Costs for compulsory motor liability insurance relate to other expenses for ordinary activities. Enterprises using the simplified tax system “Income minus expenses” when calculating the single tax base have the right to reduce income by the amount of costs listed in Art. 346.16 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Clause 7 indicates the costs of compulsory insurance; therefore, compulsory motor liability insurance is included in the costs of the simplified tax system. According to paragraph 2 of Art. 263 of the Tax Code, compulsory insurance in the expenses of the “simplified” is recognized within the framework of insurance tariffs approved in accordance with the law. If such tariffs are not approved, the entire amount of costs can be offset against expenses.
For your information! It is impossible to take into account the costs of voluntary vehicle insurance in the tax base, since such a policy is purchased on the company’s own initiative.
For example, if a company purchased and put into operation a car for which a compulsory motor liability insurance policy worth 25,000 rubles was paid. and CASCO in the amount of 55,000 rubles, the accountant has the right to take into account only 25,000 rubles in expenses. for compulsory insurance. The base cannot be reduced by the cost of the CASCO policy.
Accounting for compulsory motor liability insurance under the simplified tax system
In accounting, expenses for compulsory motor liability insurance can be recognized simultaneously in the reporting period when they were incurred, or written off throughout the entire term of the contract, distributed in equal parts (clause PBU 10/99). An acceptable method is fixed in the accounting policies. In tax accounting, such costs are recognized upon payment (Article 346.17 of the Tax Code).
Accounting for compulsory motor liability insurance under the simplified tax system “Income minus expenses” is carried out in the accounts of the relevant industries - 20th account (main), 23rd, 25th, 26th, 29th, 44th (auxiliary, commercial, servicing), corresponding to account 76 on a specially designated sub-account “Insurance settlements”.
The use of account 76 is due to the specifics of settlements with the insurance company: payment for the purchased policy does not mean that the insurance service has been fully provided, since there is always the possibility of returning part of the insurance premium upon early termination of the insurance contract, or upon compensation for damage incurred in an accident.
Compulsory employee insurance
Compulsory employee insurance includes:
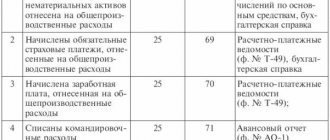
- compulsory pension, social and medical insurance (Chapter 34 “Insurance contributions” of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- compulsory insurance against industrial accidents and occupational diseases (Law of July 24, 1998 No. 125-FZ);
- insurance of citizens engaged in private detective and security activities in case of death, injury or other damage to health (Article 19 of the Law of the Russian Federation of March 11, 1992 No. 2487-1).
OSAGO under the simplified tax system “Income minus expenses”: postings
Let's look at how to take into account the purchase of an MTPL policy using an example:
On April 1, 2019, I purchased a car for production needs, paying on the same day for a compulsory motor liability insurance policy worth 15,000 rubles. for a year. According to the company's accounting policy, the entire amount of costs for compulsory motor liability insurance is written off at a time after payment.
The company's accountant will document in the accounting records on the date of payment for the transaction:
| Operation | D/t | K/t | Sum |
| MTPL policy purchased (insurance premium paid) | 76 | 51 | 15 000 |
| Purchase costs included | 20 | 76 | 15 000 |
If the company’s accounting records the write-off of the cost of the policy in parts, then by posting D/t 20 K/t 76 during the year the due share will be written off monthly in an amount depending on the number of days in the month of write-off. For example, in April 1232.88 rubles will be written off. (15000 / 365 x 30), in May 1273.97 rubles. (15000 / 365 x 31), etc.
Equal distribution of expenses simplifies the accounting for the return of a portion of the insurance amount if there is a need for early termination of the contract, since at the time of return the expenses will not yet be included in expenses, and, therefore, the returned portion of the insurance will not have to be included in income.
Accounting and postings
If an organization or individual entrepreneur that uses the simplified tax system has a car, then, of course, it needs to be insured under the MTPL program.
Moreover, the payer of the simplified tax system can purchase a CASCO or DSAGO policy. But what about when calculating the single tax? Can insurance fees paid to an insurance company be expensed? OSAGO is compulsory motor third party liability insurance. Without a compulsory motor liability insurance policy, your car will not be registered, you will not be allowed to undergo a technical inspection, and a traffic police officer will fine you on the road. OASGO is a mandatory type of car insurance.
DSAGO - additional civil liability insurance on a voluntary basis. In the case of insurance under DSAGO, the amount of payments under OSAGO (for compensation for damage to property, life and health of third parties) increases.
CASCO is a voluntary insurance contract that provides compensation for damage from car damage, theft or loss of a car (at the discretion of the policyholder).
If a company has a car, it must be insured. We will tell you in the article how to take into account the costs incurred for insurance under MTPL and CASCO contracts, what nuances of tax accounting exist for simplifiers, and what transactions to use to reflect compensation from the insurance company.
Relations regarding insurance of property and the risk of liability of the insured are regulated by the Civil Code (Articles 930, 931, 932).
All vehicle owners are required to insure their car (Article 4 of Federal Law No. 40-FZ dated April 25, 2002). To do this, you need to insure your liability by paying for a compulsory motor liability insurance policy from an insurance company. In case of damage to the property or health of another person, the insurance company will compensate for losses within the established limit.
In addition to compulsory insurance, there is also voluntary insurance - CASCO.
Car insurance costs are expenses incurred in the normal course of business. Accounting for such expenses is carried out in accordance with PBU 10/99.
Accounting for settlements with the insurance company occurs on account 76-1. This subaccount is intended specifically for accounting for insurance settlements.
Expenses under MTPL and CASCO policies should be written off evenly over the term of the agreement (policy). Insurance premiums paid to the insurer must be written off to cost accounts (20, 23, 25, 26, 44).
Some companies use account 97 “Deferred expenses” to account for car insurance. The appropriate accounting method should be fixed in the accounting policy.
Evenly writing off expenses will help to avoid differences with tax accounting, since in tax accounting insurance costs are also written off evenly.
| Operation | D/t | K/t | Sum |
| MTPL policy purchased (insurance premium paid) | 76 | 51 | 15 000 |
| Purchase costs included | 20 | 76 | 15 000 |
If the company’s accounting records the write-off of the cost of the policy in parts, then by posting D/t 20 K/t 76 during the year the due share will be written off monthly in an amount depending on the number of days in the month of write-off. For example, in April 1232.88 rubles will be written off. (15000 / 365 x 30), in May 1273.97 rubles. (15000 / 365 x 31), etc.
Equal distribution of expenses simplifies the accounting for the return of a portion of the insurance amount if there is a need for early termination of the contract, since at the time of return the expenses will not yet be included in expenses, and, therefore, the returned portion of the insurance will not have to be included in income.
For enterprises operating under the simplified tax system “Income”, vehicle insurance costs do not affect the calculation of tax, since almost all costs are not taken into account in the tax base, and tax is calculated on the amount of income received.
In accounting, the entries reflecting the purchase of an MTPL policy, the return of funds upon termination of the contract and compensation for damage are identical to the entries that apply the simplified tax system “Income reduced by expenses.”
But compensation under OSAGO under the simplified tax system “Income” is taken into account as part of non-operating income, since clause 3 of Art. 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation includes compensation for losses and damages, including the amount of insurance compensation under compulsory motor liability insurance, although the costs of vehicle repairs are not included in the calculation of the tax.
—————————————————————————Method Characteristics What is the convenience of the method——————————————————— ——————Lump-sum The cost of insurance is included 1. This accounting procedure for inclusion in expenses for ordinary types is convenient for companies whose full amount of activity at a time on the date of entry into the insurance contract is seasonal for expenses due to the (date of payment of the policy) nature and which ( clauses 5, 7 and 18 PBU 10/99). purchase insurance. Postings will be as follows: for the working period. Debit 76, subaccount “Calculations 2. The method allows property and personal insurance to be brought together,” Credit 51 and tax accounting. After all, the payment of the insurance premium is reflected; in tax accountingDebit 20 (23, 26, 44) Credit 76, under the simplified tax system for insurance, the subaccount “Calculations for property is included in expenses and personal insurance”, at a time, immediately charged to expenses after payment of the insurance premium under the insurance agreement—————————— ———————————————Uniform The cost of insurance is included. In the case of a significant write-off of the price as part of the costs of the usual types of insurance policy costs for activities on a monthly basis during this method allows the costs of the policy period (clause 3 and distribute amounts during 19 PBU 10/99). The amount of costs and expenses by month and the period of its write-off for the month is determined based on the number of days of insurance in this month. To do this, you need to calculate the cost of one day of insurance (divide the policy price by the number of days in a year) and multiply it by the number of days in a month. On the date of payment of the insurance premium, an entry is made in the accounting: Debit 76, subaccount “Calculations for property and personal insurance”, Credit 51 - payment of the insurance premium is reflected. Every month, when the insurance premium is written off as expenses, an entry is made: Debit 20 (23, 26, 44) Credit 76, subaccount “ Calculations for property and personal insurance” - the cost of the insurance premium for the current month is included in expenses—————————————————————————
Example 1. Accounting for car insurance costs
Riga LLC applies the simplified tax system with the object of taxation “income minus expenses”. On May 1, 2013, the company purchased a car for production needs and on the same day paid for an MTPL policy for one year in the amount of 8,000 rubles. And on May 7, I purchased another comprehensive insurance policy, also for a year, and paid 40,000 rubles for it. Let's see how accounting for insurance costs will differ with the two accounting methods.
May 1 according to OSAGO
Debit 76, subaccount “Calculations for property and personal insurance”, Credit 51
- 8000 rub. — payment of the insurance premium is reflected;
Debit 20 Credit 76, subaccount “Calculations for property and personal insurance”,
- 8000 rub. — the cost of the insurance premium under the insurance contract is expensed;
May 7 according to comprehensive insurance
- 40,000 rub. — payment of the insurance premium is reflected;
- 40,000 rub. — the cost of the insurance premium under the insurance contract is expensed.
May 1 according to OSAGO
- 8000 rub. — payment of the insurance premium under compulsory motor liability insurance is reflected;
- RUB 679.45 (RUB 8,000: 365 days x 31 days) — compulsory motor liability insurance expenses for May 2013 were written off;
May 7 according to comprehensive insurance
- 40,000 rub. — the cost of comprehensive insurance has been paid;
- RUB 2,739.73 (RUB 40,000: 365 days x 25 days) - comprehensive insurance costs for May 2013 were written off.
Essence of the question. To recognize car insurance costs in accounting, there are two options: write off the cost of the policy immediately or distribute it evenly based on the validity period of the insurance contract.
Memo. The cost of insurance should be taken into account on account 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors” by opening a subaccount for it “Settlements for property and personal insurance”.
In tax accounting under the simplified tax system, you can write off only the cost of compulsory insurance, which is compulsory motor liability insurance (clause 7, clause 1, article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Moreover, as stated in paragraph 2 of Art. 263 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, you can include the amount of insurance in expenses only within the limits of tariffs (clause 2 of Article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). However, you do not need to calculate these rates yourself.
Since insurance companies determine the amount of the insurance premium to be paid taking into account these limits, depending on the category of your transport: truck, passenger car, bus, etc. (clause 10 of the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated 05/07/2003 N 263). Consequently, you will need to take into account the costs of the “simplified” policy the entire paid cost of the policy immediately after its payment (clause 2 of Article 346.
17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), and it is impossible to write off the price of insurance as expenses on a monthly basis based on the period for which it was issued, as in accounting. After all, “simplers” are not subject to the requirement to evenly account for such expenses in tax accounting. It is established only for income tax payers (clause 6 of Article 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Question | Answer |
| Rent | |
| Is it possible to include rent in expenses under the simplified tax system? | Yes, after paying the landlord, include the entire amount of the rent in the tax base under the simplified tax system (subclause 4, clause 1, article 346.16 and clause 2, article 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) |
| What documents will justify payment of rent? | Lease agreement and vehicle acceptance certificate |
| Is it necessary to withhold personal income tax if rent is transferred to an employee for the use of his car? | Yes, since the rent in this case is the employee’s income. Therefore, when paying it, withhold and pay personal income tax to the budget (subclause 4, clause 1, article 208 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). This must be done no later than the day following the day the employee actually receives rent. |
| Is rent paid to an employee for the use of his car subject to insurance premiums? | The rental payment is not subject to insurance premiums if a vehicle rental agreement is concluded without a crew. The fact is that insurance premiums are not charged for remuneration under civil contracts related to the transfer of property for use (Clause 3, Article 7 of Federal Law No. 212-FZ of July 24, 2009, hereinafter referred to as Law No. 212-FZ) . When renting a car with a crew, the rental amount itself transferred to the employee will not be subject to contributions. But driving a car is already a service provided by an employee. And insurance premiums will have to be paid on the cost of this service (Clause 1, Article 7 of Law No. 212-FZ). In a car rental agreement with a crew, the remuneration amount must be divided into two parts: the rental fee itself and the fee for the provision of driving services. This will reduce the amount of insurance contributions to extra-budgetary funds. |
| Rented car repair | |
| Is it possible to take into account the cost of car repairs? | To take into account repair costs, indicate in the rental agreement that the cost of maintaining the car is borne by the renter. Then such expenses will be justified and will reduce the tax base under the simplified tax system in full (subclause 3, clause 1, article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) |
Condition | Content |
| Subject of the agreement | Indicate how the vehicle is transferred - with a crew or not. Describe the vehicle (clause 3 of Article 607 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). Indicate its make, year of manufacture and color, body and engine number, state registration number. If renting without a crew, it is also better to indicate the mileage and technical characteristics of the car. In addition, in this case, the lessor must give the lessee a vehicle registration certificate, a technical passport and a vehicle inspection certificate. |
| Rent amount | Specify the amount of rent and the procedure for its payment (Articles 614 and 654 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation) |
| Rental period | If you do not indicate the rental period of the vehicle, then it is considered that the agreement is concluded for an indefinite period. |
| Vehicle repair | According to the general rules, the lessee is obliged to carry out repairs of the vehicle (Article 644 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). However, a different procedure can be established in the contract. For example, this: “The Lessor is obliged, if necessary, to carry out major repairs of the Vehicle at his own expense. The Lessee is obliged to maintain the Vehicle in proper condition and carry out routine repairs of the vehicle at his own expense.” |
| Having a power of attorney giving the person the authority to rent a car | As a general rule, the right to lease property belongs to its owner (Article 608 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). However, any person can enter into a lease agreement on behalf of the owner. The main thing is to have a power of attorney. Without a power of attorney, the car rental agreement with a non-owner is considered invalid. Consequently, expenses under such an agreement will be recognized as unjustified as contrary to the law. At the same time, notarization of such a power of attorney is not required; it can be drawn up in any form (Articles 163 and 186 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation) |
Compensation for losses under the MTPL policy under the simplified tax system
The company has the right to terminate the contract with the insurer, for example, when selling a vehicle. In this case, part of the previously transferred premium (minus the amount attributable to the period during which the contract was actually in force) is returned to the policyholder’s account and reflected in the accounting debit of the account. 51 from credit account 76.
Example:
Let's go back to the previous example. Let’s assume that the car was sold on May 20, 2019. The company notified the insurance company of this in writing, declaring the termination of the contract and the return of funds paid for the period from 05/21/2019 to 03/31/2020.
The refund amount is calculated as follows:
CB = 15000 - 15000 / 365 days. x 50 days (30 days in April + 20 days in May) = 12945.21 rubles.
Also, in case of early termination of the contract, insurance companies can withhold the amount of expenses for conducting the case (23% of the premium amount), but the exact conditions of the return must be clarified with your insurer.
In accounting, the received amount of compensation is reflected in the structure of other income by postings:
| Operation | D/t | K/t | Sum |
| The insurer has decided to pay the balance under compulsory motor liability insurance | 76 | 91/1 | 12945,21 |
| Receipt of insurance compensation | 51 | 76 | 12945,21 |
In the same way, insurance compensation for damage from an accident is recorded in accounting, provided that the driver is innocent.
Example:
For the operation of a passenger car in an auxiliary facility, on April 1, 2019, the company purchased an MTPL policy worth 12,000 rubles. for a year. According to the accounting policy, the costs of purchasing a policy are written off in full after payment. In May 2021, an accident occurred, the damage amounted to 20,000 rubles. and was reimbursed by the insurer of the person at fault. The car was repaired for the same amount.
The listed transactions will appear in accounting as follows:
| Operation | D/t | K/t | Sum |
| The insurance premium for compulsory motor liability insurance has been paid. | 76 | 51 | 12 000 |
| The costs of purchasing the policy are taken into account | 29 | 76 | 12 000 |
| Repair work to restore the vehicle was reflected and paid for | 29 60 | 60 51 | 20 000 20 000 |
| Compensation under MTPL: | |||
| — accrued | 76 | 91/1 | 20 000 |
| - received | 51 | 76 | 20 000 |
The amounts of compensation received upon the occurrence of an insured event under compulsory motor liability insurance are taken into account as part of non-operating income for calculating the base for the single tax (clause 1 of article 346.15 and clause 3 of article 250 of the Tax Code) upon receipt of them to the current account or to the cash desk of the company.
Vehicle repair costs are recognized as expenses in the period in which they were incurred, in the amount of actual expenses (clause 1 of Article 260 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), even if the amount of insurance compensation established by the contract exceeds (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 03-03-06/2 /70 dated 03/31/2009).
Car expenses – Elba
Often, individual entrepreneurs using the simplified tax system “Income minus expenses” use a personal car in business. Let's figure out whether it is possible to take into account the costs of its purchase and maintenance when calculating the tax.
Costs of purchasing a personal car
Before taking costs into account in the simplified tax system, think about how to prove to the tax authorities that you are using the car for business. The further your type of activity is from transportation or travel, the more difficult it is to do this.
An example from life: an individual entrepreneur is engaged in the installation of metal-plastic structures and takes into account the cost of a passenger car, which he, according to him, uses to “receive orders, take measurements and deliver components.” The tax office recognized this as unlawful, “since the entrepreneur carries out a type of activity that is not related to freight and passenger transportation,” and assessed additional taxes, penalties and fines.
The entrepreneur began to sue the tax authorities, and courts of various instances supported him. Remember the key phrases from the court ruling - they will be useful in case of disputes:
- “The car was purchased and used by the entrepreneur directly in the process of business activity, with the aim of generating income from this type of activity, and the tax authority’s arguments about the use of the vehicle for personal purposes are speculative.”
- “Tax legislation does not contain restrictions on including in expenses the costs of purchasing and servicing vehicles purchased for business activities. In this regard, the inspectorate’s arguments that expenses are accepted only when carrying out activities related to freight and passenger transportation are not based on the law.” (Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Ural District dated October 18, 2007 in case No. F09-8532/07-S3).
But you cannot hope that there will be no more claims from the tax office. The Ministry of Finance, in a letter dated March 26, 2008 No. 03-04-05-01/79, states that “a passenger car used by an individual entrepreneur to travel to the bank, tax inspectorates, technical service centers, to buyers and suppliers to conclude contracts, is not may be recognized as a primary means.”
It turns out that you are taking a risk if you take into account the costs of purchasing a car that is not necessary for your business. You may have to prove your position in court. But there is no guarantee that the court's decision will be as favorable.
Once again : first decide whether you can prove to the tax authorities the benefit of a personal car for business. What do you use it for? Does it help you generate income? Why can't you generate income without it? If you have answered these questions and even rehearsed the answer with a skeptical friend, you can take into account the costs of purchasing a car in the simplified tax system.
Costs for using a car
You can include the costs of operating a car - primarily the purchase of fuel - in the costs of the simplified tax system if you drove it on business. If you are in the transportation business, the costs are classified as material expenses, and if you are in another business, they are classified as business vehicle expenses.
To take into account the cost of purchasing gasoline, ordinary gas station receipts are not enough. You need to confirm your travel route—usually waybills are used for this. The form of waybills is approved only for motor transport enterprises. If you have a different business, come up with your own form.
Free form waybill template
Waybill template for transportation of passengers and cargo
It is likely that tax authorities may have the opinion that individual entrepreneurs’ fuel costs should fall within the standards established by the “Methodological recommendations for the consumption of fuels and lubricants in road transport”, approved by order of the Ministry of Transport of the Russian Federation dated March 14, 2008 No. AM-23 -R. Therefore, it is better for individual entrepreneurs to familiarize themselves with this document and comply with its standards.
It is easier to defend the accounting of gasoline costs in the simplified tax system than the costs of purchasing a personal car, but still the risk of a dispute with the tax authorities remains.
Once, an arbitration court prohibited an individual entrepreneur from taking into account such expenses: Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the West Siberian District dated February 26, 2008 No. F04-1130/2008(973-A45-34.
There we are not talking about the taxpayer of the simplified tax system, but the court’s arguments are universal - a car is not a fixed asset, therefore the costs of its use should not be included in expenses.
Other operating expenses, such as car wash or secure parking, are even more likely to raise tax questions. Therefore, it is better not to take risks with them at all.
The article is current as of 02/04/2021
Accounting for costs and compensation under OSAGO “Income” under the simplified tax system
For enterprises operating under the simplified tax system “Income”, vehicle insurance costs do not affect the calculation of tax, since almost all costs are not taken into account in the tax base, and tax is calculated on the amount of income received.
In accounting, the entries reflecting the purchase of an MTPL policy, the return of funds upon termination of the contract and compensation for damage are identical to the entries that apply the simplified tax system “Income reduced by expenses.”
But compensation under OSAGO under the simplified tax system “Income” is taken into account as part of non-operating income, since clause 3 of Art. 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation includes compensation for losses and damages, including the amount of insurance compensation under compulsory motor liability insurance, although the costs of vehicle repairs are not included in the calculation of the tax.
Is it possible to include MTPL insurance in expenses?
Questions and answers on the topic
An agreement has been concluded between the organization and the employee for the free use of a car. The organization includes the costs of vehicle maintenance and fuels and lubricants as expenses. Can an organization include insurance in expenses (MTPL)
Yes, your company can include the cost of compulsory motor liability insurance in the expenses under the simplified tax system, but only if it is obliged to pay for compulsory liability insurance in accordance with the gratuitous use agreement. If the contract does not contain such a condition or the insurance costs are borne by the lender, then the cost of compulsory motor liability insurance cannot be taken into account under the simplified tax system. Let's explain in more detail.
MTPL insurance is mandatory (Federal Law dated April 25, 2002 No. 40-FZ). And the expenses for compulsory insurance of property, employees and liability “simplified” have the right to reflect in the tax base (subclause 7, clause 1, article 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Moreover, immediately after payment (clause 2 of Article 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
So if your organization uses a car in its activities, you have the right to take into account the costs of compulsory motor third-party liability insurance in the tax base under the simplified tax system. But only on the condition that the gratuitous agreement states that such expenses are paid by the borrower, that is, your organization.
There is a letter from the capital's tax authorities with similar explanations regarding the accounting of expenses for compulsory motor liability insurance for a rented car (letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia for Moscow dated November 20, 2006 N 18-11/3/102521). And according to paragraph 2 of Article 689 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the rules provided for in the articles regulating the lease are applied to the agreement for gratuitous use. So all the explanations regarding the costs of a rented car can also be attributed to the costs under a contract for gratuitous use.
Insurance premium rates
In 2017–2019, the total rate of insurance premiums is 30% if payments to the employee, calculated on an accrual basis from the beginning of the year, do not exceed the income limit. If payments exceed this limit, then amounts exceeding the maximum income limit are subject to contributions to compulsory pension insurance at a rate of 10% (Article 426 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The same rules were in effect in 2021.
In 2021, the income limit for calculating pension insurance contributions is 876,000 rubles and 755,000 rubles for social insurance contributions. Health insurance premiums must be paid on all payments made to employees.
A reduced rate of 20% applies to payers with a confirmed main activity (at least 70% of total receipts): construction; production (food products, mineral waters, shoes, furniture, etc.); social (education, healthcare) and household (shoe repair, car repair) spheres, etc. These “simplified people” (if their annual income does not exceed 79 million rubles) pay only pension insurance contributions at a rate of 20%.
The full list of preferential types of activities in accordance with OKVED2 (OK 029-2014) is given in subparagraph 5 of paragraph 1 of Article 427 of the Tax Code.
Read also “Reduced rates of insurance premiums under the simplified tax system”