VAT deduction from the seller upon receipt of an advance payment
In accordance with the terms of the concluded agreement, the buyer can make a full or partial advance payment for goods (work, services), property rights.
According to subparagraph 2 of paragraph 1 of Article 167 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, on the day of receipt of payment, partial payment for upcoming deliveries of goods (performance of work, provision of services), transfer of property rights, the moment of determining the tax base for VAT arises, and the tax base is determined based on the amount of payment received from taking into account tax (clause 1 of article 154 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Upon receipt of payment amounts, partial payment for upcoming deliveries of goods (performance of work, provision of services), transfer of property rights realized on the territory of the Russian Federation, the taxpayer is obliged to present to the buyer of these goods (work, services), property rights the amount of VAT calculated in the manner established by paragraph 4 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (clause 1 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Therefore, the seller must issue an invoice to the buyer for the amount of the prepayment received no later than 5 calendar days (clause 3 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The invoice is filled out in accordance with Appendix No. 1 to the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of December 26, 2011 No. 1137 “On the forms and rules for filling out (maintaining) documents used in calculations of value added tax.”
Invoices for the received amount of payment, partial payment for upcoming deliveries of goods (performance of work, provision of services), transfer of property rights are registered by the taxpayer in the sales book (clause 2 of the Rules for maintaining the sales book, approved by Resolution No. 1137).
The seller can accept VAT calculated from the prepayment amount as a tax deduction from the date of shipment of the relevant goods (work, services, property rights) (clause 8 of Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In this case, VAT amounts are deducted in the amount of tax calculated from the cost of goods shipped (work performed, services rendered), transferred property rights, in payment of which the amount of previously received advance payment is subject to offset according to the terms of the contract (if such conditions exist) (clause 6 of Art. 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The date of shipment (transfer) of goods for value added tax purposes is the date of the first drawing up of the primary document issued to their buyer or carrier for delivery of goods to the buyer, regardless of the moment of transfer of ownership established by the contract (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 14, 2019 No. 03 -07-11/16880, dated 08/28/2017 No. 03-07-11/55118).
Consequently, the right to a tax deduction arises from the seller after shipment of the goods, even if at the time of shipment the ownership of the goods, according to the terms of the concluded agreement, does not pass to the buyer.
To claim a tax deduction, the invoice issued upon receipt of an advance payment is registered by the seller in the purchase book for the amount of VAT to be deducted (clause 2 of the Rules for maintaining the purchase book, approved by Resolution No. 1137).
| 1C:ITS In the “Legislative Consultations” section you can find useful articles from 1C experts: on calculating VAT when receiving an advance; on drawing up an invoice for an advance payment; on the deduction of VAT on advances. |
VAT: Advance payment (partial payment)
Home — Articles
The composition of the invoice indicators issued upon receipt of advance payment (partial payment) is provided for in clause 5.1 of Art. 169 Tax Code of the Russian Federation . However, a special form of invoices issued for advance payment (partial payment) has not been approved. Therefore, when issuing goods, sellers of goods (works, services, property rights) use the invoice form approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation N 914, reflecting in it the indicators provided for by the above norm .
In accordance with paragraphs. 4 clause 5.1 art. 169 in the invoice issued upon receipt of payment (partial payment) for upcoming deliveries of goods (performance of work, provision of services, transfer of property rights), the name of the goods supplied (description of work, services), property rights must be indicated.
When filling out this invoice indicator, you should be guided by the name of the goods, property rights specified in the contracts concluded between the seller and the buyer.
For example, in the case of receiving advance payment (partial payment) under contracts for the supply of goods, which provide for their shipment in accordance with the application (specification) issued after payment, these contracts, as a rule, indicate the general name of the goods supplied (for example, petroleum products, confectionery , bakery products, stationery, etc.). Therefore, when issuing an invoice upon receipt of advance payment (partial payment) under such contracts, the generic name of the goods (or their groups) should be indicated.
If contracts are concluded that provide for the performance of work simultaneously with the delivery of goods, both the name of the goods supplied and a description of the work performed are indicated in the corresponding column of the invoice.
When receiving preliminary (partial) payment under contracts for the supply of goods, taxation of which is carried out at rates of both 10 and 18%, the invoice should either indicate the general name of the goods indicating the rate of 18/118, or allocate the goods into separate positions based on information contained in contracts, indicating the corresponding tax rates.
When issuing an invoice for preliminary (partial) payment received under contracts providing for different delivery times for goods, the amount of this payment should not be allocated to separate items.
According to paragraph 3 of Art. 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, upon receipt of payment amounts (partial payment) on account of upcoming deliveries of goods sold on the territory of the Russian Federation, the corresponding invoices are issued no later than five calendar days, counting from the day of receipt of the specified amounts.
If within five calendar days, counting from the date of receipt of the advance payment (partial payment), goods are shipped against this payment (partial payment), invoices for such payment should not be issued to the buyer.
Upon receipt of payment (partial payment) for upcoming deliveries of goods by a commission agent (agent) who carries out the sale of goods on his own behalf within the framework of a commission (agency) agreement, an invoice for this payment is issued to the buyer by the commission agent (agent), and the principal (principal) issues to the commission agent (agent) an invoice, which reflects the indicators of the invoice issued by the commission agent (agent) to the buyer. At the same time, the commission agent (agent) does not register invoices for payment (partial payment) for future deliveries of goods issued by him to the buyer in the sales book.
When making payment (partial payment) for upcoming deliveries of goods (performance of work, provision of services, transfer of property rights) in non-monetary form, corresponding invoices are also issued.
Under contracts for the supply of goods (provision of services), which provide for features associated with continuous long-term supplies of goods (provision of services) to the same buyer (for example, supply of electricity, oil, gas, provision of communication services), draw up invoices for payment (partial payment) received on account of such deliveries of goods (provision of services), and bill them to customers, in our opinion, at least once a month no later than the 5th day of the month following the end. In this case, the preparation of invoices should be carried out by suppliers in the tax period, when the amount of preliminary (partial) payment is received. This procedure is possible since the Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not define the concept of payment (partial payment), therefore, in this case, preliminary (partial) payment can be considered the difference formed at the end of the month between the received amounts of payment (partial payment) and the cost of goods shipped in a given month (delivered services).
In such invoices, according to the Russian Ministry of Finance, the amount of advance payment received in the corresponding month should be indicated, for which goods (services) were not shipped that month (Letter dated 03/06/2009 N 03-07-15/39). Upon receipt of payment (partial payment) for upcoming deliveries of goods (performance of work, provision of services) subject to taxation at a zero rate, as well as those not subject to this tax, invoices are not issued.
The above Letter also contains another conclusion: in the case of VAT administration in terms of the restoration of tax previously accepted for deduction when transferring payment (partial payment) on account of upcoming supplies of goods, the tax authorities, in the opinion of the Ministry of Finance, should carry out tax control measures similar to those carried out under verification of tax amounts subject to restoration when using previously acquired goods (work, services, property rights) to carry out transactions subject to taxation at a zero rate, as well as transactions not subject to this tax.
According to paragraph 12 of Art. 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, for a taxpayer who has transferred payment amounts (partial payment) on account of upcoming deliveries of goods, the tax amounts presented by the seller of these goods upon receipt of such payment amounts (partial payment) are subject to deductions. Clause 9 of Art. 172 of the Code establishes that these deductions are made on the basis of invoices issued by sellers upon receipt of advance payment (partial payment), documents confirming the actual transfer of these amounts, and in the presence of an agreement providing for their transfer.
If the contract for the supply of goods (performance of work, provision of services, transfer of property rights) provides for the transfer of preliminary (partial) payment without specifying a specific amount, VAT should be deducted, calculated based on the amount of the transferred preliminary (partial) payment specified in invoice issued by the seller. If the agreement does not provide for a provision for preliminary (partial) payment or there is no corresponding agreement, and the advance payment is transferred on the basis of an invoice, the tax on the transferred preliminary (partial) payment is not deductible.
When making preliminary (partial) payment in cash or in non-cash form, tax is not deducted, since in these cases the buyer of goods (work, services, property rights) does not have a payment order.
According to paragraph 1 of Art. 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, when calculating the amount of VAT payable to the budget, the taxpayer has the right to reduce the total amount of tax calculated for transactions recognized as the object of taxation by the corresponding tax deductions. Consequently, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides for the right of the taxpayer to deduct VAT on the listed amounts of advance payment (partial payment), and not the obligation to accept the tax for deduction. Thus, if a taxpayer uses his right to deduct tax on goods (work, services) received, and not on prepayment (partial payment) for these goods, this, according to experts from the Russian Ministry of Finance, does not lead to an understatement of the tax base and the amount of tax payable to the budget.
Difficulties that may arise for tax authorities when checking the correctness of application of these deductions do not constitute grounds for the impossibility of implementing the introduced system in practice, and even more so for refusal, as indicated in the Letter, to exercise tax control. Federal Law No. 224-FZ dated November 26, 2008 was adopted as part of the implementation of anti-crisis measures, and the procedure it introduced for deducting VAT paid as part of payment (partial payment) for upcoming supplies of goods is aimed at reducing the tax burden on the relevant taxpayers and should not lead to an increase in the burden (both tax and administrative) on VAT payers selling goods (works, services). In accordance with Art. 35 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, tax and customs authorities are responsible for losses caused to taxpayers, fee payers and tax agents as a result of their unlawful actions (decisions) or inaction, as well as unlawful actions (decisions) or inaction of officials and other employees of these bodies in the performance of their official duties. responsibilities.
VAT
Fulfillment by a simplified person of the duty of a tax agent for VAT
Taxation of returned goods
VAT on the sale of real estate
VAT refund from the budget
How to fill out a VAT return for a tax agent
Deduction of VAT from advance payment upon shipment without transfer of ownership in “1C: Accounting 8”
Let's consider an example of how the seller reflects the deduction of VAT from an advance payment when shipping goods to the buyer without transferring ownership of the specified goods in the 1C: Accounting 8 version 3.0 program.
Example
| The organization Trading House LLC (seller), in accordance with the concluded supply agreement with Clothes and Shoes LLC (buyer), ships goods for a total amount of RUB 360,000.00. (including VAT 20% - RUB 60,000.00) on condition of advance payment of 25%. According to the contract, ownership of the goods passes to the buyer after full payment for the goods. The sequence of operations is given in the table. Table |
Receiving partial advance payment
The operation of receiving partial payment on account of the upcoming delivery of goods (operation 1.1 “Receiving advance payment from the buyer”) in the 1C: Accounting 8 program, edition 3.0 is registered using the document Receipt to the current account with the transaction type Payment from the buyer, which is generated:
- based on the document Invoice for payment to the buyer (section Sales - subsection Sales - journal of documents Invoices to buyers);
- or by adding a new document to the Bank Statements list (section Bank and cash desk - subsection Bank - document journal Bank Statements).
As a result of posting the document, the following accounting entry is entered into the accounting register:
Debit 51 Credit 62.02 - for the amount of the received advance payment, which is 90,000.00 rubles.
In accordance with paragraphs 1, 3 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the buyer of goods who has transferred the prepayment amount must be issued an invoice no later than 5 calendar days, counting from the date of receipt of the prepayment.
An invoice for the received prepayment amount (operations 1.2 “Issuing an invoice for the amount of prepayment”; 1.3 “Calculation of VAT on the received prepayment”) in the program is generated on the basis of the document Receipt to the current account using the Create based button. Automatic generation of invoices for advances received from customers can also be done using the processing Registration of invoices for advance payments (section Banks and cash desk - subsection Registration of invoices).
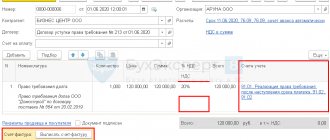
In the new document Invoice issued (Fig. 1), the basic information will be filled in automatically according to the base document:
- in the from field - the date of preparation of the invoice, which by default is set to the same date as the date of generation of the document Receipt to the current account;
- in the Counterparty, Payment document No. and from fields - the relevant information from the basis document;
- in the Invoice type field – the value For advance;
- in the tabular part of the document - the amount of the received prepayment in the amount of 90,000.00 rubles, the VAT rate in the amount of 20/120 and the amount of VAT in the amount of 15,000.00 rubles. (RUB 90,000.00 x 20/120).
Rice. 1. Invoice issued for advance payment
In addition, the following will be automatically entered:
- in the Transaction type code field - value 02, which corresponds to payment, partial payment (received or transferred) on account of upcoming deliveries of goods (work, services), property rights (Appendix to the order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated March 14, 2016 No. ММВ-7-3/ [email protected] );
- the Compiled switch is moved to the position On paper, if there is no valid agreement on the exchange of electronic invoices, or In electronic form, if such an agreement has been concluded;
- flag Issued (transferred to the counterparty) indicating the date - if the invoice is transferred to the buyer and is subject to registration. If there is an agreement on the exchange of electronic invoices, until confirmation of the electronic document management (EDF) operator is received, the flag and date of issue will be absent. If the date of transfer of a paper invoice to the buyer is different from the date of preparation, then it must be adjusted;
- The Manager and Chief Accountant fields are data from the Responsible Persons information register. If the document is signed by other responsible persons, for example, on the basis of a power of attorney, then it is necessary to enter the relevant information from the directory Individuals.
For the correct preparation of an invoice, as well as the correct reflection of the document in the accounting system, it is necessary that in the Nomenclature field of the tabular part of the document the name (or generic name) of the goods supplied is indicated in accordance with the terms of the contract with the buyer.
This information is filled in automatically indicating:
- names of specific product items from the document Invoice to the buyer, if such an invoice was previously issued;
- a generic name, if such a generic name was defined in the agreement with the buyer.
By clicking the Print document Invoice issued (Fig. 1) button, you can go to view the invoice form and then print it in two copies.
According to the Rules for filling out an invoice, approved. By Decree No. 1137, the invoice for the prepayment amount received indicates:
- in line 5 - details (number and date of preparation) of the payment and settlement document (clause "h" clause 1 of the Filling Rules);
- in column 1 - the name of the goods supplied (description of work, services), property rights (clause “a”, clause 2 of the Filling Rules);
- in column 8 - the amount of tax calculated on the basis of the tax rate determined in accordance with paragraph 4 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (clause “z” of paragraph 2 of the Filling Rules);
- in column 9 - the amount of advance payment received (clauses “and” clause 2 of the Filling Rules);
- in lines 3 and 4 and columns 2-6, 10-11 - dashes (clause 4 of the Filling Rules).
As a result of posting the document Invoice issued, an accounting entry is generated:
Debit 76.AB Credit 68.02 - for the amount of VAT calculated on the amount of advance payment received from the buyer in the amount of RUB 15,000.00. (RUB 90,000.00 x 20/120).
Based on the issued Invoice document, an entry is made in the information register of the Invoice Log.
Despite the fact that since 01/01/2015, taxpayers who are not intermediaries (forwarders, developers) do not keep a log of received and issued invoices, register entries in the Invoice Log are used to store the necessary information about the issued invoice.
Based on the document Invoice issued, registration entries are made in the Sales VAT accumulation register to form a sales book for the tax period of receiving advance payment, i.e. for the third quarter of 2021.
Shipment of goods without transfer of ownership
To enable the mechanism for calculating VAT on shipment transactions without transfer of ownership, you must set the flag for the value Accrue VAT on shipment without transfer of ownership on the VAT tab of the Taxes and Reports Settings form (Main section - subsection Settings - Taxes and Reports).
To perform operations 2.1 “Reflection of the shipment of goods without transfer of ownership”; 2.2 “Calculation of VAT on shipment without transfer of ownership”, a Sales document (act, invoice) is created with the transaction type Shipment without transfer of ownership (section Sales - subsection Sales), fig. 2. After posting the document, the following accounting entries are entered into the accounting register:
Debit 45.01 Credit 41.01 - for the cost of goods shipped;
Debit 76.OT Credit 68.02 - for the amount of VAT accrued upon shipment of goods, which is RUB 60,000.00. (300,000.00 x 20%).
Rice. 2. Shipment of goods
A registration entry is made in the Sales VAT accumulation register to create a sales book for the tax period of shipment of goods, i.e. for the third quarter of 2021.
To issue an invoice for shipped goods (operation 2.3 “Issuing an invoice for shipped goods”), you must click on the Issue an invoice button at the bottom of the document Sales (act, invoice) with the transaction type Shipment without transfer of ownership (Fig. 2) . In this case, the document Invoice issued is automatically created, and a hyperlink to the created invoice appears in the form of the basis document.
In the new posted document Invoice issued (Fig. 3), which can be opened via a hyperlink, all fields will be filled in automatically based on the data in the document Shipment without transfer of ownership.
Rice. 3. Shipping invoice
Besides:
- in the line Basis documents there will be a hyperlink to the corresponding implementation document (deliveries);
- in the Operation type code field the value 01 will be reflected, which corresponds to the shipment (transfer) of goods (work, services), property rights (Appendix to the order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated March 14, 2016 No. ММВ-7-3 / [email protected] );
- The Receipt Method switch will be set to Hard copy if there is no valid agreement with the seller to exchange invoices electronically. If there is an agreement, then the switch will be in the Electronic position;
- in the line Issued (transferred to the counterparty), a flag will be placed and the date of registration of the Sales document (act, invoice) will be indicated, which, if necessary, should be replaced with the date of actual issuance of the invoice. If an agreement has been concluded with the buyer on the exchange of invoices in electronic form, then the date of sending the electronic invoice file to the EDF operator, indicated in its confirmation, will be entered in the field.
To fulfill the requirement of subparagraph “h” of paragraph 1 of the Filling Rules, you must click on the Add button to enter in the Payment documents field of the Invoice issued document the details of the payment and settlement document for the amount of the received partial advance payment.
As a result of posting the issued Invoice document, a registration entry is made in the Invoice Journal register to store the necessary information about the issued invoice.
An additional entry will also be created in the Sales VAT accumulation register to store information about the payment and settlement document.
Using the Print document Invoice issued button (Fig. 3), you can view and print the invoice.
Amounts of tax calculated by the taxpayer from amounts of payment, partial payment received on account of future deliveries of goods (work, services) are subject to tax deduction from the date of shipment of the relevant goods (performance of work, provision of services), transfer of property rights in the amount of tax calculated from the cost shipped goods (work performed, services provided), transferred property rights, in payment for which the amount of previously received payment, partial payment in accordance with the terms of the contract (if such conditions exist) are subject to offset (clause 8 of Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 6 of Art. 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
To reflect operation 2.4 “Acceptance for deduction of VAT from advance payment”, you need to create the document Generating purchase ledger entries (section Operations - subsection Closing the period - hyperlink Regular VAT operations), fig. 4.
Rice. 4. Generating purchase ledger entries
The document is automatically filled in by clicking the Fill button. The Advance payments received tab automatically displays information about received advance payment amounts and VAT amounts previously calculated from the received advance payment amounts and offset against the shipment of the corresponding goods.
Since when goods are shipped without transfer of title, advance payment is not offset, the bookmark is not automatically filled in. Therefore, by clicking the Add button, it is necessary to enter into the tabular part of the document information about the amounts of advance payment received on account of the shipment of goods, which will be offset against payment for the shipped goods after they are sold to the buyer.
As a result of posting the document Formation of purchase ledger entries, an entry is made in the accounting register:
Debit 68.02 Credit 76.AB - for the amount of VAT calculated upon receipt of an advance payment and claimed for deduction after shipment of the relevant goods.
To register the document Invoice issued in the purchase book, an entry is made in the Purchase VAT accumulation register.
Thus, registration entries will be entered into the sales book for the third quarter of 2021 (approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 2011 No. 1137, as amended by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated January 19, 2019 No. 15) (section Reports - VAT subsection) (Fig. 5):
- according to invoice No. 22 dated September 20, 2019 - for the amount of VAT calculated on the advance payment received in the amount of RUB 15,000.00. with KVO 02;
- according to invoice No. 23 dated September 26, 2019 - for the amount of VAT accrued upon shipment of goods in the amount of RUB 60,000.00. with KVO 01.
Rice. 5. Sales book for the third quarter of 2021
A registration entry will be made in the purchase book for the third quarter of 2021 (approved by Resolution No. 1137, as amended by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated January 19, 2019 No. 15) (section Reports - VAT subsection): (Fig. 6):
- according to invoice No. 22 dated September 20, 2019 - for the amount of VAT calculated on the advance payment received and subject to tax deduction in the amount of RUB 15,000.00, with QUO 22.
Rice. 6. Purchase book for the third quarter of 2021
Section 3 of the VAT tax return for the third quarter of 2021 will reflect (section Reports - subsection 1C-Reporting - hyperlink Regulated reports):
- on line 010 - tax base in the amount of 300,000 rubles. (column 3) and the amount of VAT accrued upon shipment of goods in the amount of 60,000 rubles. (column 5);
- on line 070 - tax base in the amount of 90,000 rubles. (column 3) and the amount of VAT calculated upon receipt of partial advance payment in the amount of 15,000 rubles. (column 5);
- on line 170 - the amount of VAT calculated upon receipt of the advance payment and claimed for tax deduction from the date of shipment of the relevant goods, in the amount of 15,000 rubles. (column 3).
Receiving payment
The transaction of receipt of payment (operation 3.1 “Receiving payment from the buyer”) is reflected in the program using the document Receipt to the current account with the transaction type Payment from the buyer, which is generated:
- based on the document Invoice for payment to the buyer (section Sales - subsection Sales - journal of documents Invoices to buyers);
- or by adding a new document to the Bank Statements list (section Bank and cash desk - subsection Bank - document journal Bank Statements).
As a result of posting the document, the following accounting entry is entered into the accounting register:
Debit 51 Credit 62.02 - for the amount of payment received, which is RUB 270,000.00.
Please note that the amount of payment received by the seller after the goods have been shipped, but before they are sold, is actually an advance payment. At the same time, according to paragraph 1 of Article 167 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, upon receipt of such advance payment, the seller does not have the moment of determining the tax base, since the earliest date in this case is the day of shipment of the goods (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated January 24, 2019 No. 03-07-11 /3850). Consequently, the seller should not issue an invoice for the amount of the received advance payment and calculate the amount of VAT from this advance payment. When automatically generating invoices for advances received from customers using the processing Registration of invoices for advance payments (section Banks and cash desk - subsection Registration of invoices) after executing the Fill command before executing the Execute command Execute a line from the tabular section indicating this amount prepayments must be removed.
VAS, penalties and VAT: how to understand the new judicial practice?
Colleagues,
While studying the latest judicial practice of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation, I came across an interesting ruling. We are talking about the resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation No. 5328/12. In this case, the Presidium decided that the penalty should be calculated based on the price excluding VAT.
Previously, as many people know, the Supreme Arbitration Court, in the well-known Resolution of the Presidium No. 5451/09, made an absolutely correct decision that penalties are charged on the entire amount of the debt, including VAT. At the same time, in that decision, YOU motivated this approach by the fact that
a) the VAT allocated in the price is not a tax, but is part of the price (the tax is a payment to the budget as the difference between incoming and outgoing “VAT” at the end of the tax period) and, accordingly, the argument about the impossibility of charging a penalty for tax does not work,
b) organizations pay VAT on shipment, that is, the creditor reflects incoming VAT at the time when he shipped the goods and issued an invoice, and not when the money actually arrived, and accordingly pays VAT to the budget from his own funds, and delays in payment of the debt result in to the fact that he cannot cover this expense in a timely manner (which means that he has a civil interest in the prompt repayment of the entire debt, including VAT).
But in the new resolution No. 5382/12 the opposite decision was made. At the same time, the lower courts referred to the previous precedent, but the Supreme Court rejected this argument, citing two arguments:
1) In this case, it was not the monetary obligation that was violated (as in the plot of case No. 5451.09), but the transportation obligation. Accordingly, here YOU did not see it possible to apply your old precedent
2) Due to the special regulation of relations regarding railway transportation, the payment for transportation, to which the agreement linked the accrual of penalties, is expressed in the form of a tariff, which does not include VAT. Accordingly, here VAT is not part of the price and is, as it were, added to it.
As a result, my heart is full of doubts :) What should lawyers now say at lectures? How to understand this legal position?
It is obvious that YOU distinguished the plot of the new case from the plot of the old one, that is, created an exception to the old rule, tailored to the specific circumstances of this new case. He apparently did not overrule his old precedent and left it in force in relation to the situation of delay in ordinary monetary debts for goods supplied (services provided, work performed), but limited its application in relation to the situation described in this new case. But he did this in an extremely vague manner, highlighting two circumstances to justify this distinction: 1) “the debt is not monetary” and 2) “the specifics of tariff regulation.”
The question that now arises is: are these two circumstances now included in the hypothesis of this exception as necessary elements, or is one of them necessary, and the other, so to speak, “in passing.”
Let me clarify the question:
1) If we assume tomorrow in a new case there will be no tariff argument due to the fact that simply the customer or buyer of the goods will charge penalties for delays in the performance of work, provision of services or delivery, will this be sufficient to apply this new precedent? In other words, if there is only the “non-monetary debt” argument, but the “tariff regulation” argument does not apply, then should VAT also be excluded?
2) If, on the contrary, tomorrow Russian Railways collects a tariff from the shipper (that is, there will be a “tariffs” argument, but there will be no “non-monetary debt” argument), then will this new rule be applicable or will “ration” No. 5451/09 still apply?
3) Or do these two circumstances have to coincide in one case for the court to apply a new precedent?
I have been saying for a long time that YOU should begin to more accurately express those specific circumstances of the case (that is, essentially the elements of the hypothesis of the new rule being created) that form the basis for the decision or the formation of the “difference.”
And finally, the last thing: I’m certainly not a big tax expert, but I don’t really understand the tax aspect of this decision. After all, if the customer paid an advance payment (in this case it is not entirely clear from the decision whether the plaintiff paid the tariff, but let’s assume that he did), but does not receive the service (work, goods) on time, this means that he does not receive the invoice on time -invoice, which means it cannot submit “outgoing” VAT for deduction within the planned period. This means that a delay in the delivery of goods (provision of services, performance of work) forces the buyer (customer) to lose part of their funds due to the delay due to the inability to reduce the accumulated “input” VAT by the corresponding amount of this “output” VAT. This means that the buyer has a civil, compensatory interest in receiving the entire price on time, including VAT. Maybe, of course, I’m not taking something into account in the field of tax law, but nevertheless….