Who pays property tax
The obligation to pay property tax in accordance with Article 400–401 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is assigned to citizens who own:
- residential real estate;
- garages, parking spaces;
- unfinished construction projects;
- other real estate.
CCTV cameras https://www.minimaks.ru/catalog/videokamery/videokamera-antivandalnaya/
Common property owned by homeowners in apartment buildings is not subject to taxation.
For certain categories of citizens, the legislation has introduced benefits that provide for the exemption of the taxpayer from payments relating to one object in each of the following categories:
- apartments (rooms);
- garages (car spaces);
- individual residential buildings;
- outbuildings with an area of less than 50 m2;
- premises used by citizens exclusively for creative activities (workshops, studios, galleries).
In particular, the following are entitled to benefits:
- pensioners;
- disabled people;
- various categories of military personnel, persons equivalent to them, and members of their families.
Article 407 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation also provides for restrictions related to the use of benefits: real estate cannot be used for commercial purposes, and its cadastral value should not exceed 300 million rubles.
How to calculate the simplified tax system “income”
Profit for the purposes of its taxation with the appropriate tax is income reduced by the amount of expenses (Article 247 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). How to calculate profit for the year? The same as for reporting periods, based on the fact that both reporting and tax periods are counted from the beginning of the year (Article 285 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) and, accordingly, data for both components of the calculation of profit must be taken on an accrual basis.
The volumes of income and expenses for calculating the profit base are determined according to the rules of Chapter. 25 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, and since these rules do not always correspond to the rules used in accounting, the need arises:
- in separate tax accounting, from which information about the data for calculating profit will be taken (Article 313 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- reflection in the accounting of persons not exempt from the application of PBU 18/02 (approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 19, 2002 No. 114n), the amount of tax related to permanent and temporary differences arising between accounting and tax accounting.
We suggest you read: How to calculate your house tax using a calculator
Both tax revenues and tax expenses are divided:
- On those related to implementation. Moreover, the amount of income here will also include income from one-time sales (for example, excess inventory, which in accounting is traditionally not taken into account in the amount of income from ordinary activities).
- Non-realization.
The basic tax rate is applied to the result obtained after the last transactions.
We will show you how to calculate profit for the year using specific figures.
Signal LLC, operating in the production sector, summing up the results of work for 2021, received the following data in tax accounting for inclusion in the profit declaration:
- income from sales - 1,187,815,905 rubles;
- expenses associated with obtaining income from sales - 1,092,937,959 rubles;
- non-operating income - 25,325,673 rubles;
- non-operating expenses - RUB 18,820,380.
During 2021, the organization made a number of unprofitable sales of outdated process equipment. The total amount of such loss was RUB 2,539,141.
Signal LLC has a tax loss for 2021 in the amount of RUB 7,279,418.
For 2021, the organization accrued advances on profits in the total amount of 15,550,284 rubles, including to the all-Russian budget - 2,332,543 rubles, to the regional budget - 13,217,741 rubles.
By entering the figures from our example into the calculation of the profit tax for the year reflected in sheet 02 of the declaration for this tax, we get the following picture (in relation to the line numbers of sheet 02):
- Income from sales, line 010 - 1,187,815,905.
- Non-operating income, line 020 - 25,325,673.
- Expenses that reduce the amount of income from sales, line 030 - 1,092,937,959.
- Non-operating expenses, line 040 - 18,820,380.
- Losses, line 050 - 2,539,141.
- Total profit (loss), line 060 - 103,922,380.
- Tax base, line 100 - 103 922 380.
- The amount of loss or part of a loss that reduces the tax base, line 110 - 7,279,418.
- Tax base for calculating tax, line 120 - 96,642,962.
- Total tax rate, line 140 - 20, incl.:
- to the federal budget, line 150 - 3;
- subject's budget, line 160 - 17.
- Total amount of calculated tax, line 180 – 19,328,592, including:
- to the federal budget, line 190 - 2,899,289;
- subject budget, line 200 - 16,429,303.
- Total amount of accrued advance payments, line 210 - 15,550,284, including:
- to the federal budget, line 220 - 2,332,543;
- subject budget, line 230 - 13,217,741.
- Amount of tax to be paid:
- to the federal budget, line 270 - 566,746;
- subject budget, line 271 - 3,211,562.
Let us recall that all indicators involved in calculating the value of the tax base for calculating tax are detailed by composition in the appendices to sheet 02.
IMPORTANT! The declaration for 2021 must be submitted using a new form.
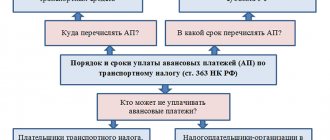
The tax base for transport tax in 2019–2020 is calculated differently for certain types of vehicles (Article 359 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides for only two methods of forming the tax base:
- Cash method, in which NB is calculated on the basis of cash transactions. For example, the amount of income is calculated on the basis of cash receipts made to the company’s bank account for goods shipped, work performed, and services performed. Only those expenses that were actually paid in the reporting period are recognized as expenses. In other words, this method reflects the real (actual) transactions of the taxpayer.
- The accrual or cumulative method, in which the date of actual receipt of income or execution of an expense transaction does not matter. Those transactions that were accrued and accumulated during the reporting period are taken into account for calculation. For example, accrued amounts of income are taken into account without taking into account the facts of payment. In this case, all accepted obligations are recognized as expenses, regardless of the payment made.
Please note that the taxpayer has the right to determine his own method of calculating NB. The only exception is personal income tax. To calculate income tax, only the cash method is used, that is, personal income tax is calculated according to the date of payment and receipt of income.
As is known, the tax base of legal entities and individual entrepreneurs is calculated in a special manner for each fiscal obligation. Let us determine the key features of calculating the national security for income tax.
When taxing personal income, the tax rate is applied to the National Bank, determined in accordance with Chapter 23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Therefore, the taxable amount of income is the tax base for calculating income tax. Please note that not all income received by a Russian or foreign citizen is subject to taxation. Officials have determined a list of income that is not taken into account when determining the tax base.
In addition to the list of excluded income, legislators also provided a number of fiscal benefits and concessions. For example, for personal income tax, these are tax deductions (property, social, standard, investment and professional).
We suggest you read: How to correctly calculate your salary, salary plus percentages
The NB for income tax is calculated using a similar method. All company income received during the reporting period is taken into account. Moreover, the amount is determined by the method that the company independently chose and established in its accounting policies. For example, under the cash method, all revenue actually credited to current accounts and cash received are considered.
Note that for income tax, legislators also determined a list of non-taxable income. Thus, when calculating the tax base, income specified in Art. 251 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. They need to be excluded from the calculation.
Then the total amount of taxable revenue is reduced by expenses actually paid or according to the volume of obligations assumed. The result obtained is the NB for corporate income tax.
Before calculating the 6% simplified tax system, you need to find the value of the tax base. Determining the tax base for this object of taxation does not present any great difficulties, since it does not involve the deduction of expenses and, accordingly, work to establish the composition of the latter for tax purposes.
In order to find out the tax base for the tax period, the actual income received is calculated quarterly on an accrual basis. At the end of the tax period (year), the overall result of income for this period is summed up.
Example
Omega LLC will calculate tax at a simplified tax rate of 6% as follows.
Before calculating the simplified tax system (USN) - income for the year, the accountant should determine the amounts of all advance payments.
- How to calculate the simplified tax system: determining the amount of the advance payment based on the results of the 1st quarter.
850,000 rub. × 6% = 51,000 rub.
51,000 rub. × 50% = 25,500 rub.
51,000 rub. – 21,000 rub. = 30,000 rub.
The advance payment due at the end of the 1st quarter will be equal to 30,000 rubles.
- How to calculate tax according to the simplified tax system 6%: determining the amount of the advance payment based on the results of the six months.
RUB 1,640,000 × 6% = 98,400 rub.
RUB 44,300 17,000 rub. = 61,300 rub.
RUB 98,400 – 49,200 rub. = 49,200 rub.
RUB 49,200 – 30,000 rub. = 19,200 rub.
Thus, at the end of the six months, the amount of the advance payment will be 19,200 rubles.
- How to calculate the simplified tax system 6%: determining the amount of the advance payment based on the results of 9 months.
RUB 2,305,000 × 6% = 138,300 rub.
66,300 rub. 17,000 rub. 7,000 rub. = 90,300 rub.
How is personal property tax calculated?
In relation to the property tax of citizens, a transition period has been established, which involves a gradual transition to the calculation of the specified fee based on the cadastral value.
The decision on such a transition is made at the regional level.
The tax for 2015 will be calculated in a new way in 28 constituent entities of the Russian Federation; in the next reporting period there will be 49 such regions.
Due to the great public interest in the new rules for calculating property tax, the Federal Tax Service (FTS) has introduced a service that allows for a preliminary calculation of the payment amount. All you need to know is the cadastral number assigned to the building or premises.
All organizations pay income tax unless they have switched to an individual payment system. Income tax: rate, calculation and filling out the declaration, read carefully.
Read more about how to calculate the single tax on imputed income here.
The state budget is replenished through various taxes and fees. Here https://businessmonster.ru/buhuchet/nalogooblozhenie/vidyi-nalogov.html we will look at what payments and deductions are due for legal entities and individuals.
Using benefits when calculating tax amounts
Benefits established by federal, regional or local legislation reduce the amount of tax deductions. This may be a full or partial tax exemption. Other options may apply. For example, when paying personal income tax, the amounts specified in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are deducted from the tax base before multiplying it by the rate.
Tax benefits allow you to save significantly. Therefore, before you start calculating the tax amount, you definitely need to find out whether you have these benefits.
Tax on cadastral value
Property tax is calculated on the basis of cadastral property in the entities that have adopted the relevant regulatory legal act. Information about the cost is contained in the state real estate cadastre.
The cadastral value is also approved by an act of the municipality or subject according to data obtained during the mass state cadastral valuation, which is carried out in each subject at least once every five years.
The basis for calculating tax taking into account various categories of real estate is the cadastral value of a specific property minus the cadastral value:
- 20 m2 (apartments);
- 10 m2 (rooms);
- 50 m2 (individual houses).
All types of housing, garages and other related buildings are taxed at a rate of 0.1%.
For owners of luxury real estate (valued at an amount exceeding 300 million rubles), buildings included in a special list (shopping, office complexes) the rate is increased to 2%. Owners of other types of property must pay 0.5%.
By regional legislation, these tariffs can be increased by no more than 3 times, or reduced to zero.
If real estate was acquired or the rights to it were lost during the tax period, then a coefficient is applied to the calculated tax amount, calculated as the ratio of the number of full months of ownership of real estate to 12 (the number of months in a year).
How to calculate the tax base based on the average (average annual) cost
The concept of average cost is applicable only in relation to property available in the reporting period (clause 4 of article 376 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). For calculations over a year, it is called the annual average (annual average). But the principles for determining the average and annual average cost are the same. This calculation is made for all taxable objects as a whole, without singling out specific units from their list. Before its implementation, those that:
- is not considered an object for taxation (clause 4 of article 374 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- exempt from tax (Article 381 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- taxed on a different basis (Article 378.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- refers to capital investments in certain facilities made during the period from 01/01/2010 to 12/31/2024 (clause 6 of article 376 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
From 01/01/2019, movable property is not subject to tax. But information about it must be displayed in the annual declaration.
The average (annual average) value of taxable property is calculated using information about its residual value, determined on the first day of each month of the billing period and on the first day of the month following this period. That is, the calculation will use the number of indicators of this value that is 1 greater than the number of months of the billing period. And by this number of indicators you will need to divide the sum of all residual value values involved in the calculation in order to obtain the average (annual average) value for the billing period.
For example, to calculate for the 1st quarter, 4 values of residual value will be required (we will denote them by letters):
- on January 01 - a;
- on February 1 - b;
- on March 01 - from;
- on April 01 - d.
Then the average cost for the 1st quarter will be determined by the formula:
Сср = (abcd) / 4.
Moreover, even if the property is missing on some date(s) or its residual value is zero, this indicator is still included in the calculation. That is, the amount of value also includes its zero value, and in the number corresponding to the number of indicators for the period, this unit with a zero value is also taken into account.
From inventory value
Until 2021, regions have the right to calculate tax based on information about inventory value.
This cost was determined by the technical inventory authorities (BTI) based on information about the technical inventory of real estate and, until March 1, 2013, was sent by them to the relevant tax inspectorates.
The tax base is calculated by multiplying the inventory value by a special deflator coefficient. The size of this indicator is established annually by the Ministry of Economic Development of the Russian Federation. When determining the amount of payment for the previous year, a coefficient of 1.147 is used. Tax rates are established by the constituent entities of the Russian Federation depending on the cost characteristics of the object of taxation.
Time limits established for advances on property
The deadline for payment of advances will vary by constituent entity of the Russian Federation (clause 1 of Article 383 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). You can check the deadlines for each region on the Federal Tax Service website.
In this case, the reporting periods should be considered quarterly periods of the year, equal in relation to the type of tax base (clause 2 of Article 379 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- quarter, half-year, 9 months, if the base is determined by the average (average annual) cost;
- quarter, if the base depends on the cadastral valuation.
These are the ones you need to focus on when determining the deadline for paying advances.
Tax according to the new rules in the first 4 years: calculation example
During the initial four-year period of application of the new procedure for calculating tax payments, a special method of calculating the amount payable to the budget is in effect. The payment amount is determined by the formula:
N = (N1 – N2) x k + N2,
- where N is the amount of tax to be paid;
- N1 – tax calculated by multiplying the tax base calculated from the cadastral value by the interest rate;
- N2 – the amount of payment paid for the previous tax period (calculated from the inventory value);
- k – coefficient (0.2 – in the first of four years of application of the special regime; 0.4 – in the second; 0.6 – in the third and 0.8 – in the fourth).
If N1 is less than N2, then this formula does not apply. In this case, as well as after four years, the tax amount is calculated as N1.
Calculation algorithm:
| Basic information about the apartment | Computations |
| Cadastral value, rub. | 3 658 800 |
| Tax rate, % | 0,2 |
| Area, m2 | 30 |
| Tax for 2014, calculated on the basis of inventory value, rub. | 401 |
| Deduction, rub. | 2,439,200 (3,658,800 / 30 x 20) |
| Tax base, rub. | 1 219 600 (3 658 800 – 2 439 200) |
| Amount of tax calculated from the cadastral value, rub. | 2439 (1,219,600 x 0.2%) |
| Tax payable for 2015, rub. | 809 ((2439 – 401) x 0.2 + 401) |
Nuances of determining the base for cadastral valuation
The tax base, depending on the cadastral valuation, arises in relation to immovable objects that have a very specific purpose (clause 1 of Article 378.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), after in a subject of the Russian Federation:
- the results of the assessment of such value were approved;
- a law was adopted on the procedure for forming the base for calculating tax on these objects;
- a list of objects subject to taxation from such a base is published no later than the beginning of the next year.
If all these conditions are met, the corresponding object in the coming year has the cadastral valuation approved for it at the beginning of this year as the basis for taxation. Throughout the year, the value of this base does not change (clause 15 of Article 378.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), but may decrease due to benefits introduced by regional law.
The tax from the cadastral valuation will have to be calculated separately for each of these objects, applying appropriate coefficients that take into account:
- share of ownership - when the taxpayer is the owner of only part of the object, which has a cadastral valuation as the basis (clause 6 of Article 378.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- location share - when an object is located simultaneously in two (or several) constituent entities of the Russian Federation (clause 2 of Article 378.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
An object included in the list of subjects subject to taxation from cadastral valuation (provided that it does not belong to the property of a foreign organization) will never be included in the base depending on the average (annual average) cost (clause 2 of Article 378.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation ).
Tax notice
All information necessary for a taxpayer on the calculation and payment of taxes is contained in a single tax notice, which is generated and sent to citizens by tax authorities no less than 30 days before the payment date.
The tax notice form also includes a section on property tax, containing the information necessary to calculate the payment and pay:
- amount of payment;
- billing period;
- calculation base;
- applied coefficients and benefits.
Payment deadlines
Payment takes place in 2 stages. First, advance payments are calculated and transferred, then the final amount of tax payable for the year is determined. Advance payments are calculated once a quarter. Based on the advances and taxes paid for the year, the organization submits a declaration to the Federal Tax Service.
Regional authorities may cancel advance payments. In this case, enterprises submit a declaration and transfer the tax itself. Each region has its own deadlines for paying advance payments and taxes.
How to find out your debt
It is also possible to obtain information about the status of property tax payments if the owner has not received notification. To do this, you can use the following electronic services:
- “Taxpayer’s personal account” on the Federal Tax Service portal;
- “Find out your debt” on the government services website.
Information about debt is provided to citizens upon personal contact with the tax office.
In some cases, entrepreneurs have the right to switch to a simplified tax payment system. Is there a simplified taxation system for LLCs? Read on.
You will find useful tips on how to open an insurance company on this page.
Checking the need to calculate the tax amount
Before you start calculating, you need to make sure. that this is necessary. In order for you to need to pay, you need to be a taxpayer and have an object of taxation.
Taxpayers are those individuals or legal entities who are required by law to pay contributions. If you are not listed as a taxpayer for a specific tax, you do not have to pay it and you do not need to calculate anything.
The object of taxation is a circumstance the presence of which causes the need to pay tax. The circumstances may be different: receiving income or profit, engaging in a certain type of business, owning certain property, etc. If you do not have an object of taxation - for example, you have not received income - you do not need to pay tax. Only after making sure that you or your organization are taxpayers does it make sense to start calculating the amount of tax.