Transactions with non-residential premises - shops, offices, garages, basements - are in demand in the real estate market and are carried out by commercial and non-profit organizations and individuals.
Rights to non-residential premises and transactions with them must be registered with Rosreestr.
To carry out the sale, purchase, exchange, and any other transaction with real estate, it is necessary to collect a package of documents, a mandatory part of which is the cadastral passport.
Cadastral passport
A cadastral passport is an official document characterizing a property. Contains a unique cadastral number and a description of the premises.
The cadastral passport indicates:
- cadastral number and date of its assignment;
- previous cadastral numbers;
- address;
- floor;
- area (accurate to tenths of sq.m)
- purpose and type of premises;
- cadastral value;
- owners and type of property;
- layout plan;
- other unique characteristics of the room.
A cadastral passport is issued on the basis of information contained in the State Real Estate Cadastre (GKN). The information in the state register is open and accessible to anyone.
To obtain a cadastral passport, you can contact the Cadastral Chamber, the MFC or electronically on the Rosreestr website. To provide the service you need to pay a state fee (200 rubles). At the MFC or Cadastral Chamber, fill out an application and present your passport. Citizens and legal entities can make requests for both their own and other people's real estate. Production time - 5 days.
1. In what cases does an organization itself need to apply for cadastral registration of real estate. It is necessary to register real estate in the cadastral register in order to register rights to it. This follows from Part 4 of Art. 1, part 4 art. 14 of the Law on State Registration of Real Estate.
In some situations, in order to conduct cadastral registration and enter information into the register, the participation of an organization is not required. In other cases, she needs to submit an application for cadastral registration. Without the participation of the organization :
- are placed on the cadastral register . Created real estate objects are constructed buildings, structures, structures, including on the site of demolished objects.
An entry permit is issued in cases where a permit is required for the construction of real estate. This follows from Part 1 of Art. 55 Civil Code of the Russian Federation. In specified cases, a building permit is not required (hence, a commissioning permit is not required). The body (organization) that issued the permit for entry must itself send the application for cadastral registration and the necessary documents to Rosreestr;
- information missing from it is entered into the register:
- about previously registered real estate;
- about real estate, the rights to which arose before January 31, 1998 and were not terminated, while cadastral registration of such real estate was not carried out.
Information about such real estate objects is entered by Rosreestr upon receipt of a request (interdepartmental request) for the provision of information. However, the copyright holder himself can submit a corresponding application. The organization itself must apply for cadastral registration , in particular:
- when creating real estate , except for the case when accounting is carried out without the participation of the organization. In this case, cadastral registration and state registration of rights to created objects are carried out simultaneously.
All premises (including common areas) and parking spaces in the created building or structure can be registered in the cadastral register:
- simultaneously taking into account such a building or structure.
Note that when registering an apartment building, apartments, non-residential premises (including common areas) and parking spaces in it are simultaneously registered;
- after registration of the owner’s rights to the created building, structure, if the cadastral registration of such premises, parking spaces was not carried out simultaneously with the building, structure, or they were registered without the participation of the organization;
- formation of real estate objects . Real estate objects (land plots, buildings, structures, premises, parking spaces, etc.) are formed in the event, for example, of their division, merging, or changing the boundaries of adjacent parking spaces.
Cadastral registration and state registration of rights to all formed objects are carried out simultaneously, with the exception of some cases. So, for example, when dividing one property into three objects, accounting and registration of the three created objects will be carried out simultaneously;
- changes in the basic characteristics of real estate. Such changes occur, for example, as a result of reconstruction or major repairs of buildings and structures;
- entering information about previously registered real estate , if it has not been entered by Rosreestr earlier.
The entry of such information may be refused on established grounds. 2. How to fill out an application for cadastral registration If cadastral registration and state registration of rights are carried out simultaneously, one application is completed. In this case, the sign “V” is affixed in column 3.1 of the application. If only cadastral registration is carried out, you must fill out the same application, but put the “V” sign in column 3.2. In detail 5 of the application, you must enter the sign “V” in the appropriate column:
- registration;
- accounting for changes. At the same time, it is also indicated why the changes are taken into account;
- entering information about a previously registered property.
3. What documents are needed to register real estate for cadastral registration ? Regardless of whether cadastral registration is carried out simultaneously with state registration or not, it is necessary to prepare a set of documents for state registration. In both cases, you must additionally attach the documents required for cadastral registration. When registering for cadastral registration, recording changes and entering information about previously registered real estate, as a general rule, the following documents are submitted, prepared as a result of cadastral work by a cadastral engineer:
- boundary plan.
Such a document is drawn up in relation to land plots. This follows from parts 1, 2 of Art. 22 of the Law on State Registration of Real Estate. Requirements for the boundary plan are given in Art. 22 of the said Law. The form and composition of information on the boundary plan, the requirements for its preparation are approved by Order of the Ministry of Economic Development of Russia dated December 8, 2015 N 921;
- technical plan.
It is drawn up in relation to buildings, structures, premises, parking spaces, unfinished construction projects and a single real estate complex. The technical plan is also drawn up for parts of buildings, structures, premises, and a single real estate complex. This is indicated in Part 1 of Art. 24 of the Law on State Registration of Real Estate. The requirements for such a document are listed in Art. 24 of the said Law. The form of the technical plan, the requirements for its preparation and the composition of the information contained in it are approved by Order of the Ministry of Economic Development of Russia dated December 18, 2015 N 953. Land survey and technical plans must be submitted for cadastral registration in the form of electronic documents signed with an enhanced qualified electronic signature of a cadastral engineer. Such documents do not need to be submitted if they are temporarily stored in the electronic storage of Rosreestr. In this case, the application must indicate the identifying document number. 4. How to submit documents for cadastral registration Both for cadastral registration together with state registration of rights to real estate, and for cadastral registration without simultaneous state registration, a uniform procedure for submitting documents has been established. 5. When and what documents are issued to confirm cadastral registration? Cadastral registration at the request of the organization is carried out within the following terms.
| Situation | Registration deadlines, if documents are submitted | |
| to the divisions of Rosreestr or the Cadastral Chamber | through MFC | |
| Carrying out cadastral registration without simultaneous state registration of rights | 5 working days (Clause 3, Part 1, Article 16 of the Law on State Registration of Real Estate) | 7 working days (clause 4, part 1, article 16 of the said Law) |
| Simultaneous cadastral registration and state registration of rights | 10 working days (clause 5, part 1, article 16 of the said Law) | 12 working days (clause 6, part 1, article 16 of the said Law) |
| Entering information about previously registered real estate | 5 working days from the date of receipt of the application or request by the rights registration authority (Part 5 of Article 69 of the said Law) | |
A cadastral number is assigned to each property (including land plots) as a result of cadastral registration. This number does not change and is not repeated over time and on the territory of the Russian Federation. The procedure for assigning cadastral numbers is given in Appendix No. 2 to Order No. 877 of the Ministry of Economic Development of Russia dated November 24, 2015. 6. How cadastral registration is certified Carrying out both cadastral registration and state registration of rights to real estate is confirmed by an extract from the Unified State Register of Real Estate. Regardless of whether cadastral registration and cadastral registration were carried out simultaneously or not, supporting documents are issued to the organization in a unified manner.
In what cases is it necessary to register the premises?
The need for cadastral registration of non-residential premises can be dictated by various reasons.
First of all, it is necessary to take into account newly formed or created non-residential premises. According to the law, a premises can be registered in the state cadastre if it is isolated (fenced off from the rest of the building by building structures). For non-residential premises there is no requirement for isolation (having a separate entrance and not being used for access to other premises), as for residential premises.
Owners of premises in new buildings can register objects before registering the entire building or simultaneously with it. Registration of a new building for cadastral registration procedure
A new non-residential premises may appear as a result of separation from a real estate property, the merger of several premises, reconstruction and other actions permitted by law. In this case, the cadastral passport indicates the cadastral number of the real estate from which the premises were allocated, converted, etc.
When converting residential premises into non-residential premises, significant characteristics change:
- type of property;
- its purpose.
In addition, the transfer is often accompanied by real estate reconstruction. Therefore, the formed non-residential premises must be re-registered in the cadastral register.
A new cadastral passport is required if redevelopment has been carried out. When carrying out redevelopment, it is necessary to comply with all procedures provided by law. Failure to comply with the law may result in refusal to register changes and the requirement to restore the premises to their original form.
How to put on the balance sheet a building received under a free use agreement?
Question from Klerk.Ru reader Tatyana (Moscow)
Tell me, please, what to do? LLC on OSNO. We won a tender to conclude an agreement for the free use of a social and domestic facility for 20 years with the condition of carrying out a thorough renovation of the building at our own expense and in the future providing bathing services to the population. The Lender remains the owner, but transfers the rights of ownership and use of the object to the Borrower. The borrower is required to record the building on its balance sheet and calculate depreciation.
1. How to put this building on the balance sheet? 2. Is it necessary to accept the building as non-operating income and calculate income tax? (Book value 0 rubles, market value 1 million rubles)
On the cap. Repairing half of the building by a contractor spent 2,500,000 rubles and was partially put into operation.
Apparently, your organization has been granted the right to own and use treasury property, that is, state (municipal) property that is not assigned the right of economic management or operational management to state (municipal) enterprises or institutions (Articles 214, 216 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
By virtue of Part 1 of Art. 17.1 of the Federal Law of July 26, 2006 N 135-FZ “On the Protection of Competition”, the conclusion of lease agreements, free use and other agreements providing for the transfer of ownership and (or) use rights in relation to the specified property with commercial organizations is carried out only based on the results of competitions or auctions the right to conclude these agreements.
According to clause 92 of the Rules for holding competitions or auctions for the right to conclude lease agreements, gratuitous use agreements, property trust management agreements, other agreements providing for the transfer of ownership and (or) use rights in relation to state or municipal property” (approved by Order of the FAS RF dated 02/10/2010 N 67) the conclusion of an agreement based on the results of a competition is carried out in the manner prescribed by the Civil Code and other federal laws. In this case, a loan agreement has been concluded with you.
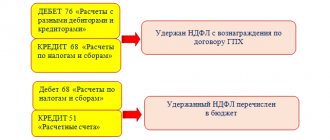
Under an agreement for gratuitous use (loan agreement), one party (the lender) undertakes to transfer or transfers the thing for gratuitous temporary use to the other party (the borrower). The borrower undertakes to return this item in the condition in which he received it, taking into account normal wear and tear or in the condition stipulated by the contract (Clause 1 of Article 689 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). In accordance with paragraph 2 of Art. 8 of the Federal Law of November 21, 1996 N 129-FZ “On Accounting”, property that is the property of an organization is accounted for separately from the property of other legal entities held by this organization.
The corresponding rules provided for a lease agreement (Clause 2, Article 689 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation) apply to a contract for gratuitous use. Therefore, the receipt of property under a loan agreement can be reflected in accounting in the same manner as for a lease, that is, taken into account in off-balance sheet account 001 “Leased fixed assets” in the assessment specified in the loan agreement (Instructions for using the Chart of Accounts). In this case, the borrower is recommended to open an inventory card for an object of fixed assets received for free use and account for it according to the inventory number assigned by the lender (clause 14, paragraph 5 of clause 21 of the Methodological Guidelines for Accounting of Fixed Assets). The borrower does not accrue depreciation on an item of fixed assets received for gratuitous use either in accounting or tax accounting (clause 50 of the Guidelines for accounting of fixed assets, clause 1 of Article 256 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
I draw your attention to the fact that the registration of a building at the current market value with the recognition of other income of the organization as depreciation accrues on it in account 91 “Other income and expenses is possible only if this building is received free of charge under a donation agreement (clause 10 of PBU 6 /01, Instructions for use of billing fees).
The fixed asset transferred by the owner under the loan agreement continues to remain the property of the lender and is reflected on his balance sheet (clause 21 of the Guidelines for accounting of fixed assets). Since in this case we are talking about treasury property, in accordance with the Instructions on budget accounting, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 30, 2008 N 148n, it is subject to accounting in account 010800000 “Non-financial assets of treasury property.” State-owned property is not subject to taxation under the corporate property tax (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 27, 2009 No. 03-05-04-01/88). An object received for free use, subject to accounting on the balance sheet, is not subject to property tax taxation for your organization (clause 1 of Article 374 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Taking into account the above, your organization (borrower) does not have the right to take on the balance sheet as a fixed asset with the subsequent accrual of depreciation on it a social and domestic building that does not belong to it.
As for income tax, when using property for free, the borrower becomes obligated to pay tax on the amount of economic benefit for this operation. In this case, the amount of income is determined based on market prices for similar services according to the rules of Art. 40 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (clause 8 of article 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 2 of the Review of the practice of resolving cases by arbitration courts related to the application of certain provisions of Chapter 25 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation does not contain an answer to the question of whether the borrower can take into account the costs of repairing property received for free use. There are examples of court decisions from which it follows that such expenses are taken into account when taxing profits (for example, Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Eastern Military District dated December 19, 2006 in case No. A11-464/2006-K2-22/135, Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the East Siberian District dated 04.07.2007 N A33-8475/06-F02-4023/07 in case N A33-8475/06 (Decision of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated October 30, 2007 No. 13936/07 refused to transfer this case to the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation)). According to the courts, the wording of paragraph 2 of Art. 260 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (let me remind you that it talks about the possibility of taking into account the costs of repairs by the tenant of fixed assets) does not exclude its use in relation to the expenses of the borrower.
Services for the gratuitous transfer of property for use are subject to VAT (Article 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). According to officials, the borrower of government property must calculate and pay VAT to the budget, performing the functions of a tax agent for VAT (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 20, 2009 No. 03-03-06/4/91). This conclusion is based on the cumulative application of the provisions of Art. 3. 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and clause 2 of Art. Art. 689 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Let me remind you that clause 3 of Art. 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation establishes that when federal property, property of constituent entities of the Russian Federation and municipal property are provided for lease on the territory of the Russian Federation by state authorities and management bodies and local self-government bodies, the tax base is determined as the amount of rent including tax.
In this case, the tax base is determined by the tax agent separately for each leased property. In this case, the tax agents are the tenants of the specified property. These persons are required to calculate, withhold from income paid to the lessor, and pay the appropriate amount of tax to the budget. On the basis of paragraph 2 of Art. 689 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the rules stipulated by the Civil Code in relation to the lease agreement must be applied to the agreement for gratuitous use.
It’s very easy to get a personal consultation with Svetlana Skobeleva online - you need to fill out a special form . Several of the most interesting questions will be selected daily, the answers to which you can read on our website.
What is the procedure for accepting a self-constructed building as part of fixed assets?
Since all costs for self-built fixed assets are accumulated on account 2930 “Construction in progress”, at the moment when the asset is ready for operation, it is included in the fixed assets based on the order of the manager, which determines, among other things, the composition of the commission. Capitalization of a fixed asset by transfer from construction in progress is formalized by the form of primary documents approved by order of the Minister of Finance of the Republic of Kazakhstan dated December 20, 2012 No. 562 - DA-1 “Acceptance and transfer certificate of long-term assets”, which is used to account for long-term assets related to fixed assets .
In addition to the acceptance certificate drawn up yourself, you need to draw up the relevant documents on the acceptance of the constructed facility into operation for the appropriate registration of property rights to the commissioned facility. Based on Article 12 of the Law “On Architectural, Urban Planning and Construction Activities in the Republic of Kazakhstan”, the use of land plots by owners or land users for development (including the laying of communications, engineering preparation of the territory, landscaping, landscaping and other types of site development) can only be carried out in accordance with those approved in in accordance with the procedure established by law, design documentation and compliance with the intended purpose or easement, zoning of the territory, red lines and lines for regulating development, rules of development and operation. Acceptance into operation of a constructed facility by the state acceptance commission is carried out when it is fully ready in accordance with the approved project and there is a positive conclusion from the working commission.
In some cases, the commissioning of a constructed facility is carried out by the owner (customer, investor, developer) independently. The list of individual cases is as follows:
1) Reconstruction (redevelopment, re-equipment) of premises (individual parts) of existing buildings, not related to changes in load-bearing and enclosing structures, engineering systems and equipment, as well as changes in the functional purpose of the premises;
2) Construction of temporary buildings, including household premises for seasonal work and transhumance;
3) Construction of household buildings on the territories of individual personal plots, buildings on the plots of gardening and vegetable gardening partnerships (societies), landscaping elements on local areas or personal (dacha) plots;
4) Construction of mobile complexes of container and block design, as well as one-story buildings (structures) for trade, public catering and consumer services, constructed from prefabricated structures and not requiring approval from sanitary and epidemiological services;
5) open-type parking lots with the number of cars no more than fifty units, as well as garages with boxes for no more than two cars;
6) construction of individual residential buildings, as well as other buildings intended for the personal use of citizens;
7) small architectural forms and fencing of territories;
 open sports grounds, sidewalks, paving around buildings (structures).
open sports grounds, sidewalks, paving around buildings (structures).
Thus, the acceptance of a building on the balance sheet is carried out after registration with the justice authorities, unless the constructed buildings belong to one of the above categories.
According to IAS 16, depreciation of an asset begins from the moment when the asset can be used for its intended purpose, i.e. when it is in the location and conditions necessary to enable the asset to perform in the manner intended by management.
In this case, depreciation of the building will be carried out after registration with the justice authorities, because Acceptance on the balance sheet is possible only after registration with the justice authorities, and not from the moment when the asset can be used for its intended purpose (if the buildings belong to one of the above categories, then in accordance with IFRS 16, before registration with the justice authorities).
A property for which ownership has not been registered. Operation and depreciation
Our company builds real estate for production purposes; accordingly, all consumables accumulate on account 08.3. Can I put objects into operation without legal registration in justice and charge depreciation? At what point can this be done?
The rules for the formation of information about the organization’s fixed assets in accounting are established by PBU 6/01 “Accounting for fixed assets”,
approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated March 30, 2001 No. 26n, according to which
an asset is accepted by the organization for accounting as fixed assets
if the conditions provided for in clause 4 of PBU 6/01 are met, that is:
– the object is intended for use in the production of products, when performing work or providing services, for the management needs of the organization, or to be provided by the organization for a fee for temporary possession and use or for temporary use;
– the object is intended to be used for a long time, i.e. a period exceeding 12 months or the normal operating cycle if it exceeds 12 months;
– the organization does not intend the subsequent resale of this object;
– the object is capable of bringing economic benefits (income) to the organization in the future.
The Chart of Accounts and Instructions for its application, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n, stipulate that account 08 “Investments in non-current assets”
is intended to summarize information about the organization’s costs into objects that, in particular, will subsequently be accepted for accounting as fixed assets.
These also include costs provided for in estimates, financial estimates and title lists for capital construction carried out by contract or on a business basis.
At the same time, it was established that the formed initial cost of fixed assets, accepted for operation and registered in the prescribed manner, is written off from account 08 “Investments in non-current assets” to the debit of the corresponding accounts for accounting for fixed assets.
Clause 41 Regulations on accounting and financial reporting in the Russian Federation
, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 29, 1998 No. 34n, it was established that real estate objects that
are not documented with documents confirming their state registration
are classified as unfinished capital investments.
A clause 52 of the Guidelines for accounting of fixed assets
, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 13, 2003 No. 91n, provided that
for real estate objects for which
capital investments have been completed, the corresponding primary accounting documents for acceptance and transfer have been drawn up,
the documents have been transferred for state registration
and actually in use,
depreciation is calculated
in general order from the first day of the month following the month the facility was put into operation.
By Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 24, 2010 No. 186n, changes were made to certain regulatory legal acts on accounting, which are applied from the financial statements of 2011.
Thus, from the Accounting Regulations the provision on
that real estate objects that
are not prepared with documents confirming their state registration
are classified as unfinished capital investments.
Consequently, in the above cases, such objects are recognized as fixed assets
.
And according to the new edition of clause 52 of the Methodological Instructions... for real estate objects for which capital investments have been completed, depreciation is calculated in the general manner
from the first day of the month following the month the object was accepted for accounting.
At the same time , real estate objects for which ownership rights are not registered
in accordance with the procedure established by law,
are accepted for accounting as fixed assets
with allocation
in a separate sub-account
to the fixed assets accounting account.
In this regard, the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation, in a letter dated March 18, 2011 No. 03-05-04-01/08, indicated that fixed assets are accepted for accounting on the basis of primary documents
.
At the same time, in order to accept real estate into accounting account 01 “Fixed Assets”, documents on state registration of rights are not required
.
Accordingly, the enterprise has the right to reduce the tax base
for property tax of organizations
from January 1, 2011
in relation to capital investments in fixed assets, if this property was transferred under an acceptance certificate and accounted for as fixed assets in accounting account 01 “Fixed Assets” (
in a separate subaccount to the account accounting of fixed assets in the absence of state registration of property rights
).
In accordance with paragraph 38 of the Guidelines, acceptance of fixed assets for accounting
carried out
on the basis of
an act
(invoice)
of acceptance and transfer of fixed assets
approved by the head of the organization , which is drawn up for each individual inventory item.
The specified act, approved by the head of the organization, together with the technical documentation is transferred to the accounting service of the organization, which, on the basis of this document, opens an inventory card
.
From the analysis of the provisions of regulations on accounting of fixed assets, it follows that at the time when the head of the organization decides to accept a real estate asset as a fixed asset, it has already been formed
in accordance with the established procedure for maintaining accounting records as an object of fixed assets, which is the basis for its accounting in account 01 “Fixed assets”.
To include an object in fixed assets and record their commissioning of completed buildings (structures, built-in and attached structures), a unified form of primary accounting documentation No. OS-1a
“Act on the acceptance and transfer of a building (structure)”, approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated January 21, 2003 No. 7.
Calculation of depreciation charges
for an object of fixed assets
begins on the first day of the month following the month in which this object was accepted for accounting
, and is carried out until the cost of this object is fully repaid or this object is written off from accounting (clause 21 of PBU 6/01).
For income tax
in accordance with
paragraph 4 of Art. 259 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, depreciation calculation
for depreciable property objects
begins on the 1st day of the month following the month in which this object was put into operation
.
Based on clause 11 of Art. 258 Tax Code of the Russian Federation
fixed assets,
the rights to which are subject to state registration
in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation,
are included in the corresponding depreciation group from the moment of documented submission of documents for registration of these rights
.
The Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation in letter dated 03/04/2011 No. 03-03-06/1/116 explains that according to these standards, the main conditions for including property in depreciation groups are that the taxpayer has ownership rights
on the property and
its actual use
for the production and sale of goods (performance of work, provision of services), as well as for the management of the organization.
At the same time, fixed assets, the rights to which, in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, are subject to state registration
, are included in the depreciable property no earlier than the period of submission of documents for registration of these rights.
Taking into account the above, to begin calculating depreciation on a fixed asset, the rights to which are subject to state registration, two conditions must be met
: inclusion of this fixed asset in the depreciation group (the presence of a documented fact of filing documents for registration of these rights), as well as its commissioning.
According to Art. 4 of the Federal Law of the Russian Federation dated July 21, 1997 No. 122-FZ “On state registration of rights to real estate and transactions with it,” ownership rights and other proprietary rights to real estate and transactions with it are subject to state registration.
In accordance with paragraph 6 of Art. 16 of Law No. 122-FZ, the applicant is given a receipt for receipt of documents for state registration
rights with their list, as well as indicating the date and time of their submission accurate to the minute. The receipt confirms receipt of documents for state registration of rights.
Thus, the Ministry of Finance points out, a document confirming the fact of filing documents for state registration of property rights
on the property,
there may be
the above
receipt
.