Any business involves certain types of costs. Among them, a significant place is occupied by the so-called commercial expenses. The efficiency of the entire economic and production system of the enterprise depends on their formation and management.
Let's consider what an organization's commercial expenses are, what influences their distribution and analysis, how to correctly reflect them in financial accounting, and also give specific examples of calculations regarding commercial expenses.
sales expenses (commercial expenses) in the accounting of a production organization if the accounting policy for accounting purposes provides for the complete write-off of such expenses to the cost of sales?
Let's decipher the term business expenses
If an organization is engaged in the production and sale of goods and/or services, it will certainly incur costs directly related to its direct activities. Costs directly for production are taken into account separately, the rest are called commercial, otherwise non-productive.
What expenses are included in business expenses ?
These types of expenses include:
- costs associated with the shipment of goods sold;
- expenses associated with the implementation process;
- the cost of packaging or containers, if it is not produced but purchased from another organization;
- payment to third-party packers if their services are used;
- costs of delivering goods to the destination specified in the contract;
- advertising and marketing expenses;
- commissions and deductions to intermediaries;
- rental of warehouses, shops, etc.;
- ensuring storage of goods;
- representation expenses;
- licensing and/or certification costs;
- wages for distributors;
- other expenses close to their intended purpose.
NOTE! It is allowed to include in business expenses costs not only for sales, but also for the purchase of goods.
Such costs are called transport and procurement costs (TPP). They are distributed between goods already sold and goods not yet sold.
Activities
If an organization keeps records of areas of activity, it is necessary to enter them in a special directory:
Section: Financial results and controlling – See also – Areas of activity
For an area of activity, indicate its name and status - “Used” or “Not used”. If necessary, you can create groups in the directory that can be selected in the “Directions group” field:
The role of commercial expenses in the economic mechanism of the organization
Only those business activities that effectively record and manage their financial results, which include business expenses, will be successful. The factors of their influence on the economic mechanism are very significant and diverse.
- A direct connection with the profitability of production - an analysis of the dynamics of business expenses and ways to manage them shows ways to increase the efficiency of business, as well as “weaknesses” that should be given increased attention.
- Determination of reserves for reducing production costs . The rise or fall of business costs clearly shows the financial potential for different types of activities and types of goods produced.
- Pricing policy – accounting for business expenses allows you to correctly set prices for the company’s products.
- Calculation of economic efficiency in case of technology changes, modernization, acquisition of new equipment, etc.
- Formation of a product range - justification for making decisions on the removal of any products from production or the introduction of new ones.
- Dominant position in the financial accounting of the organization - it is commercial indicators that are the main accounting reporting units.
- Impact on national income throughout the state.
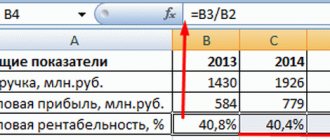
What accounting data is used when filling out line 2210 “Business expenses” ?
Financial Accounting Settings
To maintain financial accounting in the 1C: Trade Management program, you need to configure its parameters in accordance with the needs of the enterprise. This can be done in a special form.
Section: Master data and administration – Section settings – Financial accounting and controlling
The link opens the “Financial result and controlling” settings form, which contains sections for settings for financial results, accounting for goods and target indicators. Let’s look at the “Financial Result” settings section:
There are checkboxes here that enable or disable the following features:
- “Take into account other income and expenses” - accounting for income and expenses not related to core activities, as well as deferred expenses and additional expenses for goods.
- “Financial result by areas of activity” is the ability to register the company’s areas of activity in the program and then take into account income and expenses in the context of these areas.
- “Groups of financial accounting settings” – additional settings for items and calculations that allow you to group objects according to the rules of reflection in accounting.
- “Groups for analytical accounting of items” – additional analytics for items, allowing the user to independently create analytical accounting parameters, indicate them during operations and then generate reports in their context.
- “Take into account other assets and liabilities” - the ability to reflect other transactions (not related to the main activity) associated with assets or liabilities, for example, transactions with fixed assets.
- “Create a management balance sheet” – the ability to generate a “Management Balance Sheet” report to analyze the financial condition of the enterprise and control the balance of assets and liabilities.
How are business expenses calculated?
One of the key commercial characteristics of a product is its cost. It can only be determined during the production process, since it consists of the amount of funds spent on the production itself (production costs) and on sales (commercial costs).
The organization's accounting must take into account such costs in account 43 “Business expenses”. The debit shows the costs of selling products for the reporting month, the credit shows the amounts that were written off for products sold in the reporting month, and the balance shows the costs of shipped products that have not yet been paid for at the beginning dates of the month.
The debit of account 43 “Business expenses” allows you to take into account this type of cost, which passes through the credits of the following accounts:
- costs for containers and packaging – account 10 “Materials”;
- expenses for transport delivery of sold products to the buyer’s warehouse or to the point of further departure (airport, port, railway station) - account 23 “Auxiliary means”;
- payment for delivery to the buyer, if it is carried out by a third party - account 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors”;
- salaries for employees accompanying products, sellers, etc. – account 70 “settlements with personnel for wages”.
Statement 15 for accounting for general business expenses, future and non-production, reflects the result of analytical accounting of business expenses.
When the accounting month ends, these types of expenses are written off to cost of goods sold. You can use a direct route for this (for specific types of products), and it is permissible to distribute costs in proportion to the cost and number of goods sold (if it is difficult to classify products into one group or another). To do this, the following accounting entry is used:
- debit 46 “Sales of products, works, services”;
- credit 43 “Business expenses”.
FOR YOUR INFORMATION! If during the reporting month not all of the planned products were sold, but only some part of them, then it is advisable to distribute commercial expenses for the sold and unsold part of the products, for example, according to the cost of goods or in another acceptable way.
New chart of accounts and business expenses
One of the accounting innovations provides for the posting of commercial expenses in account 44 “Sales expenses”. The debit of this account accumulates the amounts of funds spent on the sale of goods, services, and work performed. The assets in this account are written off as a debit to account 90 “Sales”.
Selling expenses on the balance sheet
The balance sheet does not provide a special item for business expenses. When drawing up a balance, the balance of funds in account 43 “Business expenses” is added to the balances accumulated in account 45 “Shipped goods”.
Methods for distributing income and expenses by area of activity
In order for income or expense to be attributed to any area of activity, one or more distribution methods must be specified in the program. To do this, you need to enter them in the appropriate directory:
Section: Financial results and controlling – See also – Methods for distributing income and expenses by area of activity
When entering a method, you must select a distribution rule: proportional to income, expenses, gross profit or coefficients. In addition, the tabular part indicates the areas of activity for which distribution will be made in this way. If the tabular part is left empty, the distribution of income or expense will occur in all directions.
When choosing the “Proportional to coefficients” rule, you must specify a coefficient for each area of activity. If you enter only one direction and specify any coefficient for it, then the income or expense will be completely attributed to this direction.
In the future, the distribution method can be used when distributing both other income or expenses and sales from core activities.
When reflecting other income or expenses, the item of income and expense that is selected in the document “works” (for example, a payment document, sale or receipt of services and other assets, etc.). If the article specifies the distribution option “By areas of activity,” then the distribution method must also be selected. The amount of income or expense will be distributed between areas of activity according to this method. For more information about other income and expenses, see our materials on management accounting in UT - “Other income” and “Other expenses”.
Also, distribution methods can be used in setting up automatic sales distribution.
Business expenses and taxation
The difficulty is that it is necessary to separate the costs of selling products and advertising costs, which are also non-sales, but are standardized according to another article of the Tax Code (clause 4 of Article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In the income tax, the share of advertising tax will be no more than 1% of revenue, which will make the difference in tax and accounting.
FOR EXAMPLE. For the reporting period, Primavera LLC received incremental revenue in the amount of RUB 6,500,000. excluding value added tax. Advertising expenses according to accounting data amounted to 70,000 rubles. Let's calculate how much advertising costs can be used to calculate income tax.
According to the rate of advertising costs given in paragraph 4 of Art. 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, advertising expenses cannot exceed 1% of revenue: 6,500,000 x 1% = 65,000 rubles. This percentage is less than the funds actually spent on advertising - 70,000 rubles. Consequently, income tax will be calculated only on 65,000 rubles, and the difference in tax and accounting will be 5 thousand rubles.
Optimization of business expenses
Effectively reducing sales costs is a direct path to increased profitability and profitability. The following ways to optimize this type of expense can be identified:
- cost reduction should not be an end in itself; it is much more important to organize effective management;
- any unit of spending should bring the most effective result;
- it should be remembered that expenses are the result of both actions and inactions;
- cost reduction is impossible without corresponding costs invested in it;
- maintaining the level of spending at an optimal level is already considered successful from the point of view of economic efficiency;
- one should not skimp on expenses that will help insure against more significant costs;
- Analytical work to optimize commercial costs must be ongoing.
Financial results
After completing the routine operations for closing the month, sales will be distributed according to the settings. This will be reflected in the reports. Let's look at the "Financial Results" report.
Section: Financial results and controlling – Reports on financial results – Financial results
The report is generated in the management accounting currency. Sales revenue and cost of sales are distributed by business area. Please note that in the direction “Add. services”, only revenue is distributed, and there is no cost (since it cannot exist for a service).