- depreciation group number, useful life of the fixed asset and actual service life;
- the amount of depreciation accrued before the transfer of the fixed asset, its residual value;
- information about the content of precious metals and stones;
- other characteristics of the fixed asset.
The act must contain the conclusion of the commission, which is created in the organization to control the disposal of fixed assets. The members of the commission must be the chief accountant, financially responsible persons and other employees appointed by the manager. The composition of the commission must be approved by the head of the organization by issuing an order.
This procedure follows from the instructions approved by Decree of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated January 21, 2003 No. 7, and paragraphs 77–81 of the Methodological Instructions approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 13, 2003 No. 91n.
If the organization contributes a building as a contribution to the authorized capital, draw up an act in form No. OS-1a. If an organization transfers several homogeneous fixed assets, draw up an act in form No. OS-1b. When filling out these acts, use the same procedure as when drawing up an act in form No. OS-1. This procedure is provided for by the instructions approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated January 21, 2003 No. 7.
Simultaneously with drawing up the act in form No. OS-1 (OS-1a, OS-1b), enter information about the disposal of fixed assets in the inventory card in form No. OS-6 (OS-6a) or in the inventory book in form No. OS-6b ( intended for small businesses). Enter the information on the basis of the transfer and acceptance certificate drawn up at the time of transfer of the fixed asset. This procedure is provided for by the instructions approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated January 21, 2003 No. 7.
If an organization receives a fixed asset containing precious metals, at the end of the year it will have to draw up a report according to Form No. 4-DM, approved by Rosstat Resolution No. 88 of November 14, 2007. In the report, indicate the amount of precious metals contained in the fixed asset.
In what valuation is the property included in the Criminal Code reflected in the accounting records?
Any fixed asset based on clause 7 of PBU No. 6/01 is accounted for at its original cost. For assets that are received as a contribution to the management company, such value is determined as a monetary value, which is individually (!) (clause 2 of article 15 of the Law “On LLC”, clause 9 of PBU 6/01) accepted by the founders of the enterprise and recorded in the Minutes of the general meeting of founders (or in the Decision) on the creation of the Company.
Moreover , if this assessment exceeds 20 thousand rubles, then an independent appraiser is invited to confirm it . Subsequently, this assessment is further clarified (clause 12 of PBU 6/01).
It is very important to understand that the provisions of PBU 6/01 and other regulations governing accounting apply to a newly created company only after its state registration.
Therefore, it is possible to decide on the procedure for accounting for assets, if their value is equal to or does not exceed 40 thousand rubles, only after receiving documents confirming the registration of the enterprise and after approving its Accounting Policy.
Thus, initially the value of the asset is recognized as equal to the founder’s valuation and only then, if its final value, formed on the basis of PBU 6/01, is equal to or less than 40 thousand rubles, it is subject to write-off in a separate manner - as part of the inventory.
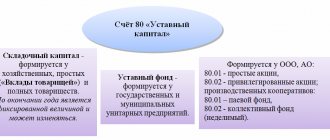
At the same time, the asset included in the Criminal Code must be entered into accounting records by the date of registration of the company. This will reflect the amount of authorized capital paid by the founders as of the date of registration of the company. The process of forming the authorized capital using fixed assets will look like this:
Debit of account 08 “Investments in non-current assets” Credit of account 75 “Settlements with founders” - reflects the receipt of a contribution to the management company at a cost approved unanimously by the founders;
Debit account 75 Credit account 80 “Authorized capital” - reflects the formation of the management company at the expense of contributions from the founders;
Debit of account 01 “Fixed assets” Credit account 08 – assets recognized as fixed assets are accepted for accounting, according to the assessment formed on the basis of PBU 6/01;
or
Debit account 10 “Materials” subaccount “Low-valued fixed assets” Credit account. 08 – the value of assets recognized as fixed assets, but with a value within 40,000 rubles, is written off.
The procedure for reflecting the formation of authorized capital through the above entries is set out in paragraph 28 of the Methodological Instructions for Accounting for Fixed Assets (approved by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation in Order No. 91n dated 10/13/2003). As for the last posting (using account 10), it is permitted by clause 5 of PBU No. 6/01 and the Instructions for the Chart of Accounts. This Instruction states that the accounting correspondence schemes proposed in it are standard and, if an enterprise needs it to reflect business transactions, then it can independently enter its own postings, observing the uniform approaches established in the Instructions.
Moreover, in favor of the last posting (correspondence between the debit of account 10 and the credit of account 08) is evidenced by PBU No. 6/01 itself in paragraph 12, which states that the value of an asset received by the management company consists of its assessment and expenses accepted by the founders, that are associated with its entry. For example, these may be the costs of installation and assembly of equipment, its delivery, etc. And all these expenses accumulate on account 08, making it possible to ultimately determine the full cost of the asset, i.e. whether it exceeds the established limit of 40 thousand rubles or not. Moreover, these expenses are already borne by the organization itself, and not by its founders, and it needs them to put the asset into operation.
On the wiring it will look like this:
Debit of account 08 Credit of account 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors”, account 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors”, etc. – expenses associated with the receipt of the asset into the organization and its commissioning are reflected.
Thus, the monetary value of the property adopted by the founders may differ from the one at which this asset will be accepted for accounting. At the same time, an increase in this assessment occurs only for accounting purposes, but does not change the amount of the authorized capital and the share of the founder in it.
Accounting
The founding organization's contributions to the authorized capitals of other organizations are accounted for in account 58 “Financial investments”. Reflect the debt on deposits by posting to the debit of account 58 in correspondence with the settlement account. For example, with account 76, to which open a separate sub-account “Calculations for contributions to the authorized (share) capital”:
Debit 58 Credit 76 subaccount “Settlements on contributions to the authorized (share) capital” - reflects the debt on contributions to the authorized capital of the subsidiary.
Make a note like this:
- when creating joint-stock companies or LLCs - on the basis of an agreement on the creation of a company or on the basis of a decision of the sole founder (shareholder, participant) (clause 5 of article 9 of the Law of December 26, 1995 No. 208-FZ, article 11 of the Law of February 8 1998 No. 14-FZ);
- when increasing the authorized capital:
- in joint-stock companies - on the basis of the minutes of the general meeting of shareholders on increasing the authorized capital (decision of the board of directors (supervisory board), if, in accordance with the charter, such a decision is within its competence) or the decision of the sole founder (shareholder) on this (Article 28, paragraph. 3, Article 47, Article 63 of the Law of December 26, 1995 No. 208-FZ);
- in an LLC - on the basis of the minutes of the general meeting of participants on increasing the authorized capital or the decision of the sole founder (participant) on this (Article 17–19, paragraph 6 of Article 37, Article 39 of the Law of February 8, 1998 No. 14-FZ ).
From the next month after the transfer of the fixed asset, stop accruing depreciation on it (clause 22 of PBU 6/01).
In accounting, reflect the disposal of fixed assets contributed as a contribution to the authorized capital at the residual value (clause 85 of the Methodological Instructions approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 13, 2003 No. 91n).
To account for the disposal of such property on account 01, open a separate sub-account “Retirement of fixed assets”. At the time of transfer of the object, reflect its original (replacement) cost in the debit of the account. For a loan - the amount of depreciation accrued during the period of operation of the disposed facility. In this case, make the following entries:
Debit 01 subaccount “Disposal of fixed assets” Credit 01 – reflects the initial (replacement) cost of the fixed asset transferred to the authorized capital of the subsidiary;
Debit 02 Credit 01 subaccount “Disposal of fixed assets” - reflects depreciation accrued for the period of operation of the facility transferred to the authorized capital of the subsidiary.
As a result, the balance on account 01 “Retirement of fixed assets” will reflect the residual value of the transferred fixed asset. Determine the residual value using the formula:
| Residual value of fixed asset | = | Initial (replacement) cost of fixed assets | – | The amount of accrued depreciation during the operating period |
Reflect the transfer of fixed assets to the authorized capital of another organization by posting:
Debit 76 subaccount “Calculations for contributions to the authorized (share) capital” Credit 01 subaccount “Disposal of fixed assets” - a fixed asset was made as a contribution to the authorized capital of a subsidiary.
If the residual value of the transferred fixed asset differs from its valuation agreed upon by the founders, take into account the difference as part of other income or expenses. Make the following wiring:
Debit 76 subaccount “Calculations for contributions to the authorized (share) capital” Credit 91-1 - reflects the positive difference between the valuation of the fixed asset agreed upon by the founders and its residual value;
Debit 91-2 Credit 76 subaccount “Calculations for contributions to the authorized (share) capital” - reflects the negative difference between the valuation of the fixed asset agreed upon by the founders and its residual value.
This procedure is provided for in paragraph 85 of the Methodological Instructions, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 13, 2003 No. 91n, and the Instructions for the chart of accounts (accounts 01, 76, 91).
Transfer of fixed assets to the authorized capital of another organization
If a fixed asset is made as a contribution to the authorized capital of a joint-stock company, then in accordance with paragraph 3 of Article 34 of the Federal Law of the Russian Federation of December 26, 1995 “On Joint-Stock Companies”, when paying for shares in kind, an independent appraiser must be involved to determine the market value of the transferred fixed asset . The value of the monetary valuation made by the founders of the joint-stock company and the board of directors cannot be higher than the value of the valuation made by an independent appraiser. If the fixed asset is contributed as a contribution to the authorized capital of a limited liability company, then it is necessary to be guided by paragraph 2 of Article 15 of the Federal Law of the Russian Federation of February 8, 1998 No. 14-FZ “On Limited Liability Companies”. In accordance with this clause, the monetary value of non-monetary contributions to the authorized capital of the company made by the company's participants is approved by a unanimous decision of the general meeting of the company's participants. If the nominal value (increase in the nominal value) of the share of a company participant in the authorized capital of the company, paid for by a non-monetary contribution, is more than two hundred minimum wages established by federal law on the date of submission of documents for state registration of the company or corresponding changes in the company’s charter, then such contribution must assessed by an independent appraiser. The nominal value (increase in the nominal value) of the share of a company participant, paid for by such a non-monetary contribution, cannot exceed the amount of valuation of the specified contribution, determined by an independent appraiser.
One of the ways to dispose of fixed assets is to transfer them to the authorized capital of another organization. According to clause 101 of the Guidelines for accounting of fixed assets, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 20, 1998 N 33n (hereinafter referred to as the Guidelines), the write-off of the value of retired fixed assets is reflected in accounting in detail:
- on the debit of the account for recording the write-off (sale) of fixed assets - the initial cost of the object, recorded in the account for fixed assets, and the costs associated with the disposal of fixed assets, which are previously accumulated in the account for accounting for the costs of auxiliary production (accrued wages and social contributions made). insurance of employees participating in operations for the disposal of fixed assets, taxes and fees paid from proceeds from the sale of fixed assets, etc.);
- on the credit of the specified account - the amount of accrued depreciation charges, the amount of proceeds from the sale of valuables related to fixed assets.
Income, expenses and losses from the write-off of fixed assets from the balance sheet are reflected in accounting in the reporting period to which they relate. Income, expenses and losses from the write-off of fixed assets from the balance sheet are subject to crediting from the write-off (sales) account to the financial results of the organization (clause 103 of the Methodological Instructions).
The transfer of fixed assets as a contribution to the authorized capital of other organizations is formalized by the Acceptance and Transfer Certificate. Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated January 21, 2003 N 7 approved the following forms of primary accounting documentation for accounting of fixed assets:
- Act on acceptance and transfer of fixed assets (except for buildings, structures) - form N OS-1;
- Certificate of acceptance and transfer of a building (structure) - form N OS-1a;
- Act on acceptance and transfer of groups of fixed assets (except for buildings, structures) - form N OS-1b.
These exclusions of an object from fixed assets are entered into the inventory card (book) for accounting for fixed assets (forms N OS-6, N OS-6a, N OS-6b).
In accordance with the Chart of Accounts for accounting financial and economic activities of organizations and the Instructions for its application, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n, account 58 is intended to reflect transactions related to making contributions to the authorized (share) capitals of other organizations “Financial investments”/sub-account “Units and shares”. Account 91 reveals the financial result (profit or loss), which is reflected in accounting as part of operating income (expenses) as income (expenses) associated with participation in the authorized capital of other organizations (clause 7 of PBU 9/99 approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated May 6, 1999 N 32n, clause 11 PBU 10/99 approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated 05/06/1999 N 33n).
In the accounting of an organization, the contribution of fixed assets as a contribution to the authorized capital of another organization is reflected by the following entries:
Account Dt 01 / “Disposal of fixed assets” - Account Dt 01 - the original (replacement) cost of the transferred fixed asset item is written off;
Dt account 02 - Kt account 01 / “Disposal of fixed assets” - the amount of accrued depreciation is written off;
Dt account 91-2 - Kt account 01 / “Disposal of fixed assets” - reflects the residual value of the transferred fixed asset item;
Dt invoice 58 - Kt invoice 91-1 - 1,000,000 rubles. — reflects the monetary value of the contribution agreed upon by the parties.
Dt account 91-9 - Kt account 99 – financial result (profit) is reflected.
Dt account 99 - Kt account 91-9 – financial result (loss) is reflected.
3.1.
income tax The procedure for calculating income tax on transactions related to the transfer of property as contributions to the authorized capital of other organizations is regulated by Article 277 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
According to paragraph 2 of paragraph 1 of Article 277 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the difference between the value of the property contributed as a contribution and the nominal value of the acquired shares (shares, rights) is not recognized as profit (loss) of the taxpayer - shareholder (participant, shareholder). At the same time, for tax accounting purposes, the value of the acquired shares is recognized as equal to the value (residual value) of the contributed property, determined according to tax accounting data on the date of transfer of ownership of the specified property, taking into account additional expenses that, for tax purposes, are recognized by the transferring party upon such contribution.
If the founder makes a non-monetary contribution to the authorized capital of another organization, then for tax purposes this operation is not recognized as a sale in the founder’s accounting. The founder, who is a legal entity, makes contributions to the authorized capital at the expense of his own profit remaining after paying income tax. According to paragraph 3 of Article 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, expenses of a participant (founder) in the form of contributions to the authorized (joint) capital do not reduce the tax base when calculating income tax.
Thus, the financial result from the transfer of fixed assets, identified in accounting on account 91, will not be taken into account for profit tax purposes.
3.2. VAT
In accordance with paragraph 4, paragraph 3, Article 39 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the transfer of property, if such a transfer is of an investment nature, including the transfer of property as a contribution to the authorized (share) capital of business companies or partnerships, is not recognized as a sale for tax purposes.
Thus, the transfer of fixed assets as a contribution to the authorized capitals of other organizations is not recognized as subject to VAT (clause 1, clause 2, Article 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
According to paragraph 4, paragraph 2, Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, amounts of input VAT on goods (work, services) used in carrying out operations that are not recognized as sales in accordance with paragraph 2 of Article 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are not accepted for deduction, but are subject to inclusion in the price of the relevant goods (works, services).
If an organization, as a contribution to the authorized capital, transfers fixed assets, the amounts of input VAT on which were previously deducted, then at the time of transfer to the organization it is necessary to restore the amount of input VAT attributable to the residual value of the transferred objects and pay this amount to the budget (p .3 Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In accounting, VAT restoration is reflected by posting:
Dt 91 Kt 68 – for the amount of restored VAT.
Example.
In May 2003, the organization transferred its fixed assets to another organization in the form of a contribution to the authorized capital. The initial cost of the fixed asset is 84,000 rubles, the amount of depreciation accrued at the time of transfer is 30,000 rubles, the cost of dismantling the transferred fixed asset is 6,000 rubles.In accordance with the constituent documents, the amount of the contribution to the authorized capital is 95,000 rubles.
To reflect transactions in accounting, we will use the following names of subaccounts:
01-1 “Fixed assets in the organization”
01-2 “Disposal of fixed assets”
| Contents of operations | Debit | Credit | Amount (rub.) |
| The initial cost of a fixed asset transferred to the authorized capital of another organization is reflected | 01-2 | 01-1 | 84 000 |
| The amount of accrued depreciation is reflected | 02 | 01-2 | 30 000 |
| The residual value of the transferred fixed asset item is written off | 91-2 | 01-2 | 54 000 |
| The amount of additional expenses of the organization is reflected | 23 | 76 | 6 000 |
| Additional expenses associated with the transfer of fixed assets are written off | 91-2 | 23 | 6 000 |
| The valuation of the fixed asset is reflected in accordance with the constituent documents | 58 | 91-1 | 95000 |
| The amount of profit is reflected due to the difference between the residual value of the fixed asset and the par value of the acquired shares (95,000 rubles - 54,000 rubles - 6,000 rubles) | 91-9 | 99 | 35 000 |
| VAT has been restored from the residual value of fixed assets (RUB 54,000 x 20%) | 91 | 68 | 10 800 |
In tax accounting, the founder's expenses in the form of a contribution to the authorized capital, which, according to paragraph 3 of Article 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, will not reduce the tax base when calculating income tax, will amount to 54,000 rubles, that is, they will be equal to the residual value of the transferred fixed asset.
Additional expenses in the amount of 6,000 rubles. in accordance with paragraph 2 of Article 277 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, they reduce the tax base for income tax.
Income tax
When transferring a fixed asset as a contribution to the authorized capital, the organization has neither income nor expenses (subclause 2, clause 1, article 277, clause 3, article 270 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). For more information about this, see How to reflect the disposal of depreciable property in tax accounting. If the residual value of the transferred fixed asset differs from its valuation agreed upon by the founders, a permanent difference is formed in accounting, which leads to the emergence of a permanent tax liability or a permanent tax asset (clauses 4 and 7 of PBU 18/02). They should be reflected by postings:
Debit 99 subaccount “Permanent tax liabilities” Credit 68 subaccount “Calculations for income tax” - reflects the permanent tax liability from the negative difference between the residual value of the fixed asset and its valuation agreed upon by the founders;
Debit 68 subaccount “Calculations for income tax” Credit 99 subaccount “Permanent tax assets” - reflects a permanent tax asset with a positive difference between the residual value of the fixed asset and its valuation agreed upon by the founders.
An example of how to reflect in accounting and taxation the transfer of fixed assets as a contribution to the authorized capital
In July, Alfa CJSC contributed a computer to the authorized capital of Torgovaya LLC. In the accounting and tax accounting of the transferor:
- the initial cost of the computer is 41,000 rubles;
- the amount of depreciation accrued before the transfer of the computer is 16,000 rubles;
- the residual value of the computer at the time of transfer is 25,000 rubles. (41,000 rubles – 16,000 rubles);
- the amount of input VAT accepted for deduction when purchasing a computer is 7,380 rubles.
The monetary value of the contribution, according to the decision of the founders of Hermes, is considered equal to 30,000 rubles. Alpha did not have any additional expenses associated with the contribution of property to the authorized capital of the subsidiary.
To reflect transactions in accounting, Alpha’s accountant opened sub-accounts:
- to account 76 – subaccount “Settlements on deposits in the authorized (share) capital”;
- to account 01 – subaccount “Disposal of fixed assets”.
When transferring the computer to the authorized capital of Hermes, the Alpha accountant made entries.
July:
Debit 58 Credit 76 subaccount “Settlements on deposits in the authorized (share) capital” - 30,000 rubles. – Alpha’s debt on contributions to the authorized capital of Hermes is reflected;
Debit 01 subaccount “Disposal of fixed assets” Credit 01 – 41,000 rub. – reflects the initial cost of the computer transferred to the authorized capital of Hermes;
Debit 02 Credit 01 subaccount “Disposal of fixed assets” – 16,000 rubles. – reflects depreciation accrued for the period of operation of the computer transferred to the authorized capital of Hermes;
Debit 76 subaccount “Settlements on contributions to the authorized (share) capital” Credit 01 subaccount “Disposal of fixed assets” - 25,000 rubles. – the fixed asset was contributed as a contribution to the authorized capital of another organization;
Debit 76 subaccount “Settlements on deposits in the authorized (share) capital” Credit 91-1 – 5000 rubles. (30,000 rubles - 25,000 rubles) - reflects the positive difference between the valuation of the fixed asset agreed upon by the founders and its residual value.
When transferring the computer, the accountant restored part of the input VAT previously accepted for deduction and included the tax in the initial cost of the financial investment. The amount of restored VAT is 4,500 rubles. (RUB 7,380 × (RUB 25,000 : RUB 41,000)). At the same time, the accountant made the following entry:
Debit 19 Credit 68 subaccount “VAT calculations” – 4500 rubles. – VAT previously accepted for deduction has been restored;
Debit 58 Credit 19 – 4500 rub. – the restored VAT amount was transferred to the Hermes balance sheet.
The transfer of a computer does not affect the calculation of income tax. Due to the fact that tax accounting did not take into account the difference between the valuation of the fixed asset agreed upon by the founders and its residual value, the accountant made the following entry:
Debit 68 subaccount “Calculations for income tax” Credit 99 subaccount “Permanent tax assets” – 1000 rubles. (RUB 5,000 × 20%) – a permanent tax asset is reflected from the difference between the valuation of the fixed asset agreed upon by the founders and its residual value.
Case Study
Medea LLC contributed a laptop to the authorized capital of Les LLC. The agreed monetary value of the founders is 40,000 rubles.
The initial cost of the laptop is 76,700 rubles. (including VAT - 11,700 rubles). The amount of accrued depreciation is RUB 32,500.
Solution:
- Debit 01 subaccount “Disposal of fixed assets” Credit 01 - 65,000 rub. (76,700 - 11,700) - the initial cost of the laptop has been written off.
- Debit 02 Credit 01 subaccount “Disposal of fixed assets” - 32,500 rubles. — accrued depreciation is written off.
- Debit 58.1 Credit 01 subaccount “Disposal of fixed assets” - 32,500 rubles. (65,000 - 32,500) - the residual value of the laptop has been written off.
- Debit 19 Credit 68 - 5,850 rub. ((32,500: 65,000) x 11,700) — VAT has been restored.
- Debit 58.1 Credit 19 - 5,850 rub. the restored VAT is taken into account as part of financial investments.
- Debit 58.1 Credit 91.1 - 7,500 rub. (40,000 - 32,500) - reflects the positive difference between the founders’ assessment and the residual value of the laptop.
- Debit 68 Credit 99 - 1,500 rub. (7,500 x 20%) - a permanent tax asset is reflected.
VAT
The transfer of a fixed asset as a contribution to the authorized capital of a subsidiary is not recognized as a sale (subclause 4, clause 3, article 39 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Therefore, there is no need to charge VAT on this operation (subclause 1, clause 2, article 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The input tax on a fixed asset previously accepted for deduction will have to be restored in a part proportional to the residual value of the object (subclause 1, clause 3, article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The transferring party includes the restored VAT in the initial cost of financial investments (clause 9 of PBU 19/02, letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 19, 2006 No. 07-05-06/302, dated October 30, 2006 No. 07-05-06/ 262). Indicate the amount of the restored VAT in the act in form No. OS-1 (OS-1a, OS-1b) (clause 14 of section II of Appendix 5 to the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2011 No. 1137, subclause 1, clause 3 of Art. 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). To do this, in the “Other characteristics” section of the act, write: “The amount of restored VAT on the fixed asset is ___ rubles.” Based on this entry, the receiving party will be able to accept the restored VAT for deduction (clause 14 of section II of Appendix 4 to the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2011 No. 1137, subclause 1, clause 3, article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, subclause 3.1, clause. 1 Article 251 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
simplified tax system
When transferring a fixed asset to the authorized capital of a subsidiary, the organization applying the simplification does not have any income or expenses (Articles 346.15, 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
When transferring fixed assets, draw up primary accounting documents according to the forms approved by Decree of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated January 21, 2003 No. 7. This must be done, since organizations using the simplified procedure are required to keep accounting, including fixed assets, in the general manner (h 1 Article 2 of the Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ, letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 23, 2012 No. 03-11-09/80). Therefore, it is mandatory to reflect transactions on the transfer of property to the authorized capital using the Chart of Accounts and the double entry method.
Legal subtleties
If the cost (the amount contributed to the authorized capital in monetary equivalent) is more than 20 thousand rubles, then an independent property appraiser must take part in the case, otherwise actions to transfer any property will be considered illegal. Most often, cars are such transferred property, but it happens that equipment, premises, etc. are transferred. Moreover, practice shows that the founders continue to use this property even after the transfer of ownership rights.
Important: in order for the transfer to be possible in principle, it is necessary to spell out its nuances in the adopted Charter of the “fresh” legal entity. Otherwise, the actions will not have legal force.
UTII
The object of UTII taxation is imputed income (clause 1 of Article 346.29 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Therefore, expenses associated with the transfer of fixed assets to the authorized capital of another organization do not affect the calculation of the single tax.
When transferring fixed assets, prepare primary accounting documents according to the forms approved by Decree of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated January 21, 2003 No. 7. Reflect all transactions related to the transfer of fixed assets using the Chart of Accounts and the double entry method. This must be done, since organizations that pay UTII are required to keep accounting records in full (Part 1, Article 2 of Law No. 402-FZ of December 6, 2011).