What is consolidated reporting and why is it needed?
The definition of consolidated financial statements is related to the definition of a group of companies.
A group of companies is two or more enterprises that have legal status and are united into one group, which as an economic unit is not considered a legal entity.
Control over enterprises (subsidiaries) is exercised by the parent (parent or management) company, which determines the financial and economic activities of its subsidiaries to obtain financial benefits. The most common forms of creating groups of enterprises are holding companies and concerns.
Consolidated financial statements (KFO) are a type of reporting that contains reliable information about the property and financial condition of a group of companies, the economic results of its activities, and the prospects for future development.
The CFO is compiled independently of the financial statements and is not submitted to the tax service or other government bodies. The document gives only a general idea of the affairs of the entire interconnected group as one whole, but not for each enterprise separately.
International Financial Reporting Standard (IFRS) 10 Consolidated Financial Statements .
The CFR must comply with IFRS standards and be for informational purposes only. It is provided to third party users interested in the group of companies and is aimed at increasing their trust. Based on such a report, users make decisions regarding a group of enterprises.
REFERENCE. To improve the level of accounting and reporting, the Government of the Russian Federation carried out a corresponding reform that brought Russian accounting and reporting standards closer to International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS).
Violations and errors encountered when taking annual swelling
09/21/2020 The Accounts Chamber published the Conclusion on the report on the execution of the federal budget for 2021, containing, among other things, subsection 5 “Result of verification and analysis of the preparation and presentation of budget reporting, maintaining budget accounting”, as well as Appendix 5 to subsection 5, containing information about violations and shortcomings in maintaining budget accounting and preparing annual reports. This Conclusion was analyzed and the most common errors were presented.
1. Errors in reflecting deferred income:
- 401.40 “Deferred income” KBK “ХХХХХХХХХХХХХХ120” in f. 0503169 “Information on accounts receivable and payable” (accounts payable) (hereinafter f. 0503169) as of January 1, 2021 reflects the accrual of deferred income not confirmed by accounting registers;
- in f. 0503169 as of January 1, 2021, allowed the indicator of account 401.40 to exceed the indicators of accounts 205.21 “Calculations for income from operating leases” and 205.23, since the documents for reflecting in the accounting records the recognition of future income as income of the current period are not presented in full.
2. Errors in accounting for capital investments:
- violation of the requirements of clause 127 of the Unified Chart of Accounts and instructions for its application, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 1, 2010 No. 157n (hereinafter referred to as Instruction No. 157n), according to which investments in the amount of the actual costs of the institution in objects of non-financial assets during their acquisition, construction ( creation), modernization, manufacturing, as well as costs associated with the implementation of research and development work, which will subsequently be accepted for accounting as non-financial assets, are taken into account in account 106.00 “Investments in non-financial assets”, expenses incurred by the government establishment in 2021 for the object, in f. 0503130 “Balance sheet of GRBS, RBS, PBS” (hereinafter f. 0503130) are reflected in line 570 “Financial result of an economic entity”, and not in line 120 “Investments in non-financial assets” (010600000)” and are not reflected in f. 0503190 “Information on investments in real estate, unfinished construction projects” (hereinafter f. 0503190) for this object.
3. Errors in accounting for intangible assets:
- violation of clause 56 of Instruction No. 157n, which determines that intangible assets include objects of non-financial assets intended for repeated use and (or) constant use in the activities of an institution for a long time, that is, a useful life lasting more than 12 months, in f. 0503130 on line 040 “Intangible assets (book value 010200000)” and on line 060 “Intangible assets (residual value, line 040 - 050)” the value of intangible assets is overstated.
- violation of clause 56 of Instruction No. 157n on account 010200000 “Intangible assets” in f. 0503130 the value of the intangible asset is not reflected.
4. Errors in accounting and classification of accounts receivable:
- under account 205.32 “Calculations for income from payments for the use of natural resources” in f. 0503169 as of January 1 in section 1 in column 9 “Amount of debt at the end of the reporting period, total”, column 11 “Overdue debt” and in section 2 “Information on overdue debt” accounts payable, repaid in accordance with the writ of execution, are reflected unreasonably;
- under account 209.71 “Calculations for damage to fixed assets” in f. 0503169 as of January 1, 2021, reflects unconfirmed receivables with an expired statute of limitations;
- in f. 0503169 long-term accounts receivable includes overdue accounts receivable;
- violation of the requirement of paragraph 3 of the decision to recognize the debt on payments to the federal budget as uncollectible, approved by the order, was unreasonably recognized as uncollectible and the receivables were written off. The debt is subject to restoration in accounting, as a result of which f. 0503169 and corresponding f. 0503110 “Certificate for concluding accounts” (hereinafter f. 0503110) and f. 0503130, subject to correction;
5. Errors in accounting for fixed assets:
- violation of clause 53 of Instruction No. 157n in f. 0503168 “Information on the movement of NFA” (hereinafter f. 0503168) in column 4 “Availability at the beginning of the year” and column 11 “Availability at the end of the year” on lines 011 and 012 of the consolidated budget reporting and reporting of the central office, the cost of the object is reflected unreliably. The accounting object, which, in accordance with the data of the Unified State Register of Real Estate (hereinafter, EGRN) is a non-residential building, is reflected in account 101.11 “Residential premises” instead of account 101.12 “Non-residential premises (buildings and structures)”, which resulted in a distortion of the relevant reporting indicators;
- violation of paragraph 5, paragraph 45 of Instruction No. 157n, paragraph. 2 clause 10 of the FSBU “Fixed Assets”, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia No. 257N, according to which an object of fixed assets is recognized as an object of property with all fixtures and accessories or a separate structurally isolated item intended to perform certain independent functions, communications inside buildings, necessary for their operation, in particular internal telephone and signaling networks; ventilation devices for general sanitary purposes; lifts and elevators are part of the building and are not separate inventory objects; when an institution takes into account the acquired real estate object, two passenger elevators and a supply and exhaust ventilation system, an air conditioning system, a fire alarm system purchased as part of the building, which can only perform their functions as part of the building, and not independently, were placed on the balance sheet as movable property with separate inventory numbers, which underestimated the book value of the building. Thus, the indicators f. 0503168 are unreliable, since the amount on line 012 “Non-residential premises (buildings and structures)” is underestimated, and the amount on line 014 “Machinery and equipment” is overstated.
6. Errors in applying budget classification:
- the part of the payment received in 2021 to the appropriate CBK was not clarified, as a result of which the indicators of cash receipts in the fund were distorted. 0503127 “Report on budget execution” (hereinafter f. 0503127) and f. 0503169.
7. Errors in filling out reporting forms.
8. Errors in the working chart of accounts:
- violation of paragraphs. “b” clause 9 of the Federal Accounting Standards Accounting Policy “Accounting Policies, Estimates and Errors” The accounting policy of the institution does not contain the applicable accounting accounts that were used in 2019.
9. Errors when taking inventory:
- violation of part 1 of Art. 11 Federal Law No. 402 “On Accounting”, which establishes that an inventory is mandatory before drawing up annual budget reporting, except for property whose inventory is carried out no earlier than October 1 of the reporting year, the inventory of accounting accounts has not been carried out in full.
10. Errors when accounting for the authorization of expenses:
- in the consolidated report f. 0503128 “Report on Liabilities” (hereinafter f. 0503128) reflects obligations that are not included in the reports included in the consolidated report.
11. Errors in accounting for financial results:
- violation of clause 44 of Instruction No. 191n in the consolidated f. 0503110 indicators columns 2, 3,4,5,6 in account 040130000 are overestimated.
Let's consider the general scheme for correcting mistakes of past years. According to the Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated September 14, 2020 No. 198N, which entered into force, which introduced Amendments to Instruction No. 157, accounts for correcting errors of previous years were changed. Although these accounts began to operate on January 1, 2021, the Ministry of Finance does not deny the possibility of applying these accounts to accounting transactions in 2021, subject to their inclusion in the institution’s Accounting Policy for 2021.
Conventionally, accounting accounts for correcting errors of previous years can be divided into two groups:
Group 1 - errors identified by the institution independently. For this group of errors, Instruction No. 157n provides the following accounts:
The year preceding the reporting year: 304.86, 401.18, 401.28.
Past Fiscal Years: 304.96, 401.19, 401.29.
Group 2 - violations that were identified during control activities by the body authorized to draw up a protocol on an Administrative Offense. For this group of errors, Instruction No. 157n provides the following accounts:
The year preceding the reporting year: 304.66, 401.16, 401.26.
Past Fiscal Years: 304.76, 401.17, 401.27.
At the same time, please note that the following accounting accounts were excluded: 304.84,304.94.
Thus, in case:
1. A business transaction to reflect the income of an institution is subject to correction.
Initial operation: DT 205.XX - CT 401.10
Correction operation: DT 205.XX - CT 401.18 (401.19)
2. The business transaction to reflect the expenses of the institution is subject to correction:
Initial operation: DT 401.20 - CT 104.XX
Correction operation: DT 401.28 (401.29) - KT 104.XX
3. A business transaction that does not contain income and expenses of the institution is subject to correction:
Initial operation: DT 302.XX - CT 206.XX
Correction operation: DT 302.XX - KT 304.86 (304.96)
DT 304.86 (304.96) - KT 206.ХХ
As for off-balance sheet accounts, today there are no special accounts for off-balance sheet accounts to correct errors of previous years. There is also no mechanism for reflecting in reporting forms the correction of errors of previous years in off-balance sheet accounts. However, starting from 2021, the Ministry of Finance announced a change to form 0503173 (0503773) “Information on changes in balance sheet currency” to reflect adjustments in terms of correcting errors of previous years made in the form “Information on the presence of property and liabilities on off-balance sheet accounts”, presented as part of Balance (f. 0503130, 0503730).
List of legal entities providing CFO
In the Russian Federation, any groups that have subsidiaries are required to provide such reporting. The preparation, presentation, audit and disclosure of financial statements is regulated by the Federal Law “On Consolidated Financial Statements” dated July 27, 2010 No. 208-FZ (latest edition). According to Art. 2 clause 1 of the above law, CFOs are obliged to form:
- credit organizations;
- clearing organizations;
- NPF - non-state pension funds;
- companies whose securities are participating in trading;
- insurance companies, except for the medical sector;
- management companies of non-state pension funds and investment funds, including mutual funds;
- other groups of companies, the list of which is determined by law.
What are the analytical capabilities of consolidated reporting to characterize financial stability?
By whom and for whom are consolidated statements prepared?
The KFO is compiled by the parent company of the group and determines the categories of reporting recipients. These are:
- Participants and owners of enterprise property - shareholders, founders, board of directors. They are the first to receive annual/interim reporting within the deadlines established by law: 120 and 60 days, respectively, from the end of the reporting period.
- The Central Bank of the Russian Federation receives the CFO in the manner and within the time limits established by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation.
- Users of interest are suppliers, investors and others. For them, reporting is posted on public resources such as media and Internet portals for 30 days.
Composition and features of CFO
KFO has some differences from standard financial statements. Firstly, information about economic activities comes not from one, but from several organizations. Secondly, consolidated reporting has a different range of users. Thirdly, a different report generation technique is used.
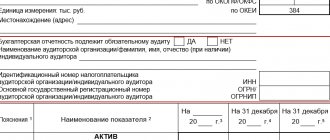
What KFO contains:
- the entire balance sheet with the necessary attachments and summaries (Form 1);
- a complete profit/loss report for the entire group of companies (Form 2);
- information summary about the group members: their full list, registration addresses and the share of the parent company in the authorized capital.
Consequently, the essence of the formation of the CFO is to combine the reports of the management and subsidiaries into one document. In this case, settlement transactions carried out between group members are excluded from the results of financial activities. This is done to provide information related to the group's performance in the external environment. Otherwise, the final indicators will be distorted.
When preparing reporting, the size of the share in the authorized capital of a subsidiary owned by the parent company plays an important role. If the share is more than 51% or the company holds a controlling stake, then the full financial indicators of the subsidiaries are included in the report. If the share of participation is less than 20%, the financial indicators of this organization are not included in the report. In other cases, indicators are proportional to the share of participation.
Assets and liabilities
The balance sheet consists of two large parts, equal to each other - assets and liabilities. A company balance sheet in which assets do not equal liabilities is erroneous. The thing is that assets and liabilities do not exist separately in the real world. Both assets and liabilities are the same thing, just grouped according to different criteria.
There is no word “liabilities” in foreign reporting. Instead of “liabilities” on foreign balance sheets you will see “capital and liabilities”. Alas, financially illiterate translators often translate liabilities as “liabilities,” although obligations are only part of liabilities. To avoid confusion, I use the term “liabilities” as is customary in Russian accounting practice.
Among novice investors, thanks to Kiyosaki, there was an impression that assets are good and liabilities are bad. Even after correcting the translators' mistake, this statement is inherently false. Assets cannot exist without liabilities. Both assets and liabilities are the property of the company.
Assets are the company's property, grouped by its type.
Liabilities are the company's assets, grouped by their sources.
Assets show what the company has now, and liabilities tell where it came from.
Other consolidated reporting requirements
- The assessment of the reports of subsidiaries should be carried out according to principles common to all.
- The report must be generated in one language and in one currency (for the Russian Federation - Russian and in rubles).
- The accuracy of all information and the order in which it is presented must be observed. The head of the parent company is responsible for this.
- A uniform procedure and exact deadline for submitting reports to the parent organization by subsidiaries is mandatory.
- The reporting requirement must be met by absolutely all group members.
- The CFO must have an auditor's report, which must be presented and disclosed along with the financial statements.
IMPORTANT! If the parent company has subsidiaries located abroad, then their data on financial and economic activities must be reflected in the report. Moreover, all information must be in Russian or with a translation attached to the document.
Methods for forming CFO
In order to process a large amount of data, several methods for generating CFOs are used. The choice of method is made by the parent organization, which is influenced by the nature of the enterprise’s activities and the share of the company that it owns.
Full consolidation
The method is used when consolidating reports by the parent organization from dependent (subsidiary) enterprises. This approach requires a clear definition of the structure of the group of companies. Here, the method of adding up the indicators of the balance sheet items of the same name minus intragroup settlement transactions is used.
Share
The method is relevant if the investor has a share of the capital of the organization, but is not its member. Consequently, profit and loss are determined based on the actual cost of the share, followed by an adjustment to the share of the organization's profit.
Interest pooling method
When several firms equally own an enterprise, but there is no parent organization in the structure, the pooling of interests method is used. In this case, when preparing reports, each owner must reflect information regarding all subsidiaries.
Combined reporting
Combined reporting is formed in cases where there is a group of companies without a parent company, but essentially owned by one owner without any legal connection. As a result, reports are first compiled for each organization, after which all indicators (including capital) are summarized in one document, after which intra-group calculations are subtracted.
The right to sign financial documents
Financial documents are important components of the successful operation of any enterprise that is engaged in foreign economic activity. It is necessary to correctly draw up and certify these papers so that they do not lose their legal force.
The first and second signing rights belong to the director of the enterprise and the chief accountant, respectively. The remaining rights can be transferred to authorized persons. To obtain the right to perform this procedure, they must have a power of attorney. You can verify it in two ways:
- Inside the enterprise, by drawing up a special order. This method is used most often. It does not require large financial and time expenditures, and is also easy to implement.
- Through a notary. This method is much less common.
The right to sign is often held by the company's accountant. But if necessary, it can be transferred to any other authorized employee.