The activities of most enterprises are aimed at making a profit.
Only with proper organization of accounting for all transactions performed can one correctly compare the organization’s income and expenses and assess the degree of profitability of the organization. Any enterprise needs to organize competent accounting, tax and management accounting and ensure a close relationship between them.
The purpose of accounting is to collect, record and summarize information about business transactions, as well as the assets and liabilities of a company for use in management activities.
The task of management accounting is to analyze and control the results of an enterprise’s activities in order to plan further work and development in order to increase profits.
The task of tax accounting is to collect and summarize information on income and expenses to calculate the tax base for various taxes.
What is accounting in simple words
Accounting or accounting (eng. “accounting”) is a systematic collection of information about the economic activities of an enterprise, including data on liabilities and property.
Maintaining financial statements is the responsibility of all organizations. According to the law, in some cases relaxations may be applied. Starting from 2021, documents need to be submitted only to the tax service, without duplication for Rosstat. But, some organizations must additionally submit an audit report to the tax authorities.
Accounting is carried out only in monetary terms.
In addition, all accounting reports will be published on the official website of the tax service. The website will contain all audit reports and accounting reports starting in 2021. Regarding data for 2021 and earlier, to obtain this information you will have to contact Rosstat.
What are the requirements for accounting?
Despite the inflation processes that often occur in the economic world, accounting requirements do not change. The main requirements include:
- Documentation of economic events;
- Comparison of financial indicators with planned ones;
- Maintaining the completeness of accounting information;
- Timely submission of reports;
- Reporting form;
- Data accuracy;
- Significance of data;
- Validity of information;
- Clarity and dissemination of information;
- Economic indicators and rational use;
Is it difficult to figure it out on your own?
Try asking your teachers for help
Solving problems Tests Essays
As for the documentation of economic events, they must be presented in written or electronic form; this is decided by the parties to the transaction. This information structure should be used by tax authorities. If the document is in electronic form, it must be certified with an electronic signature and seal, respectively, after which it takes on the appearance of a real paper document. The unavailability of a document means that the event did not happen, and if it did not happen, then this is considered as an intentional distortion of data.
Comparison of financial indicators with planned ones is a requirement that affects the performance of the control function. The forecast of the financial condition of the enterprise is made on the basis of data comparison, and the data cannot be obtained without accounting.
Compliance with the completeness of accounting information is the volume that meets management requirements and is determined in monetary terms. Too voluminous information will not allow for correct accounting, and will also complicate decision-making, at the same time reducing the effectiveness of control. But in some cases, a decrease in control may be due to insufficient information, so certain boundaries are respected.
Timely reporting involves submitting the required financial statements to interested parties, according to the law, within the prescribed time frame.
The requirement for the reporting form is compliance with legal norms regulated by regulatory documents, but as practice shows, this is quite problematic to implement.
The accuracy of data in accounting reveals the whole essence of correct or incorrect accounting.
Significance - this requirement is taken into account if it does not go beyond the scope of economics and influences decision making. In this case, it does not matter whether the distortion of accounting data occurs intentionally or accidentally, but most importantly the size. An explanatory note is written for the annual accounting report, which sets out the basic and essential information about the enterprise. Such information includes financial position, comparison of data from several periods, accounting items that relate to the problem that has arisen.
The validity of information is an indicator of data that must correspond to turnover and balances on the first day of each month. Clarity and dissemination of information provides the opportunity to directly use accounting information.
Economic indicators are one of the main requirements in management. The information must be significant, its value cannot be lower than the cost of the results. The absence of such a situation means that the accounting department is not coping with its responsibilities. In no case should a simplified accounting system negatively affect the work of the entire enterprise.
Accounting tasks
One of the main tasks of accounting is the collection and systematization of truthful and as complete information as possible about the activities of the organization, as well as property. This data may be needed by the owners of this property, as well as investors, founders, company management, creditors and other persons interested in such information.
Thanks to accounting data, employees of the organization have the opportunity to conduct activities such as:
- Monitoring the need to carry out any operations;
- Monitoring the fulfillment of obligations;
- Search and identification of reserves in case of financial instability;
- Property control;
- Monitoring the appropriateness of using labor, material and financial resources;
- Monitoring the compliance of the company’s work with estimates and standards specified in the charter, as well as in accordance with current legislation;
- Timely identification of negative phenomena that can harm the financial stability of the organization.
Who does the accounting
Maintaining accounting records is the responsibility of the organization's chief accountant. The main provisions on maintaining this type of documentation can be found in the Federal Law “On Accounting” No. 402. If this is a small company and management does not have the opportunity to hire a chief accountant, the following can keep records:
- Third-party organizations;
- Accountant;
- Director (in case there is no accountant on staff of the organization).
Individual entrepreneurs are exempt from accounting. Their task is to annually prepare documents on sales and income. In addition, there are concessions for some types of business. They are provided for:
- Small business;
- Organizations that have received the status of a company engaged in development and research. In the future, their responsibilities include developing proposals for the commercialization of the results obtained;
- Non-profit organizations.
Organization of accounting is the task of the organization's management. To keep records, it is necessary to find an experienced specialist, since mistakes made in this documentation can lead to negative financial consequences.
What information should an accounting specialist have?
If the specialist who will be involved in accounting does not have sufficient experience in this field, he should pay attention to the following recommendations for starting work as an accountant:
- The first stages of an organization’s activities include the mandatory preparation of a working chart of accounts. We are talking about a list of accounts that are necessary to enter information about each transaction carried out in monetary terms. In addition, the initial stage of the company’s activities includes the choice of the form of accounting. She may be:
- journal-order;
- simplified;
- memorial warrant;
- automated;
- magazine-main;
- Every day it is necessary to keep records of every transaction performed. They should be displayed in primary documents.
- This documentation must be registered in accounting registers. Their varieties can also be different depending on the previously chosen form of accounting.
- The monetary amount that accompanied the transaction must be reflected in the account using postings.
- Accounting is a continuous process that can be stopped only after the organization ceases its activities.
- Regarding summing up interim results, that is, calculating balances and turnover, this work is carried out at the end of the month.
- As a result, the accountant must file the appropriate turnover sheets.
- At the end of the year, the chief accountant or other person involved in accounting prepares the annual financial statements, drawing up a balance sheet.
The correctness of accounting will be at the proper level only if the balance sheet liabilities and assets are equal. In addition to these recommendations, before starting to understand accounting, a specialist must study the basic concepts of accounting, including postings, accounting accounts, as well as the features of displaying and evaluating assets and liabilities.
- What are assets and liabilities;
Lesson 1 Summary
- Accounting consists of collecting, processing, recording and storing information about transactions performed in an enterprise.
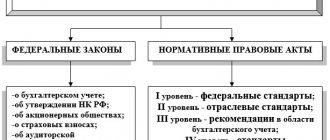
- Accounting at an enterprise is regulated by Federal Law No. 402-FZ and PBU.
- Accounting at an enterprise is continuous and closely interconnected with management and tax accounting.
- For each operation, a document is filled out.
- A posting is made for each transaction.
- Posting is carried out on the basis of the primary document.
- Accounting is carried out in monetary terms.
- Accounting is correct if assets and liabilities are equal at any given time.
Accounting principles
The basic principles of accounting include the following:
- Double entry principle. Each business transaction should be displayed as a debit and a credit on two accounts, but for the same amount;
- Accrual principle. Transactions carried out should be reflected in documents as they are carried out, and not when funds are received into accounts. They must also relate to the period in which they were committed. This principle is divided into the principle of compliance (the ratio of income of the reporting period to the expenses that brought these incomes) and the principle of registration of revenue (reflection of income in documents according to the period of receipt);
- The principle of monetary changes. The currency of the state in whose territory the organization operates is the instrument of any monetary changes in the process of economic activity;
- The principle of independence. Each organization must maintain its autonomy as a legal entity. Regarding property, documents should display only those objects and other valuables that belong to the company;
- Operating principle. The organization operates and secures its place in the market through the timely fulfillment of all obligations to partners, creditors and clients;
- The principle of periodicity. In this case, we are talking about the regular preparation of accounting records and other related documents. Thanks to this, the company’s management keeps accountable data under control, which as a result helps to more effectively and efficiently analyze financial stability, as well as evaluate achievements or timely record monetary losses;
- The principle of caution. Company management must exercise caution in making judgments that help it make correct calculations in times of uncertainty. This is necessary to correctly display data on income and assets in documents in order to avoid overestimating or underestimating the real results of the company’s activities. Compliance with the basic rules of this principle will protect the organization from the formation of hidden or excessive resources. The same applies to expenses and obligations to partners;
- The principle of confidentiality. All data related to internal accounting is a trade secret of the company. For causing harm to economic activity by disclosing this data, according to the law, punishment is provided;
- The principle of objectivity. Here we are talking about the fact that each of their operations should be displayed in documents. Each of them should be registered according to the period of occurrence. In addition, documents confirming this or that fact should be attached to the record.
AccountingGroup of authors
INVENTORY
Inventory is understood as checking the property and liabilities of an enterprise by counting, measuring, weighing. Inventory is a way to clarify accounting indicators and control over the safety of property. The purpose of the inventory is to identify the actual availability of property and compare it with accounting data, as well as check the completeness of the reflection of liabilities in accounting.
All property and all types of financial obligations are subject to inventory. In addition, - industrial inventories and other types of property that do not belong to the organization, but are listed in the accounting records (rented, received for processing, or in custody), as well as property that is not accounted for for any reason.
There are complete and partial inventories, which differ in the degree of coverage of the verification of the organization’s property and obligations. A complete inventory covers all types of property and financial liabilities of an organization without exception, a partial inventory covers one or more types of property and liabilities (cash, materials, etc.).
Inventory surveys can be planned, which are carried out within a predetermined time frame, or sudden. Surprises are carried out in order to establish the presence of valuables unexpectedly for the financially responsible person. They are carried out by order of higher authorities, heads of organizations, and at the request of auditors, investigative and control authorities.
The number of inventories, dates, list of property and liabilities checked during each of them are established by the head of the enterprise. In addition, there are cases when an inventory is required, namely:
- when transferring the property of an enterprise for rent, during the purchase, sale, transformation of a state or municipal enterprise;
— before drawing up annual financial statements, except for property, the inventory of which was carried out no earlier than October 1 of the reporting year. An inventory of fixed assets can be carried out once every 3 years, and of library collections - once every 5 years. In the regions of the Far North and in similar areas, inventory of goods. raw materials and materials can be carried out during the period of their smallest balances;
— when changing financially responsible persons (on the day of acceptance and transfer of cases);
— when facts of theft, abuse or damage to property are revealed;
— in case of a natural disaster, fire, accident or other emergency situations caused by extreme conditions;
— during liquidation (reorganization) of an enterprise and in other cases provided for by law.
To carry out the inventory, a permanent inventory commission is created. If the volume of work is large, working inventory commissions are created to simultaneously conduct an inventory of property and financial obligations. If the amount of work is insignificant, the inventory may be entrusted to the audit commission. The composition of permanent and working inventory commissions is approved by the head of the enterprise. The order (resolution, instruction) on the composition of the commission is registered in the book of control over the implementation of orders to conduct an inventory.
The inventory commission includes representatives of the administration, accounting employees, specialists (engineers, economists, technicians, etc.), representatives of the internal audit service of the organization or independent audit organizations. The absence of even one member of the commission during the inventory serves as grounds for declaring its results invalid.
Inventory is preceded by preparatory activities. At the same time, material assets are sorted and stacked by name, grade, size; In storage areas, labels are posted indicating the quantity, weight or measure of the values being checked. All documents on the receipt and expenditure of valuables must be processed and recorded in analytical accounting registers. A receipt is taken from financially responsible persons stating that they have no valuables that have not been capitalized or written off. The chairman of the inventory commission endorses all incoming and outgoing documents attached to the registers (reports), indicating “before the inventory on... (date),” which serves as the accounting department’s basis for determining the balance of property at the beginning of the inventory according to the accounting data.
The availability of funds in kind is checked with the obligatory participation of the financially responsible person. The results of counting, measuring and weighing are entered into inventory lists or inventory acts in at least two copies, the acts are signed by all members of the commission. Financially responsible persons confirm on each document that there are no claims against the commission and that the verified values have been accepted by them for storage.
The responsibilities of the enterprise manager include creating conditions that ensure a complete and accurate check of the availability of property within the established time frame. The head of the enterprise must provide the commission with labor for rehanging and moving cargo, working weighing equipment, measuring and control instruments.
During the inventory of damaged or damaged valuables, acts are drawn up, which indicate the nature and degree of damage, its causes, and names of those responsible for damaging the valuables.
The results of the inventory of funds and securities are documented in an act without recording them in the inventory list.
Completed inventory records and acts are submitted to the accounting department for verification, then the actual availability of funds is compared with accounting data. The comparison results are recorded in the comparison sheet. The comparison statement indicates the actual availability of funds according to inventory data, the availability of funds according to accounting data and the results of comparison (surplus or shortage).
In the comparison sheet, values are recorded indicating the quantity and amount by group, type, and grade in accordance with the classification adopted in accounting. Only those values for which surpluses or shortages are identified are recorded, and the remaining values are shown in the statement as a total amount. The amounts of surpluses and shortages in the matching statements are indicated in accordance with their assessment in accounting.
To document inventory results, unified registers can be used, which combine the indicators of inventory lists and reconciliation sheets. For values that do not belong to the organization, but are listed in the accounting records, separate matching statements are compiled.
In addition, the inventory commission is obliged to identify the causes of shortages or surpluses discovered during the inventory. The conclusions and proposals of the commission are documented in a protocol and approved by the head of the enterprise. After this, the inventory results are reflected in accounting.
Discrepancies between the actual availability of property and accounting data identified during the inventory are reflected in the accounting accounts in the following order:
- excess property is accounted for and the corresponding amount is credited to the financial results of the organization (for a budgetary organization - to increase funding);
- shortage of property and its damage within the limits of natural loss norms are attributed to the costs of production or circulation, and in excess of the norms - to the account of the guilty persons. If the perpetrators are not identified or the court refuses to recover damages from them, then losses from the shortage of property and its damage are written off to the financial results of the organization, and for a budgetary organization - to a decrease in funding.
Let us list the transactions that are carried out during inventory. The discovered surpluses are accounted for as previously unaccounted for fixed assets that were in use and received free of charge:
1. Dt count. 01 “Fixed assets” - initial cost,
K-t sch. 87-3 “Values received free of charge” - initial cost.
2. Dt count. 87-3 “Values received free of charge” - amount of depreciation,
K-t sch. 02 “Depreciation of fixed assets” - the amount of depreciation.
The shortage of fixed assets identified during inventory is reflected in accounting as follows:
1. The initial cost of the object is written off:
Dt sch. 47 “Sales and other disposal of fixed assets” - initial cost,
K-t sch. 01 “Fixed assets” - initial cost.
2. The wear and tear of the object is written off:
Dt sch. 02 - amount of wear,
K-t sch. 47 - amount of wear.
3. The fact of a shortage is recorded on the active account 84 “Shortages and losses from damage to valuables”:
Dt sch. 84 ~ residual value,
K-t sch. 47 - residual value.
When a shortage is reflected, the residual value of the missing item must be reimbursed. If the culprit of the shortage is not found, the amount of the shortage is written off as production costs:
Dt sch. 26 — residual value,
K-t sch. 84 - residual value.
If the guilt of the financially responsible person for the shortage is established, the residual value of the object is recovered from him.
The cost of the object is written off to the culprit:
Dt sch. 73-3 “Settlements with personnel for compensation of material damage” - residual value,
K-t sch. 84 “Shortages and losses from damage to valuables” - residual value.
The residual value of the missing item is compensated by the culprit either by depositing money into the cash register or into a current account, or by deductions from wages:
Dt sch. 50, 51, 70 - residual value,
K-t sch. 73-3 - residual value.
Methodological elements of accounting
The tasks that accounting faces from legislative acts and the organization's charter can be solved using several methods. Their totality can be called “accounting methods”. This includes the following:
- Financial statements. We are talking about indicators that are entered into special tables. These data reflect the movement of assets, the financial position of the enterprise, its property and liabilities for the reporting period;
- Document flow. Each of the company’s business transactions must be recorded in documents, which subsequently gives it legal force;
- Inventory (what is inventory). According to accounting rules, it is necessary to regularly check the condition of the property on the company’s balance sheet. To do this, you can apply the method of mutual reconciliation, weighing, description, evaluation and identification of funds. The information obtained must be compared with previous reports;
- Balance sheet. It is the source for obtaining data. In addition, the balance sheet is one of the ways to systematize the company’s property by sources of formation, location, and composition. All this must be expressed in monetary terms, and the inventory must be compiled as of the date in accordance with the organization’s charter;
- Grade. This is a way to display funds on the organization’s balance sheet, as well as indicate the sources and amount of income received;
- Calculation. We are talking about determining the cost of manufactured products, services or work. In simple terms, this process is called costing.
Basic Accounting Rules
Proper accounting must be carried out in compliance with basic rules and basic principles. Following them will help:
- maintain correct accounting records in accordance with current international standards;
- the method of valuation of certain items or obligations that affect the formation of property;
- the true value of material assets, taking into account the price index in the process of inflation;
- the ability to obtain information by external users through public reporting;
- the correctness of the information in the report is verified and confirmed by an audit.
Thus, we can say that the basic principles of accounting make it possible to create harmony in individual accounting systems that operate in different countries of the world. In such cases, each country can rightfully use its own accounting model and structure, which will be consistent with other systems in the world.
Accounting procedure
Business transactions carried out through accounting affect the financial position of the company. Therefore, the specialist who keeps records must carefully study the process of generating this reporting:
- At the first stage, management must select accounts. This also includes the formation of a working chart of accounts.
- Every day, company employees perform a large number of transactions. For each of them, a primary document must be drawn up.
- At the next stage, this documentation must be registered in the accounting registers, after which it is sent to the accountant.
- Based on the received papers, the specialist must draw up a posting. This means entering the transaction amount into the accounting accounts.
- Throughout the month, each of the transactions must be reflected in the accounts using postings.
- The basis for entering this information is previously received primary documents.
- Every month the results are summed up. To do this, you should calculate the balance and turnover of the accounts.
- The final results obtained are used to compile the turnover sheet. Based on it, management can correctly assess the current state of the organization and check the correctness of the data included in the reports.
- At the beginning of the next month, accounts are opened again.
- Regarding the ending balance from the previous month, it should be transferred to the new one.
- Further, the accounting of each completed operation continues.
- At the end of the current month, the accounts will be closed again, after which it is necessary to read the balance, turnover and generate the appropriate statements. With the arrival of the next month, each of the processes is repeated.
These steps are the basis for accounting and imply the constant registration, processing and collection of information about transactions in the course of the organization’s business activities, expressed in monetary terms.
Simplified accounting
Since 2013, every small organization has the opportunity to keep accounting records by choosing a simplified form.
According to current legislation, organizations whose annual income does not exceed 800 million rubles and whose number of employees does not exceed 100 people can be classified as small businesses.
According to the recommendations regarding the use of a simplified method of accounting, an organization can choose one of three simplified accounting options:
- Full form;
- The simplest;
- Abbreviated;
The full version of accounting is recommended for those companies that regularly carry out a large number of household activities. operations of various types.
This accounting is characterized by the use of abbreviated charts of accounts, where related accounts can be combined into one. In addition, this method will allow you to identify and correct mistakes made in the current reporting period. Speaking about the abbreviated form of simplified accounting, it is practically no different from the full one.
But, in this case, you can maintain only one register. We are talking about a journal that records the facts of a company’s activities. A sample of the journal can be found by downloading it from the official website of the Ministry of Finance. Regarding the simplest form of accounting, it is recommended to be used by micro-organizations whose staff includes no more than 15 specialists and whose annual income is less than 120 million rubles.
Thanks to this type of accounting form, management may not maintain double entries where credit and debit transactions should be displayed. An accountant can keep a book of records of the facts of an organization's activities using groups of articles in reporting documentation. This method of accounting is called class accounting.
Each of the three forms is characterized by simplified financial statements. Small businesses can only submit financial statements and balance sheets to the tax service. Before deciding on the form of accounting, it is necessary to take into account that such simplification is not available for:
- NPOs performing the functions of foreign agents;
- Companies whose activities cannot do without an audit;
- Notary chambers and law offices;
- Consumer credit and housing construction cooperatives;
- Financial organizations providing microloans;
- Companies belonging to political parties or the public sector.
Accounting
Our organization provides a full range of accounting services for enterprises and individual entrepreneurs.
Accounting at an enterprise is an important part of its activities. Only if the accounting procedures established by current legislation are observed, there can be no doubt that during inspections by regulatory authorities, no penalties will be imposed on the organization.
The organization of accounting at an enterprise is a complex process that includes maintaining primary accounting, accounting for transport services, accounting for the provision of services, preparing reports, documents and other activities. The organization of accounting at an enterprise directly affects its work: the more professionally the accounting is kept, the more successful the business as a whole. Accounting for an organization makes it possible to preserve property and protect funds from irrational use. In addition, qualified accounting of an enterprise allows you to combine all the disparate information into an orderly, systematized report.
With a competent and professional analysis of the information that is revealed by the organization of accounting in the accounting department, it becomes possible to improve the company’s development paths. The manager can avoid serious mistakes and correct shortcomings in a timely manner. Thus, a well-organized accounting procedure allows for timely mutual settlements with partners, and timely submission of well-developed reports to tax authorities and extra-budgetary funds, as well as statistical authorities.
Organization of accounting under the simplified tax system
Currently, individual entrepreneurs and small businesses are increasingly using the simplified taxation system (STS), in which only one type of tax is calculated and paid. The simplified tax system is applied on a voluntary basis; every organization can switch to this form of taxation subject to certain conditions of the current legislation and notification of the tax authorities. Since the simplified taxation system was specifically designed to facilitate accounting in small companies and enterprises, it corresponds to a simplified form of accounting. However, after the new Law on Accounting No. 402-FZ came into force, all enterprises, without exception, must maintain accounting records, regardless of their form of ownership and accounting systems.
There are 3 types of simplified tax system:
- USN patent – only for individual entrepreneurs;
- STS 15% – the balance is taxed after subtracting “income minus expenses”;
- STS 6% – tax is imposed on all revenue received through a cash register or current account, which can be reduced by up to 50% due to insurance premiums.
- UTII - applies only in the regions (except Moscow and St. Petersburg), which can also be reduced through insurance premiums (but not more than 50%)
Maintaining OSNO accounting: main features
Maintaining a simplified accounting system is applicable only for small enterprises with a small volume of business transactions. Companies and enterprises of various organizational and legal forms of ownership that work with VAT and larger turnover of fixed and working capital are forced to keep records using the general taxation system (OSNO). When using OSNO, the process of maintaining accounting, preparing document flow and reporting for regulatory authorities is much more complicated than using a simplified system.
Under the general taxation system, organizations pay several types of taxes: value added tax, profit tax, property tax, and also necessarily make contributions to pension, insurance and other funds, regardless of the type of activity.
Restoration of accounting
Full or partial restoration of accounting is one of the quite popular and in-demand services, which involves putting in order the entire document flow of the customer organization in accordance with the requirements of current legislation, as well as submitting missing or updated reports to the relevant authorities and funds.
Services for restoring accounting and tax records are necessary if, during a certain period, the customer did not properly maintain records that complied with legal requirements.
Properly performed restoration of accounting allows you to submit corrected accounting and tax reporting to regulatory authorities, thereby reducing the amount of taxes and fees, as well as reducing penalties levied on the enterprise.