Classification of balances
Buh. balances are classified according to various criteria:
- Based on time:
- Opening balance – formed when registering a new company.
- Initial balance - its formation is carried out annually to determine the financial position of the company after a whole year of activity.
- Interim balance - it is formed every quarter, at the end of the year it is allowed to be adjusted.
- Closing balance sheet – it is formed upon liquidation of the company.
- Based on the completeness of the information provided:
- General balance sheet - includes data on the property and liabilities of the company as a whole.
- Private balance sheet - includes information about the property assets and liabilities of a separate part of the company.
Filling Features
Experts recommend drawing up several balance sheet forms for different categories of stakeholders. The law does not regulate the reporting structure. However, there are certain standards and rules. They contain only the list and economic content for specific articles. The level of detail of the balance sheet is determined independently by the company’s accountant. Today in Russia there is a tendency to simplify the structure of the document. Thus, over the past 30 years, the number of items in the balance sheet has been halved.
Balance sheet asset
The assets of the balance sheet group households. means according to their functional role in the production process. The active part of the balance sheet is divided into two groups: current and non-current assets.
Non-current assets include:
- OS objects;
- Intangible assets;
- Investments in non-current assets;
- Profitable investments in mat. objects;
- Economic investments of a long-term nature
Current assets include:
- Inventories of finished products and raw materials;
- Money;
- Debts of debtors;
- Economic investments of a short-term nature.
general characteristics
When explaining what a balance sheet is, you should pay attention to the method that is used to construct it. The complex of available data is entered into a two-way table. This method is widely used in economic analysis, accounting and planning. The system of planned balances contains labor, money and material. With their help, the formation and subsequent distribution of certain types of raw materials, goods, finance, as well as working reserves are predicted.
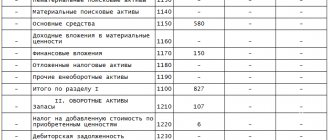
Table of composition of active and passive parts
Consider the table of assets and liabilities of the balance sheet:
| The first section is non-current assets | |
| 1110 | Intangible objects |
| 1120 | Results of the carried out developments and studies |
| 1130 | Intangible objects of search nature |
| 1140 | Mat. search objects |
| 1150 | OS objects |
| 1160 | Profitable investments in mat. objects |
| 1170 | Economic Investments |
| 1180 | Deferred tax assets |
| 1190 | Other objects |
| Second section – current assets | |
| 1210 | Company inventories |
| 1220 | VAT amount for purchased objects |
| 1230 | Debts of debtors |
| 1240 | Economic investment (less cash equivalents) |
| 1250 | Cash and cash equivalents |
| 1260 | Other negotiable items |
| The third section is formed reserves and capital | |
| 1310 | UK |
| 1320 | Company shares purchased from shareholders |
| 1340 | Results of revaluation of non-current assets |
| 1350 | DK |
| 1360 | RK |
| 1370 | Retained income (loss) |
| The fourth section – long-term obligations | |
| 1410 | Funds borrowed for a long period of time |
| 1420 | Deferred tax liabilities |
| 1430 | Estimated obligations |
| 1450 | Others |
| Fifth section – short-term obligations | |
| 1510 | Funds borrowed for a short period of time |
| 1520 | Accounts payable |
| 1530 | Deferred profit |
| 1540 | Estimated obligations |
| 1550 | Others |
Similar articles
- Assets and Liabilities
- Tangible and intangible non-current assets
- Long-term assets on the balance sheet
- Assets on Balance Sheet
- Permanent asset index: balance sheet formula
Grouping accounts in tables
| Assets | Receiving a profit |
| Bank deposits | Money stored in a bank account (ruble or foreign currency) generates passive income thanks to accrued interest on the investment |
| Business | Money can be invested in a business that will generate income over time |
| Stock | When purchasing shares, the owner can expect to receive dividends from business profits. You can make a profit both from annual income and from the sale of shares |
| Bonds | Purchasing long-term bonds will create a stable source of income for many years. Interest on bonds is accrued once or twice a year |
| Real estate | Investing in real estate is considered the most reliable way to generate passive income. Such a purchase guarantees the owner a constant flow of funds from rent. In addition, the price of real estate increases every year |
| Shares and units in mutual funds (mutual investment funds) | This method is usually used by people who want to quickly and easily invest their capital, without thinking about what and where. For profitable and effective use, the money is placed under the management of professionals who charge a certain percentage for their services. |
| Precious Metals and Collectibles | Investing in gold, silver, paintings, rare coins and other items is one of the best and most reliable ways to invest your savings, as their value is constantly growing |
| Machinery, equipment, transport and more | The owner of these things can receive revenue from their operation |
Information sources
They are used as accounting accounts. As a rule, their name coincides with the name of the accounting object. There are two parts to any account: debit and credit. This division is due to the movement of funds - decrease or increase. Each accounting account has an initial balance - a balance for a certain object, and subsequently it decreases or increases. This way you can set the ending balance at any time. To do this, the amount of the increase is added to the original balance, and the amount of the decrease is subtracted from the resulting balance.
Differences between own and borrowed liability objects using an example
It was already indicated above that the structure of the balance sheet gives an idea of the stability of the company. Availability of own funds is a serious advantage of the enterprise. Proper use of liabilities will ensure independence and well-being.
An example of using your own funds. The company bought premises for offices. The property is for rent. Rental funds continuously flow into the company's budget. The organization receives net profit that does not imply liabilities. Funds can be used both for capital formation and for increasing turnover. Profits do not decrease due to inflation, since office rental prices are constantly rising.
An example of the use of borrowed funds. The company took out a million rubles on credit to rent retail space and purchase a batch of products. The loan was short-term. The premises were rented. Products are displayed on the trading platform. The product became popular among consumers. In just a few months, we managed to receive more than 2 million rubles. The million was used to repay the loan.
But another situation is also possible. The company took out a million rubles on credit. The money was also used for rent and purchase of products. However, the product was not successful with the consumer. In a few months we managed to get 200,000 rubles. There was not enough money for the subsequent rent of the retail space, as well as for repaying the loan on time. Creditors went to court to collect the debt. The company had to declare itself bankrupt.
ATTENTION! Based on the examples given, it becomes clear that it is beneficial for an enterprise to have its own reserves. However, most enterprises also have borrowed funds. This is completely normal. The main thing is to monitor the proportions between your own and borrowed funds.
Example
| date | Equity | Assets | CA |
| 31.12.2017 | 1640 | 4600 | 0,36 |
| 31.12.2018 | 2024 | 4610 | 0,44 |
| 31.12.2019 | 2480 | 4500 | 0,55 |
The table shows that CA is growing steadily and reaching the average standard value as of the last reporting date.
- Solvency. The main indicator that characterizes a company's ability to pay off its obligations is the total liquidity ratio. It is equal to the ratio of current assets to short-term liabilities
Klo = OA / KP
Current assets are the sum of inventories, accounts receivable and cash.
OA = page 1210 + page 1230 + page 1250
Short-term liabilities are the sum of all short-term debts of the enterprise.
KP = page 1510 + 1520 + page 1550
The Klo standard can vary from 1 to 2.5. Those. Even in the most extreme case, debts with short maturities should be fully covered by liquid assets.
And here, too, a lot depends on the direction of the company. Trading firms can allow a reduction in KLo to values slightly exceeding 1, because their inventory is usually easy to sell if necessary.
It is usually more difficult for manufacturing enterprises to sell stock balances in warehouses, therefore KLo for them should be higher, approximately in the range of 1.5 - 2.5. But there is no need to increase this coefficient too much either, because while resources are in reserves.
In the dictionary D.N. Ushakova
BALANCE, balance, man. (French balance, lit. scales). Consolidated statement of expenditures and receipts when concluding accounts (accounting). Reduce the balance. Trade balance. Balance of the national economy. | The ratio of the total value of exports to imports (economy). Active balance (with excess exports). Passive balance (with excess imports). II. BALANCE , balance, plural. no, husband (see balance ) (special). Forest material for pulp mills in the form of bark-free lumps.
Example
| date | Current assets | Short-term liabilities | Klaw |
| 31.12.2017 | 3480 | 2960 | 1,18 |
| 31.12.2018 | 3550 | 2586 | 1,37 |
| 31.12.2019 | 3500 | 2020 | 1,73 |
CL is steadily increasing and reached 1.73 as of the last reporting date. This indicator allows you to ensure solvency for a company from any field of activity.
Why does a director need to understand financial statements?
The manager is responsible for everything that happens in his company, including accounting. Although the chief accountant or another financial specialist prepares the reports, it is the director who certifies them. The current balance sheet form does not provide for a second signature at all.
Naturally, the manager must understand what he is signing and be able to identify dubious places in the report.
In addition, balance sheets of other organizations often end up on the director’s desk. The fact is that when signing an agreement with a new partner, businessmen usually request detailed information about him, which includes financial statements.
Of course, the counterparties' reports will first be analyzed by the company's financiers. But the last word on concluding a contract in any case remains with the director. He must weigh all the factors, including independently studying the reporting of a potential partner, without relying only on the opinion of his subordinates.
We will consider the analysis methodology using the example of simplified forms of financial statements.
The current form of the balance sheet shows data for three dates: the beginning and end of the reporting year, as well as the beginning of the previous year. Form No. 2 also includes two years of information. Therefore, you can see how the indicators change over time
Balance sheet (form No. 1)
Financial results report (form No. 2)
Important point
Before annual accounts can be prepared, the balance sheet must be reformed. What it is? This is a procedure during which the profit received is distributed during the year or the loss is written off. The new financial period will start as if from scratch. Thus, on December 31 of the reporting year, the balance sheet is reformed. What is this for a novice specialist? This is resetting the balance of the financial result accounts. In this case, you should close the account. “Sales” (90), “Other expenses and income” (91), and “Losses and profits” (99).
Balance sheet form (form)
Previously, the balance sheet bore the official name “Form No. 1”. But in 2011, the Ministry of Finance made changes, and now it is called simply “Balance Sheet”. However, the former name is still used among specialists.
The current form of the balance sheet was approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 2, 2010 No. 66n. There is an option that is generally used by all companies (given in Appendix No. 1 to this order). Each line is marked with a special code. For example, intangible assets - 1110, inventories - 1210, short-term borrowed liabilities - 1510, etc.
Fill out and print your balance sheet using the current form for free
For organizations that have the right to use simplified accounting methods and submit simplified reporting, a separate balance sheet form has been developed. It is given in Appendix No. 5 to Order No. 66n.
Categories by time of compilation
At the moment of establishment of the company, introductory documentation is drawn up. What the current balance is is clear from the name itself. These summary tables are compiled throughout the entire period of the organization's activities. In turn, the current balance is divided into initial, intermediate and final. Liquidation documentation is drawn up upon termination of activities. When a large company is divided or one or more divisions are transferred to another company, a separation balance sheet is formed. When merging, appropriate documentation is drawn up.
In Dahl's dictionary
m. French preponderance, being at an advantage, in balance, in weight; balance, balance: the pole lies in balance, in weight, in preponderance; keep balance on a rope, about a dancer, walk, dance on weight. | Summary of receipts and expenses, summary of ends; compilation of mutual trading accounts; comparison of the total value of released and imported goods; comparison of results. | Carpenters, when cutting a hut on chairs, the first run along them is called a balance, on which the first crown is placed. Balance sheets, conclusions. To balance, to hold something, or to keep oneself in balance, at an advantage. He balances the sword on his nose; he balances while standing on a horse; dance around, dance along a rope or in another difficult position on a point, without support. Balancing cf. balancing g. this action. Balancer m. balancer w. a buffoon, a buffoon, a buffoon, a merry-go-round, a high-dancer, dancing on a tightrope or doing other balancing tricks; balancing (balanced), related to this matter. A balancer is a rocker arm, a lever, a rocker in machines, transmitting the movements of the piston to a leg (connecting rod) taken by the crankshaft, by the crankshaft or by the crankshaft. Balancer, rocker, rocker, lever, rocker.
Detailing indicators
To obtain more specific information, synthetic and analytical accounts are used. The first reflect the generalized values that characterize economic assets. Analytical accounts use more detailed characteristics of accounting objects. They detail information obtained from synthetic articles. Analytical accounts reflecting inventory values contain not only monetary indicators, but also natural ones. Both of these groups show the same facts about the company's economic activities. In this regard, the totals for entries in both analytical and synthetic accounts must match.
Balance sheet changes since 2019
From 06/01/2019, the balance sheet form is valid as amended by Order of the Ministry of Finance dated 04/19/2019 No. 61n. The key changes in it (as well as in other financial statements) are as follows:
- now reporting can only be prepared in thousand rubles, millions can no longer be used as a unit of measurement;
- OKVED in the header has been replaced by OKVED 2;
- The balance sheet must contain information about the audit organization (auditor).
The auditor mark should only be given to those companies that are subject to mandatory audit. Tax authorities will use it both to impose a fine on the organization itself if it ignored the obligation to undergo an audit, and in order to know from which auditor they can request information on the organization in accordance with Art. 93 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Other categories
The main activity is the direction that corresponds to the course and charter of the company. All other activities are considered non-essential. The departments that deal with it may maintain a separate balance sheet. Depending on the cancellation method, there are gross and net balances. The first includes regulatory articles. They are those in which, when forming the actual cost of funds, amounts are subtracted from the value of one or another item. The net balance excludes regulatory areas. This procedure is called “cleaning”.