Each company that is registered as an individual entrepreneur or LLC has a bank account, and maybe more than one. Nowadays it is very difficult to imagine a company or organization without an account through which most of the organization’s funds are held. Banks for this are selected according to user preferences. In order to choose a bank to open and maintain an account, you need to study all the offers of various banks. The conditions for maintaining a current account are different in each bank.
A current account is opened only for legal entities in order to see all monetary transactions belonging to the organization. The mandatory presence of a bank account is regulated by the law of the Russian Federation. Legislation allows one organization to have several and an unlimited number of different accounts only in different banks. Many organizations open accounts in different banks to move funds and write off payments. And another so that money comes to the account and expenses for the organization.
What is a current account
In short, a current account is a bank account that is opened by a legal entity or individual entrepreneur to carry out non-cash banking procedures, such as non-cash payments, invoicing other legal entities, purchasing goods from suppliers and much more.
The purpose of payments distinguishes a current account for entrepreneurs and legal entities from a bank account of an individual. To identify the client, the bank assigns him an individual account number. For a company, the number is an important part of bank details.
The checking account is an exclusive 20-digit number of numbers that allows the bank to identify the client.
Regulatory documents governing the maintenance of a current account
Any current account transaction must be accompanied by official documents. The legislation of the Russian Federation clearly stipulates the maintenance of all documents. At the same time, mandatory documentation is constantly monitored by inspection authorities. In no case should record keeping deviate from the strict rules that are adopted and prescribed by law.
If a bank of any level does not follow the rules for maintaining documentation, there is a risk of losing its license. Only with strict implementation of the rules is it possible to continue banking activities.
A legal entity must also strictly follow certain rules for maintaining records. And this even applies to internal management. If the inspection reveals violations in the maintenance of documents on the current account, the responsible person may face criminal liability.
Regulatory acts regulating activities:
- Law “On Accounting” No. 129-FZ;
- Tax Code of Russia;
- Civil Code of Russia;
- Regulations on Non-Cash Payments of 2002;
- Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 94n;
- Instruction of the Central Bank of Russia No. 111-I;
- Directive of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation No. 1676-U;
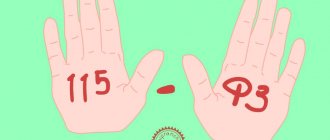
- 115-FZ.
Why do you need a current account?
Firstly, by having a current account, you will expand your business opportunities: the list of potential counterparties will increase, and you will have the opportunity to participate in tenders.
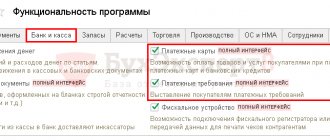
The manager will also be able to use additional banking services:
- connect acquiring - with it you can accept payments from bank cards;
- be able to transfer employee salaries to the card without extra expenses;
- hand over the proceeds to the bank and store it in a non-cash account;
- availability of overdraft and various types of loans;
- pay taxes, contributions to the Pension Fund and Social Insurance Fund;
- possibility to connect;
- carry out international operations;
- the ability to manage your business remotely.
An LLC cannot operate without a current account, the laws of the Russian Federation say so. For individual entrepreneurs such an opportunity exists.
Opening a current account for an individual entrepreneur in a bank will be relevant for you if:
- The payment amount under one contract is over 100,000 rubles. By law, such transactions must be paid for in cash.
- Do you want to receive payments by cards? More and more clients pay with cards because it is convenient and fast.
- You pay taxes and contributions to government funds.
How to transfer from a current account to a card
An individual entrepreneur can safely transfer his own funds from a current account to a bank card issued in his name.
If a transfer from a current account is made to a third party, then the recipient of the payment must be prepared to pay income tax on the income received.
To avoid questions from the tax authorities when transferring money to a person not associated with the business, it is better for an individual entrepreneur to:
- Transfer to your own card.
- Transfer from your own card to the recipient's card.
LLC has the right to transfer money from a current account to an individual’s card, indicating the purpose of the payment, which may be:
- payment of wages or loans to an employee;
- issuance of money on account;
- dividend payment;
- payment for supplier services under the contract;
- transfer of alimony.
The transfer must be formalized by payment order.
What operations can be carried out on a current account?
Having a current account, you can carry out the following operations:
- Replenish an account.
- Withdraw cash from your account. The withdrawal fee depends on the specific tariff. There are cases when this operation is performed only through the cash register, using a checkbook.
- Transfer money to legal entities and individual entrepreneurs. To do this, you need to create payment orders. Almost all current banks that provide cash settlement services make it possible to make payment documents online, which is much more convenient and faster.
- Mandatory payments to the Tax Service, Pension Fund and Social Insurance Fund. Most banks automatically generate payments to government agencies. There is no transfer fee.
- Transfers to individuals. If you are an entrepreneur who does not have subordinates, then with the help of this you will be able to transfer proceeds to a card, which will be issued as to an individual. At most banks, this is cheaper than cashing out at a cash register.
- Have the opportunity to receive non-cash payments from individuals and legal entities.
Procedure for maintaining a bank account
A current account is opened and maintained at the request of a representative of a legal entity, that is, an enterprise or organization. This can be either the owner himself or an accountant who deals with documentation.
Opening an account, opening it and closing it are the responsibilities of bank employees. However, all operations performed must be carried out and recorded only bilaterally. That is, in the bank by bank employees, and in the organization by the accounting department, which must have an idea of every minimal transaction carried out on the current account.
All transactions are carried out only in cash and with the obligatory presence of accompanying documents. Documents can be in paper or electronic form. Such operations as write-off and accrual are carried out.
A write-off is an operation in which funds are spent from a current account.
Accrual is a banking transaction in which funds are transferred to a bank account.
In order for the debit to be made, there must be a sufficient amount of money in the account. But there are situations when a large number of documents are received on the account that require debiting. And if there are not enough funds in the account to pay payment requests, debits from the account are carried out in turn.
For this purpose, the bank has a strictly distributed order:
- Write-off upon presentation of a writ of execution. This could be payment of alimony or compensation for damage related to health;
- Salaries for all employees in the organization;
- Payment of taxes or other payments to the budget;
- Payment according to writ of execution. In this case, it is written off to pay debts, loans and other obligations;
- The remaining write-offs alternate according to the date of receipt of payment orders.
It is worth noting that it is possible to independently carry out operations that relate to the movement of the company’s money. This is usually done by an accountant who has access to the organization’s online banking.
What do the numbers in the current account mean?
At first glance, it seems that the numbers in the current account were chosen randomly. But they all have their meaning.
Explanation of the account from left to right:
- 1-3 digits - balance account number.
- 4-5 digits - second-order balance account number. Together with them we get “40802”, this means that the account from the “other” category belongs to an individual entrepreneur.
- 6-8 digits - currency code. So “810” is the code for Russian rubles.
- The 9th digit is a control digit, which is calculated individually and is used to check the validity of the number.
- Digit 10-13 is the code of the bank division that services the current account.
- Digit 14-20 is the client’s internal number, it is set in the banking department.
How to open a current account
In order to open a current account, you need to contact the nearest bank branch or submit an application online. The easiest way to choose a bank is on our website.
List of profitable banks for opening an account
View list
Let's look at the first option first:
1. This point will be relevant for both the first option and the second. At the initial stage, you choose a bank. Things to consider here:
- Your company's needs. You need to make a list of the services you need to run your business.
- Tariff plan. Study bank packages. Please pay attention to the cost of monthly maintenance and fees for various operations.
- Customer reviews. Study reviews on the Internet about the bank that interests you.
- Bank daily routine and operating day.
- Number and location of service offices, ATMs.
- Check out the bonuses. For example, when opening an account for the first time.
- Quality of technical support.
2. Contact a bank branch and get advice.
3. Collect all documents.
4. Take them to the bank.
5. A couple of days after the check, visit the bank again and sign the agreement.
Second option:
1. Select a bank.
2. Submit an application to open a current account. Please provide the required information in your application.
3. A bank employee will call you back and tell you about the conditions and basic tariffs. It will also tell you what documents you will need to collect.
4. You collect documents and transfer them. The bank manager will come to your office at a time convenient for you.
5. The bank will check the documents. If everything is done correctly, a contract is concluded.
Most modern banks that offer to open a current account make it possible to reserve details in advance. So, after submitting your application, you will immediately receive your account details and will be able to use them for your work.
Documents for opening a current account for individual entrepreneurs and LLCs
In the table we have collected the main documents that may be required to open a current account.
| Type of documents | IP | Entity |
| Documents required to be provided | Passport of a citizen of the Russian Federation or other document that certifies the identity of an individual entrepreneur | Charter of LLC, CJSC, PJSC, NJSC |
| A prescribed application form that you will fill out at the branch. | Certificate of registration of a legal entity, extract from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities, which was received no earlier than a month before | |
| TIN certificate | ||
| Card with samples of the entrepreneur’s signature (you will fill it out at the branch) | A document that confirms the authority of the manager | |
| Certificate of registration of an individual entrepreneur or a sheet of the Unified State Register of Entrepreneurs on registration of an individual entrepreneur | Order/power of attorney, if you give an employee the right to manage the company’s non-cash funds | |
| Tax report for the previous period (if the activity has been carried out for more than 3 months) | A sheet from the statistics department with the organization’s activity codes | |
| Additional documents | Samples of signatures and seals certified by a bank employee or notarized | |
| Licenses and permits, if required | ||
| Power of attorney if you are not opening an account in person | ||
| Sheet of information about the beneficiaries of the company | ||
Additional documents may also be required for an LLC:
- document on ownership of the premises or lease agreement;
- certificate of business reputation;
- accountant's reports, tax return, certificate of absence of overdue debt.
For an individual entrepreneur, they sometimes request in addition:
- data from key counterparties (as well as future ones, if you are just starting your journey). For example, Sberbank employees may ask for this.
Chapter 5. Accounting for settlement transactions on bank customer accounts
Carrying out settlement operations (intermediation in payments) is the main function of a commercial bank. The technique of performing any banking operations is based on the non-cash payment system organized by banks, which covers the entire range of relationships between the bank and clients regarding the transfer of funds to accounts opened in banks.
General principles of organization and accounting of settlement transactions:
1. The relationship between the bank and the client in the process of settlement operations is regulated by a bank account agreement.
2. Settlement transactions involve their implementation through accounts opened for clients at the bank. The client can open settlement (current) and other types of accounts. The number of current accounts that a client can have with the bank is not limited. Current accounts are accounts for the client's main activities. The formation of funds in other client accounts is carried out, as a rule, by transferring funds from their settlement (current) accounts.
3. Current accounts are opened to the client after providing the relevant documents (application, certificate of state registration of the enterprise, a notarized copy of the charter and constituent agreement, certificate of registration with the inspection bodies of the Ministry of Taxes and Duties and Extra-Budgetary Funds, notarized card with sample signatures and seal impression, etc.). Depending on the type of current account (current, current, temporary settlement, sub-current, budget), there are features in the preparation of a set of documents provided to the bank for opening an account.
When opening current accounts for branches, representative offices of a legal entity (as separate divisions of a legal entity), in addition to the above set of documents, it is necessary to provide an application from this legal entity and documents confirming the creation of a branch or representative office, which may be: regulations on the branch, representative office or other separate division; decree (order) on its creation; power of attorney issued by a legal entity to the head of a separate division.
To open current accounts to account for transactions related to business activities and other income-generating transactions, it is also necessary to provide permission from the federal treasury authority, if the organization is financed from the federal budget, or permission from the relevant financial authority, if the organization is financed from budget funds subjects of the Russian Federation or local budgets. Accounts are valid within the periods specified in the permits. Permissions to open current accounts to record funds received from business or other income-generating activities must be signed by the head and chief accountant of the relevant federal treasury or financial authority.
To open current accounts in foreign currency, it is not necessary to provide certificates from extra-budgetary funds on the taxpayer’s registration, since payment of wages in foreign currency is prohibited in the Russian Federation.
To open a settlement sub-account, you need an order from the bank in which the main account of the legal entity is opened (indicating its regime), and a petition from the owner of the main account.
Copies of decisions on the creation and charters of institutions funded by the federal and local budgets and public organizations of a republican scale are not required.
When opening budget accounts to account for funds received for temporary use by organizations from the federal budget and subject to return upon expiration, it is necessary to obtain an application from the client and permission from the relevant federal treasury authority. Accounts are valid for the period specified in the permit. Accounts are opened with the federal treasury authorities.
Joint ventures created with the participation of foreign capital provide a notarized registration certificate issued by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation.
Entrepreneurs without the formation of a legal entity do not provide copies of the charter, constituent agreement and notarized seal. Cards with sample signatures of entrepreneurs with and without legal entity formation have only one signature.
To open a temporary current account, the following documents must be submitted to the bank: an application from the founders, a notarized memorandum of association and a notarized charter. To open temporary current accounts, it is not necessary to provide a certificate of registration of the taxpayer, since these accounts are opened to legal entities that have not yet been registered.
All accounts opened for clients are registered in the account book. The basis for opening an account and registering it is the order of the head of the bank to open the account. The bank informs the inspection authorities of the Ministry of Taxes and Duties at the place of registration of the legal entity as a taxpayer about the opening of a current account for the client within the prescribed period.
4. The following reasons may serve as grounds for closing a bank account: application from the client; absence of transactions on the account within the established period (if this is determined by the bank account agreement); the presence of a balance in the account during the established period in an amount below the minimum (if this is determined by the bank account agreement); reorganization or liquidation of an enterprise by decision of the court or body that created the enterprise. Current accounts for recording funds received from business or other income-generating activities are closed upon expiration of the permit issued by the federal treasury authorities or local financial authorities. Closing bank accounts is also accompanied by mandatory notification of the inspection of the Ministry of Taxes and Duties at the place of registration of the taxpayer.
5. Synthetic accounting of settlement transactions is carried out in the 4th section of the bank’s balance sheet “Operations with clients” on balance sheet accounts of the 1st order No. 405-408 (P), grouped depending on the type of ownership of the client (federal, state (except federal), non-state, others). 2nd order accounts to accounts No. 405-408 are built depending on the nature of the client’s activities (financial organizations, commercial enterprises, non-profit organizations).
On balance sheet accounts of the 2nd order, opened to the 1st order account No. 409 “Funds in settlements” (P), individual specific settlement transactions, grouped by type of settlement, are taken into account.
In analytical accounting, separate personal accounts are opened for the specified accounts for each enterprise and organization.
6. There is no special section in the balance sheet for accounting for clients’ currency transactions. Accounts in foreign currency are opened on all accounts where transactions in foreign currency can be accounted for in the prescribed manner. The analytical accounting personal account number includes a three-digit digital currency code. Additional characteristics of a foreign currency account (current, transit, special transit) are indicated in the free digits of the serial number of the personal account in the account registration book.
7. On accounts for recording transactions on current accounts, separate personal accounts may be opened for clients to record transactions involving the use of funds for capital investments, accounts for accumulating funds and for other purposes. The opening of these accounts and the execution of transactions on them is carried out on contractual terms on the same balance sheet account where transactions on current accounts are recorded.
To carry out certain operations (accepting payments from clients for subsequent transfer to direct recipients), transit accounts are provided. Funds from this account must be transferred in the manner and within the terms specified in the agreement with the recipients of the funds.
8. When the bank receives amounts of unknown purpose, which at the time of receipt cannot be posted to the corresponding accounts according to their ownership, they are recorded on balance sheet accounts No. 47416 “Amounts received in correspondent accounts before clarification” (P) and No. 47417 “Amounts written off from correspondent accounts pending clarification” (A).
Analytical accounting is kept on one personal account with a transcript attached to it indicating the amounts and the date of crediting to accounts No. 47416 and 47417.
The Bank takes prompt measures to transfer funds as intended. If the owners of the funds are not identified within 5 working days, then the amounts credited to the account for accounting for amounts received in correspondent accounts before clarification are credited at the place where the correspondent accounts of the sending banks are maintained.
9. Settlement transactions are carried out on the basis of payment documents of the established form, which are processed only through the bank. The form of payment documents is established by the Central Bank of Russia and is mandatory for use on the territory of the Russian Federation.
10. Settlement transactions are carried out within the free balance of the bank client’s current account. The bank account agreement may provide for a mechanism for using an “overdraft”.
11. If there are sufficient funds in the client’s current account to satisfy all claims, payments are made in the calendar order in which payment documents are received by the bank. If the current account funds are not enough to satisfy all claims, then payments are made in the order of payments established by Article 855 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, which is applied taking into account the requirements of Article 29 of the Federal Law of December 27, 2000 No. 150-FZ “On the Federal Budget for 2001” year":
- in the first place, funds are written off according to executive documents providing for the transfer or issuance of funds from the account to satisfy claims for compensation for harm caused to life and health, as well as claims for the collection of alimony;
- secondly, write-offs are made according to executive documents providing for the transfer or issuance of funds for settlements for the payment of severance pay and wages with persons working under an employment contract, including under a contract for the payment of remuneration under an author's agreement;
- in the 3rd stage, write-offs are made according to payment documents providing for payments to the budgets of all levels of the budget system of the Russian Federation and the budgets of state extra-budgetary funds, as well as the transfer or issuance of funds for settlements of wages with persons working under an employment contract;
- in the 4th stage, write-offs are made according to executive documents providing for the satisfaction of other monetary claims;
— in the 5th turn, debits are made for other payment documents in the order of the calendar order of payments.
Debiting funds from the account for claims related to one queue is carried out in the order of the calendar order in which documents are received by the bank.
Write-off of funds from budget accounts and personal accounts of recipients of budget funds, if there are insufficient funds to satisfy all existing claims, is carried out in the order established by Article 255 of the Budget Code of the Russian Federation.
12. To account for the amounts of settlement documents not paid on time due to the lack of funds in the payer’s account, off-balance sheet account No. 90902 “Settlement documents not paid on time” (A) is provided. Analytical accounting maintains card files and personal accounts opened for each payer.
If it is impossible to make a payment due to the lack of funds in the bank’s correspondent account, customer funds written off from their current accounts are taken into account on balance sheet account No. 47418 “Funds written off from customer accounts, but not posted to the correspondent account of a credit organization due to insufficient funds” (P ). Accounting for payment documents not paid due to a lack of funds in the bank's correspondent account is kept on off-balance sheet account No. 90903 “Customer payment documents not paid on time due to a lack of funds in the correspondent accounts of the credit organization” (A).
13. Settlement transactions can be performed in the following forms:
— settlements by payment orders;
— settlements under a letter of credit;
- payments by checks;
— settlements for collection (payment requests and collection payment orders).
14. When using collection settlements to account for the amounts of payment requests awaiting acceptance for payment, an off-balance sheet account No. 90901 “Settlement documents awaiting acceptance for payment” (A) is provided, in analytical accounting for which card indexes and personal accounts are kept, opened for each payer. The acceptance period is determined by the terms of the agreement between the supplier and the buyer, but cannot be less than 5 days.
15. For conducting settlement operations, the bank charges a fee, the amount of which is established in accordance with bank account agreements (cash settlement services) and the tariffs of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation.
16. For violation of the rules for conducting settlement operations, banks and enterprises are liable in accordance with current legislation.
Settlement transactions on bank customer accounts are reflected in the bank's accounting records using the entries given in table. 5.1.
Table 5.1
Typical accounting entries for recording the main forms of non-cash payments
| Contents of operation | Account correspondence |
| SETTLEMENTS BY PAYMENT ORDERS | |
| Transactions in the payer bank: | |
| 1. Acceptance of payment orders for payment and placing them in the file cabinet of account No. 90902 in the absence or insufficient funds in the client’s account | D-t 90902 “Settlement documents not paid on time” D-t 99999 |
| 2. Write-off of funds from settlement (current) accounts of clients | D-t settlement (current) accounts of clients K-t 30102 “Correspondent accounts of credit institutions in the Bank of Russia” K-t 30110 “Correspondent accounts in correspondent credit institutions” K-t 30301 “Settlements with branches located in the Russian Federation” |
| Continuation of the table. 5.1 | |
| Contents of operation | Account correspondence |
| 3. Write-off of payment orders previously placed in the file cabinet for account No. 90902, upon their full or partial payment | D-t 99999 K-t 90902 (for the payment amount) |
| Transactions in the recipient bank: | |
| 4. Crediting funds to clients’ settlement (current) accounts | Dt 30102, 30109, 30302 Settlement (current) accounts of clients |
| CALCULATIONS FOR COLLECTION | |
| Settlements with payment requests with acceptance | |
| Transactions in the payer bank: | |
| 1. Placing the supplier’s documents in the file cabinet for off-balance sheet account No. 90901 until the payer’s acceptance is received | D-t 90901 “Settlement documents awaiting acceptance for payment” D-t 99999 |
| 2. Write-off of funds from the payer’s settlement (current) account if he fails to submit an application for refusal of acceptance in the full amount of the payment request or in a partial amount of the payment request when the payer submits an application for partial refusal to accept | D-t settlement (current) accounts K-t 30102, 30110, 30301 |
| 3. Write-off of the payment request from the card index to off-balance sheet account No. 90901 upon receipt or non-receipt of a refusal to accept (in full amount) | D-t 99999 K-t 90901 |
| 4. Placing documents in a file cabinet for off-balance sheet account No. 90902 in the absence of funds in the payer’s account and failure to receive an application for refusal of acceptance within the prescribed period | D-t 90902 K-t 90901 |
| Transactions in the recipient bank: | |
| 5. Crediting funds to the supplier’s settlement (current) account | Dt 30102, 30110, 30301 Settlement (current) accounts of clients |
| Settlements with payment requests without acceptance and collection payment orders | |
| Balance-sheet and off-balance sheet accounting of settlement transactions when using a payment request without the payer’s acceptance and a collection payment order is similar to accounting when using a payment order in settlements | |
| PAYMENTS BY LETTER OF CREDIT | |
| Settlements with covered (deposited) letters of credit | |
| Transactions in the issuing bank: | |
| 1. Transfer of the letter of credit amount (covering) at the expense of the payer to the executing bank | D-t settlement (current) accounts K-t 30102, 30110 |
| 2. Off-balance sheet accounting of the issued letter of credit (simultaneously with posting No. 1) | D-t 90907 “Issued letters of credit” D-t 99999 |
| 3. Write-off of the issued letter of credit from off-balance sheet accounting based on received documents from the executing bank on the use of the covered letter of credit or its cancellation | D-t 99999 K-t 90907 |
| 4. Reinstatement of the letter of credit (in the amount of non-use, reduction or revocation) | Dt 30102, 30110 Settlement (current) accounts of clients |
| Transactions in the executing bank: | |
| 5. Opening a covered letter of credit upon receipt of funds and documents from the issuing bank | D-t 30102, 30110 K-t 40901 “Letters of credit for payment” |
| 6. Use of a covered letter of credit and crediting funds to the supplier’s account upon fulfillment of the terms of the letter of credit | Dt 40901 Settlement (current) accounts of clients |
| 7. Closing of a letter of credit upon expiration of the period upon the supplier’s application to refuse further use of the letter of credit, upon the buyer’s application to revoke the letter of credit (for the amount of non-use, reduction or cancellation) | D-t 40901 K-t 30102, 30110 |
| Settlements under uncovered (guaranteed) letters of credit | |
| Transactions with the issuing bank: | |
| 1. Opening an uncovered letter of credit to the supplier on the basis of an agreement with the buyer (opened if the issuing bank has a correspondent account with the executing bank) | D-t 99998 D-t 91404 “Guarantees issued by the bank” |
| 2. Closing of an issued letter of credit on the basis of documents received from the executing bank on the use of an uncovered letter of credit | Dt 60315 “Amounts not collected by the bank under its guarantees” Dt 30110 |
| Continuation of the table. 5.1 | |
| Contents of operation | Account correspondence |
| 3. Removal from off-balance sheet accounting of the amount of guarantee provided to the buyer when using a letter of credit (simultaneously with posting No. 2) or in case of refusal to use the letter of credit, its reduction or cancellation | D-t 91404 K-t 99998 |
| Transactions in the executing bank: | |
| 4. Off-balance sheet accounting of an issued uncovered letter of credit based on documents received from the issuing bank | D-t 91305 “Guarantees received by the bank” D-t 99999 |
| 5. Crediting funds to the supplier’s account based on the submitted documents on fulfillment of the terms of the letter of credit from the correspondent account of the issuing bank | Dt 30109 “Correspondent accounts of correspondent credit institutions” Settlement (current) accounts of clients |
| 6. Closing the off-balance sheet account of the guarantee received by the bank when using a letter of credit (simultaneously with posting No. 5) or upon the supplier’s application to refuse further use of the letter of credit, or upon the buyer’s application to revoke the letter of credit (for the amount of non-use, reduction or cancellation) | D-t 99999 K-t 91305 |
| PAYMENTS BY CHECKS | |
| 1. Depositing funds by enterprises and organizations for settlements by checks from settlement (current) accounts | D-t settlement (current) accounts K-t 40903 “Settlement checks” |
| 2. Write-off of settlement check forms from off-balance sheet accounting | D-t 99999 K-t 91207 “Strict reporting forms” |
| 3. Payment of checks received by the payer’s bank for collection, if the check holder is a client of the bank | Dt 40903 Settlement (current) accounts |
| 4. Payment of checks received by the payer’s bank for collection, if the check holder is a client of another bank | D-t 40903 K-t 30102 “Correspondent accounts of credit institutions with the Bank of Russia” |
| 5. Return to the payer’s settlement (current) account of the unused deposited amount | Dt 40903 Settlement (current) accounts |
| 6. Receipt of funds by the supplier’s bank for crediting to the supplier’s settlement (current) account | Dt 30102 Settlement (current) accounts |
Conducting settlement transactions is regulated by the following regulatory documents:
1. Civil Code of the Russian Federation (parts one and two);
2. Tax Code of the Russian Federation - part one of July 31, 1998 No. 146-FZ and part two of August 5, 2000 No. 117-FZ;
3. Budget Code of the Russian Federation;
4. Instruction of the State Bank of the USSR dated October 30, 1986 No. 28 “On settlement, current and budget accounts opened in banking institutions”;
5. Instruction of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation dated October 12, 2000 No. 93-I “On the procedure for opening by authorized banks of non-resident bank accounts in the currency of the Russian Federation and conducting transactions on these accounts”;
6. By letter of the State Tax Service of the Russian Federation, the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation and the Central Bank of the Russian Federation dated August 13, 16, 1994 No. ВГ-4-13/94н, 104 “The procedure for applying the provisions of the Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of May 23, 1994 No. 1006 “On the implementation of comprehensive measures for timely and full payment of taxes and other obligatory payments to the budget"";
7. Letter of the State Bank of the USSR dated July 9, 1999 No. 359 “On the procedure for opening accounts for entrepreneurs”;
8. Regulations of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation dated April 9, 1998 No. 23-P “On the procedure for issuing bank cards by credit institutions and making settlements on transactions carried out using them”;
9. Regulations of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation dated December 8, 1998 No. 7-P “On the procedure for calculating and collecting fees for settlement On non-cash payments in the Russian Federation”;
11. Rules for maintaining accounting records in credit institutions located on the territory of the Russian Federation, dated June 18, 1997 No. 61;
12. Directive of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation dated June 18, 1999 No. 579-U “On the procedure for opening and maintaining accounts of organizations financed from the federal budget, budgets of constituent entities of the Russian Federation and local budgets, for accounting for funds received at the temporary disposal of organizations financed from their federal budget, budgets of constituent entities of the Russian Federation and local budgets, in institutions of the Central Bank of Russia.”
How much does it cost to maintain a current account?
When connecting to settlement and cash services, most banks do not charge a fee. Therefore, the amount is based on the following factors:
- Cost of monthly account maintenance. Some banks reduce its cost if the client pays for the service in advance.
- Commission for transfers. It is worth noting that a certain number of payments are included in the service package, while the rest are paid separately.
- Cashing and replenishment. The commission is taken as a percentage of your amount.
Which bank to choose
According to our website statistics, the most loyal banks for opening a current account are Tochka, Modulbank and Tinkoff. They combine ease of service, low tariffs and very useful bonuses for entrepreneurs.
| Dot | Modulbank | Tinkoff | |
| Link to open an account | tochka.com | modulbank.ru | www.tinkoff.ru |
| Service | From 0 to 25,000 rub. | 0 — 4900 rub. | From 490 to 4,990 rubles |
| Opening an account | For free | For free | For free |
| Bonuses | Up to 270,000 rubles in bonuses for business development (for the first advertising campaign, mobile communications, online accounting, etc.) | Up to 530,000 rubles: 10,000 rubles for advertising in Yandex.Direct, up to 50,000 bonuses for advertising in the metro, 10,000 rubles for a Google advertising campaign through Aori, etc. | Up to 10,000 rubles for advertising in Yandex, Up to 50,000 rubles for advertising from “myTarget” in Odnoklassniki and VKontakte and others |
| Overdraft | — | — | Eat |
| Cash | From 0% | From 0% | From 0.15% |
| Cash withdrawal | From 0% | From 0% | From 1% |
| Translations of physical persons | From 0% | From 0% | From 1% |
What to do after opening an account
After you have entered into an agreement with the bank, you will be given the opportunity to manage your account online through Internet banking or mobile banking.
If you need additional services, for example, a payroll project, acquiring, currency control, collection or any other, you can also submit an application without leaving your home. It is also possible to open a deposit and receive a loan remotely.
It makes no sense to call or go to the Pension Fund. The bank itself will notify them about the opening of a current account. This is their direct responsibility.
Accounting for transactions on a bank account
All available funds of the organization are stored in bank service institutions in specially opened current accounts. The bank assigns a number to each current account, which must be indicated on all documents when debiting or receiving money to the account.
Banks open settlement, current, currency and other accounts for organizations.
A current account is an account opened with a bank and intended for storing ruble funds of an organization and conducting non-cash payments with other legal entities and individuals. The current account is the main account of the organization through which all monetary payments are made without restrictions. The number of current accounts is not limited by law. Current accounts can be opened by any legal entity, regardless of the form of ownership.
To open a current account, you must provide the following documents to the bank:
— application for opening an account of the established form;
— notarized copies of the organization’s charter, constituent agreement and registration certificate;
— a certificate from the tax authority confirming the organization’s registration as a taxpayer;
— copies of documents on registration as payers in the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation and the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund;
— a card with sample signatures of the manager, deputy manager and chief accountant with an imprint of the organization’s seal in the prescribed form, certified by a notary.
If the organization does not have the position of chief accountant, only the head of the organization will sign the card. In government organizations, the signatures of the manager and chief accountant can be certified by higher-level organizations instead of notaries. Foreign legal entities (non-residents) can open ruble accounts only at the location of their representative offices and branches in the manner established by special instructions. If the created organization temporarily lacks a seal, the head of the bank allows, within the period necessary for the production of the seal, documents to be submitted to the bank without a seal impression. After checking the documents, by order of the bank manager, the chief accountant of the bank makes a note on the original copy of the charter that the current account has been opened, indicating the account number and certifying it with an official seal. All documents are kept in the account file, and one copy of the card with sample signatures and seal imprint is stored in a special file cabinet with the executor (controller). After submitting the necessary documents to the bank, including cards with sample signatures of the director and chief accountant, an agreement for settlement and cash services is concluded between the bank and the enterprise, which, as a rule, stipulates: the cost of opening an account, the cost of services for settlement and cash services, the cost of cash circulation, interest paid by the bank to the client for funds in accounts. The bank assigns a specific serial number to the company's current account.
In the event of a reorganization of an enterprise as a result of a merger, accession, division, or separation for re-registration of a current account, all documents must be submitted anew. If the name of an enterprise or its subordination changes, a new application for opening an account, a copy of the decision on the change, and a new card with sample signatures and a seal imprint are submitted to the bank. Based on these documents, the account is reissued. If the nature of the activity changes, a copy of the new charter is submitted to the bank. If there is no cash flow on the current account for three months, it is closed. Enterprises, if they have self-supporting units (branches, representative offices) in other regions of Russia, can open settlement (or current) accounts in banks at the location of the branches (representative offices). To do this, the company must submit an application to the bank to open a current or current account, indicating the nature of the transactions performed and the persons who are given the right to dispose of the account. The petition is signed by the head of the enterprise and the chief accountant and sealed. Businesses are required to inform their tax office about all open accounts. At the same time, the same obligation is assigned to bank branches in which enterprises opened accounts.
After opening an organization's settlement, current, loan, deposit, currency and other account, banks send the tax authority a notice of opening an account for the taxpayer organization. The tax authorities, no later than the next business day, send an information letter of the established form to the bank regarding receipt of notification of the opening of an account. Operations to withdraw or transfer funds from the account are carried out by the bank only after receiving the specified letter.
In turn, the organization is also obliged to notify its tax office within 7 days after opening (closing) the account. For failure to comply with this requirement, the organization may be subject to a fine in accordance with Article 118 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation in the amount of 5,000 rubles.
A message about opening (closing) an account with the Pension Fund and the Social Insurance Fund must be submitted no later than seven working days. In this case (by analogy with the notification of the tax authority), it is necessary to inform the authorities monitoring the payment of contributions only about those settlement (current) and other accounts that are opened on the basis of a bank account agreement. There is no obligation to report the opening (closing) of deposit, loan and transit accounts.
Letter No. 02-10/05-13656 of the Federal Insurance Service of the Russian Federation dated December 28, 2009 provides the recommended form of notification by the policyholder about the opening (closing) of an account. The Pension Fund of the Russian Federation recommends forms of messages about opening (closing) an account and changing the details of the account of the payer of insurance contributions are posted on the website of the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation.
For failure to provide notice of opening to the social insurance fund and pension fund, a fine of 1,000 - 2,000 rubles for organizations is provided.
Transactions on the current account are reflected in accounting on the basis of the credit institution's statements on the current account and the monetary settlement documents attached to them. The bank submits a statement daily, which represents the second copy of the organization’s personal account opened for it by a credit institution.
The statement indicates all receipts and debits from the current account, the balance of funds on it at the beginning and end of the day. In a bank statement, information about cash flows is reflected by entering a code corresponding to the content of the transaction.
The accounting department of the enterprise checks the statement and the compliance of the amounts received and written off according to the supporting settlement and payment documents attached to it. If an error is detected, the company reports this to the bank institution. The attached supporting documents are numbered - 1, 2, etc. When accounting for an extract from a current account, the corresponding accounts for each business transaction are entered in its fields to the right of the corresponding amount and the serial numbers of the attached supporting documents are placed on the left.
Funds can be credited to the organization’s current account from buyers of products, works, services; from debtors to repay debts; in the form of a bank loan; in the form of a cash loan, etc., as well as when handing over cash from the organization’s cash desk.
The credit organization writes off funds by order of the director and chief accountant or without the order of the account owner in cases provided for by law. Indisputably, the bank can write off funds by court decision, at the request of the tax inspectorate for the payment of tax arrears and penalties accrued based on the results of the audit. If there are insufficient funds to satisfy all the requirements presented to it, the funds are written off as they are received in the order established by law.
The bank carries out all operations to write off funds from the current account with the consent of the owner or on the basis of his orders (documents of the established form) in the calendar sequence of occurrence of obligations.
Banks carry out transactions on accounts on the basis of settlement documents drawn up in accordance with the requirements of the Regulations of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation “On non-cash payments in the Russian Federation” dated November 3, 2002 No. 2-P, within the limits of funds available in the account, unless otherwise provided in the agreements concluded between the Central Bank of the Russian Federation or credit institutions and their clients. A settlement document is a document drawn up on paper, filled out using typewriters or electronic computers in black font, with the exception of checks, which are filled out with pens with paste, black, blue or purple ink (checks can be filled out on a typewriter in black font colors). Signatures on payment documents are affixed with a pen with paste or black, blue or purple ink. The seal impression and the bank stamp imprinted on payment documents must be clear. Corrections, blots and erasures, as well as the use of correction fluid in settlement documents are not allowed. Payment documents are valid for presentation to the servicing bank for ten calendar days, not counting the day of their issue. Settlement documents are presented to the bank in the number of copies required for all participants in the settlements. All copies of the payment document must be filled out identically. The second and subsequent copies of settlement documents can be produced using carbon paper, duplicating equipment or electronic computers.
Payers have the right to revoke their payment orders, recipients of funds (collectors) - settlement documents accepted by the bank in the order of settlements for collection (payment requests, collection orders), not paid due to insufficient funds in the client's account. Partial withdrawal of amounts from settlement documents is not permitted.
When making non-cash payments, the following payment documents are used:
- money orders;
— payment requirements;
- collection orders.
A payment order is an order from an enterprise (payer) to its servicing bank, documented as a settlement document, to transfer a certain amount of money to the recipient’s account opened in this or another bank. The payment order is executed by the bank within the period provided for by law, or within a shorter period established by the bank account agreement or determined by business customs applied in banking practice.
Payment orders can be made:
— transfers of funds for goods supplied, work performed, services rendered. The accountant records this operation with the following accounting entry: debit 51 “Current account” from credit 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers”;
— transfers of funds to budgets of all levels and to extra-budgetary funds. When carrying out this operation, the following entry is made: debit 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees”, 69 “Calculations for social insurance and security” from credit 51 “Current account”;
— transfer of funds for the purpose of returning/placing credits (loans) and paying interest on them. Repayment of the loan and interest on it is recorded accordingly with the following entries: debit 66 “Settlements for short-term loans and borrowings”, 67 “Settlements for long-term loans and borrowings” from credit 51 “Current account”; debit 91 “Other income and expenses” from credit 51;
— transfer of funds for other purposes provided for by law or agreement.
In accordance with the terms of the main agreement, payment orders can be used for advance payment of goods, work, services or for making periodic payments.
The bank is obliged to inform the payer, upon his request, about the execution of the payment order no later than the next business day after the payer contacts the bank, unless a different period is provided for in the bank account agreement. The procedure for informing the payer is determined by the bank account agreement.
Funds stored in current accounts are accounted for in the active synthetic account 51 “Current accounts”. The debit of this account records the receipt of funds in the current account, and the credit records the decrease in funds in the current account. The basis for entries in the current account are bank statements with supporting documents attached to them. Analytical accounting is maintained for each current account.
Cash and non-cash payments can be made using the current account. In case of cash payments, the movement of funds in the current account is formalized by a cash check and an announcement for a cash deposit.
A cash check is an order from an enterprise to the bank to issue the amount of cash specified in it from its current account. The company receives check books from the bank that serves it at the request of the owner. They are strict reporting forms and are stored in the organization’s safe. The check is filled out by hand using ink or a ballpoint pen. It indicates the amount, date of issue, name of the recipient, as well as information about the purpose of the amounts received. For each amount received from the bank, the accountant issues a cash receipt order addressed to the recipient indicating the check number. Cash checks are signed by the manager and chief accountant and affixed with the company seal. Corrections and blots are not allowed.
The bank accepts cash into the company's current account upon announcement of a cash deposit. The advertisement must be filled out in one copy, indicating the source of the money being contributed. For the accepted amounts, the bank issues a receipt to the cashier, which serves as the basis for drawing up a cash order for writing off funds at the cash desk.
Forms of non-cash payments are chosen by the enterprise independently and are provided for in the agreement concluded with the bank.
A payment request is a settlement document containing a demand from the creditor (recipient of funds) under the main agreement to the debtor (payer) to pay a certain amount of money through the bank.
Payment requirements are applied when making payments for goods supplied, work performed, services rendered, as well as in other cases provided for by the main agreement. Settlements through payment requests can be carried out with prior acceptance and without the payer’s acceptance.
When issuing a payment request, the accountant makes the following entries: debit 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors”, 76 “Settlements with other debtors and creditors” from credit 51 “Current account”.
Collection settlements are a banking operation through which the bank (hereinafter referred to as the issuing bank), on behalf and at the expense of the client, on the basis of settlement documents, carries out actions to receive payment from the payer. To carry out collection settlements, the issuing bank has the right to attract another bank (hereinafter referred to as the executing bank).
Settlements for collection are carried out on the basis of payment requests, payment of which can be made by order of the payer (with acceptance) or without his order (in an unaccepted manner), and collection orders, payment of which is made without the order of the payer (in an indisputable manner). Payment requests and collection orders are submitted by the recipient of funds (collector) to the payer's account through the bank serving the recipient of funds (collector). The issuing bank, which has accepted payment documents for collection, undertakes the obligation to deliver them to their destination. In case of non-fulfillment or improper execution of the client’s order to receive payment on the basis of a payment request or collection order, the issuing bank is liable to him in accordance with the law.
Enterprises using the 1C program: Accounting for account 51 can generate the following types of reports: account card 51, analysis of account 51, analysis of account 51 by dates, analysis of account 51 by subconto, turnover for account 51, balance sheet for account 51, and also a journal order for account 51, a journal order and a statement.
In the report, “Journal order and statement of account” is essentially a report on the movement on the account (beginning balance, turnover with other accounts and ending balance), detailed by dates (periods) or by transactions (operations). In the order journal, entries are formed on the debit and credit of account 51 “Current accounts” in correspondence with other accounts.
Enterprises in accounting make the following entries to the debit of account 51 and the credit of accounts:
50 “Cash desk” - when depositing cash into a current account (deposited wages, proceeds from the sale of products, works, services, etc.);
55 “Special accounts in banks” - crediting unused balances of funds under letters of credit and check books to current accounts;
62 “Settlements with buyers and customers” - receipt of revenue for products sold from procurement organizations and other buyers and customers;
66 “Settlements for short-term loans and borrowings” - when crediting short-term loans and borrowings received by the organization for a period of no more than 12 months to current accounts;
76-1 “Calculations for property and personal insurance” - transfer by insurance companies of insurance compensation for crops and other insured property lost as a result of natural disasters;
76-2 “Settlements for claims” - receipt of funds to the current account from organizations in order to satisfy claims, etc.
Also, entries are made for the issuance and transfer of funds from the current account on the credit of account 51 “Current accounts” to the debit of other accounts:
50 “Cash desk” – issuance of cash from a current account;
55 “Special accounts in banks” - issuing letters of credit from a current account, purchasing check books by clients;
60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” - payment of invoices from suppliers for supplied inventory, contractors - for work performed on core activities and investments in non-current assets;
66 “Settlements for short-term loans and borrowings” - when repaying from the current account short-term loans and borrowings received by the organization for a period of up to 12 months;
68 “Calculations for taxes and fees” - when transferring payments to the budget (personal income tax, deductions from profits, etc.) and fees from the current account;
69 “Calculations for social insurance and security” - when transferring payments from the current account to the Social Insurance Fund. Pension fund and compulsory health insurance funds;
70 “Settlements with personnel for wages” - transfer of due wages to employees to their personal accounts in banks and other accounts.