Line 1170 “Financial investments”
Line 1170 reflects information about the organization’s financial investments, the circulation (maturity) period of which exceeds 12 months after the reporting date:
plus
(in terms of amounts on deposit accounts related to long-term investments)
minus
(in terms of amounts related to long-term investments)
plus
(in terms of long-term interest-bearing loans issued to employees)
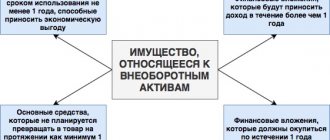
Financial investments include:
- state and municipal securities;
- securities of other organizations, including debt securities in which the date and cost of repayment are determined (bonds, bills);
- contributions to the authorized (share) capital of other organizations (including subsidiaries and dependent business companies);
- loans provided to other organizations;
- deposits in credit institutions;
- receivables acquired on the basis of assignment of the right of claim;
- other similar investments.
Financial investments include:
- own shares purchased by the joint-stock company from shareholders for subsequent resale or cancellation;
- bills issued by the organization-promissory note to the organization-seller when paying for goods sold, products, work performed, services rendered;
- investments of an organization in real estate and other property that has a tangible form, provided by the organization for a fee for temporary use (temporary possession and use) for the purpose of generating income;
- precious metals, jewelry, works of art and other similar valuables acquired for purposes other than normal activities.
The actual costs of acquiring assets as financial investments are:
- amounts paid in accordance with the contract to the seller;
- amounts paid to organizations and other persons for information and consulting services related to the acquisition of these assets. If an organization is provided with information and consulting services related to making a decision on the acquisition of financial investments, and the organization does not make a decision on such acquisition, the cost of these services is included in the financial results of a commercial organization (as part of other expenses) or an increase in the expenses of a non-profit organization of that reporting period when the decision was made not to purchase financial investments;
- remuneration paid to an intermediary organization or other person through which assets were acquired as financial investments;
- other costs directly related to the acquisition of assets as financial investments.
The initial cost of financial investments received by an organization free of charge, such as securities, is recognized as:
- their current market value as of the date of acceptance for accounting. For the purposes of these Regulations, the current market value of securities is understood as their market price, calculated in the prescribed manner by the organizer of trading on the securities market;
- the amount of funds that can be received as a result of the sale of received securities on the date of their acceptance for accounting - for securities for which the market price is not calculated by the organizer of trading on the securities market.
When disposing of an asset accepted for accounting as a financial investment for which the current market value is not determined, its value is determined based on an assessment determined in one of the following ways:
- at the initial cost of each accounting unit of financial investments; at the average initial cost;
- at the original cost of the first financial investments acquired (FIFO method).
In the financial statements, at least the following information is subject to disclosure, taking into account the materiality requirement:
- methods for assessing financial investments upon their disposal by groups (types);
- the consequences of changes in the methods of assessing financial investments upon their disposal;
- the value of financial investments for which the current market value can be determined, and financial investments for which the current market value cannot be determined;
- the difference between the current market value as of the reporting date and the previous assessment of financial investments by which the current market value was determined;
- for debt securities for which the current market value has not been determined - the difference between the initial value and the nominal value during their circulation period;
- value and types of securities and other financial investments encumbered with collateral;
- the value and types of retired securities and other financial investments transferred to other organizations or persons (except for sale);
- data on the reserve for impairment of financial investments, indicating: the type of financial investments, the amount of the reserve created in the reporting year, the amount of the reserve recognized as other income of the reporting period; reserve amounts used in the reporting year;
- for debt securities and loans provided - data on their valuation at discounted value, on the value of their discounted value, on the discounting methods used (disclosed in the notes to the balance sheet and profit and loss statement).
Related links:
PBU 19/02 “Accounting for financial investments”
Financial investments on the balance sheet: definition, list
Contrary to the opinion of some accountants, the following assets cannot be accepted by an organization for accounting as financial investments:
Take our proprietary course on choosing stocks on the stock market → training course
- Own shares of the enterprise that were purchased from shareholders with the purpose of their cancellation or resale;
- material assets purchased for purposes other than normal activities, such as works of art, jewelry, precious metals, etc.;
- bills issued as payment for sold goods, products, works or services issued by the drawer to the seller;
- investments in real estate that have a tangible form and are transferred by the company on a reimbursable basis to other persons for temporary possession (use);
- fixed assets, intangible assets and various types of inventories.
The assets listed below, on the contrary, are full-fledged financial investments, the value of which can be recorded on line 1170 (subject to the requirements from the list following the list):
- municipal and state securities;
- securities of other companies, including debt - bills of exchange, bonds (provided that they indicate the cost and maturity date);
- receivables repurchased in connection with the assignment of claims;
- contributions to the authorized (share) capital of other companies (including subsidiaries and affiliates);
- bank deposits;
- loans issued to other companies;
- other similar investments.
Assets and investments can be accepted for accounting as financial investments only if all the following conditions are met:
- The enterprise must retain documents proving the fact of making a financial investment in the object.
- The investing company must have certain financial risks related to the acquired income-generating assets.
- There must be a probability that financial investments will bring economic benefits in the future in its various forms (in the form of dividends, an increase in the initial cost, etc.).
| Business valuation | Financial analysis according to IFRS | Financial analysis according to RAS |
| Calculation of NPV, IRR in Excel | Valuation of stocks and bonds |
List of actual expenses for the acquisition of assets as financial investments
The accounting records of an enterprise must necessarily contain information about the expenses actually incurred by the company in connection with the need to acquire assets in the form of financial investments. Only the following costs may be included in such costs:
- The amount paid to the seller in accordance with the purchase and sale agreement at the time of purchase of an asset that is planned to be accounted for as a financial investment.
- Expenses for the services of intermediaries involved in the transaction of purchase and sale of an asset acquired as a financial investment.
- Costs for paid services of lawyers and experts who are ready to advise the company on financial investments on a paid basis. If, after the organization paid for information (consulting) services, management decided that it was inappropriate to make a financial investment:
- non-profit organizations include such costs in the increase in expenses of the reporting period, during which it was decided not to invest in the purchase of an asset as a financial investment;
- commercial firms include costs for “unused” consultations and information resources as other expenses.
- Other costs that are directly related to the purchase of assets taken into account as financial investments.
Important! At least once a year, an enterprise is required to check its financial investments for impairment (as of December 31 of the reporting period) if signs of impairment are detected. In addition, studies can be scheduled for interim reporting dates. If, based on the results of the audit, a significant decrease in the value of financial investments is established, it is necessary to create an impairment reserve. The amount of the reserve is determined by deducting their estimated value from the initial cost of financial investments.
Regulatory regulation
The rules for recognizing investments as short-term financial investments in the assets of an enterprise are reflected in accounting in accordance with PBU 19/02, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 10, 2002 No. 126n.
Example 1
In 2021, Aktsia LLC decided to temporarily withdraw a certain amount of funds from circulation and place them as a bank deposit. Terms of the deal: deposit amount – 500 thousand rubles, contract period – 3 months.
Since the bank deposit agreement stipulates a period for the return of funds and it is 3 months, at the end of the reporting year, Aktsia LLC will display the amount of invested funds in line 1240 of the balance sheet.
Example 2
Solnyshko LLC and Kod LLC entered into an agreement on the provision of borrowed funds on December 12, 2017:
- loan amount: Solnyshko LLC provides a loan in the amount of 250 thousand rubles;
- repayment period of obligations: according to the agreement, the loan must be fully repaid, including all accrued interest on it, no later than 10/12/2018;
- borrowed funds are issued at 10% per annum.
Posting in the accounting records of Solnyshko LLC: Dt58.03 Kt51.
Since the terms of the loan agreement stipulate the terms of repayment of obligations, and there is also evidence that these funds were transferred for the purpose of generating additional income, this transaction is reflected in the accounting records of Solnyshko LLC as part of financial investments. Since the contract period is 10 calendar months, the company will display information about the short-term placement of funds in line 1240 of the balance sheet at the end of 2021.
Calculation of the indicator on line 1170 “Financial investments”: formula based on the balance sheet
As can be seen from the name of the line of the Balance Sheet, on line 1170 “Financial investments” it is customary to reflect information about the financial investments of the enterprise, the circulation (maturity) period of which is more than 1 year after the reporting date . The indicator value is calculated using the following formula based on the company’s balance sheet data:
The “Explanations” column provides an indication of the disclosure of the indicator. In cases where a company decides to draw up Explanations for Form No. 1 and OFR using the forms from the Examples of Explaining Explanations (Appendix 3 to Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 66n), Tables 3.1 and 3.2 should be indicated in the “Explanations” from line 1150 “Financial investments” .
The cost of long-term financial investments is reflected in the balance sheet as of 2 dates: December 31 of the previous year and the same day of the year preceding the previous one.
Conclusions about what a change in indicator means
If the indicator is higher than normal
Not standardized
If the indicator is below normal
Not standardized
If the indicator increases
Usually a positive factor
If the indicator decreases
Usually a negative factor
Notes
The indicator in the article is considered from the point of view not of accounting, but of financial management. Therefore, sometimes it can be defined differently. It depends on the author's approach.
In most cases, universities accept any definition option, since deviations according to different approaches and formulas are usually within a maximum of a few percent.
The indicator is considered in the main free online financial analysis service and some other services
If you need conclusions after calculating the indicators, please look at this article: conclusions from financial analysis
If you see any inaccuracy or typo, please also indicate this in the comment. I try to write as simply as possible, but if something is still not clear, questions and clarifications can be written in the comments to any article on the site.
Best regards, Alexander Krylov,
The financial analysis:
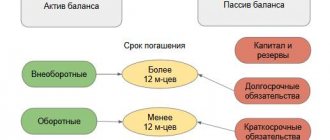
- II. CURRENT ASSETS Current assets are property used in the activities of an enterprise for less than a year or used in one production cycle, which also does not exceed one year. Its entire cost...
- I. NON-CURRENT ASSETS Non-current assets are property used in the activities of an enterprise for more than a year. Its value is transferred in parts to the cost of finished products. A sign of assets is the ability to generate income for the organization.…
- Balance sheet liability The balance sheet liability is the second part of the balance sheet. It contains a list of those financial resources that were used to acquire property, that is, assets that...
- IV. LONG-TERM LIABILITIES Section IV. Long-term liabilities are the fourth section of the balance sheet. At the same time, it is also the second section of the liability side of the balance sheet, which shows the sources of financing for the property. AND…
- III. CAPITAL AND RESERVES Section III Capital and Reserves is the third section of the balance sheet. But what is more important is the first section of financial sources, that is, the liability side of the balance sheet. By this he...
- V. CURRENT LIABILITIES Section V. Current liabilities is the fifth section of the balance sheet. At the same time, it is also the third section of the liability side of the balance sheet, which shows the sources of financing for the property. AND…
- Balance sheet asset A balance sheet asset is a part of the balance sheet containing data on the assets of the enterprise, that is, on its property. The balance sheet asset reflects property, property rights and cash...
- Financial analysis of budgetary organizations online for free: state (municipal) institutions and... This is a new free analysis service taking into account changes in reporting for 2021 and beyond. For earlier reporting, the analysis is here: analysis of data from a budgetary organization...
- Analysis of enterprise bankruptcy Hello, my dear reader. This service allows you to analyze the bankruptcy of an enterprise using a number of popular bankruptcy risk assessment models, as well as using some indicators from regulatory…
- Price of work Hello, my dear reader. On this page you can estimate the value of your work using popular exchanges.
An example of determining the cost of financial investments (calculation, postings)
JSC “Your Housing” decides to buy out 1,200 shares of JSC “Stroy Vostok” in January of the current period. Each security cost the joint-stock company 2,300 rubles. In addition, the company had to incur costs for specialist consultation in the amount of 21,000 rubles (including VAT of 4,215.33 rubles). The accountant will record the transactions in the following order:
| Operations | Amount (rubles) | DEBIT | CREDIT |
| Securities accepted for accounting | 2 760 000 | 58.01 | 76 |
| Additional costs involved in the formation of the initial cost of shares are taken into account | 21 000 | 58.01 | 76 |
| The money was transferred to the counterparty, the accounts payable under the transaction were repaid | 2 760 000 | 76 | 51 |
So, since the amounts of additional costs are also taken into account when forming the value on line 1170, the accountant will reflect on the specified line of the balance sheet an indicator equal to 2,760,000 rubles.
Example of filling out line 1170 “Financial investments”
Let's imagine a hypothetical enterprise, Kras Finance LLC. Let's turn to the company's balance sheet - there are no account indicators in the accounting. 55 s/sch. 55.3. Let's consider the available indicators for accounts 58, 59, 73 s/sch. 73.1:
The information will be reflected in the Balance Sheet as follows (fragment of form No. 1):
Let's calculate the cost of the company's long-term financial investments minus the formed reserve:
Now we can imagine how the received information will be reflected in Form No. 1 of the Kras Finance LLC enterprise:
Results
Financial investments in the balance sheet are reflected on lines 1170 and 1240. At the same time, in accordance with the current accounting legislation, it is necessary to organize separate accounting of short-term and long-term financial investments.
Sources
- https://finzz.ru/finansovye-vlozheniya-v-balanse-chto-vxodit-raschet.html
- https://buh-spravka.ru/buhgalterskij-uchet/buhgalterskij-balans/stroka-balansa-1240-rasshifrovka.html
- https://ppnf.ru/buhgalter/1240.htm
- https://moneymakerfactory.ru/spravochnik/stroka-1240-balansa/
- https://ppnf.ru/buhgalter/1170.htm
- https://WiseEconomist.ru/poleznoe/21772-finansovye-vlozheniya-formirovanie-pervonachalnoj-stoimosti
- https://moneymakerfactory.ru/spravochnik/stroka-1170-balansa-finansovyie-vlojeniya/
- https://nalog-nalog.ru/buhgalterskij_uchet/vedenie_buhgalterskogo_ucheta/finansovye_vlozheniya_v_balanse_eto/
- https://www.audit-it.ru/terms/accounting/finansovye_vlozheniya.html
What information is subject to disclosure in financial statements regarding financial investments?
The accountant of an enterprise making financial investments must disclose in the financial statements at least the information listed below (provided that they are material):
- methods chosen by the organization for assessing financial investments in the event of their disposal (by groups, types) and the expected consequences of changing the methods of such assessment;
- information on issued borrowed funds and available debt securities (namely data on their valuation at discounted value, on the amount of such value, on the selected discounting methods) - such information is subject to disclosure in the notes to the Profit and Loss Statement and the balance sheet;
- the cost of financial investments for which it is realistic to find out the current market value;
- the value of financial investments for which it is impossible to determine the amount of the current market value;
- the difference between the previous assessment of financial investments, which the company relied on to calculate the current market value, and the current market value as of the reporting date;
- information about the reserve formed in case of depreciation of financial investments (here you will need to explain the type of investment, the amount of the formed reserve for the reporting year, the amount of the reserve used during the reporting year, the amount of the reserve included in other income in the reporting year);
- types and value of financial investments, taking into account securities that were transferred to other legal entities (not sold);
- the cost and types of securities and other investments that are encumbered with collateral;
- the difference between the size of the initial cost and the nominal value during the circulation period of the securities (for debt securities for which the current market value could not be determined).
How to reflect financial investments in accounting
Important! Before information about current financial investments is reflected on line 1170 of the Balance Sheet, their value is collected in account 58 “Financial Investments”. At the same time, deposits must be accounted for in subaccount 55.3 “Deposit accounts” of account 55 “Special accounts in banks”. Interest-bearing loans issued to employees of an organization can be reflected in account 73 “Settlements with personnel for other operations” (subaccount 73.1 “Settlements on loans provided”).
If a company has made financial investments in securities, the following information about them must be reflected in analytical accounting:
- full name of the issuer of securities;
- price of securities;
- details, name of the paper;
- the total number of securities purchased;
- storage location for purchased papers;
- the date of purchase of the asset and the day of their disposal.
No matter what accounts information about investments is generated, financial indicators will always be reflected on line 1170 of the balance sheet.
Explanation of credits and loans to the presented balances
After all, the Chart of Accounts and the Instructions for its application do not provide for the transfer of short-term credits and borrowings from account 67 to account 66 (Order of the Ministry of Finance dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n).
For each balance line, you need to enter the corresponding code in the column. What code to put if a line includes several indicators, each of which has its own code? Clause 5 of Order No. 66n of the Ministry of Finance “On Forms of Accounting Reports of Organizations” states that the code corresponding to the largest share is assigned.
Let me tell you right away, this is not an easy task. First, I recommend checking the arithmetic calculations. If there are no problems with arithmetic, proceed to checking the accounting entries in OSV.