Accept is not only a famous rock band from Germany, but also an important legal term. The word “acceptus” (“accepted”) comes from the Latin language and has many centuries of history. Such a simple term for consent has meaning in the right-wing world. He affirms the concept of free contract: no one can be forced to enter into an agreement against their will. What is an offer and what is an acceptance? Where are these terms used and what is their essence? Let's talk about this in more detail.
Accounting for settlements with suppliers and contractors in accounting
The receipt of material assets, works, and services from suppliers is carried out on the basis of concluded supply, contract, commission, power supply, etc. contracts.
Primary documents for accounting for settlements with contractors include invoices (TORG-12), acts of service provision, invoices and other documents issued by contractors and suppliers, as well as bank and cash payment documents:
To reflect information about settlements made with suppliers, a separate accounting account is used - 60. This account is active-passive, so in accounting it can be displayed both in credit and debit turnover:
- The debit of this account displays the amounts of fulfilled obligations - advance payments and full mutual settlement. It should be noted that the amounts of payments made are taken into account separately.
- The loan takes into account the cost of purchased goods and services. Lending is carried out on the basis of settlement documents received from the supplier.
Analytical accounting is carried out in the context of presented invoices. In addition, proper accounting for this account allows you to group suppliers by payment terms, uninvoiced deliveries, bill transactions, etc.
Where and when is acceptance used these days?
Now acceptance is used in banking payments, lending, and business. The rules for concluding public contracts in online trading also require issuing offers and receiving acceptances. Let us consider the conditions for the use of acceptance in various fields of activity.
Acceptance in lending
Bank acceptance, or loan acceptance, is the conclusion of a loan agreement. The bank transfers funds to the borrower on the terms previously determined between the parties. How does this happen in practice?
You applied for a loan by filling out a form on the bank's website. You indicated the required amount and loan term, indicated your monthly income, and selected additional options in the form of insurance or bank cards.
The bank regards such actions as your desire to enter into a loan agreement. After the system processes the questionnaire, a bank employee will call you and inform you about the offer that has been created for you - an offer to sign a loan agreement under certain conditions or about the bank’s unwillingness to lend to you. Next, you will be invited to the branch to sign a loan agreement. By signing a loan, you accept the bank's offer to provide a loan.
Acceptance in settlements between organizations
Preliminary and subsequent acceptance are used in bank payments. Their main difference is in determining the point in time when the payer gives his consent to pay the payment document. This is relevant when settlements between organizations occur using payment orders.
Nowadays, preliminary acceptance is predominantly used in settlements. In this case, calculations occur according to this scheme. The supplier submits a payment request-order to the payer's bank, the bank notifies the payer about the document and waits three days. If after three days the payer does not receive a written refusal to pay, the request-order is considered accepted and the money is transferred to the supplier.
Unlike the preliminary one, with the subsequent type of acceptance the money is transferred to the supplier immediately, on the day of receipt of the payment document. But he can use them only after three days. These three days are given to the payer to return the funds in cases where he does not agree with the payment request-order and refuses.
Such a refusal can be either complete - the entire amount is returned, or partial - when only part of the money is returned. The reasons for refusal to accept are most often violations in deliveries, assortment of goods, delays in the completion of work and other cases of violation of agreements.
The main advantage of payments made using acceptance is the acceleration of settlements. The supplier himself issues a payment document and presents it to the payer's bank.
Acceptance of letter of credit
Payments using a letter of credit are one of the modern forms of non-cash payment. Typically used under supply contracts. A letter of credit is an order from the accepting bank to another bank that maintains the current account of the offering supplier. The participation of banks guarantees the reality of delivery and controls the completion of the transaction between organizations. The letter of credit specifies the amount, terms, delivery conditions and other conditions. Read the separate article for more details:
For example, you sold a batch of grain to a foreign partner. After the goods have been shipped, your employee provides supporting transport documents to the bank. The bank checks and issues a letter of credit for the delivery amount to the bank where your buyer has an account. Then you receive money without waiting for the grain to arrive at its destination. The bank gives you this money. Funds will be debited from the buyer's current account only when the grain arrives. This payment method is convenient for both you and your partner. You received the money and can use it in your activities, and the buyer has no fear that the goods will not arrive.
Depending on the agreements of the parties to the transaction, a letter of credit may or may not require acceptance (consent) from the buyer. Acceptance of a letter of credit means the buyer's confirmation of payment.
Accounting for suppliers and contractors according to account 60
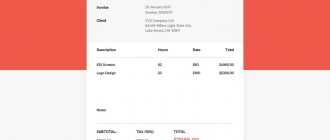
| Account Dt | Kt account | Transaction amount, rub. | Wiring Description | A document base |
| Postings and transactions reflected in the debit of account 60 | ||||
| 60 | 50 | 17 500 | Payment was made from the company's cash desk to the supplier for the material received (posting) | RKO |
| 60 | 51 (52) | 54 000 | Payment to the service provider by bank transfer was made in national (foreign) currency | Payment order, bank statement |
| 60 | 55-1 | 37 900 | The amount of an unused letter of credit has been written off in favor of the service provider | Payment order |
| 60 | 62 | 15 000 | Settlement of counter homogeneous claims has been carried out | Accounting certificate-calculation |
| 60 | 66 | 105 000 | Accounts payable were converted into a short-term loan | Agreement |
| 60 | 67 | 94 000 | Accounts payable were converted into a long-term loan | Agreement |
| 60 | 76-2 | 28 900 | Admitted claims are withheld from funds that were to be transferred to the supplier's bank account | Claim certificate |
| 60 | 91-1 | 39 700 | Inclusion of overdue accounts payable in other income (the statute of limitations has expired) | Accounting certificate-calculation |
| 60 | 91-1 | 28 500 | A positive exchange rate difference was received, which is included in other income | Accounting certificate-calculation |
Paid the contractor's invoice for the wiring work performed
Return by the supplier of excess funds paid to him to the organization's cash desk 51 60 Return by the supplier of excess funds paid to him to the organization's current account 52 60 Return by the supplier of excess funds paid to him to the organization's foreign currency account 76. 02 60 The amount of the claim against the supplier is reflected 91 02 60 Reflection of negative exchange rate differences on accounts payable in foreign currency 94 60 Reflection of shortages upon acceptance of valuables received from the supplier 97 60 Reflection of debt to suppliers for work performed, for which costs are charged to deferred expenses Account 60 in accounting All operations, related to payments for purchased goods, materials, consumed services or accepted work are reflected in account 60, regardless of the fact of their payment.
Postings for settlements with suppliers
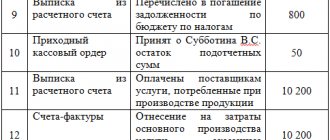
| Account Dt | Kt account | Transaction amount, rub. | Wiring Description | A document base |
| Postings and transactions reflected on account credit 60 | ||||
| 07 | 60 | 480 000 | Equipment that requires additional installation has been registered | Transfer and Acceptance Certificate |
| 08 | 60 | 108 000 | Invoice accepted for payment for purchased fixed assets | Check |
| 10 | 60 | 45 800 | Posting of purchased materials | Purchase Invoice |
| 15 | 60 | 32 750 | The expenses that were incurred during the procurement of inventories are taken into account (if account 15 is used) | Check |
| 19 | 60 | 6 666,66 | VAT is charged on capital assets recorded | Check |
| 20 (25, 26) | 60 | 105 000 | The cost of services performed is included in the main production (general production costs, general business expenses) | Invoice, certificate of completed work |
| 28 | 60 | 29 750 | Services were performed that were included in the costs of correcting the defect | Invoice, certificate of completed work |
| 41 | 60 | 89 000 | Posting of purchased goods | Purchase Invoice |
| 44 | 60 | 18 500 | Marketing services were performed, which were subsequently included in sales expenses | Invoice, certificate of completed work |
| 50 | 60 | 16 800 | Overpaid funds were returned to suppliers in cash. | Receipt cash order |
| 51 (52) | 60 | 16 800 | Funds that were overpaid to the service provider were credited to the company's current (currency) account | Bank statement |
| 76-2 | 60 | 15 500 | The amount of claims against the supplier has been accrued | Accounting certificate-calculation |
| 91-2 | 60 | 25 000 | Accounts receivable for which the statute of limitations has expired have been written off | Accounting certificate-calculation |
| 91-2 | 60 | 68 500 | Accepted invoices for payment related to the disposal of fixed assets | Invoice, certificate of completed work |
| 91-2 | 60 | 88 000 | A negative exchange rate difference was accrued on accounts payable | Accounting certificate-calculation |
| 94 | 60 | 26 900 | The shortage received upon receipt of goods and materials from the supplier is reflected | Claim certificate |
| 97 | 60 | 12 800 | Debt to the supplier is included in deferred expenses | Claim certificate |
Accounting account 60 is an active-passive account “Settlements with suppliers and contractors”, opens the “Settlements” section of the chart of accounts and serves to summarize information on all types of settlements of the organization:
- With various legal entities and individuals;
- Including on-farm payments.
All transactions related to payments for purchased goods, materials, consumed services or accepted work are reflected in account 60, regardless of the fact of payment. Account 60 is credited according to the supplier's settlement documents, debited for the amount of fulfillment of obligations, that is, payment of bills, including advances and prepayments, in correspondence with cash accounts, etc. In this case, the amounts of advances issued are accounted for separately in a separate sub-account.
For account 60, analytical accounting is maintained for each supplier invoice received, and settlements are made in the order of scheduled payments, that is, for each supplier separately.
Types of settlements on account 60:
Bankers' acceptances
The main purpose of bank acceptance is to guarantee the reality of the transaction and compliance with all its conditions. The parties can conduct transactions with bank acceptance while being not only in different cities, but also in different countries. The bank guarantees financial security.
Most often, bills of exchange are used in such transactions. A promissory note is an obligation of a debtor to pay an agreed sum of money within an agreed upon time. The bank accepts the bill - that is, it confirms that the payer has money that will actually be paid after some time.
When paying with bills of exchange, there are several types of acceptance:
- guarantor - a bank or a third party undertakes the obligation to execute the bill payment;
- intermediary - a third party is ready to take responsibility based on the terms of the contract;
- unconditional - the party accepting the bill fully and without reservation agrees with all the terms of the transaction;
- conditional - the parties establish the conditions under which the bill will be accepted; if the conditions are not met, the contract is canceled;
- local – when the fee is paid in a strictly defined place;
- limited - the party that accepts the bill is ready to accept it, but minor changes in the terms are required (for example, changing the timing of payment of the bill).
Acceptance of a bill gives confidence that all terms of the transaction will be met and speeds up the transaction.
The conclusion of contracts always begins with negotiations. Citizens and organizations are free to negotiate; they independently and voluntarily determine the conditions and rules for concluding agreements.
How to accept a contract
Accepting a contract means expressing your agreement with its terms. The process of accepting a contract consists of several stages:
- Stage No. 1. You receive an offer that describes the terms of the transaction;
- Stage No. 2. You carefully study all the terms of the proposed contract. If necessary, engage specialists who will give an opinion on the possibility of executing such an agreement;
- Stage No. 3. You accept the contract or refuse. If there are no objections, you can put an o on the draft agreement and sign it;
- Stage No. 4. Notify your contract partner of the decision made.
Acceptance of a contract is an important component of the contractual relationship between the parties. Without it, the contract will not be considered concluded.
Deadlines for accepting the contract
As a general rule, the deadline for acceptance - a response to an offer - is established by the offeror in the text of the offer. It is very important that the acceptance is received exactly within the specified time frame. Therefore, if you accept the contract in writing, it is worth considering the time required to send the documents. Sending an acceptance by mail on the last day of the deadline is a sure way to be late with consent.
Sometimes the offer does not specify a deadline for accepting the terms of the contract. In this case, the acceptor has two options. He can give his consent verbally and begin to execute the contract. Or send a written acceptance to the offeror no later than 1 month after receiving the offer.
If the offeror receives acceptance after the specified time, he can inform the acceptor and confirm acceptance of the acceptance. In this case, the contract will be considered agreed and concluded.
Typical wiring
Let's look at the main transactions for account 60 in the table:
| Account Dt | Kt account | Wiring Description | A document base |
| 07/10/41 | 60 | Payment to the supplier for equipment/materials/goods | An invoice for payment |
| 60 | 50.01/51/52 | Payment of debt to the supplier | |
| 94/76 | 60 | Write-off of shortages within the normal natural loss/in excess of the norm, in case of an error or price discrepancy | Acceptance certificate |
| 19 | 60 | VAT on purchased assets | Invoice for payment, invoice |
| 50/51/52 | 60 | Payment of invoice to supplier/contractor | RKO, extract from current or foreign currency account |
| 10/15/41 | 60 Non-faculty supplies | Material assets were capitalized without invoices for payment | Material acceptance certificate |
| 60 Non-defective deliveries | 60 | Payment of invoices for previously recorded materials without payment documents | An invoice for payment |
| 60/91.02 | 91.01/60 | Writing off exchange rate differences on an account, positive/negative | Calculation |
| 91.02/63 | 60 Advances issued | Write-off of advance payment not returned by the supplier/contractor at the expense of profit/reserve for doubtful debts | Reference |
Analysis of account 60: balance sheet, account card
The balance sheet for account 60 is a report in the form of a table, which presents the beginning and ending balances, turnover for the selected period by account or subaccounts, subaccounts, currency amounts, and expanded balance.
An account card is a report with details down to the posting (account).
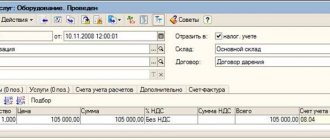
You can analyze mutual settlements and the movement of documents for settlements with suppliers in the 1C Enterprise Accounting program using standard reports Account Card and Turnover Balance Sheet (hereinafter referred to as SALT) for account 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” with a specific counterparty or in general for all.
It is correct to do this according to subaccounts:
- Subaccount 60.01 reflects the settlements with suppliers themselves;
- Subaccount 60.02 reflects advances issued.
In SALT, the balance on subaccount 60.01 is reflected as a credit, and the balance on subaccount 60.02 is reflected as a debit.
For example, when posting a bank, if it is paid to the counterparty on an invoice, then the goods are received and the payment should be reflected in the debit of subaccount 60.01. If there was an advance payment for goods or materials to the counterparty, then - by debit of subaccount 60.02.
If the posting is done incorrectly, then the balance with a minus will “hang” in the SALT for account 60. If there is a minus balance on the loan of the subaccount 60.01, this means that the prepayment was reflected incorrectly, not on the subaccount 60.02.
Example
Snegir LLC transfers an advance to Bor LLC for goods in the amount of 23,600 rubles. A few days later, the goods arrived from the supplier on account of the previously issued advance in the amount of 23,600 rubles.
Postings to account 60 for the advance payment issued to the supplier:
| Account Dt | Kt account | Transaction amount, rub. | Wiring Description | A document base |
| 60.02 | 51 | 23 600 | Transfer of advance payment to Bor LLC | Payment order/Bank statement |
| 10/41 | 60.01 | 20 000 | Receipt of goods from Bor LLC | Waybill, invoice |
| 19 | 60.1 | 3 600 | We allocate VAT | Waybill, invoice |
| 60.01 | 60.02 | 23 600 | We count the advance from the prepayment | Reference |
Forms of expression of acceptance
Now it is difficult to imagine that the person concluding an agreement will go out into the middle of the square and solemnly inform those around him of his intention. Over the centuries, the forms of expression of acceptance have changed. Nowadays, acceptance is consent, expressed in writing or in another way. Let's look at how to correctly accept an offer:
- Written acceptance. This is the name given to sending a written notification of acceptance to the opposite party or directly signing the agreement as a document. You were provided with an agreement form - you signed it. It's simple. By the way, the written form implies not only the execution of a single contract form. Written acceptance is considered received if a scan of the document is transmitted via email, fax, telex, or other modern communication channels.
- Public form of acceptance. A new method that allows you to confirm your consent to an offer made to an unlimited number of people. Examples of a public offer are goods in a store, contracts posted on websites, vending machines. When purchasing in an online store, you will accept (agree with the public offer) when you check the special box on the site. This way you confirm your agreement with the terms of sale and the properties of the selected product.
- Actual actions of the person for whom the offer is intended. In some cases, you can express your consent to the terms of the contract at the time of performing certain actions. If you bought a ticket to travel on a bus, you have agreed to the terms and conditions for the carriage of passengers. We filled out the guest card at the hotel - in fact, we accepted the rules of living in it.
- Conclusive actions of a person. This is the behavior of a party that shows its desire to enter into an agreement. An excellent example of such actions is paying a received invoice. Regardless of the conclusion of a paper contract, the person who paid the invoice agrees that the goods or services specified in the invoice will be provided to him.
Sometimes a dispute arises about how to speak correctly - to accept or to accept. The meaning of the word “accept” is similar and means the same thing as “accept”. The common verb is to accept.
Posting the transfer of debt to suppliers
Each entity of financial and economic activity is required to keep accounting records for all types of mutual settlements with its counterparties. The latter refers to enterprises that supply a variety of materials, raw materials, goods and other inventory items, provide various services, or perform some kind of work.
Any mutual settlements with counterparty enterprises take place in the enterprise’s accounting department under account No. 60, which has a similar name: “Settlements with suppliers and contractors.” Information on it for each counterparty is shown separately. According to the purposes of management accounting, various sub-accounts can be opened for it. In this article we will examine in detail the accounting features of transferring debt to suppliers.
Accounting for repayment and write-off of debt to suppliers
In its structure, account No. 60 is active-passive: its debit records the amounts of obligations fulfilled to suppliers (taking into account advances and prepayments), its credit records the cost of completed work (services rendered) accepted for accounting in correspondence with the corresponding accounts for their accounting.
The basis for the entry is such primary documents from the supplier as a delivery note, a certificate of completion of work, an invoice, etc. In practice, management accounting is more often maintained by enterprises in the context of specific invoices presented for payment. A well-structured individual chart of accounts for a specific organization can allow for separate accounting, for example, by the maturity of debts, uninvoiced supplies, etc.
Important! All transactions taking place on account 60 must be reflected on it in a timely manner and regardless of the fact of payment. All received inventory items are reflected strictly in the same amount as they were determined in the provided settlement documents.
For uninvoiced deliveries, the invoice will be credited for the value stated in the valid contract between the buyer and supplier.
Repayment of debt to the supplier (contractor) is reflected in the debit of account 60
Any resulting accounts payable to any suppliers of goods and materials and services can arise exclusively in two cases:
- when the organization has not paid its counterparties for the goods (services) supplied;
- when any advance payment has been received, but the organization has not yet fulfilled its obligations.
Let us remind you that any outstanding accounts payable must be written off within the time limits established by PBU No. 34. Business rules usually operate for a period of three years (the statute of limitations).
Accounting for all financial transactions with counterparties can also be kept in journal order No. 6, which combines both analytical and synthetic accounting.
Any resulting debt is written off as a debit to the account we are considering.
Below are examples of such operations:
| D | TO | Description |
| 60 | 50 | The accumulated debt to suppliers was transferred from the company’s cash |
| 60 | 51 | A similar debt of the enterprise to suppliers was repaid/paid from the current account |
| 60 | 52 | Repayment of a similar debt in foreign currency |
| 60 | 62 | Settlement of counterclaims |
| 60 | 76 | Withholding the amount of the claim from accounts payable to the counterparty |
| 60 | 91 | Outstanding accounts payable are included in the company's expenses |
If three years have passed since the indebtedness to the supplier (contractor) arose (that is, the statute of limitations has expired), then you must write it off
Transfer of advance payment to the supplier
If an advance is transferred to the supplier in advance, then a sub-account with the same name “Advance issued” should be opened on account 60. After receiving the delivery for which the advance was issued, it is offset by the following entry: D60 K60 (subaccount “Advance issued”).
Let's give an example: organization “One” transferred an advance payment to its supplier organization “Two” in the amount of 100,000 rubles. A week later, goods from organization “Two” arrived at organization “One” for the full cost of the advance payment.
At the time of transfer of the advance, “Odin” makes the following entry:
D 60/2 K 50 (51.52) 100,000 rubles (based on a payment order or bank statement).
In a week we will receive the goods received:
D 10 (41) K 60/1 84,446 rubles (based on the delivery note, invoice).
We immediately note VAT:
D 19 K 60/1 15,254 rubles (100,000 * 18: 118) (based on invoice).
And we offset the advance:
D 60/1 K 60/2 100,000 (based on a certificate).
If you do not want to exercise the right to deduct VAT on advances paid to the supplier, do not use it. Applying such a deduction is your right, not your obligation.
Paying off debt in cash
Repayment of debt to the supplier for goods in cash from the company's cash desk is reflected in the following entry: D 60 K 50.
In this case, various subaccounts to account No. 50 can be used:
- 1, if the money is issued from the main cash register of the enterprise;
- 2, if the money is issued from various commodity cash desks: post offices, commodity offices, etc.;
- 3, if bills of exchange and similar monetary documents were used.
Requirements for acceptance
In business document flow, special rules and requirements for acceptance are established:
- Acceptance of the offer must repeat its terms; changing the clauses of the contract is unacceptable;
- You cannot violate the deadline set for acceptance. In cases where no time period is specified, a reasonable period of time is considered acceptable. In business, a period of one month is considered reasonable. Usually this time is enough to think and send consent to acceptance or refusal to partners;
- If a written offer is received, the acceptance must also be formalized in the form of a response letter or agreement;
- Revocation of acceptance is possible. However, the offeror must receive notice of the revocation before or at the same time as the acceptance. For example, you are in St. Petersburg, and your partners are in Kazan. Having received the contract from them, you accepted it and sent it by courier service. Mail delivery time is 3 days. For some reason, the next day you change your mind. Send your revocation of acceptance by email or telegram. Thus, the offeror will receive a refusal to accept before the signed contract itself.
Invoice accepted: posting
Update: July 6, 2021
To correctly reflect the acceptance of an invoice in accounting, as well as to understand which entry will reflect a fact of economic life in which, for example, a supplier’s invoice for received materials is accepted, a clear understanding of what fact of economic life is meant by this definition is necessary. The concept of acceptance is given in Art. 428 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, which explains that acceptance is a response to full and unconditional acceptance of the terms of the offer. In accounting, invoice acceptance is considered based on this regulatory definition.
How to record the implementation of works (services) in accounting
The second option is when the customer refused to accept the work because he discovered shortcomings (inadequate quality). In this case, the customer is obliged to justify his refusal by making appropriate entries in the acceptance and transfer documents (clauses 1 and 2 of Art.
720 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). In such a situation, do not recognize income. Tax legislation regards work not justifiably accepted by the customer as work in progress (clause 1 of Art.
319 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In addition, in agreement with the customer and subcontractor, correct the compiled primary documents: acts of acceptance of work performed (on form No. KS-2) and certificates of the cost of work performed and expenses (on form No. KS-3). Corrections in them must be certified by the persons who previously signed these documents, indicating the date the adjustments were made (Part 7, Article 9 of the Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ).
The first option is when the contractor completed the work on time, but the customer did not show up to accept it and did not show such intention. In such a situation, sign the act of acceptance and transfer of completed work unilaterally with a note indicating the customer’s refusal to sign the act for no apparent reason (clause 4 of article 753 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). The date the act is signed by the executor unilaterally will be the date on which the income must be reflected (clause
1, 3 tbsp. 271 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Arbitration practice recognizes as legitimate the fact of transferring the results of work by signing a certificate of work performed unilaterally in the case where the customer had no justified reasons for refusing to sign the report (see, for example, paragraph 14 of the information letter of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated January 24, 2000 No. 51, resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Ural District dated May 18, 2011 No. F09-1885/11-S4, Moscow District dated May 19, 2011 No. KG-A40/3985-11).
Tax legislation understands a service as an activity whose results do not have material expression and are sold and consumed in the process of this activity (Clause 5 of Article 38 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The drawn up act only formally confirms that the service has been provided.
Therefore, income from the sale of services must be reflected on the date of their actual provision (clause 1, article 39, clause 3, article 271 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
A similar point of view is contained in letters from the Federal Tax Service of Russia for Moscow dated September 2, 2008 No. 20-12/083102 and dated April 30, 2008 No. 20-12/041989.
The concept of acceptance in accounting
The concept of acceptance, based on the above definition in the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, is applicable to an offer. In turn, an invoice for payment can be considered as an offer in which the seller (supplier) offers the buyer to purchase a certain product or service for a certain amount. According to Art. 435 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, an offer is recognized as a specific proposal sent to addressees (one or more), which fully expresses the intention of the person who sent it to enter into a contractual relationship with the addressee. In the case of acceptance of an invoice, such an action is its full or partial payment. Thus, in order to reflect the acceptance of the invoice, it is necessary to reflect the entries for the accrual of debt, the accrual of VAT, if necessary, and the payment made on this invoice.
In the business tradition, in particular, an approach is used according to which an invoice is called accepted if the responsible person has agreed to pay it (the invoice has been endorsed for drawing up a payment order to the bank).
Composition of an invoice for payment of goods, works and services
The definition of an offer does not regulate the list of information that an invoice for payment should contain. The only requirement for an offer is a listing of the essential terms of the contract, for example, the subject of the contract, the amount of the contract, details of the parties.
Invoices for payment are not included in the list of primary documents, since they do not reflect a fait accompli of the economic life of the enterprise, and therefore the composition of the invoice information is not rigid. Typically, a company develops its own form on which invoices are issued. According to business traditions, the invoice includes:
- invoice number and date;
- name of organizations (seller and buyer);
- addresses and details of both parties for the possibility of paying the invoice;
- list of goods or services sold;
- their number;
- units of measurement of goods (pieces, packages, kilograms, etc.);
- price;
- total invoice amount.
Accounting entries to reflect acceptance
The most relevant business transactions for which an invoice can be accepted are:
- purchasing materials or services, including utilities;
- transportation of inventory items not included in their cost;
- supply and installation of equipment.
To reflect facts of economic activity related to accepted supplier invoices for goods or services, the following entries are used:
Results
So, acceptance is a positive response from a citizen or company to whom a commercial offer is made. In some cases, it means agreement to enter into a contract, in others it means to purchase goods or services, and sometimes it means approval of a settlement. To give acceptance, you must first receive an offer.
Special rules and deadlines are established for acceptance. If they are violated, the contract is considered unconcluded.
In everyday life, we often come across offer and acceptance. This happens when making purchases, when ordering air tickets and many other everyday situations. However, in colloquial speech these terms are practically not used. These are more legal concepts, which, nevertheless, are useful to know for people far from jurisprudence.
Video for dessert: Squirrel knocked on the window every day
Accepted bill for electricity, gas, water
Dt 20, 23, 25, 26 Kt 60 – debt accrued to suppliers for work performed and services rendered, incl. provision of energy, gas, steam, water for production needs, experimental work and maintenance.
Dt 60 Kt 50, 51 – the utility bill has been paid.
From the above examples it is clear that in order to reflect an accepted invoice from suppliers of materials and services, it is necessary to reflect in accounting the accrual of debt on a loan and the occurrence of a corresponding asset in debit, the accrual of VAT on purchased values and payment of the invoice.
Accountants of enterprises often encounter the concept of acceptance in the process of mutual settlements with counterparties. What does “accepted invoice” mean under Russian civil law? How to reflect in the company's accounting a transaction when a supplier's invoice is accepted. What kind of wiring is this? Let's look at the regulatory features.
The invoice of the transport organization for the delivery of materials has been accepted
If materials were delivered to the buyer at the buyer’s expense, then it is necessary to record the cost of delivery by including it in the cost of materials:
| Dear visitors! The site offers standard solutions to problems, but each case is individual and has its own nuances. |
| If you want to find out how to solve your particular problem, call toll-free ext. 504 (consultation free) |
Dt 10 subaccount “TZR Kt 60, 76 – debt accrued to suppliers for the delivery of materials.
Dt 60, 76 Kt 50, 51 – the invoice for the delivery of materials has been paid.
Dt 19 Kt 60, 76 – VAT is charged on transport services.
Acceptance of an invoice is...
The term invoice acceptance is regulated in stat. 438 Civil Code of the Russian Federation. According to this norm, acceptance is the unconditional and complete acceptance by the recipient of the addressed terms of the offer. In turn, an offer is a proposal for cooperation addressed to one person (or several), containing specific contractual terms. By its legal essence, acceptance implies the unconditional fulfillment of the obligation of the buyer of the product to pay the full cost of the product (or service). You cannot transfer funds partially or set your own conditions for fulfilling obligations.
An accepted invoice is the acceptance of consent to pay for a received document by non-cash debit. In this case, the exact terms of debt repayment are approved in the agreement with the supplier. This is the most common option for mutual settlements between consumers and utility service providers. In this situation, a contract for the supply of, for example, electricity is previously concluded, which specifies the terms of payment. The buyer is then issued an invoice, which goes directly to the bank based on an additional agreement between the bank and the client. And finally, the financial institution repays the acceptance within the established time frame, that is, debits the funds from the payer’s account in favor of the electricity supplier.
What is acceptance
In a broad sense, “acceptance” means the consent of a citizen or company to enter into a contract. The simplest example of acceptance is the purchase of goods. Imagine that you came to the store and saw pickled cucumbers, with a price tag next to it - 95 rubles. Having taken the jar, you go to the checkout and pay for your purchase. That's it, this is acceptance. You agreed to enter into a contract for the purchase and sale of pickled cucumbers at the price offered by the store.
In the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, several articles are devoted to acceptance (Article 438 – Article 443, Article 621). All of them are related to the contracting process. And this is no coincidence. Acceptance is a mandatory stage in concluding any contract. Closely related to this concept is the term “offer” - an offer to sign an agreement on specified conditions.
It all always starts with a proposal, where one of the parties to the agreement describes the terms and rules of the future contract. Then the second party gives consent and acceptance. So she approves of the proposed terms of the contract and expresses her desire to sign it.
The main terms used in the text come from the words “offer” - proposal, and “acceptance” - agreement.
The person who made the proposal is usually called the offeror.
The acceptor is the one whose consent is sought. To accept means to approve the agreement.
A little about the history of the concept
The concept of acceptance comes from the Latin acceptus - accepted. In ancient Roman law, the conclusion of an agreement consisted of two stages:
- Offer – a proposal to conclude a contract;
- Acceptance – acceptance of the terms of the agreement.
The contract was considered valid only when all the important terms of the agreement were specified, the form of the contract was observed, and the real parties to the contract participated. Signing documents through representatives was not recognized at that time.
The offer had to clearly describe the subject of the contract, as well as the grounds for its conclusion. In order for the agreement to take place, the parties to the agreement had to not only agree, but also perform certain actions symbolizing their agreement with the terms.
For example, in the presence of witnesses, a certain thing was transferred in respect of which a storage agreement was concluded. In oral agreements, both parties had to utter special phrases that indicated that the agreement was being concluded voluntarily. The fact of uttering phrases was recorded in written acts and confirmed by witnesses.
Nuances of acceptance in accounting
We figured out that when they say “invoice accepted”, this only means acceptance of the documentation for payment. The fact of payment is reflected after the funds are written off. How are such transactions reflected in the accounting of the enterprise? How should the time interval between acceptance and payment of the invoice be taken into account?
In the accounting of the enterprise, all accepted invoices are subject to reflection on the account of settlements with suppliers, that is, the account. 60. Here, synthetic and analytical accounting is maintained for counterparties, dates of occurrence/repayment of obligations, range of products (services), accepted documents ready for payment, positively approved by the head of the organization. Postings are formed according to the rules of Order No. 94n of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 31, 2000.
The general acceptance procedure includes two main steps. First, the supplier supplies the buyer with the necessary products (or provides services, performs work). After which, an invoice for payment will be issued directly within 5 days. According to civil law, the amount must be paid by the buyer from his current account in full and without any changes.
What cannot be called acceptance
Acceptance is always acceptance of the offer in full and without reservations or reciprocal actions. Lack of action on the part of the party to whom the offer is directed cannot be considered acceptance. You did not receive a response, which means your offer was not accepted.
Let's imagine that you are entering into a contract for the installation of plastic windows. The surveyor determined the parameters of the future window, calculated its cost and left you with a contract to sign. So, until you sign the contract and hand it over to the company’s employees, they will not begin manufacturing and installing the ordered products. And all because you did not give your acceptance to their offer (agreement) (you did not sign or hand over the document).
Sometimes the party who received the offer is not satisfied with something and wants to change the terms of the contract. Such actions are considered a refusal of acceptance and a new offer. Let's say that in the previous example you did not sign the contract, but came to the office and chose a new profile and fittings for the windows. This will also be regarded as a refusal to accept.
Acceptance of an invoice from a supplier of goods or services
Let's look at examples of what is an accepted supplier's invoice for materials or services?
Let’s assume that Rostekhstroy LLC entered into an agreement for the purchase of building materials for RUB 236,000.00. (VAT – 18% in the amount of RUB 36,000.00). Under the terms of the transaction, the supplier ships the goods on November 14, 2017, and as part of the agreement with the buyer, an invoice for payment was issued on November 17, 2017. The obligations are fulfilled by Rostekhstroy LLC on the same day, in full, by debiting the required amount from the current account.