One of the main changes in the field of taxation that affected individual entrepreneurs in 2021 was the introduction of a new procedure for calculating property tax. Moreover, now all entrepreneurs will be required to make this payment to the treasury, regardless of the tax regime under which they operate. Thus, entrepreneurs working on UTII and the simplified tax system also fall into the ranks of payers.
Who pays and when
Until 2021, various assets, including movable ones, were considered property for tax purposes. Now only real estate is subject to payments. Legal entities pay corporate property tax on it, and individual entrepreneurs pay personal property tax. Both of these payments are regional, which means there are many nuances of taxation in each specific subject of the Russian Federation.
As for simplified companies and individual entrepreneurs, according to Article 346.11 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, their real estate should be exempt from taxation. Instead of property tax and a number of others, they make payments in connection with the application of the simplified tax system. However, there are exceptions to the rules of this article, and they significantly change everything.
Organizations
Paragraph 2 of Article 346.11 states that property tax under the simplified tax system is levied on real estate, the base for which is determined as their cadastral value. This applies to the company’s own real estate, as well as those owned by it under the right of economic management or received under a concession agreement.
Individual entrepreneurs
What about individual entrepreneurs on the simplified tax system and property tax in 2021? The situation is similar to that described above. The only difference is that entrepreneurs pay property tax for individuals, not organizations. It is levied on own real estate, which:
- used in business activities;
- is included in the list of objects for which the base is calculated as cadastral value.
Along with this, a citizen who is an entrepreneur may have personal real estate - an apartment, a dacha. She will be subject to the same tax, but at a different rate.
Free tax consultation
Method four. “Functional use of real estate” - and not only that
But it turned out that the property belonging to your company was included in the cadastral List, and at the same time it is impossible to remove it from there. In this case, I advise you to carefully analyze the cadastral valuation of the property itself, which often turns out to be overestimated.
Here you need to know that the functional use of a particular property plays a very important role in the pricing issue. After all, the coefficients can vary significantly; for example, between free-use premises and office premises, such differences amount to neither more nor less, about 40%.
What exact coefficient was used when assessing the cadastral value in your case? To find out, check with the State Cadastral Valuation Data Fund. Study the technical inventory and cadastral registration documents relating to your property. In this case, pay special attention to the content of the “Functional use” paragraph. If there are discrepancies, report this to the State Budgetary Institution that conducted the state cadastral valuation. To confirm the fairness of your requirements, provide a photo report, contracts and other documents that can confirm that in fact the premises are used differently than it was recorded.
It is important that the documents attached to your application, which support your application, are dated no later than the start date of the last cadastral valuation.
Strict adherence to the listed parameters can give business owners a 40% reduction in property taxes. But it should be remembered: pricing, and therefore the amount of taxes paid, can be affected not only by the “functional use of the property.” There are a great many nuances that should not be overlooked.
Cadastral valuation
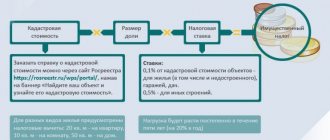
So, the cadastral value is a mandatory condition under which property tax is calculated on the property in 2021. It is not a constant, that is, it can change depending on various factors. To determine this value, a cadastral valuation of real estate is carried out.
Exactly which objects should be valued at cadastral value for tax purposes is specified in Article 378.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. These include:
- administrative, business and shopping centers;
- premises for offices, trade, catering establishments and services;
- some types of objects of foreign legal entities;
- residential real estate, garages, parking spaces, country houses, outbuildings on plots for individual housing construction or subsidiary plots, as well as unfinished construction projects.
This is a general list of object types. In each region, by decision of the authorities, their cadastral value is assessed. This year, the vast majority of regions (74 out of 85) evaluate real estate at cadastral value. Such an assessment can be carried out either selectively or in relation to all types of real estate. As an example, the administration of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation decides to conduct an assessment of all apartment buildings.
After determining the cadastral value, a law is issued stating that taxation of objects should be carried out on its basis.
List of taxable objects
A list of objects, the base for which is calculated as their cadastral value, is compiled in each constituent entity of the Russian Federation at the beginning of the year. It must be posted on the website of the executive authority and sent to the regional Federal Tax Service.
Thus, a business entity using a simplified system needs to check the list on the website of the administration of its region. If the object is included in it, therefore, it is subject to real estate tax even despite the application of the simplified tax system.
For example, in 2021 in St. Petersburg, 5,796 objects were subject to taxation, including residential premises, non-residential buildings and structures for various purposes, garages and parking spaces.
Property tax rates and calculation
After determining the cadastral value, a law is issued stating that taxation of objects should be carried out on its basis.
The company's real estate must be reflected in accounts 01 or 03. You can find out whether your property is included in the cadastral list by requesting this list from the tax office. You can also clarify real estate data in the region's Rosreestr by sending there a request for an extract from the cadastre about the value of the building.
On April 1, the Russian Government adopted a new Federal Law, the need for which was caused by extraordinary circumstances - the coronavirus pandemic. Due to the quarantine regime, many enterprises have difficulty paying taxes, insurance premiums and salaries. The adoption of Federal Law No. 70 made it possible to extend the deadline for repaying tax obligations throughout 2021.
To avoid paying large fines, use a ready-made solution from ConsultantPlus. Experts have sorted out all the nuances of taxes on the simplified tax system: what, how and when to pay. The link below has free access.
Property taxes for legal entities and individuals are considered regional. Each subject of the Russian Federation independently approves the procedure for determining the cadastral valuation of real estate and adopts a law on its use as a tax base.
Each of the constituent entities of Russia develops its own laws on it in relation to the region, guided by the Tax Code. In them, regional legislators specify the scope of benefits, the tax rate, the procedure and terms of payment. The Tax Code stipulates only maximum tax rates.
Is it permissible to simultaneously send a notification of the provision of a tax benefit and a notice of refusal to provide a tax benefit for one application for a benefit?
Property tax for organizations under the simplified tax system
The maximum rates at which objects of one type or another are subject to corporate property tax are prescribed in the Tax Code. But they are precisely determined by regional authorities. Property tax for simplified taxation system payers is levied at a maximum rate of 2%. Along with this, a zero rate is also applied.
The law allows regional authorities to set different rates for certain objects, payers, and tax periods. For example, in the Irkutsk region, for organizations using the simplified tax system in 2021, a rate of 1% applies to taxable property (by 2023 it will gradually increase to 1.5%). This is defined in the regional law dated October 8, 2007 No. 75-OZ.
For property tax on legal entities, benefits are provided at the federal level, which can be supplemented by regional ones.
Organizations usually pay property tax in 2021 quarterly: 3 advance payments and one final payment. The specific payment deadlines depend on the region, but generally this must be done before the end of the month following the reporting quarter. However, in a particular subject, a reporting period may not be established, so there is only a tax (calendar) year. In this case, the payment is made 1 time.
In 2021, the rules for taxation and reporting of property tax for legal entities were changed. Here are the main innovations that affect organizations:
- You now need to submit a declaration to the Federal Tax Service only once a year - until March 30 of the next year. Previously, it was necessary to submit calculations of advance payments;
- Previously, real estate assessed at cadastral value was taxed, provided that it was listed on the balance sheet as a fixed asset. Now there is no such condition;
- in 2021, the tax base of garages, parking spaces, construction “unfinished” and other objects is considered at the cadastral value.
In addition, this year the world is experiencing a crisis associated with the threat of the coronavirus pandemic. In this regard, some temporary changes to the commercial property tax were adopted.
Thus, the deadline for filing the declaration for 2021 was postponed - instead of March 30, it had to be submitted on June 30. In a number of regions, authorities have reduced tax rates and provided installment plans and other preferences. For example, in Moscow it was decided not to carry out a cadastral revaluation this year, although it was planned before the onset of the coronavirus crisis. To calculate taxes, the cadastral value of 2018 will be used. This will allow property owners to save about 3% on tax payments.
How to count
The formula for calculating the tax amount for the year is as follows:
Cadastral value * Rate.
To find out the cadastral value, you need to go to the Rosreestr website. You can check the rate for your property with the Federal Tax Service. In regions where there is a reporting period, the resulting value is divided by 4. This amount is paid once a quarter.
✐ Example ▼
Let’s take an organization from the Irkutsk region using the simplified tax system and calculate the property tax on its own retail premises, the cadastral value of which is 15 million rubles. We apply a rate of 0.5%: 15,000,000 * 0.5% = 75,000 rubles. This is the tax amount for the year. The size of each payment will be: 75,000 / 4 = 18,750 rubles.
How to deal with cadastral value
An organization or individual entrepreneur using the simplified tax system has found out that they are obliged to pay tax on the cadastral value. How to do this practically? First of all, on the basis of Art. 378.2, the tax base in the entity in which the company is registered as a taxpayer must be established by the cadastral value of real estate. It’s easy to find out on the Rosreestr website.
If disagreements arise based on the results of the assessment, the value of the object can be challenged in court or out of court. In the second case, you should submit an application within six months from the date the object was entered into the cadastral register to a special commission dealing with this issue. This requires compelling reasons: either the area of the property is incorrectly determined, or the cost does not correspond to the market assessment. You will also need to attach the necessary documents:
- cadastral passport;
- documents on the ownership of the disputed property, certified by a notary;
- documents on the basis of which you claim that the cadastral valuation is biased;
- conclusion of an expert member of the SRO on the assessment of the market value of the property.
If after the appeal the cadastral value has changed, then the amount payable is recalculated from the beginning of the period, even if the decision was made in December.
Individual entrepreneur tax on simplified tax system
With the tax on the property of entrepreneurs, which they use in business, everything is much simpler, since they do not have to calculate it themselves. This is what the Federal Tax Service does. Everything is exactly the same as with a citizen’s personal property. You just need to make sure that the tax authority knows about the property, and when the receipt arrives, pay the specified amount.
Tax payment is made once, since only the tax period is established. The deadline is December 1 of the following year. There is no need to submit any reports to the tax authority.
The maximum rate at which property tax is levied under the simplified tax system is 2%. The authorities of a particular subject of the Russian Federation can reduce it to zero or increase it, but not more than 3 times. As in the case of corporate property tax, rates can be differentiated.
Let's give an example of rates in St. Petersburg:
- garages and parking spaces are taxed at a rate of 0.3%;
- expensive real estate (more than 300 million rubles) - at a rate of 2%;
- residential real estate - at rates from 0.1 to 0.25% depending on the type and cost;
- some other objects - at a rate of 0.1%.
Residential Properties
Is property tax paid under the simplified tax system on residential buildings and premises? Residential real estate is recognized as an object of taxation. But there are exceptional rules for such objects.
A residential property is recognized as taxable if it is not listed in the organization as a fixed asset. That is, residential real estate is taxable if it is taken into account in the organization’s balance sheet in the following accounts:
- 08 “Investments in non-current assets”;
- 41 "Products";
- 43 “Finished products”.
In relation to such objects, property tax under the simplified tax system “Income minus expenses” for LLCs in 2021 is calculated according to the cadastral value (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated May 19, 2017 No. 03-05-05-01/30753, dated January 25, 2019 No. 03-05 -05-01/4064).
IMPORTANT!
If residential real estate is taken into account in or 03 “Profitable investments in material assets,” then it is not recognized as a taxable object (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 22, 2017 No. 03-05-05-01/86054).
conclusions
We looked at the property tax of organizations and the tax on property of entrepreneurs that is used in business, which are valid for payers of the simplified tax system. They are levied on the real estate for which the cadastral value has been determined. If it has not yet been installed, you do not need to pay taxes.
You can find out exactly whether a particular commercial real estate property is taxable or not by checking the list that is posted on the website of the regional executive authority. Individual entrepreneurs don’t have to worry - the Federal Tax Service will calculate the tax itself and send a receipt.
The taxes that business entities pay on their real estate are regional. Therefore, specific rates, payment terms, and benefits may vary. To find out all the nuances, we recommend that you familiarize yourself with the laws of the relevant constituent entity of the Russian Federation.
Accounting
Organizations using the simplified tax system are required to maintain accounting records, and they need to reflect all tax transactions in them. To reflect accrued amounts of property tax in accounting, follow the general rules for recognizing expenses. Thus, in PBU 10/99, all expenses of the organization, depending on their nature, conditions of implementation and areas of activity, are divided into:
- expenses for ordinary activities;
- other expenses.
All expenses other than expenses for ordinary activities are recognized as other. The calculated amounts relate to expenses for ordinary activities. The Ministry of Finance warns about this in letter No. 03-05-05-01/16.
To make accounting entries, the instructions for using the chart of accounts for accounting the financial and economic activities of organizations, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n, are used. It says that entries in property tax accounting are reflected by an entry in the debit of account 26 “General business expenses” and the credit of account 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees.” The wiring looks like this:
- Debit 26, 44 Credit 68 - accrued;
- Debit 68 Credit 51 - transferred.