The obligation of an employer who sends his employee on a business trip is to reimburse the latter’s expenses. The employee is reimbursed for food, accommodation, daily allowance, and travel to the destination. Regardless of what transport the employee used and how the ticket was purchased, the expenses incurred by him are subject to reimbursement. Payment for the ticket and reimbursement to the employee are subject to reflection in the employer's accounting. In this article we will look at how air tickets are accounted for in accounting.
Features of air ticket accounting
An air ticket is a contract of carriage concluded between a passenger and an airline and gives the right to air transportation services, in the form of a registered document. A ticket is a means of control that must be registered before departure, after which the passenger is issued a boarding pass.
Important! Accounting for air tickets is carried out on the basis of documented costs incurred by employees to travel to their destination. These expenses are classified as other expenses and are taken into account when determining the taxable base for income tax.
The employer is obligated to reimburse the employee's expenses on a business trip, including daily allowances, food and accommodation, and travel. Employees are reimbursed for their travel, regardless of what type of transport was used and how the ticket was purchased. The main thing is that the employee can provide the employer with justification for the amounts spent.
Calculations for travel expenses
The rules for sending employees on a business trip are established by regulations approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated October 13, 2008 No. 749. According to clause 10 of this document, funds are issued to the employee before the trip to pay for:
- accommodation;
- travel;
- additional expenses due to being away from home.
The advance report must be submitted before the expiration of the working days established by the employer after returning from a business trip. Supporting documents must be attached for all expenses (except for daily allowance).
For BU, there are some restrictions on the amount of reimbursement for domestic Russian business trips, established by paragraph 1 of Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated October 2, 2002 No. 729. If expenses exceed the limits, they can be reimbursed from saved budget funds or from funds from the commercial activities of BU ( clause 3 of resolution No. 729). The following table shows the maximum limits:
| Type of expenses | Amount of reimbursed expenses | |
| Expenses confirmed | Expenses are not confirmed | |
| Renting housing | No more than 550 rub. per day | 12 rub. per day |
| Daily allowance | 100 rub. in a day | |
| Travel by train | No more than the cost of a ticket for a compartment carriage of a fast branded train | Cost of a reserved seat |
| Travel by water | No more than the cost of the ticket:
| Ticket price:
|
| Travel by plane | No more than the cost of an economy class ticket | – |
| Travel by car | Not more than the cost of a ticket for a public vehicle (except taxi) | Public bus ticket cost |
For business trips abroad, standards for compensation of expenses for rental housing have also been developed - this is Order No. 64n of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated August 2, 2004, and for daily allowances the norms are regulated by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 2005 No. 812. The limit values are described in the context of the countries where the employee is sent.
Let us note that for civil servants there is a separate document regulating business trips - Decree of the President of the Russian Federation dated July 18, 2005 No. 813.
Accounting for air tickets in accounting
Reflection in the accounting of expenses for the purchase of air tickets by employees is possible if the following documents are attached to the expense report:
- an air ticket, upon purchase of which a receipt was issued, or an itinerary receipt, which reflects all the data about the trip, including the cost of the flight;
- boarding pass, which reflects passenger information, dates of departure and arrival, as well as information about the seat.
Electronic tickets are reflected in subaccount 50.3. This amount is written off as expenses after the expense report is approved. Let's take a closer look at examples.
Example 1: A company paid by bank transfer for an electronic air ticket for an employee going on a business trip. The ticket cost was 10,000 rubles. The accounting transactions will include the following:
| Business transaction | D | TO |
| Payment for an electronic ticket in the amount of 10,000 rubles | 60 | 51 |
| Receipt of electronic itinerary receipt | 50.3 | 60 |
| The employee was issued a route receipt | 71 | 50.3 |
| Upon return, the employee submitted an advance report and the costs were recognized. | 26 | 71 |
Example 2: A company paid for an electronic ticket worth 12,000 rubles by bank transfer. Due to the fact that the date of the trip had changed, the air ticket was returned on the same day. The airline withheld the fee, resulting in the refund amounting to 10,000 rubles. The reflection of these transactions in accounting in this case will be as follows:
| Business transaction | D | TO |
| Payment for an electronic ticket in the amount of 12,000 rubles | 60 | 51 |
| Receipt of electronic itinerary receipt | 50.3 | 60 |
| Air ticket refunded | 60 | 50.3 |
| The airline received money for the returned air ticket to the company's bank account, the amount is 10,000 rubles | 51 | 60 |
| The difference is included in the company's expenses, the amount is 2000 rubles (12000 - 10000) | 91.2 | 60 |
How to reflect an advance on a business trip
Let’s say an employee contacts the institution’s cash desk to receive money for a business trip. The employee has a calculation note in his hands, approved by the manager.
Cashier actions:
- We check the administrative document. Let us remind you that such a document can be a management order, an employee statement, or a separate calculation note. All documents must be signed by the director.
- We issue a cash order if a subordinate wishes to receive an advance payment in cash for a business trip. Or we draw up a payment order to transfer funds to the employee’s bank card.
- We hand over the cash to the employee against his signature. At the same time, we make an accounting entry: Debit 71 Credit 50 “issued from the cash desk for travel expenses” - posting.
For state employees, when issuing an advance from the cash desk for a business trip, the posting will be different: Debit 0 208 12 560 Credit 0 201 34 610.
When transferring money to current accounts, use similar transactions:
- for non-profit organizations - an advance was issued for travel expenses, posting: Dt 70 Kt 51;
- for state employees - Dt 0 208 12 560 Kt 0 201 11 610.
IMPORTANT!
To establish the amount of payments to a business traveler, you need to issue a special order and Regulations on business trips.
Reflection of service fees in accounting
It is often assumed that the service fee should be classified as a travel expense. However, this type of commission for an intermediary company is not included in the list of travel expenses .
Important! The commission to the intermediary, not included in the transportation tariff, is recognized for tax accounting purposes as other expenses related to production and sales.
The service fee is written off not after the end of the business trip, but when purchasing an air ticket. The postings will be as follows:
| Business transaction | D | TO |
| The service fee has been paid from the current account | 60 | 51 |
| Itinerary receipt received | 50.3 | 60 |
| The cost of the service fee is reflected | 26 | 60 |
Features of the accounting and registration scheme for travel allowances
That is, when a government agency returns a ticket, there may be talk of termination of a previously concluded contract for the carriage of a passenger.
Sending women with children under 3 years of age on business trips is permitted only with their written consent and provided that this is not prohibited to them in accordance with a medical certificate. Women must be informed in writing of their right to refuse assignment on a business trip.
It often happens that companies pay for travel to and from their business trip from their current account, booking air and train tickets in advance: for many this is cheaper and more convenient.
Fuel and lubricants are included in inventories (MPI) and are accepted for accounting at actual cost in accordance with the Accounting Regulations “Accounting for inventories” (approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 06/09/2001 No. 44n, hereinafter referred to as PBU 5 /01). According to the Chart of Accounts, the program uses subaccount 10.03 “Fuel” to account for fuel and lubricants.
The procedure for recording an electronic ticket in an advance report
Accounting expenses are confirmed by primary documentation drawn up in accordance with Art. 9 of Law 402-FZ “On Accounting”. There is no mandatory list of documents that confirm travel expenses. Therefore, in order to recognize expenses for the purchase of electronic air tickets, the following documents should be used:
- A receipt or itinerary, an electronic ticket printed on paper, which indicates the cost of the flight. This will allow you to confirm the costs of purchasing an air ticket.
- A boarding pass issued at check-in when boarding a flight. This document confirms the flight on the route indicated on the ticket.
Lost documents
There are situations when business travelers lose electronic tickets and boarding passes. In this case, the employee simply needs to print out the itinerary receipt from his electronic mailbox again.
The boarding pass cannot be restored. However, the company will still be able to take into account the costs of purchasing an electronic ticket for tax purposes. Firstly, it is enough to confirm the costs indirectly with the help of documents certifying the business trip and the fact of the employee’s stay at the place of the business trip (for example, a hotel bill for accommodation), and a printout of the electronic ticket. Secondly, you can use an archival certificate issued by the carrier company at the request of the passenger and containing the passenger’s last name, first name, patronymic, direction and flight number, departure date and ticket price (see letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 22, 2010 No. 03-03- 06/1/168).
Even if the boarding pass is lost, the cost of the ticket will not be recognized as the employee’s income: according to pop. 3 tbsp. 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, compensation amounts for employee travel expenses are exempt from personal income tax if they have proper documentary evidence. And since the Ministry of Finance of Russia believes that an electronic ticket is in itself sufficient documentary evidence for calculating personal income tax, then the fact of loss of the boarding pass in this case does not matter (letter of the department dated March 21, 2011 No. 03-04-06/6-49).
VAT on air tickets
Sometimes the cost of air tickets purchased to send an employee on a business trip constitutes a large part of all travel expenses. Therefore, the company's desire to reimburse these costs can be explained. VAT on travel expenses can be deducted, so if the company bought the ticket directly from the airline there should be no problem. The seller will issue an invoice, on the basis of which the company will be able to deduct VAT in the usual manner. However, in practice, the employee is often simply given money, with which he independently buys his own air ticket.
According to Art. 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, VAT on travel expenses is accepted for deduction on the basis of the following documents:
- invoice issued by the seller;
- another document in cases provided for in paragraphs 3,6,7,8 of Art. 171 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
If an employee buys a ticket on his own, he is not issued an invoice. Therefore, to obtain a VAT refund, the company has the right to present other documents. For travel expenses, VAT is deductible on the basis of the BSO (strict reporting form) issued to the employee and included in the documents attached to the report. The form must contain a separate line with highlighted VAT. This BSO is subject to registration in the Purchase Book. Also, the conditions for accepting VAT for deduction correspond to the printed route of the electronic ticket. It is necessary that VAT be highlighted as a separate line. You must also keep your boarding pass to confirm your expenses. The tax authority must be able to identify the seller, but if the ticket is issued in a foreign language, this will not be possible. That is, the air ticket must be issued in Russian, and translation of only the necessary details will be sufficient.
How to reflect monetary documents in accounting policies
Let's consider the accounting entries for travel expenses, a list of costs and typical situations when reflecting documents received from an employee who has returned from a business trip.
The itinerary receipt of an electronic air ticket and the control coupon of an electronic railway ticket are strictly accountable documents and are used for cash payments and (or) payments using payment cards without cash registers.
According to the chart of accounts, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 31, 2000 No. 94 n, paid air tickets are accounted for in account 50-3 “Cash documents”. Tickets should be received on the day they are received by the organization. The procedure is equally applicable for tickets on paper and for tickets in electronic form. The balance of unused amounts based on the employee’s application was withheld from his salary.
In this regard, analytical accounts have also changed in order to reflect such expenses in accounting. From January 1, 2019, the procedure for applying KOSGU codes regarding travel expenses has changed. In this regard, analytical accounts have also changed in order to reflect such expenses in accounting.
You will learn about current changes in the CS by becoming a participant in the program developed jointly with Sberbank-AST JSC. Students who successfully complete the program are issued certificates of the established form.
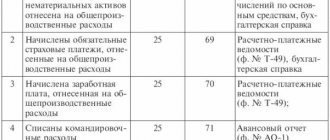
This report (AO-1) is compiled by the employee together with the accounting department and approved by the manager. At the very bottom, the number of documents and sheets on which they are attached to the report is indicated (checks are usually pasted in whole packs onto A4 sheets).
It is a mistake to include the price of a flight as an expense at the time of purchase or issuance. The cost of air travel can be included in expenses only when the business trip has taken place and the employee has submitted an advance report. Purchasing a ticket does not prove the fact of a decrease in economic benefits; the trip may not take place and the ticket will have to be returned with certain monetary losses.
The control coupon is issued and must be sent electronically via the information and telecommunications network to the passenger. It is impossible to accept checks from restaurants and cafes for accounting and tax accounting: it is assumed that food expenses are compensated by the amount of daily allowance, but if a company wants to record such expenses in accounting, then this should be done at the expense of the company’s net profit, without reflecting such expenses in tax accounting.
Accounting of travel tickets
The employer, when sending his employees to places remote from work, is obliged to reimburse the cost of travel tickets. This cost is reflected in account 50.3 as part of the cost of monetary documents. Expenses for business trips are not immediately written off as expenses and are not attributed to reporting employees without intermediate entries. The procedure for reflecting employee travel expenses is as follows:
| Business transaction | D | TO |
| Obtaining travel documentation | 50.3 | 60 |
| VAT is deducted from the ticket price | 19 | 60 |
| Issuing tickets to an employee (amount excluding VAT) | 71 | 50.3 |
| Recognition of travel expenses after the advance report has been approved | 26 | 71 |
Important! You can deduct VAT on travel only if you have an invoice. This is also possible if the tax amount is separately allocated in the travel document.
How to record the purchase of electronic tickets in the accounting of a budgetary institution?
In this article, we will recall the basic rules for sending employees on business trips, talk about the guarantees and compensation that are provided in this case, and also consider the procedure for reflecting travel expenses in the accounting of state (municipal) institutions, based on the changes that occurred from 01/01/2019 in the order of application KOSGU.
Therefore, it is convenient to use account 76.05 “Settlements with other suppliers and contractors” as a settlement account. The same account should be indicated when reflecting payment to the supplier, then there will be no difficulties with offsetting advances.
As we can see, the attribution of travel expenses can be carried out according to various CVR and KOSGU, depending on whether funds are issued (compensated) to the employee or whether the institution purchases services for him.
According to letter No. 03-03-06/1/35212 of the Russian Ministry of Finance, the boarding pass, including its electronic form, issued for electronic registration must have a mark confirming the provision of air transportation services. This mark is an inspection stamp.
At the same time, the difference between the cost of the ticket and the amount of money returned by the air carrier can quite reasonably be attributed to the financial result of the institution’s activities in terms of expenses.
Daily allowances in the Organization in accordance with the Regulations on Business Travel are paid at the rate of 1,500 rubles/day - 4,500 rubles. for 3 days.
The employee is given an advance to purchase travel documents and pay for the hotel, and is paid a daily allowance.
Today in Russia there is no normative definition for the concept of “monetary documents”. A unified register of monetary documents has not been developed either.
Air travel costs typically account for a significant portion of business travel budgets. Business travel expenses are included in other expenses and reduce the amount subject to income tax (Article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 1.12), and when using a simplified taxation scheme, they are included in expenses (Article 252, clause 1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
A correctly drafted local regulatory act should justify the advisability of using monetary documents in a budgetary institution. To do this, you need to carefully define the algorithm by which employees will confirm their expenses.
A business trip is a trip by an employee by order of the employer for a certain period of time to carry out an official assignment outside the place of permanent work.
Since the institution has already paid, but has not yet redeemed the monetary documents, they must be kept in the cash register.
A business trip is a trip by an employee by order of the employer for a certain period of time to carry out an official assignment outside the place of permanent work.
First, we note that an electronic ticket is used to certify a long-distance passenger transportation contract, in which information about the passenger transportation is presented in electronic digital form and is contained in an automated passenger transport management system.
Accounting for tickets for railway transportation in accounting
Confirmation of the fact of purchasing an electronic ticket is a control coupon. It contains all the details about the passenger, transport, and trip. This form belongs to the BSO. In the event that tickets are lost, the costs incurred by the employee can be reimbursed using duplicate documents. If the ticket and other supporting documents are drawn up in a foreign language, then you will need to translate the main details into Russian. If an employee purchases tickets independently, for cash, the postings will be as follows:
| Business transaction | D | TO |
| The employee was given money from the cash register to buy a train ticket. | 71 | 50 |
| Based on the advance report submitted by the employee, the costs are recognized in accounting | 26 | 71 |
If the ticket was purchased through third parties, a commission will be paid to the intermediary. In this case, the wiring will be as follows:
| Business transaction | D | TO |
| Funds for the ticket and service fee were transferred from the current account | 60 | 51 |
| Control coupon received | 50.3 | 60 |
| The cost of intermediary services is included in expenses | 26 | 60 |
Registration of settlements with accountants in the accounting department
According to clause 213 of the instructions for the use of a unified chart of accounts for budgetary structures (Appendix 2 to the order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 1, 2010 No. 157n), money for reporting is issued to the employee on the basis of an application, which must indicate the following information:
- purpose of payment;
- calculation of the necessary funds or explanation of the amount of the advance.
ATTENTION! As of November 30, 2020, the rules for issuing reports have been simplified. Now, in the application for the issuance of accountable money, it is not necessary to indicate the amount of the advance and the period for which the accountable amounts are issued. Employers were also allowed to issue one order for several cash payments to one or more employees. In this case, you need to indicate the name, amount and period for which the money is issued for each employee.
ConsultantPlus experts told us what other innovations in the procedure for recording cash transactions came into effect on November 30, 2020. Get trial access to the K+ system and go to the review material for free.
For public sector employees, there is also a general instruction of the Bank of Russia on the conduct of cash transactions dated March 11, 2014 No. 3210-U, according to which money is issued according to an expenditure cash order, the form of which with code 0310002 was approved for accounting by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated March 30, 2015 No. 52n . Within the period no later than the working days established by the institution after the end of the period for which the money was issued, the employee must report on the expenses incurred by submitting an advance report (form 0504505, approved by the same order No. 52n). All supporting documents are attached to the report.
If the employee does not return the unspent money on time, the employer has the right to deduct the amount of debt from the salary in accordance with Art. 137 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, but only within a month after the expiration of the period allotted for reporting on funds issued for reporting, and also in the absence of disagreements with the employee regarding the grounds and amount of the debt. In addition, we must not forget about Art. 138 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which establishes that only 20% of each salary payment can be used for withholding, i.e., withholding can last for several months.
For information on how to take into account the cash flow in the accounting department, read the material “Accounting for cash transactions in budgetary institutions (nuances)” .