Finished products in the balance sheet
However, these reporting forms are list-based, i.e.
contain information about all employees. This means transferring a copy of such a report to one employee means disclosing the personal data of other employees. {amp}lt; {amp}amp;#8230; Old “profitable” errors can sometimes be corrected in the current period. If an organization discovers that in one of the previous reporting (tax) periods an error was made when calculating income tax, it can be corrected in the current period only if two conditions are met. {amp}lt; {amp}amp;#8230; Attention
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7F4AOdR9oVA
Depending on the type of activity and the specifics of the organization’s work, the entries to reflect the receipt of revenue and write-off of expenses may differ. But the reflection of profit or loss from sales will be the same regardless of what activity the company conducts.
To properly understand how profit from sales is formed, it is best to analyze which turnovers fall into the 90th account:
- Revenue is reflected by posting Dt 62 Kt 90.1. But in retail trade, the wiring will look like Dt 50 Kt 90.1 or Dt 57 Kt 90.1.
- The cost of services and work is written off with such entries as Dt 90.2 Kt 20 (23, 26, 25, etc.).
In wholesale trade, the cost of goods will be written off by operation Dt 90.2 Kt 41, and sales expenses - Dt 90.2 Kt 44. In retail, you additionally need to take into account the markup Dt 90.2 Kt 42.
So, for such persons you need to take both SZV-M and SZV-STAZH! {amp}lt; {amp}amp;#8230; When paying for “children’s” sick leave, you will have to be more careful. A certificate of incapacity for caring for a sick child under 7 years of age will be issued for the entire period of illness without any time limits.
But be careful: the procedure for paying for “children’s” sick leave remains the same! {amp}lt; {amp}amp;#8230; Online cash register: who can take the time to buy a cash register Individual business representatives may not use online cash register until 07/01/2019.
However, for the application of this deferment there are a number of conditions (tax regime, type of activity, presence/absence of employees). So who has the right to work without a cash register until the middle of next year? {amp}lt; {amp}amp;#8230;
InfoOverhead expenses in the form of salaries, rent, taxes amounted to another 30 thousand rubles. We count:
- VP = OP {amp}amp;#8212; S/S = 200 {amp}amp;#8212; 90 = 110 thousand rubles.
- CP = VP {amp}amp;#8212; Expenses = 110 {amp}amp;#8212; 30 = 90 thousand
- OP = (Fixed costs Profit) : (Price per unit – Variable costs per unit).
To determine your target sales volume, use the following formula:
- OP = (Fixed costs Earnings before interest) : Marginal profit.
- MP = Price {amp}amp;#8212; Variable costs per unit.
As mentioned earlier, in order to determine the efficiency of the enterprise, it is more appropriate to calculate the net sales volume in the balance sheet.
You can, for example, determine sales volume. There is no balance formula as such. Since this data is reflected in the “Profit and Loss Statement”. Line 2110 indicates the amount of products sold in monetary terms after deducting VAT. All costs for the production and delivery of products are also reflected here: page 2120 page 2210 page 2220.
The organization may have other unforeseen expenses (p. 2350) and income (p. 2340). This way you can calculate net profit or net sales in the balance sheet: Line 2400 = 2110 – (2120 2210 2220) 2340 – 2350 – 2410, where 2410 is the amount of income tax.
Net sales on the balance sheet can be calculated by subtracting retained earnings (uncovered loss) at the end of the period from the value at the beginning of the period. A positive difference indicates a net profit, and a negative difference indicates losses.
General business expenses include:
- administrative and management expenses;
- maintenance of general business personnel not related to the production process;
- depreciation charges and expenses for repairs of fixed assets for management and general economic purposes;
- rent for general business premises;
- expenses for payment of information, audit, consulting and other similar services;
- other administrative expenses similar in purpose.
Organization {amp}amp;#8212; a professional participant in the securities market under article {amp}amp;#171;Administrative expenses{amp}amp;#187; reflects the amount of costs of its activities. The amount on line 040 is equal to the amount of costs written off in the reporting period from the credit of account 26 to the debit of account 90.2 {amp}amp;#171;Cost price{amp}amp;#187;.
- amounts received under commission agreements, agency agreements and other similar agreements in favor of the principal, principal, etc.;
- amounts of advances received as advance payment for products, goods, works, services;
- receipts as collateral, if the agreement provides for the transfer of the pledged property to the pledgee;
- amounts received to repay a loan provided to the borrower.
Income recognized in accounting as income from ordinary activities, if it is significant or without knowledge of which it is impossible for interested users to assess the financial results of the organization's activities, must be reflected separately in the form of a transcript to line 010 or in an appendix to the profit and loss statement (in if it is developed and adopted by the organization independently).
Every year, companies prepare financial statements. Using data from the balance sheet and profit and loss report, you can determine the effectiveness of the organization’s activities, as well as calculate the main planned indicators. Provided that management and the finance department understand the meaning of terms such as profit, revenue and sales on the balance sheet. Terminology Sales volume of products in the balance sheet {amp}amp;#8212; This is the amount of revenue received for the sale of goods in the reporting period.
In this case, the form of calculations does not matter. Products can be sold on credit, for cash, with deferred payment or at a discount. Therefore, for a more accurate calculation, the formula for calculating net sales in the balance sheet is used, when the revenue received is adjusted by the amount of goods shipped on credit.
Sales volume reflects the amount of funds received by the company. Therefore, it should be calculated by all organizations.
Having false information is worse than not having it. Therefore, it is important that financial statements are prepared correctly.
Unfortunately, even accountants make mistakes. The use of technical means allows you to avoid arithmetic errors, but not methodological ones. Also, reporting may be distorted due to the low skills of a specialist. Therefore, reporting is always done “with a reserve”. In the registers you can always find costs that will reduce the profitability indicator. For example, write off more inventory, non-current assets or bad debts. After all, it is always easier to lose profit than to increase it.
Gross output can be distinguished from marketable output by the amount of change in the balances of work in progress (the beginning and end of the planning period), which is the only evaluative indicator of the company's activity.
The volume of gross output includes:
- Finished products,
- Work in progress, which is products that have not yet been completed and are subject to further processing.
- Changing the balance of semi-finished products.
The corresponding composition of gross output depends on the sectoral affiliation of the enterprise (production). For example, at machine-building enterprises, most often the gross output does not include work in progress and semi-finished products due to their small volume. In such situations, gross and marketable products are the same in composition, but may differ in price.
The gross output formula can be calculated by summing the marketable output and the difference in the balances of work in progress (at the end and beginning of the reporting period).
VP = TP Nnp – Nkp
Here VP is gross output (in rubles);
TP – volume of commercial products (rub.);
Nnp and Nnp – the corresponding value of the balances of work in progress at the beginning and end of the period (rub.).
Accounting for changes in work in progress balances occurs at enterprises that are characterized by:
- long production cycle (from 2 months),
- large volume of work in progress, can change quickly over time.
The gross output formula can only be calculated in comparable prices. It is used in the process:
- Accounting and planning of production costs,
- Determining the needs for material resources,
- Calculation of the number of employees,
- Establishing the dynamics of products, including the proportions of development of industries.
It should be noted that assessing a company's performance in accordance with the gross output formula has several disadvantages.
The main drawback of the formula is that the value of gross output is influenced, in addition to the balances of work in progress, by the cost of the objects of labor consumed in the production process.
Unjustified excess of work in progress, decrease in product quality and changes in its assortment create only the appearance of successful work of the company.
In addition, the gross output indicator does not create an incentive for organizations to reduce the material intensity of products, so it is often excluded from the number of evaluative indicators of a company’s activities.
All indicators of production volume are determined in prices that include, together with the newly created value, the transferred cost of production assets (current and fixed assets). At the same time, the higher the material intensity of a product, the higher its price, therefore, the greater the production volume in value terms. In order to eliminate this deficiency, enterprises calculate the net production indicator.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FLkYKZ6Ubsg
Attention
You can, for example, determine sales volume. There is no balance formula as such. Since this data is reflected in the “Profit and Loss Statement”. Line 2110 indicates the amount of products sold in monetary terms after deducting VAT.
All costs for the production and delivery of products are also reflected here: page 2120 page 2210 page 2220.
Send by mail
Revenue from sales of products which line in the balance sheet
Moreover, this indicator will not provide an understanding of the amount of profit from sales over the entire history of the company. Line 1370 of the “Capital and Reserves” section reflects the balance of account 84.
This means that the indicator is equal to the amount of accumulated loss or profit received (not only from sales, but also taking into account non-operating income and expenses, taxes) minus expenses that were incurred at the expense of profit (this could be, for example, accrued dividends, formation of reserve capital and other expenses). To learn about the principles by which accounting statements are compiled, read the article “Accounting statements for LLCs - features and nuances.”
Financial results report for the analysis of economic activities It is the financial results report that will make it possible to analyze the structure of the enterprise's profit, its dynamics in comparison with previous reporting periods.
Attention
Attention
At what price should goods be shown on the balance sheet?
ANSWER: Clause 30 of the Instructions for filling out and submitting accounting reporting forms, approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Finance of the Republic of Belarus dated March 7, 2007 No. 41, stipulates that the balances of goods accounted for under account 41 “Goods” are shown on line 215 “finished products and goods for sale” " The order of reflection remained the same, i.e.
, as before (see paragraph 23 of the Instructions on the procedure for generating financial reporting indicators, approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Finance of the Republic of Belarus dated February 17, 2004 No. 16), the balance of goods is reflected in the balance sheet at the cost of their acquisition. When a retail trade organization accounts for goods in accordance with the established procedure at sales prices, the difference between the acquisition cost and the cost at sales prices (gross income (profit)) is reflected in the financial statements separately in the income statement.
When an organization purchases imported goods, the purchase price of incoming goods (materials, semi-finished products, equipment, etc.) is calculated based on their value stipulated in the contract (agreement), customs duties, transportation costs and other procurement and transportation expenses.
Thus, for goods accounted for at sales prices, the order of reflection in the balance sheet in 2007 did not change, and they are reflected at purchase prices.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=n1rkL-mJPys
07/31/2007
Galina Khimchenko, economist
For a more detailed study, see the manual
From the editor: Since March 7, 2008, Resolution of the Ministry of Finance of the Republic of Belarus dated 03/07/2007 No. 41 “On approval of financial reporting forms, Instructions for filling out and submitting financial reporting forms and declaring as invalid certain normative legal acts of the Ministry of Finance of the Republic of Belarus” based on the resolution Ministry of Finance of the Republic of Belarus dated February 14, 2008 No. 19 has become invalid.
Short:
- Purpose of the article: reflection of information about reserves.
- Line number in the balance sheet: 1210.
- Account number according to the chart of accounts: Debit balance - 10, 11, 15, 16, 20, 21, 23, 28, 29, 43, 41, 44, 45, 97, Credit balance - 14, 42.
Unsold products fall into line 1210 of the balance sheet as a debit balance.
Debit balance of 41 “Goods in warehouse” account - credit balance of 42 “Trade margin” account, debit balance of 44 “Sales expenses” account, debit balance of 45 “Goods shipped” account.
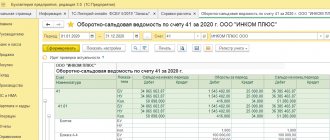
| Account, sub-account | Balance at the beginning of the period | Period transactions | balance at the end of period | ||
| Debit | Credit | Debit | Credit | Debit | Credit |
| 250 000,00 | 200 000,00 | 50 000,00 | |||
| 100 000,00 | 150 000,00 | 50 000,00 | |||
| 150 000,00 | 100 000,00 | 50 000,00 | |||
| 16 000,00 | 10 000,00 | 6 000,00 | |||
| Total expanded | 516 000,00 | 460 000,00 | 106 000,00 | 50 000,00 |
50 – 50 50 6 = 56 thousand.
These are costly bills. They are called so because on them the company collects all expenses that relate directly to the production process.
Author's note! Ideally, at the end of the year, all expenses should be closed, that is, reset to zero.
Finally, it is necessary to take into account the debit balance of account 97 “Deferred expenses”. These are expenses that the company spent on in the current month, but they will be deducted in the next time period. The list of expenses may include:
- certification and licensing;
- insurance;
- software products and subscription services;
- other deferred expenses.
For example, if an object is insured for a year, then the company buys an insurance policy at full cost. But the insurance will be written off monthly.
27,000 / 12 months = 2,250 rubles.
Typical wiring:
- Debit 76 accounts Credit 51 accounts – an insurance policy in the amount of 27,000 rubles was paid.
- Debit 97 account Credit 76 account – an insurance policy was received from an insurance company in the amount of 27,000 rubles.
- Debit 23 (20, 26) accounts Credit 97 accounts – 2,250 rubles written off as expenses for the month.
- 2,250 rubles * 4 months = 9,000 rubles.
- 27,000 – 9,000 = 18,000 rubles.
Accordingly, line 1210 of the balance sheet from deferred expenses will include the amount that has not been written off as of December 31, that is, 18,000 rubles.
Debit 10, 11 – Credit 14 Debit 15, 16 Debit 20, 21, 23, 28, 29 Debit 43 Debit 41 – Credit 42 Debit 44, 45 Debit 97.
Inventories on the balance sheet are a current asset that indicates the company’s financial security. The absence or sharp decrease in indicators in line 1210 of the current assets section, which collects all data on inventories, may indicate a scarcity of resources in the enterprise’s warehouses. On the other hand, there is an option that the process of turning an asset into money occurs so quickly that the company can barely keep up with its marketing service.
Since financial receipts to the company’s accounts depend on the rate of inventory turnover, it is necessary to maintain the proper level of resources by pursuing an effective marketing policy.
But regardless of how the release of finished products is reflected in accounting, finished products in the warehouse in the balance sheet are indicated on line 1210 “Inventories” (Order of the Ministry of Finance dated July 2, 2010 No. 66n). If the amount of finished products in the organization's total reserves is significant, the organization must reflect information about product output in a separate line in the balance sheet or indicate the relevant information in the notes to the balance sheet.
Of course, finished products are reflected in accounting on line 1210 only in terms of product warehouse balances. How are sold finished products reflected in the balance sheet?
Debit of account 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers” - Credit of account 90 “Sales”, subaccount “Revenue”
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3lV_5B_Jt10
Consequently, unpaid receivables from customers, which are equal to sales revenue, will be reflected in line 1230 “Accounts receivable” of the balance sheet. But here it is important to take into account that the revenue in line 1230 will be taken into account together with VAT, while the income statement indicates net revenue, i.e. reduced by the amount of VAT accrued on revenue.
For profit from sales of products, line 1370 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss)” is used in the balance sheet. In this case, in this line, profit from the sale of products will be taken into account in total with the financial results from other operations, both for ordinary activities and for other activities, as well as with the profit (loss) of previous years.
Product sales volume in the balance sheet: line
Revenue from sales of products is not reflected in the balance sheet, since it records the results, i.e., profit or loss as of the reporting date. The sold product is neither an asset nor final information. The revenue indicator is included in the financial performance statement (FIR) and plays a key role in calculating the financial result achieved by the company for a certain period.
However, there are options when revenue is recorded as an asset on the balance sheet. This happens if the sold products are not paid for by the purchaser in the reporting period. In this case, the cost of the consignment of goods goes into the category of accounts receivable and is indicated in line 1230, provided in the balance sheet for data on debts of debtors accounted for on account 62.
Revenue from the sale of inventory items is recorded by posting D/t 62 K/t 90/1. At the end of the reporting period, the amount from the debit of the 62nd account increases the amount of accounts receivable. Thus, the unpaid debt is reflected in the amount owed. When money is received from the buyer, posting D/t 51 K/t 62 will neutralize the debt, and the amount of proceeds will be reflected in the financial statement. It is important to remember that in balance sheet line 1230, unreceived revenue is taken into account together with VAT, while in the general financial report it is recorded without tax.
Proceeds from the sale of goods what line in the balance sheet
a. — in the balance sheet asset as part of non-current assets
b. – on the balance sheet as part of current assets
c. - in the liabilities side of the balance sheet as part of capital and reserves
d. - in the liability side of the balance sheet as part of long-term liabilities
e. - on the balance sheet liability side as part of short-term liabilities
a. - transfer of products from the seller to the buyer
b. — transfer of ownership of products from the seller to the buyer
c. - receipt of funds for products by the seller from the buyer
d. — shipment of products by the seller to the buyer’s address
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=16grd2ZbzEs
Transfer of ownership from seller to buyer
a. - at the time of shipment, unless otherwise provided by law
b. - only after payment of funds
c. - at the time of shipment, unless otherwise provided by law or contract
Attention
Attention
Inventories on the balance sheet consist of several categories:
- materials, raw materials;
- finished products;
- Future expenses;
- unfinished production;
- goods for sale.
The specifics of raw materials can be very diverse depending on what the enterprise does. For example, when making wine, the raw material can be grapes and all the accompanying ingredients needed in the preparation process.
Materials, in addition to raw materials, are divided into narrower subtypes:
- Purchased semi-finished products and components.
- Tara.
- Fuel.
- Spare parts.
- Materials outsourced for processing.
- Construction materials.
- Inventory and tools.
- Workwear.
- Other stocks.
Each category in the Chart of Accounts has its own subaccount. In accounting materials during the year:
- are bought;
- are written off;
- participate in the manufacture of the product of the technological process.
However, they are displayed at actual cost excluding VAT. This means that the cost of the material includes, in addition to the price in the invoice, associated costs for:
- transportation;
- workpiece;
- insurance;
- acquisition consultations;
- customs duties;
- bonuses to intermediaries.
But inventories can be written off in three different ways at the organization’s discretion. The most common method and easiest to use is writing off at actual cost.
Note from the author! If the organization does not have warehouse accounting, then at the end of the year materials should be written off as much as possible. The presence of inventories in accounting causes confusion among inspectors, since there is nowhere for the balances to be stored. Only overalls can be left.
Materials must reflect fixed assets worth less than 40,000 rubles. Of course, they will not be written off permanently, but at the end of the month they should be transferred to the balance sheet as low-value assets, so they should not be in Form No. 1.
Debit balance of 10, 11 accounts – credit balance of 14 accounts, debit balance of 15, 16 accounts.
Account 43 “Finished products” is used to accumulate manufactured but not sold products of the enterprise. It is formed as a result of the use of raw materials and materials, after processing of which the final product appears.
Debit 43 Credit 20 – products arrived at the warehouse.
Debit 43 Credit 40 – products in the warehouse are capitalized.
Once the products are in the warehouse, they need to be sold.
Reliability of information on finished products
Evaluation of finished products
In what accounts are finished products recorded?
Some features of accounting for finished products
Accounting for deviations in cost
Another nuance of reflecting the finished product
If the products are used for the needs of the enterprise, then account 43 is not used, and the products are reflected in account 10. In this case, the indicator is not used to form the overall balance on line 1210 of the balance sheet, but is entered in the line “Raw materials, supplies and other material assets”.
Account 45 is used when we are talking about shipped products. In other words, if payment for sold and shipped products has not yet been received, then the indicators are formed on account 45:
- debit 45 – credit 43 – actual shipment of products;
- debit 90 - credit 45 – recognition of revenue from the sale of finished products.
To determine the deviation between the actual and standard cost, account 40 is used, which is closed monthly to account 90.
As a result, to form the overall indicator, it is necessary to take into account the indicators in accounts - 43, 40 and 45 of accounting.
The PBU, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance dated July 29, 1998 No. 34n, states that financial statements must include information that has factual and material confirmation. When preparing a balance sheet or any other financial statements, the responsible person must be guided by the specified accounting provisions. accounting or other standards.
Based on existing rules, at the end of the calendar year, the company’s financial statements must reflect data on the volume of production and material inventories based on cost accounting determined using special methods. The accounting rules indicate that the assessment of inventories at the end of the reporting period should be carried out using the disposal method.
When manufacturing a product, its actual cost is determined taking into account the expenses incurred. As a result, in line 1210 of the balance sheet, finished products can be reflected at actual or accounting cost.
The choice of accounting methodology depends on the nuances of the company’s work and should subsequently be reflected in the accounting policy of the enterprise.
As we have already said, the line “Finished products and goods for resale” must be filled out. The formation of the general indicator occurs by balancing all data at the end of the reporting year on accounts 43 “Finished products” and 41 “Goods”. Before obtaining accurate data, the information indicated on accounts 45 and 40 is additionally taken into account.
If the product is outdated, has partially or completely lost its original qualities, or its price has decreased, then the indicator will be reflected in the balance sheet minus reserves for reducing the price of the product.
Send by mail
How are finished product indicators formed?
Initially, data on finished products is formed on account 43 of accounting. At the same time, the cost of products is not indicated and is written off as expenses to account 90:
Products intended for further sale or that will be used for the needs of the enterprise are formed in the form of the following entries:
Debit 43 – Credit 40 (or 20-29)
If the products are used for the needs of the enterprise, then account 43 is not used, and the products are reflected in account 10. In this case, the indicator is not used to form the overall balance on line 1210 of the balance sheet, but is entered in the line “Raw materials, supplies and other material assets”.
Account 45 is used when we are talking about shipped products. In other words, if payment for sold and shipped products has not yet been received, then the indicators are formed on account 45:
- debit 45 – credit 43 – actual shipment of products;
- debit 90 - credit 45 – recognition of revenue from the sale of finished products.
To determine the deviation between the actual and standard cost, account 40 is used, which is closed monthly to account 90.
As a result, to form the overall indicator, it is necessary to take into account the indicators in accounts - 43, 40 and 45 of accounting.
The role of finished goods in relation to balance
That is, a full reflection of the financial situation of an enterprise that deals with finished products is impossible without its reflection in the balance sheet, since in this case equality between Asset and Liability is impossible, which is a mandatory requirement for this type of reporting documentation.
The difficulty for an accountant is that in order to display finished products on the balance sheet, it is necessary to examine all the investments and costs that participate in the formation of the cost of this type of product. Again, if this is not done or the calculations are not done correctly, the balance between Asset and Liability will not be achieved. Such expenses may include:
- Production costs.
- Costs of paying wages to employees.
- Depreciation costs for equipment used in production.
- Insurance premium costs.
- Purchase of raw materials for production, etc.
It is the correctly calculated cost of production that will influence the reflection of the amount of the asset for this item in the balance sheet for a full overview of the financial condition of the enterprise.
The cost of these finished products is written off, and the balance is entered into line 1210 of the balance sheet. That is, the balances are included in the balance sheet, forming the amount from the actual cost or its standard version.
How to evaluate finished products
The accountant of an enterprise, when drawing up a balance sheet, or more precisely, forming line 1210, must be guided by Accounting Regulations 5/01. This provision is the main instruction when forming the cost of inventories for material and production purposes, which include finished products.
This provision defines the principles by which the cost of manufactured products can be calculated. The method used by the accountant should be applied throughout the tax period. Its purpose is to fix as clearly as possible the amount that is the cost of the product.
The specific cost of a given type of product must be based on production costs, which can be direct or indirect.
The accounting policy of the enterprise must establish how general production expenses will be distributed among the balances of finished products, as well as in what ways and in what order the process of writing off general business expenses will take place.
In order to collect objective and reliable information about products classified as finished, it is necessary to record their disposal: both by cost and by units of the product itself.
Accounting for finished products in accounting. Example, classification
| Did you like the site? Tell your friends! |
It is impossible to give a resigning employee a copy of SZV-M. According to the law on personal accounting, when dismissing an employee, the employer is obliged to give him copies of personalized reports (in particular, SZV-M and SZV-STAZH). However, these reporting forms are list-based, i.e. contain information about all employees. This means transferring a copy of such a report to one employee means disclosing the personal data of other employees. {amp}lt; {amp}amp;#8230;
Finished product (FG) is a completed product that has been released as a result of production.
It must meet the requirements of GOSTs or technical specifications, undergo quality control, be assembled into a complete set and sent for storage to the warehouse of the enterprise or customer.
GPs are classified into several types:
- Gross is the product produced by an enterprise over a certain period of time. Expressed in monetary terms and includes intermediate, completed and final products.
- Gross turnover is the totality of gross output for all workshops of the enterprise, including production work and the internal turnover of the organization for a certain period of time.
- Comparable products are products that the company produced previously.
- Incomparable products – manufactured for the first time in the current reporting period
After production, finished products come under the control of the warehouse employee under financial responsibility. Receipts are recorded in quantitative terms, if necessary, divided into categories of goods. For accounting, a card or cardless method is used. GP warehouse balances are regularly checked by inventory.
For the final product, the following mandatory documents required when releasing goods from the warehouse must be prepared:
- declaration or certificate of conformity,
- hygienic certificate,
- quality certificate,
- packaging label and other papers corresponding to the product category, confirming its quality and completeness.
Without these documents, the company does not have the right to sell its goods.
All transactions carried out with the participation of a state enterprise are accompanied by primary documents. Each operation has its own established document form.
This is carried out using the Invoice for the transfer of finished products to storage locations in the MX-18 form. It presents:
- from where and where the goods are transferred,
- correspondent account,
- basic information about the product,
- its characteristics.
The document is signed by the submitting and receiving persons, after which it is sent to the accountant.
This operation can also be carried out using the Acceptance and Delivery Note, which indicates data about the warehouse, workshop, quantity of goods being moved and information about it. In parallel, they use the Acceptance Sheet and Acceptance Certificate, which simplify warehouse accounting procedures.
Any movement of GP within the warehouse premises is recorded in warehouse records cards (form M-17) or warehouse records book (form M-40). Cost indicators are reflected in accounting.
Goods are regularly shipped from the warehouse, the registration of which is carried out using an invoice (form M-19), an invoice for the release of materials to the third party (form M-15) and an invoice order.
All of these are types of waybills, which detail the categories of goods being shipped.
Registration of the process of moving goods to the buyer is carried out using a consignment note in form 1-T and a waybill for freight vehicles (form No. 4-P). These documents contain information about the cargo and the features of its transportation. To receive the goods, the buyer's representative must have a power of attorney to receive the goods.
From the point of view of PBU 5/01 “Accounting for inventories,” finished products are considered to be the organization’s inventories, the purpose of which is to be sold to make a profit.
In the balance sheet, actual or planned cost is used to account for SOEs. The chosen method determines the further reflection of the goods on balance sheet accounts.
WTP can be assessed using any of the following methods:
- Actual production cost. This is the totality of all expenses (including general expenses) for the production of a product. They are posted to account 20 “Main production”, which contains information about all production costs. Used for small production volumes.
- Incomplete production cost. This is a complex of all production expenses with the exception of general business expenses: salaries of management personnel, vacation and travel allowances, depreciation, etc. Thanks to such an assessment, “net” production costs are determined, which allows for effective planning of activities with the limited resources available.
Shipped and sold products of industrial enterprises
Shipped products (SP) is the cost of products for which all shipping documents have been drawn up in a given period and which have been sent to the buyer, but have not yet been paid for by him (it is also called products on the road).
Can be calculated using the formula:
OP = TP – (Ok – He),
where Ok, He are the balances of products in the warehouse, respectively, at the end and at the beginning of the period.
Commodity products include all products produced for distribution by the enterprise to third parties, prepared by the enterprise for transfer into national economic circulation. But in the products prepared by the enterprise for distribution to the outside, there is or may be a part of the product that, for one reason or another, has not been sold and thus has not entered the national economic circulation. Reasons may include failures in product supply agreements, changes in market demand, market conditions, discrepancies between plans for production and sales of products, production of low-quality products, etc.
Sold products (RP) of an industrial enterprise is the cost of products produced at this enterprise, actually released (shipped) to the side and paid by the buyer and thereby transferred into national economic circulation (money came to the account or cash desk of the enterprise).
The volume of products sold is determined using the factory method, i.e. without intra-factory turnover, without the cost of products of own production, included in further industrial processing at the same enterprise. Exceptions are allowed only for certain industries, subject to the transfer of semi-finished products from workshop to workshop at established wholesale prices. Selling products to your own capital construction and other non-industrial enterprises of your enterprise is also an outsourcing; therefore, these types of holidays are included in sold products. The issue of the cost of the customer's material is resolved in the same way as is customary in relation to commercial products.
The volume of products sold during the reporting period includes products sold externally at the moment money is received from the buyer in the company’s current account, and for turnover within the company at the moment it is reflected by the company itself in the “Sales” account.
Thus, the following elements are included in the sold products of an industrial enterprise for the reporting period, provided that they are actually sold to third parties and paid for by the buyer in the reporting period:
- finished goods; produced by the main and secondary workshops of the enterprise, both from their own material and from the customer’s material (in the latter case, without the cost of this material);
- semi-finished products of their own production;
- products manufactured in subsidiary and auxiliary workshops;
- industrial work;
- major repairs of own equipment;
- in some cases, specifically specified in the instructions of planning and statistical authorities, internal turnover reflected in the reporting period by the enterprise itself on the “Sales” account.
The sold products of an industrial enterprise may differ from its commercial products due to the following elements:
- finished products produced in the reporting period, located in the enterprise’s warehouse and not yet released to the outside;
- finished products, semi-finished products of their own production, products of subsidiary and auxiliary workshops, industrial work supplied to the outside during the reporting period, but not yet paid for by the buyer;
- finished products, semi-finished products of own production, products of subsidiary and auxiliary workshops, industrial work, outsourced to the period in previous periods, but paid by the buyer in the reporting period.
The first two elements reduce sold products compared to marketable products, and the third increases them compared to marketable products. It goes without saying that this increase and this decrease take place or can take place only in relation to a certain reporting period.
Also, sold products can be calculated through shipped products using the formula:
RP = OP – (OOPk – OOPn),
where OOPk, OOPn are the balances of shipped but unpaid products at the end and beginning of the period, respectively.
Sales of products can also be represented by the following dependence:
RP=OP?Kv?Kt?Ko?Kr,
where KV is a coefficient characterizing the ratio of gross output and gross turnover, and showing how many hryvnias of gross output are per 1 day. units gross turnover;
CT is the marketability coefficient, reflecting how much money. units marketable products account for 1 day. units released gross output;
KO - shipment coefficient, reflecting how many days. units Products shipped per day. units released commercial products (the more KOs, the faster the finished products are shipped to consumers);
KR – sales coefficient, reflecting how much money. units Products sold in this period account for 1 day. units shipped products.
In the reporting of industrial enterprises, products sold are shown at the current wholesale prices of the enterprises.
However, from an accounting point of view, in accordance with the current Accounting Regulations of P(S)BU, all products shipped and released to the consumer outside the enterprise are considered sold, regardless of whether or not payment for the product occurs at that moment. And such products are called released products. This is due to the fact that currently different types, forms, and methods of payment for products are used, which involve prepayment, payment in installments, deferred payments, and so on. Based on this, in the event of non-payment for products, the company has receivables.