Tax accounting according to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation
Tax accounting data for a Russian taxpayer must reflect, in particular, the procedure for generating the amount of income and expenses and the amount of debt for settlements with the budget for taxes.
Forms of analytical tax accounting registers for determining the tax base, which are documents for tax accounting, must necessarily contain the following details:
- register name;
- period (date) of compilation;
- transaction meters in kind (if possible) and in monetary terms;
- name of business transactions;
- signature (decryption of signature) of the person responsible for compiling these registers.
Tax accounting data is confirmed by:
- primary accounting documents (including an accountant’s certificate);
- analytical tax accounting registers;
- calculation of the tax base.
The taxpayer establishes the procedure for maintaining tax accounting in the accounting policy for tax purposes (Article 313 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
By reducing the amount of income by expenses incurred, we obtain the value of the tax base. But expenses must be supported by documents and economically justified.
Expenses are considered confirmed if there are properly executed primary documents that directly or indirectly indicate the payer’s expenses.
Lack of a cash receipt for cash payments. Can expenses be taken into account?
The organization, which is on the general taxation system, paid for the purchased materials in cash. A delivery note and a receipt for the cash receipt order were received from the counterparty working with VAT. Does an organization have the right to take into account cash expenses incurred in order to determine the tax base for income tax if the documents received from the counterparty on payment by the organization for materials (goods, works, services) do not contain a cash receipt?
In accordance with paragraph 1 of Art. 252 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
In order to determine the tax base and calculate income tax, the taxpayer reduces the income received by the amount of expenses incurred.
Expenses
Justified and documented expenses (and in cases provided for in
Article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation
, losses) incurred (incurred) by the taxpayer are recognized.
Under reasonable expenses
refers to economically justified costs, the assessment of which is expressed in monetary form.
Under documented expenses
means expenses confirmed by documents drawn up in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, and (or) documents indirectly confirming expenses incurred (including a customs declaration, business trip order, travel documents, report on work performed in accordance with the contract).
Any expenses are recognized as expenses, provided that they are incurred to carry out activities aimed at generating income.
If the documents required to confirm expenses are not drawn up in the prescribed manner, then such expenses cannot be taken into account when determining the tax base for income tax.
At the same time, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not establish a specific list of documents
necessary to confirm expenses incurred by taxpayers.
According to Art. 313 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
Taxpayers calculate the tax base at the end of each reporting (tax) period based on tax accounting data.
Tax accounting data must reflect the procedure for forming the amount of income and expenses, the procedure for determining the share of expenses taken into account for tax purposes in the current tax (reporting) period.
Tax accounting data is confirmed by
:
– primary accounting documents
(including an accountant's certificate);
– analytical tax accounting registers;
– calculation of the tax base.
Clause 1 Art. 11 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
It has been established that the institutions, concepts and terms of civil, family and other branches of legislation of the Russian Federation used in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are applied in the meaning in which they are used in these branches of legislation, unless otherwise provided by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Based on this, the concept of “primary accounting documents”
should be determined in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation on
accounting
.
Under primary accounting documents
are understood as supporting documents that document all business transactions of the organization and on the basis of which accounting is carried out (clause 1, article 9 of the Federal Law of November 21, 1996 No. 129-FZ
“On Accounting”
).
According to paragraph 2 of Art. 9 of Law No. 129-FZ, primary accounting documents are accepted for accounting
, if they are compiled according to the form contained in the albums of unified forms of primary accounting documentation, and
documents whose form is not provided for in these albums must contain the following mandatory details
:
- Title of the document;
– date of document preparation;
– name of the organization on whose behalf the document was drawn up;
– content of the business transaction;
– measuring business transactions in physical and monetary terms;
– names of positions of persons responsible for carrying out a business transaction and the correctness of its execution;
– personal signatures of these persons.
The cash receipt does not have the cashier's signature, so it cannot be recognized as a primary accounting document that meets the requirements of the Accounting Law.
the accrual method for profit tax purposes
, then in accordance with
paragraph 1 of Art.
272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation , expenses accepted for tax purposes
are recognized
as such in the reporting (tax) period to which they relate,
regardless of the time of actual payment of funds
and (or) other forms of payment and are determined taking into account the provisions
of Art.
318-320 Tax Code of the Russian Federation .
Therefore, for the recognition of expenses in tax accounting using the accrual method, it does not matter what document confirming payment in cash the organization has
.
The main thing is to have a complete package of shipping documents.
Consignment note according to the unified form No. TORG-12
, approved by Decree of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated December 25, 1998 No. 132,
refers to the primary accounting documentation for the accounting of trade operations
and is used to register the sale (release) of inventory items.
A copy of the delivery note received by the buyer is the basis for the buyer to accept the acquired values for accounting.
.
That is, the delivery note and the receipt for the cash receipt order received by your organization from the supplier when purchasing materials in cash are documents confirming the expenses incurred for profit tax purposes.
And if the organization uses the cash method
accounting for income and expenses, then in accordance with
clause 3 of Art.
273 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, expenses of taxpayers are recognized as
expenses after their actual payment
.
For income tax purposes, payment for goods (works, services and (or) property rights)
The termination of the counter-obligation by the taxpayer - the purchaser of the specified goods (work, services) and property rights to the seller, which is directly related to the supply of these goods (performance of work, provision of services, transfer of property rights) is recognized.
Likewise for taxpayers under the simplified tax system
.
According to paragraph 1 of Art. 2 of the Federal Law of May 22, 2003 No. 54-FZ “On the use of cash register equipment when making cash payments and (or) settlements using payment cards”
CCT
, included in the State Register,
is used
on the territory of the Russian Federation
without fail
by all organizations and individual entrepreneurs
when they make cash payments
and (or) payments using payment cards in cases of selling goods, performing work or providing services.
Without the use of CCT
may make cash payments, in particular, organizations and individual entrepreneurs -
payers of UTII
when carrying out the types of business activities established
by clause 2 of Art.
346.26 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation , organizations and individual entrepreneurs in
the case of providing services to the population
, subject to the issuance of the appropriate strict reporting forms, organizations and individual entrepreneurs
due to the specifics of their activities or the characteristics of their location
when carrying out types of activities established by law (clause 2, clause 2.1, Clause 3 of Article 2 of Law No. 54-FZ).
In all other cases
Organizations and individual entrepreneurs, when making cash payments,
are required to use cash registers and issue
cash register receipts printed by cash register
at the time of payment (Clause 1, Article 5 of Law No. 54-FZ).
That is, the absence of a cash receipt is a violation
requirements of Law No. 54-FZ
on the part of the supplier
.
But not from the buyer's side.
The Ministry of Finance claims that the expenses of a taxpayer applying the simplified tax system
payments made in cash,
on the basis of
invoices, invoices and
receipts for a cash receipt order,
can be taken into account when determining the tax base
only if there is a cash receipt
(letter dated 02/21/2008 No. 03-11-05/40).
In accordance with clause 3.1 of the Regulations on the procedure for conducting cash transactions with banknotes and coins of the Bank of Russia on the territory of the Russian Federation
, approved by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation dated October 12, 2011 No. 373-P,
cash
is accepted by a legal entity or individual entrepreneur
using cash receipt orders
.
Unified form No. KO-1 “Cash receipt order”
approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated August 18, 1998 No. 88.
Thus, if when an organization purchased materials for cash, the supplier issued a receipt for the cash receipt order in form No. KO-1
, filled out in compliance with the requirements provided for in paragraph 2 of Art.
9 of Law No. 129-FZ, this receipt is a document confirming the fact of payment of expenses for the purchase of materials
.
In a letter dated May 18, 2012 No. 03-11-06/2/69, the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation reported that for taxpayers using the simplified tax system, confirmation of the amounts of payment expenses
purchased goods (works, services)
are primary documents
(
payment documents
, acceptance certificates, invoices, concluded contracts, etc.), duly executed.
Therefore the corresponding costs
when making cash payments and (or) payments using payment cards, in cases established by law,
they can be confirmed not only by cash register receipts printed by cash register equipment, but also by other documents
(sales receipts, receipts)
confirming the receipt of funds
for the relevant product ( work, service).
It would seem that the Ministry of Finance has softened its position.
But officials emphasize that you can do without a cash receipt in cases established by law.
.
That is, in cases where the seller has the right not to use cash register systems when making cash payments.
That tax legislation does not contain provisions stating that a cash receipt is the only document
, which can confirm the taxpayer’s expenses when making cash payments, the courts say.
FAS Ural District
, for example, indicates that
the taxpayer’s
failure to submit cash receipts in the presence of other documents
does not in itself refute the fact of payment of cash and the presence of corresponding expenses.
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not establish a list of documents
, subject to registration when the taxpayer carries out certain expense transactions, does not impose any special requirements for their registration (filling out).
The decision on the possibility of accounting for certain expenses if they are connected with the taxpayer’s profit-making activities for tax purposes depends on whether the documents available to the taxpayer confirm the fact of the implementation of the expenses declared by him or not (resolution dated January 12, 2009 No. F09 -10009/08-С2, dated 07/31/2008 No. Ф09-5433/08-С3, dated 10/18/2007 No. Ф09-8532/07-С3, dated 07/03/2007 No. Ф09-4997/07- C3).
Therefore, receipts for cash receipts are acceptable evidence of expenses incurred.
.
This position is supported by other courts (decrees of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Volga District
dated July 31, 2008, No. A06-7444/07,
Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Central District
dated March 6, 2008, No. A09-930/07-30).
Justification of expenses
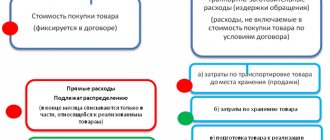
Production and sales costs are given in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Their list is not closed or exhaustive. Expenses that are not included can also reduce a company's profit. The main thing is that the costs are related to generating income.
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation requires that expenses be justified and documented (clause 1 of Article 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). And the law on accounting states that every fact of economic life must be documented in primary accounting documents (Article 9 of the Federal Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ “On Accounting”, hereinafter referred to as Law No. 402-FZ).
That is, for one or another type of company expenses there must be documents that confirm them.
When a sales receipt is issued: specifics of application in the context of Law No. 54-FZ
It contains a number of provisions that do not contradict Law No. 54-FZ, a legal act with greater legal force, but complement it and are mandatory for application. Decree No. 55 requires sellers, regardless of whether they are required to use online cash registers or not, to issue a sales receipt to customers if:
Such sellers include, in particular, individual entrepreneurs and legal entities that pay UTII. Until July 1, 2021, they are given the opportunity not to use online cash registers, subject to the issuance of sales receipts - instead of cash receipts - to customers.
Mandatory details of primary documents
Law No. 402-FZ makes it possible to independently develop forms for primary documents, as well as use unified forms or combine both.
In any case, the form of the primary accounting document must contain the following mandatory details (Part 2, Article 9 of Law No. 402-FZ):
- name of the document (form);
- date of document preparation;
- name of the organization on behalf of which the document was drawn up;
- content of a business transaction;
- business transaction meters (in physical and (or) monetary terms, indicating units of measurement);
- the names of the positions of the employees responsible for the execution of the business transaction and its registration, and their personal signatures. In addition to the signatures of these persons, it is necessary to indicate their last names and initials, or other details that will help identify them.
According to the accounting law, every fact of economic life must be documented as a primary accounting document.
In what cases is a sales receipt issued without a cash register, nuances of issuance in 2021
- Document's name.
- Number and date when it is filled out.
- Name of the organization
- Taxpayer code (TIN or EDRPOU).
- Name of the service or product.
- Number of items purchased.
- Price per unit.
- The total cost of each item.
- Total purchase amount.
- Personal information of the person who issued the receipt, his signature and position.
- provision of household services, services related to the zoological sphere;
- repair, maintenance and washing of vehicles;
- provision of temporary use of parking spaces for vehicles;
- transportation of goods and passengers, if the vehicle fleet does not exceed 20 vehicles;
- distribution of advertising on the street or in transport;
- provision of temporary use of premises for living, if the area of the premises does not exceed 500 m 2;
- provision of temporary use of retail and food outlets without premises for customers;
- provision of land for rent for the placement of retail and food outlets without premises for customers.
Legislation
At the legislative level, the issue of the reasons and grounds for the use of cash and sales receipts is resolved.
In particular, mention should be made of Federal Law-290, which amended Federal Law-54 “On the use of cash register systems in the implementation of cash and non-cash payments.” Article 2 explains the detailed procedure for using a sales receipt rather than a cash receipt.
It is also necessary to mention the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, or more precisely:
- clause 2 art. 346.26, which regulates the list of business activities that are subject to a single tax on income received.
- clause 2 art. 346.43, which provides a list of types of business that are subject to the patent tax system.
These articles of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation clearly delimit the list of entrepreneurial activities for which the use of a sales receipt instead of a cash register is permitted.
ConsultantPlus: Forums
Question: Our organization is engaged in public catering (bar), transferred to the payment of UTII. There is a production need to purchase products frequently and in small quantities. Is it possible to capitalize them on the basis of cash receipts from supermarkets, which indicate the name of the product, quantity, price and purchase amount?
At the same time, we draw your attention to the fact that in accordance with the Guidelines for accounting of inventories, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 28, 2021 N 119n, materials purchased by the accountable persons of the organization are subject to delivery to the warehouse. The receipt of materials is carried out in the generally established manner on the basis of supporting documents confirming the purchase (invoices and receipts from stores, a receipt for a cash receipt order - when purchasing from another organization for cash, an act or certificate of purchase on the market or from the public), which are attached to the advance payment report of the accountable person.
Capitalization of goods: documents, postings - Kontur.Accounting
To organize efficient production, it is important to maintain competent warehouse records. Knowing the documents used to register goods in the warehouse will help you protect your rights and keep records correctly. Correctly executed documentary support will protect against problems with the received goods and facilitate communication with the tax authorities.
Documents for registration of goods receipt
The posting of goods includes the reception and initial accounting of receipts. The goods can be accepted by a financially responsible person or a person by proxy. The receipt of goods is accompanied by the execution of primary documents by the supplier. These include:
- packing list;
- waybill (Bill of Lading) – it is needed to take into account the movements of goods and materials and pay for road transport;
- invoice.
An invoice is issued if the supplier pays VAT. An invoice allows you to offset VAT on the goods received for reimbursement. Organizations and entrepreneurs operating under the simplified taxation system do not pay value added tax and may not issue an invoice, and if the document is issued by the supplier on OSNO, they may not accept input VAT for reimbursement.
Before accepting the goods, check the correctness of the invoice: it must contain the details of the buyer and supplier, name of the product, quantity, price, cost, VAT.
To post the goods after acceptance, the invoice is stamped and signed by the responsible persons. The invoice is drawn up in two copies: one remains with the buyer, and the other is given to the seller. For the buyer, the invoice is a receipt document, and for the seller it is an expense document.
Universal transfer document (UDD)
This document is both a waybill and an invoice. Legislatively introduced in 2013 and not mandatory for use. You can decide for yourself whether you want to draw up two documents or just the UPD. Like an invoice, UTD provides the basis for obtaining a tax deduction.
The use of a universal document simplifies the process of transfer and acceptance of inventory items. Use it to formalize the supply of goods, works or services and the transfer of property rights. The UPD is signed by the authorized person responsible for the preparation of primary documents or purchase and sale transactions.
In the legally established form of the UPD there is a status field. It determines which document you are submitting the UPD instead of:
- Invoice and delivery note;
- Packing list;
- Invoice (for electronic form).
The status of the document changes the order in which it is filled out: for status 2, you do not need to fill out some lines, the UPD number and the required signatures change. To use the UPD in an organization, its form must be approved. The official form is advisory in nature, and the organization may make changes to it. But all mandatory details of the primary documents must comply with the requirements.
Acceptance of goods
At the first stage of acceptance of goods, we check whether the type and quantity of goods corresponds to the information in the accompanying documents. This is necessary to ensure completeness of accounting. The second stage is acceptance of the goods for quality and completeness.
Acceptance of goods is carried out by the financially responsible person in the presence of a representative of the supplier, unless other conditions are specified in the contract.
If all the goods are in place and no defects are found, confirm compliance with the organization’s stamp and signature.
Based on the results of acceptance of the goods, a TORG-1 act and a TORG-11 product label are drawn up. Product label data is needed to conduct an inventory list.
Violation of the inspection deadlines and acceptance rules will deprive you of the right to file a claim against the supplier or carrier. For certain types of goods, the terms are established by law, for others they are specified in the contract. Registration of the return of low-quality goods depends on the moment of detection of the defect:
- if a shortage of goods or defects is detected during acceptance, the commission draws up a report on the discrepancy in quantity and quality; the act is drawn up in the TORG-2 form; if properly executed, it will serve as the basis for making claims;
- when a defect is discovered after the goods are registered, an invoice is drawn up indicating the quantity of the goods being returned, a statement of identified defects, a letter of claim and a return invoice;
- if one of the types of goods was not delivered to you, cross them out from the invoice and adjust the invoice.
At the end of acceptance, capitalize the received goods and materials according to the actual quantity and amount.
What to do if there are no accompanying documents
For accounting, the main thing is documents. If there is no document, there is no accounting object. When a supply agreement is available, but the supplier has not provided accompanying documents, the goods received must also be capitalized.
For such cases, a TORG-4 acceptance certificate is provided. In the absence of a delivery note and an invoice, it is difficult to determine the price at which the goods arrive. The price must be taken from the contract, and if there is no contract, then the goods are purchased at the market price. The TORG-4 act contains information about the actual availability of the received goods.
The acceptance certificate is drawn up by a special commission that accepts the goods. TORG-4 is drawn up in two copies, one is transferred to the financially responsible person of the supplier, and the other to the accounting department.
Receipt of goods - postings
In accounting, the recording of the acquisition of goods varies and depends on the method of transfer of ownership.
Payment deferment. Ownership passes when the goods are transferred to the buyer. Include the costs of delivery and procurement costs in the actual cost of goods received.
Debit Credit
| Goods received (without VAT) | 41 | 60 |
| VAT charged | 19 | 60 |
| Shipping costs | 41 | 60 |
| VAT charged on delivery | 19 | 60 |
| VAT is accepted for deduction | 68 | 19 |
| Debt repaid | 60 | 50(51) |
Prepayment. The contract states that ownership of the goods passes after payment.
Debit Credit
| Payment transferred to the supplier | 60 | 50 (51) |
| Goods received (without VAT) | 41 | 60 |
| VAT charged | 19 | 60 |
| VAT deductible | 68 | 19 |
As part of the receipt of goods, it is worth noting situations related to the return of goods to the supplier. Depending on whether the goods were accepted for accounting and whether they were paid for, the postings change.
- If a defect is discovered during acceptance of the goods, the goods have not yet been accepted for accounting and have not been paid for, in this case the goods are recorded on off-balance sheet account 002. Return of goods to the supplier should be reflected on the credit of this account.
- If a defect is discovered after registration and payment, record the return of goods to the supplier and write off VAT if it has not yet been deducted. If VAT has already been refunded, then restore it.
Debit Credit
| The defect was returned to the supplier | 76 | 41 |
| VAT restored | 76 | 68 |
| or VAT written off | 76 | 19 |
| Money returned for goods of poor quality | 51 | 76 |
Elizaveta Kobrina
Keeping records of goods receipts will become easier using automated programs. The cloud service Kontur.Accounting allows you to store all information about goods in one place and simplifies the procedure for posting goods. Enter invoices, invoices, and bill payment information. Keep records of receipts and disposals of inventory items.
To count money in business, a bank account statement and the feeling that everything is going according to plan are not enough. This requires financial or management accounting. We'll tell you how and with what tools to do it.
, Elena Kosmakova
Business requires regular choices - from simple and routine to strategic. We will talk about methods for making management decisions and practical tools that help a manager.
, Elena Kosmakova
From 2021, the UTII regime will cease to apply. Officials periodically propose extending the imputation, but the Ministry of Finance and the Federal Tax Service firmly insist on its abolition.
This means that companies and entrepreneurs on UTII must choose a new tax system (SNO) by the end of 2021 and prepare to work in the new conditions.
Our review contains step-by-step instructions for changing the mode and a calculator for choosing a new aid to navigation.
, Elena Kosmakova
Source: https://www.B-Kontur.ru/enquiry/427-dokumenty-dlya-oprihodovaniya-tovara
How to register the purchase of goods through an accountable person
Within three days from the end of the period for which the advance was issued, the employee is required to report on the money spent. To do this, he must submit an advance report to the accounting department using the unified form No. AO-1 or a form developed by the organization independently. The main thing is that the document contains all the necessary details. Whatever form you use, it is first approved by the manager with an order to the accounting policy.*
To receive cash against the report, the employee must write an application in any form. Indicate in it the required amount, as well as for what purposes it will be spent. The head of the organization must make an inscription on the application stating what amount and for what period must be issued according to this application.*